化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (9): 1108-1112.DOI: 10.6023/A23040175 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
研究通讯
徐续盼a, 范凯a, 赵胜泽a, 李健a, 高珊b, 吴忠标b, 孟祥举a,*( ), 肖丰收a
), 肖丰收a
投稿日期:2023-04-28
发布日期:2023-07-20
作者简介:基金资助:
Xupan Xua, Kai Fana, Shengze Zhaoa, Jian Lia, Shan Gaob, Zhongbiao Wub, Xiangju Menga( ), Feng-Shou Xiaoa
), Feng-Shou Xiaoa
Received:2023-04-28
Published:2023-07-20
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

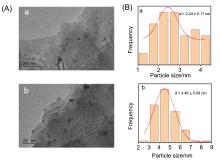
甲烷催化燃烧是处理尾气/废气中微量甲烷最有效的方法之一, 而设计高效催化剂是提升甲烷催化燃烧技术的核心. 使用高分子聚合物聚二甲基二丙烯基氯化铵(PDADMAC)为介孔模板剂制备一系列介孔Beta沸石, 并负载Pd用于甲烷催化燃烧反应. 样品经过X射线衍射(XRD)、氮气吸附、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、X射线光电子能谱技术(XPS)、程序升温还原(H2-TPR)等一系列表征, 证实介孔存在条件下, Pd的纳米颗粒更小且更易于还原, 因此介孔Beta沸石负载Pd催化剂在甲烷催化燃烧反应中表现出更好的活性. 动力学研究表明, 介孔Beta沸石负载Pd催化剂在该反应中具有更低的表观活性能.
徐续盼, 范凯, 赵胜泽, 李健, 高珊, 吴忠标, 孟祥举, 肖丰收. 介孔Beta沸石负载钯在甲烷催化燃烧反应中的性能研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1108-1112.
Xupan Xu, Kai Fan, Shengze Zhao, Jian Li, Shan Gao, Zhongbiao Wu, Xiangju Meng, Feng-Shou Xiao. Enhanced Performance for Mesoporous Beta Zeolites Supported Pd in the Methane Catalytic Combustion★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1108-1112.
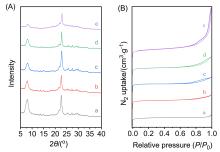

| Sample | PDADMAC/SiO2 | SBET/ (m2•g–1) | Vmicro/ (cm3•g–1) | Vmeso/ (cm3•g–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Beta | 0 | 484 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H1 | 0.067 | 501 | 0.20 | 0.17 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H2 | 0.133 | 474 | 0.19 | 0.20 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H3 | 0.155 | 427 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H4 | 0.200 | 485 | 0.12 | 0.95 |
| Sample | PDADMAC/SiO2 | SBET/ (m2•g–1) | Vmicro/ (cm3•g–1) | Vmeso/ (cm3•g–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Beta | 0 | 484 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H1 | 0.067 | 501 | 0.20 | 0.17 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H2 | 0.133 | 474 | 0.19 | 0.20 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H3 | 0.155 | 427 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H4 | 0.200 | 485 | 0.12 | 0.95 |

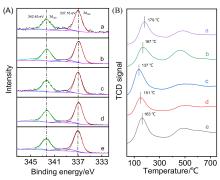

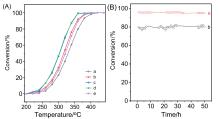

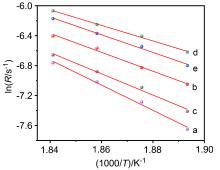
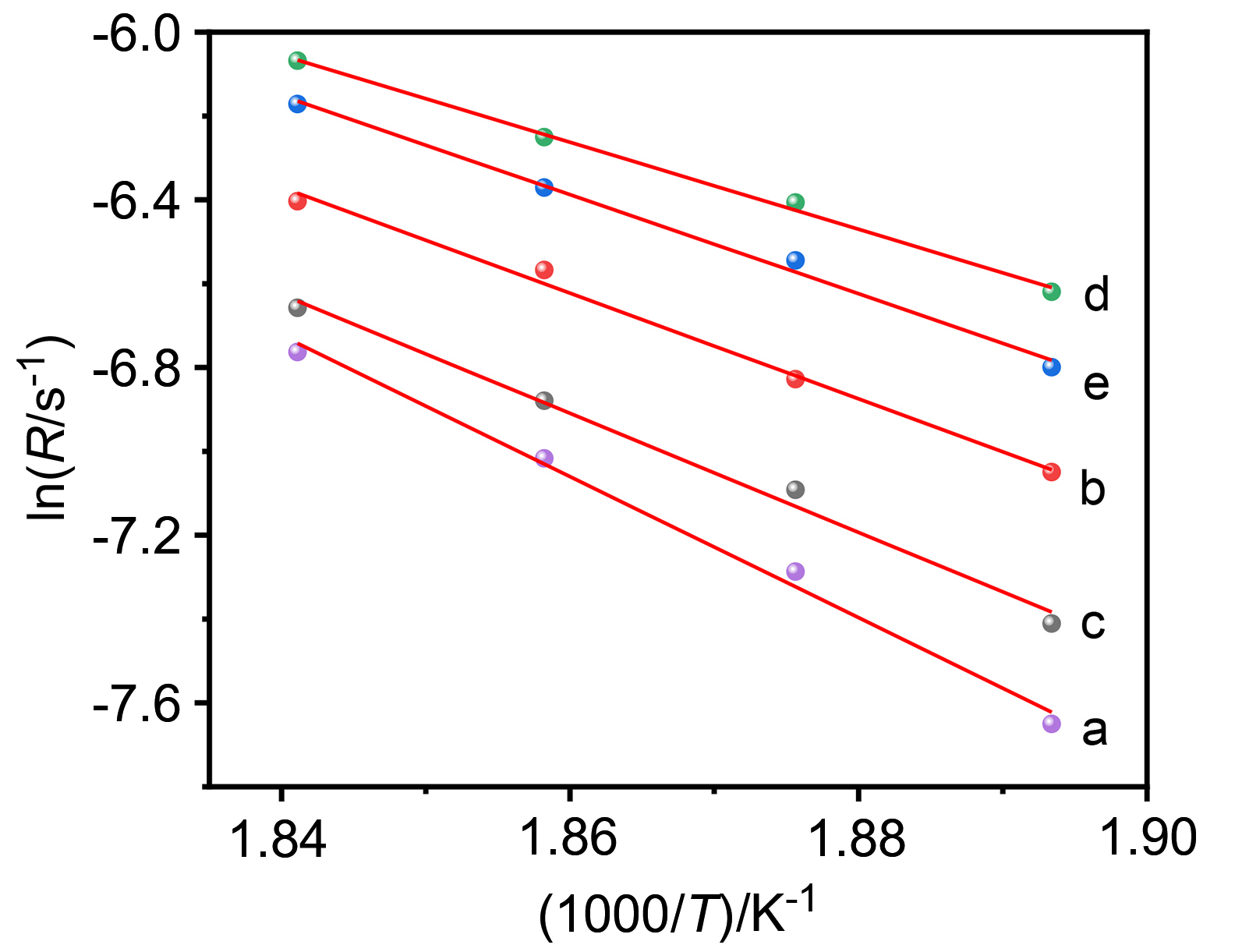
| Catalyst | Ea/(kJ•mol–1) | Reaction order of methane | Reaction order of oxygen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Beta | 140 | 0.69 | 0.40 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H1 | 105 | 0.66 | 0.45 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H2 | 98 | 0.68 | 0.43 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H3 | 86 | 0.66 | 0.44 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H4 | 118 | 0.70 | 0.44 |
| Catalyst | Ea/(kJ•mol–1) | Reaction order of methane | Reaction order of oxygen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Beta | 140 | 0.69 | 0.40 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H1 | 105 | 0.66 | 0.45 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H2 | 98 | 0.68 | 0.43 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H3 | 86 | 0.66 | 0.44 |
| Pd/meso-Beta-H4 | 118 | 0.70 | 0.44 |
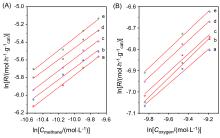

| [1] |
Feng, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, D.; Tian, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Li, K. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 75, 173.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.001 |
| [2] |
Wang, Y.; Hu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4299.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01262A |
| [3] |
Lambert, C. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 554.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0303-x |
| [4] |
Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Da, W.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Appl. Catal., B 2018, 236, 404.
|
| [5] |
Habibi, A.; Semagina, N.; Hayes, R. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8160.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b01338 |
| [6] |
Zhao, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138937.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138937 |
| [7] |
Danielis, M.; Colussi, S.; Leitenburg, C.; Soler, L.; Llorca, J.; Trovarelli, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10212.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.32 |
| [8] |
Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Weng, W. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2022, 43, 20210816. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王明智, 郑燕萍, 翁维正, 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43, 20210816.)
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210816 |
|
| [9] |
Galinskya, N.; Shafiefarhood, A.; Chen, Y.; Neala, L.; Li, F. Appl. Catal., B 2015, 164, 371.
|
| [10] |
Fiuk, M.; Adamski, A. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 131.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.029 |
| [11] |
Tao, F.; Shan, J.; Nguyen, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, W.; Zeng, S. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7798.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8798 |
| [12] |
Du, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gong, M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 1651. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杜小春, 刘志敏, 罗勇悦, 陈耀强, 龚茂初, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 1651.)
|
|
| [13] |
Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Yi, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Cui, W.; Yang, X. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1228.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63055-4 |
| [14] |
Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Bellettre, J.; Yue, J.; Luo, L. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109589.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109589 |
| [15] |
Cargnello, M.; Jaen, J.; Garrido, J.; Bakhmutsky, K.; Montini, T.; Gamez, J.; Gorte, R.; Fornasiero, P. Science 2012, 337, 7137.
|
| [16] |
Yang, J.; Peng, M.; Ren, G.; Qi, H.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Deng, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Pan, X.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Li, W.; Qiao, B.; Ma, D.; Zhang, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 18522.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.42 |
| [17] |
Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, W.; He, H. Fuel 2023, 340, 127493.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127493 |
| [18] |
Zhang, M.; Yan, T.; Dai, W.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1404. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080346 |
|
(张梦婷, 颜婷婷, 戴卫理, 关乃佳, 李兰冬, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1404.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080346 |
|
| [19] |
Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Appl. Catal., B 2020, 276, 119142.
|
| [20] |
Gao, M.; Gong, Z.; Weng, X.; Shang, W.; Chai, Y.; Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 1689.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63775-5 |
| [21] |
Wang, G.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, A.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3274.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC00513C |
| [22] |
Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Meng, X.; Zheng, X.; Gao, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Appl. Catal., B 2013, 140, 19.
|
| [23] |
Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Shen, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 3464.
doi: 10.1039/D2CY00307D |
| [24] |
Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, M.; Rui, Z. Catal. Today 2021, 376, 119.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.005 |
| [25] |
Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, C.; Shan, Z.; Xiao, F.-S. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 131, 58.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.12.001 |
| [26] |
Weng, X.; Ren, W.; Chen, M.; Wan, H. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2598.
doi: 10.1021/cs500510x |
| [1] | 洪梅, 高金强, 李彤, 杨世和. 原位刻蚀调控多级孔分子筛策略及其应用进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 937-948. |
| [2] | 田茹心, 杨苗, 陈果, 刘豇汕, 袁梦梅, 原弘, 欧阳述昕, 张铁锐. 钌/石英滤纸: 可回收型CO2甲烷化光热催化膜★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 869-873. |
| [3] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [4] | 陈治平, 孟永乐, 芦静, 周文武, 杨志远, 周安宁. Fe@Si/S-34催化剂的制备及其合成气制烯烃性能[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 14-19. |
| [5] | 邓权政, 毛文婷, 韩璐. 介观尺度多孔材料的电子显微学结构解析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1203-1216. |
| [6] | 谢晨帆, 徐玉平, 高明亮, 徐忠宁, 江海龙. MOF基Pd单位点催化CO酯化制碳酸二甲酯[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 867-873. |
| [7] | 江辉波, 林姗姗, 徐玉平, 孙径, 徐忠宁, 郭国聪. NaY分子筛Lewis酸促进甲醇经亚硝酸甲酯分解制二甲氧基甲烷※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 438-443. |
| [8] | 张蒙茜, 冯霄. 共轭微孔聚合物膜的制备策略及其分离应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 168-179. |
| [9] | 穆春辉, 张艺馨, 寇伟, 徐联宾. 镍氮掺杂有序大孔/介孔碳负载银纳米颗粒用于高效电催化CO2还原[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 925-931. |
| [10] | 张梦婷, 颜婷婷, 戴卫理, 关乃佳, 李兰冬. 分子筛稳定的孤立Mo物种催化氧化脱硫研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1404-1410. |
| [11] | 傅方舟, 张志诚, 孙倩怡, 徐冰, 沙菁㛃. 纳米孔技术对PD-1抗原抗体结合检测的实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(3): 287-292. |
| [12] | 吴庆远, 秦瑞轩, 臧丹丹, 张无用, 吴炳辉, 郑南峰. 表面具丰富羟基的介孔TiO2稳定Pt-OH-Fe(III)催化界面[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(8): 617-621. |
| [13] | 冯爱虎, 于洋, 于云, 宋力昕. 沸石分子筛及其负载型催化剂去除VOCs研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 757-773. |
| [14] | 杨晓东, 王新苗, 高善彬, 王安杰. Pd/ZSM-5/MCM-41催化剂加氢脱硫性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(5): 479-484. |
| [15] | 张思伟, 张俊, 吴思达, 吕伟, 康飞宇, 杨全红. 钠离子电池用碳负极材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(2): 163-172. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||