化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (6): 641-657.DOI: 10.6023/A24030094 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-05-06
作者简介: |
刘金宇, 副教授. 主要从事串联反应、不对称有机催化、杂环化合物的合成、轴手性化合物的合成、氨基酸衍生物的合成工艺改进等方面的研究工作. 现工作于成都理工大学材料与化学化工学院(锂资源与锂电产业学院). |
Received:2024-03-20
Published:2024-05-06
Contact:
* E-mail: 文章分享

吲哚骨架在药物分子、生物活性分子和天然产物中普遍存在, 因而引起合成化学家的广泛关注. 由于吲哚骨架的电子云密度特性, 使其反应位点多集中于五元杂环, 这也令吲哚骨架的合成与修饰也大多被焦聚在吡咯环. 吲哚碳环反应活性较低, 因而官能团化研究相对较少. 近几十年, 随着过渡金属领域的发展, 尤其是碳氢活化策略的提出, 吲哚碳环官能团化策略得到了一定的发展. 有机催化相比于过渡金属催化, 虽然在催化活性与底物使用范围上受限, 但也因为其在手性控制、成本和操作性上的优势, 被研究者们应用于吲哚碳环的官能团化, 并取得了迅速的发展. 重点综述了利用有机催化剂实现吲哚碳环官能团化的研究成果.
郑灏宁, 刘金宇. 有机催化吲哚碳环官能团化研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 641-657.
Haoning Zheng, Jinyu Liu. Research Progress on Organocatalytic Functionalization of Indole in the Carbocyclic Ring[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(6): 641-657.
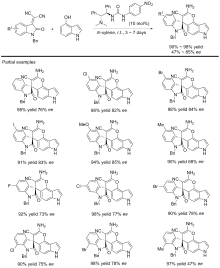
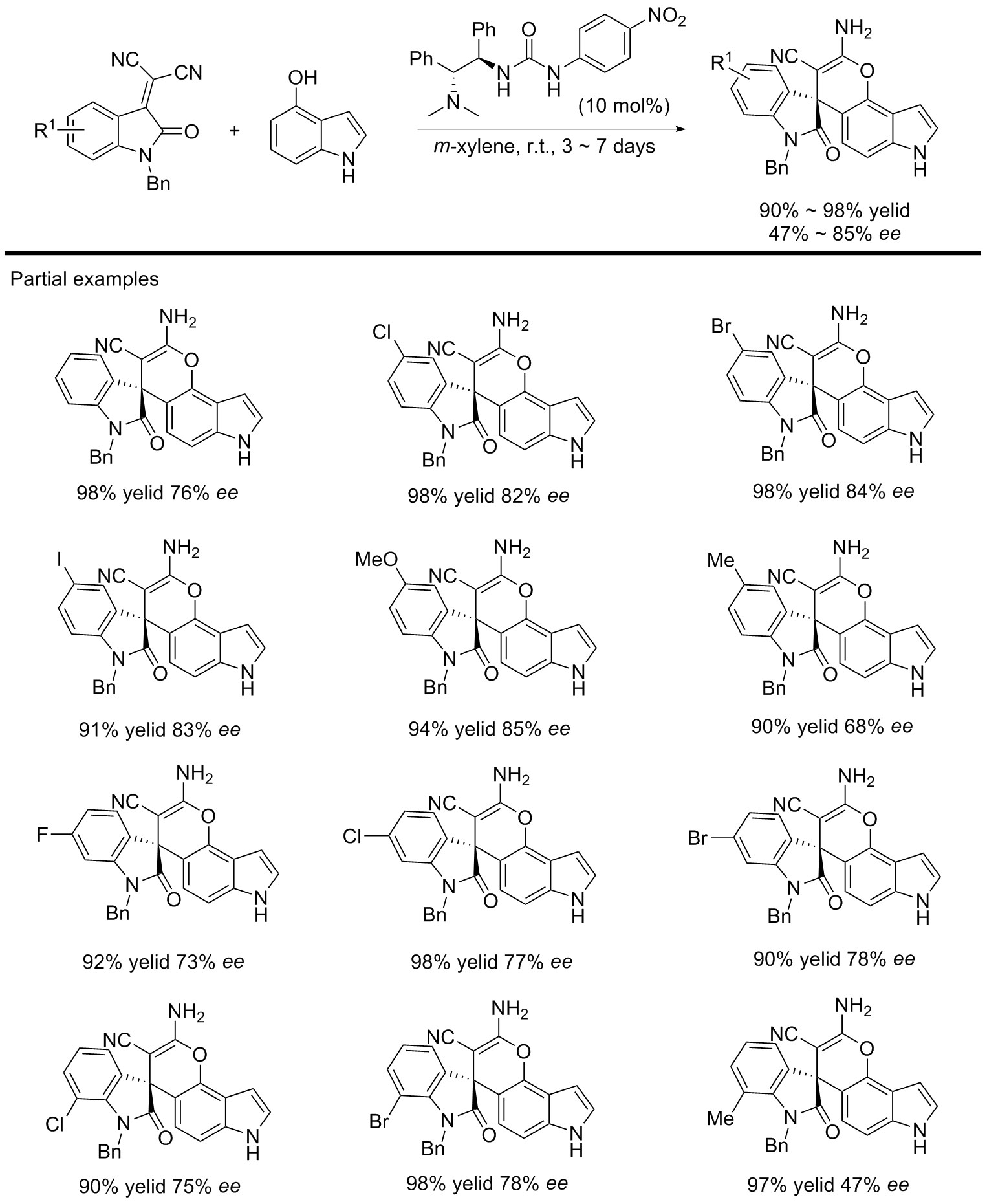
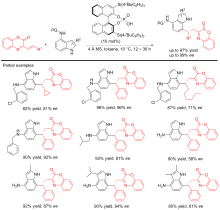

| [1] |
Baeyer, A. D. A.; Drewsen, V. B. A. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1882, 15, 2856.
|
| [2] |
Huisgen, R. Angew. Chem.,Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 297.
|
| [3] |
De Meijere, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7836.
|
| [4] |
Chadha, N.; Silakari, O. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 159.
|
| [5] |
Singh, T. P.; Singh, O. M. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 9.
|
| [6] |
Festa, A. A.; Voskressensky, L. G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4401.
|
| [7] |
Chu, N. N.; Feng, C. L.; Ji, M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 1459. (in Chinese)
|
|
(楚宁宁, 冯成亮, 吉民, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1459.)
doi: 10.6023/A13070689 |
|
| [8] |
Zheng, C.; You, S. L. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1589.
doi: 10.1039/c8np00098k pmid: 30839047 |
| [9] |
Dalpozzo, R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 742.
doi: 10.1039/c4cs00209a pmid: 25316161 |
| [10] |
Sravanthi, T. V.; Manju, S. L. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.05.025 pmid: 27237590 |
| [11] |
Shen, L. L.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Z. T.; Qin, T. Z.; Huang, Z. X.; Zi, W. W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217051.
|
| [12] |
Kovacikova, L.; Prnova, M. S.; Majekova, M.; Bohac, A.; Karasu, C.; Stefek, M. Molecules 2021, 26, 2867.
|
| [13] |
De Sá Alves, F.; Barreiro, E.; Fraga, C. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 782.
|
| [14] |
Welsch, M.; Snyder, S.; Stockwell, B. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 341.
|
| [15] |
Thanikachalam, P.; Maurya, R.; Garg, V.; Monga, V. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 15, 562.
|
| [16] |
Kumari, A.; Singh, R. K. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 103021.
|
| [17] |
Cockroft, J. R. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drug. 2007, 7, 303.
|
| [18] |
Patel, S. S.; Nakka, S. Curr. Med. Chem.: Anti-Cancer Agents 2017, 17, 955.
|
| [19] |
Ried, L. D.; Tueth, M. J.; Handberg, E. Psychosom. Med. 2005, 67, 398.
|
| [20] |
Yan, F.; Hu, Y.; Di, B.; He, P. L.; Sun, G. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 15, 208.
|
| [21] |
Lou, C.; Yokoyama, S.; Saiki, I.; Hayakawa, Y. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2072.
|
| [22] |
Qin, N.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. J.; Qiao, Y. T.; Qu, W.; Feng, F.; Sun, H. P. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112960.
|
| [23] |
Cox, E. D.; Cook, J. M. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1797.
|
| [24] |
Bonjoch, J.; Solé, D. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3455.
pmid: 11777429 |
| [25] |
Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2873.
|
| [26] |
Humphrey, G. R.; Kuethe, J. T. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2875.
pmid: 16836303 |
| [27] |
Zhang, D.; Qin, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 147. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12121037 |
|
(张丹, 秦勇, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 147.)
doi: 10.6023/A12121037 |
|
| [28] |
Mao, Y. J.; Lu, Y. N.; Li, T. Z.; Wu, Q.; Tan, W.; Shi, F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3895. (in Chinese)
|
|
(毛雨佳, 陆一楠, 李天真, 吴琼, 谭伟, 石枫, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3895.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005096 |
|
| [29] |
Zhang, D.; Song, H.; Qin, Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 447.
|
| [30] |
Zi, W. W.; Zuo, Z. W.; Ma, D. W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 702.
|
| [31] |
Zhang, Y. C.; Jiang, F.; Shi, F. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 425.
|
| [32] |
Yang, B. M.; Ng, X. Q.; Zhao, Y. Chem. Catal. 2022, 2, 3048.
|
| [33] |
Zhang, H. H.; Shi, F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 3351. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张洪浩, 石枫, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 3351.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202203018 |
|
| [34] |
Xiang, Y. Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, Q. P.; Peng, Y. Y. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 919.
|
| [35] |
Sandtorv, A. H. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2403.
|
| [36] |
Sun, B.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Kanai, M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1491.
|
| [37] |
Bhat, A.; Tucker, N.; Lin, J. B.; Grover, H. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 10556.
|
| [38] |
Bhattacharjee, P.; Bora, U. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 2343.
|
| [39] |
Nozaki, H.; Moriuti, S.; Takaya, H.; Noyori, R. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966, 7, 5239.
|
| [40] |
Yang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Y.; Shi, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 495.
|
| [41] |
Xu, L.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Tan, L.; Ma, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 321.
|
| [42] |
Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Jia, Y. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 4528.
|
| [43] |
Yang, G.; Lindovska, P.; Zhu, D.; Kim, J.; Wang, P.; Tang, R. Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10807.
|
| [44] |
Iwao, M. Heterocycles 1993, 36, 29.
|
| [45] |
Chauder, B.; Larkin, A.; Snieckus, V. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 815.
pmid: 11869135 |
| [46] |
Montesinos-Magraner, M.; Vila, C.; Rendón-Patiño, A.; Blay, G.; Fernández, I.; Muñoz, M. C.; Pedro, J. R. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2689.
|
| [47] |
Jia, Y. X.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, S. F.; Zhang, C. M.; Zhou, Q. L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5565.
|
| [48] |
Saha, S.; Alamsetti, S. K.; Schneider, C. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1461.
|
| [49] |
Han, X.; Ouyang, W. J.; Liu, B.; Wang, W.; Tien, P.; Wu, S. W.; Zhou, H. B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 8463.
|
| [50] |
Wolf, C.; Zhang, P. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 760.
|
| [51] |
Zhang, H. H.; Shi, F. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2562.
|
| [52] |
Sheng, F. T.; Yang, S.; Wu, S. F.; Zhang, Y. C.; Shi, F. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2151.
|
| [53] |
Jin, L.; Shi, B. F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 657. (in Chinese)
|
|
(金良, 史炳锋, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 657.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202400006 |
|
| [54] |
Hang, Q. Q.; Wu, S. F.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, Y. C.; Shi, F. Sci. Chin. Chem. 2022, 65, 1929.
|
| [55] |
Liu, J. Y.; Yang, X. C.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y. C.; Lu, H.; Gu, Y. C.; Fang, R.; Xu, P. F. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5219.
|
| [56] |
Lou, S.; Moquist, P. N.; Schaus, S. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12660.
|
| [57] |
Demopoulos, V. J.; Nicolaou, I. Synthesis 1998, 1519.
|
| [58] |
Poulsen, P. H.; Feu, K. S.; Paz, B. M.; Jensen, F.; Jørgensen, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8203.
|
| [59] |
Montesinos-Magraner, M.; Vila, C.; Blay, G.; Fernández, I.; Muñoz, M. C.; Pedro, J. R. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1546.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00354 pmid: 28346791 |
| [60] |
Liu, J. Y.; Yang, X. C.; Lu, H.; Gu, Y. C.; Xu, P. F. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2190.
|
| [61] |
Xiao, M. J.; Xu, D. F.; Liang, W. H.; Wu, W. Y.; Chan, A. S. C.; Zhao, J. L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 917.
|
| [62] |
Vila, C.; Tortosa, A.; Blay, G.; Muñoz, M. C.; Pedro, J. R. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 130.
|
| [63] |
Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Cao, J.; Liang, D.; Lin, Y.; Duan, H. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9788.
|
| [64] |
Liu, H.; Zheng, C.; You, S. L. J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 1047.
|
| [65] |
Zhou, L. J.; Zhang, Y. C.; Zhao, J. J.; Shi, F.; Tu, S. J. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 10390.
|
| [66] |
Wu, Q.; Li, G. L.; Yang, S.; Shi, X. Q.; Huang, T. Z.; Du, X. H.; Chen, Y. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 3462.
|
| [67] |
Zhou, J.; Zhu, G. D.; Wang, L.; Tan, F. X.; Jiang, W.; Ma, Z. G.; Kang, J. C.; Hou, S. H.; Zhang, S. Y. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8662.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03276 pmid: 31638819 |
| [68] |
Fukuda, T.; Maeda, R.; Iwao, M. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 9151.
|
| [69] |
Hartung, C. G.; Fecher, A.; Chapell, B.; Snieckus, V. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1899.
|
| [70] |
Paul, S.; Chotana, G. A.; Holmes, D.; Reichle, R. C.; Maleczka Jr, R. E.; Smith III, M. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15552.
|
| [71] |
Shah, T. A.; De, P. B.; Pradhan, S.; Punniyamurthy, T. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 572.
|
| [72] |
Shi, F.; Zhang, H. H.; Sun, X. X.; Liang, J.; Fan, T.; Tu, S. J. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3465.
|
| [73] |
Xun, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, B.; Meng, S.; Chan, A. S. C.; Qiu, F. G.; Zhao, J. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 590.
|
| [74] |
Huang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, S.; Chan, A. S. C.; Zhao, J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 3632.
|
| [75] |
Zhao, Y.; Cai, L.; Huang, T.; Meng, S.; Chan, A. S.; Zhao, J. L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1309.
|
| [76] |
Cai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, T.; Meng, S.; Jia, X.; Chan, A. S.; Zhao, J. L. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3538.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00821 pmid: 31058509 |
| [77] |
Zhao, Y.; Xiao, R.; Fang, W.; Zhao, J. L. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 718.
|
| [1] | 罗江浩, 马浩文, 张杰豪, 周伟, 蔡倩. 串联炔-异氰[3+2]环加成/Boulton-Katritzky重排/扩环反应构建吡咯并[3,2-d]嘧啶-4-酮化合物★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 898-904. |
| [2] | 王瑞祥, 赵庆如, 顾庆, 游书力. 金/铱接力催化炔基酰胺环化/不对称烯丙基苄基化串联反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 431-434. |
| [3] | 邱孔茜, 李杰, 马浩文, 周伟, 蔡倩. 捕捉环加成反应中的有机亚铜中间体构筑氮杂环化合物研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 42-63. |
| [4] | 王晓晨, 季泽尧, 刘健, 王炳福, 金辉, 张立新. 硫酯参与的有机催化不对称反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 64-83. |
| [5] | 赵庆如, 蒋茹, 游书力. 铱催化串联不对称烯丙基取代/双键异构化构建轴手性化合物[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1107-1112. |
| [6] | 邓卓基, 欧阳溢凡, 敖运林, 蔡倩. 铜催化不对称去对称化分子内烯基C—N偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 649-652. |
| [7] | 杨妲, 张龙力, 刘欢, 杨朝合. 双功能配体修饰的Ir催化剂在“氢甲酰化-缩醛化”串联反应中的共催化作用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 658-662. |
| [8] | 尚阳, 肖检, 王雅雯, 彭羽. 不对称构筑二芳基次甲基立体中心的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1303-1319. |
| [9] | 李翼, 徐明华. 不对称Petasis反应在手性胺类化合物合成中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1345-1359. |
| [10] | 陈友根, 丁远生. 有机催化基团转移聚合的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(8): 733-745. |
| [11] | 程磊, 周其林. 镍催化构筑C(sp3)—C(sp3)键反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(10): 1017-1029. |
| [12] | 许健, 张世樊, 罗莹, 张荔, 张帆, 黄挺菁, 宋秋玲. 自由基促进硫甲基取代的炔酮的环化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 932-938. |
| [13] | 王强, 顾庆, 游书力. 过渡金属催化不对称C—H键官能团化反应构建轴手性联芳基化合物研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(8): 690-704. |
| [14] | 姚坤, 刘浩, 袁乾家, 刘燕刚, 刘德龙, 张万斌. 钯催化三组分烯丙基串联反应: 化学专一性合成N-酰亚甲基-2-吡啶酮[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(10): 993-998. |
| [15] | 叶文波, 晏子聪, 万常峰, 侯豪情, 汪志勇. 一种新的肉桂酸类化合物的脱羧/甲基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 99-102. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
