Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (7): 772-781.DOI: 10.6023/A24030085 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
罗倩钰a, 汪诚艳c, 张天龙a, 夏培元c, 张潇c,*( ), 杨明b,*(
), 杨明b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-03-14
发布日期:2024-06-04
基金资助:
Qianyu Luoa, Chengyan Wangc, Tianlong Zhanga, Peiyuan Xiac, Xiao Zhangc,*( ), Ming Yangb,*(
), Ming Yangb,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-14
Published:2024-06-04
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:Share
Qianyu Luo, Chengyan Wang, Tianlong Zhang, Peiyuan Xia, Xiao Zhang, Ming Yang. Metal Ion-gemcitabine Monophosphate Nanoparticles for Effective Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(7): 772-781.
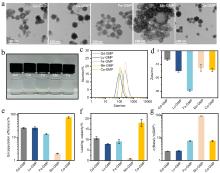

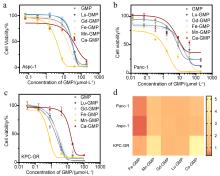

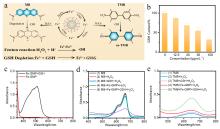

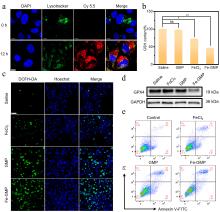

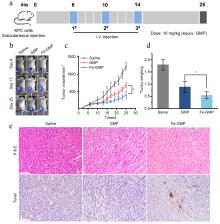

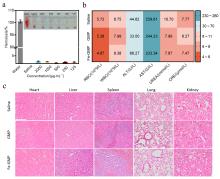

| [1] |
Siegel R. L.; Miller K. D.; Wagle N. S.; Jemal A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17.
|
| [2] |
Strobel O.; Neoptolemos J.; Jäger D.; Büchler M. W. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 16, 11.
|
| [3] |
Saung M. T.; Zheng L. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2125.
doi: S0149-2918(17)30904-9 pmid: 28939405 |
| [4] |
Gu Z. Y.; Du Y. X.; Zhao X.; Wang C. Cancer Lett. 2021, 521, 98.
|
| [5] |
Dubey R. D.; Saneja A.; Gupta P. K.; Gupta P. N. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 147.
|
| [6] |
Saiki Y.; Yoshino Y.; Fujimura H.; Manabe T.; Kudo Y.; Shimada M.; Mano N.; Nakano T.; Lee Y.; Shimizu S.; Oba S.; Fujiwara S.; Shimizu H.; Chen N.; Nezhad Z. K.; Jin G.; Fukushige S.; Sunamura M.; Ishida M.; Motoi F.; Egawa S.; Unno M.; Horii A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 98.
|
| [7] |
Yamamoto M.; Sanomachi T.; Suzuki S.; Uchida H.; Yonezawa H.; Higa N.; Takajo T.; Yamada Y.; Sugai A.; Togashi K.; Seino S.; Okada M.; Sonoda Y.; Hirano H.; Yoshimoto K.; Kitanaka C. Neuro-oncol. 2021, 23, 945.
|
| [8] |
Li X.; Porcel E.; Menendez‐Miranda M.; Qiu J. W.; Yang X. M.; Serre C.; Pastor A.; Desmaële D.; Lacombe S.; Gref R. ChemMedChem 2019, 15, 274.
|
| [9] |
Das M.; Li J.; Bao M.; Huang L. AAPS J. 2020, 22, 88.
|
| [10] |
Sun H.; Cai H.; Xu C.; Zhai H. Z.; Lux F.; Xie Y.; Feng L.; Du L. Q.; Liu Y.; Sun X. H.; Wang Q.; Song H. J.; He N. N.; Zhang M. M.; Ji K. H.; Wang J. J.; Gu Y. Q.; Leduc G.; Doussineau T.; Wang Y.; Liu Q.; Tillement O. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 449.
|
| [11] |
Chen Y.; Huang Y. K.; Zhou S. L.; Sun M. L.; Chen L.; Wang J. H.; Xu M. J.; Liu S. S.; Liang K. F.; Zhang Q.; Jiang T. Z.; Song Q. X.; Jiang G.; Tang X. J.; Gao X. L.; Chen J. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6780.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02622 pmid: 32809834 |
| [12] |
Lv Y. G.; Chen X.; Shen Y. P. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121434.
|
| [13] |
Cai Z.; Zhang Y. W.; Jiang L. P.; Zhu J. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 481 (in Chinese).
|
|
(蔡政, 张颖雯, 姜立萍, 朱俊杰, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 481.)
doi: 10.6023/A20120583 |
|
| [14] |
Li J. J.; Wei J. J.; Gao Y. X.; Zhao Q.; Sun J. J.; Ouyang J.; Na N. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107662.
|
| [15] |
Cordani M.; Resines-Urien E.; Gamonal A.; Milán-Rois P.; Salmon L.; Bousseksou A.; Costa J. S.; Somoza Á. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 66.
|
| [16] |
Guo W.; Hu C. Y.; Zhen S. J.; Huang C. Z.; Li Y. F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1583 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A22070304 |
|
(郭湾, 胡聪意, 甄淑君, 黄承志, 李原芳, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1583.)
doi: 10.6023/A22070304 |
|
| [17] |
Yu X. Y.; Shang T. Y.; Zheng G. D.; Yang H. L.; Li Y. W.; Cai Y. J.; Xie G. X.; Yang B. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1895.
|
| [18] |
Simón M.; Jørgensen J. T.; Khare H. A.; Christensen C.; Nielsen C. H.; Kjaer A. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1284.
|
| [19] |
Wang J.; Zhuo L. G.; Zhao P.; Liao W.; Wei H. Y.; Yang Y. C.; Peng S. M.; Yang X. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3502.
|
| [20] |
Man X. Y.; Yang T. F.; Li W. J.; Li S. H.; Xu G.; Zhang Z. L.; Liang H.; Yang F. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7268.
|
| [21] |
Sun H. S.; Zhou J.; Liu C.; Chen X.; Du Y. J.; Li Y. L.; Jiang H.; Wang J. Q.; Song Z.; Guo C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1250 (in Chinese).
|
|
(孙宏顺, 周进, 刘成, 陈旭, 杜怡璟, 李玉龙, 蒋蕻, 王建强, 宋喆, 郭成, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1250.)
doi: 10.6023/A22050226 |
|
| [22] |
Chou T. C. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440.
|
| [23] |
Yang Z. B.; Luo Y.; Hu Y. N.; Liang K. C.; He G.; Chen Q.; Wang Q. G.; Chen H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2007991.
|
| [24] |
Bai Y.; Pan Y. J.; An N.; Zhang H. T.; Wang C.; Tian W.; Huang T. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107552.
|
| [25] |
Dong L. P.; Ding J. S.; Zhu L. M.; Liu Y. J.; Gao X.; Zhou W. H. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108192.
|
| [26] |
Yang Y. H.; Wang Y. F.; Xu L. G.; Chen T. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1801.
|
| [27] |
Raza A.; Hayat U.; Rasheed T.; Bilal M.; Iqbal H. M. N. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 705.
doi: S0223-5234(18)30702-5 pmid: 30138802 |
| [28] |
Ouyang J.; Wang L. Q.; Chen W.; Zeng K.; Han Y.; Xu Y.; Xu Q.; Deng L.; Liu Y.-N. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3468.
|
| [29] |
Lei G.; Zhuang L.; Gan B. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2022, 22, 381.
|
| [1] | Chengjun Wang, Yueliang Wang, Huiqiao Wang, Zhaoxiang Deng. Unveiling the Chemical Incompatibility of Au-Ag Heteronanoassembly [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(7): 763-771. |
| [2] | Wenjie Wei, Wenlong Chen, Xiaobin Dai, Li-Tang Yan. Theory of Anomalous Diffusion Dynamics in Biomacromolecular Media★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 967-978. |
| [3] | Fengbin Zheng, Kun Wang, Tian Lin, Yinglong Wang, Guodong Li, Zhiyong Tang. Research Progress on the Preparation of Metal-Organic Frameworks Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticle Composites and Their Catalytic Applications★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 669-680. |
| [4] | Xufa He, Kangle Jia, Longfei Yu, Mingjie Liu, Xiaoshan Zheng, Huanling Li, Jinlan Xin, Linjia Huang. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Synergistically Stabilized by Maleopimaric Acid and Alumina Nanoparticles [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 765-771. |
| [5] | Xuezhi Yang, Dawei Lu, Weichao Wang, Hang Yang, Qian Liu, Guibin Jiang. Nano-Tracing: Recent Progress in Sourcing Tracing Technology of Nanoparticles※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 652-658. |
| [6] | Jinyuan Zhao, Qian Zhang, Jian Wang, Qi Zhang, Heng Li, Yaping Du. Advances in the Scavenging Materials for Reactive Oxygen Species [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 570-580. |
| [7] | Ruomei Liu, Yanhui Feng, Zhuo Li, Shan Lu, Tianyong Guan, Xingjun Li, Yan Liu, Zhuo Chen, Xueyuan Chen. A Novel Near-infrared Responsive Lanthanide Upconversion Nanoplatform for Drug Delivery Based on Photocleavage of Cypate※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 423-427. |
| [8] | Junmin Chen, Chengqian Cui, Hanlin Liu, Guodong Li. Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Quinoline Catalyzed by Composites of Metal-Organic Framework and Pt Nanoparticles※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 467-475. |
| [9] | Yanran Li, Zigui Wang, Zhaohui Tang. Water Soluble IR-780 Polymer for Mitochondria-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 291-296. |
| [10] | Jinghuang Chen, Tian Meng, Lie Wu, Hengchong Shi, Fan Yang, Jian Sun, Xiurong Yang. Study on Synthesis and Antibacterial Properties of AgNPs@ZIF-67 Composite Nanoparticles※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(2): 110-115. |
| [11] | Ju Huang, Zhen Li, Zhihong Liu. Functionalized Upconversion Nanoparticles for Disassembly of β‑Amyloid Aggregation with Near-Infrared Excitation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057. |
| [12] | Chunhui Mu, Yixin Zhang, Wei Kou, Lianbin Xu. Nickel-Nitrogen-Doped Ordered Macro-/Mesoporous Carbon Supported Ag Nanoparticles for Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(7): 925-931. |
| [13] | Heqi Gao, Di Jiao, Hanlin Ou, Jingtian Zhang, Dan Ding. High Performance Aggregation-Induced Emission Nanoprobes for Image-Guided Cancer Surgery [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 319-325. |
| [14] | Xiaomeng Zhang, Xiya Li, Wanfeng Xiong, Hongfang Li, Rong Cao. Ultrafine Platinum Nanoparticles Derived from Supramolecular Crystal for Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 180-185. |
| [15] | Yijun Guo, Bing Wei, Xiang Zhou, Dongbao Yao, Haojun Liang. DNA Walker-Programmed Nanoparticle Superlattice [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 192-199. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||