有机化学 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 567-581.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202006060 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2020-06-28
修回日期:2020-08-04
发布日期:2020-09-16
通讯作者:
张玉辉
作者简介:基金资助:
Lijuan Wangb, Xianliang Shenga, Jie Wanga, Yuhui Zhanga,*( )
)
Received:2020-06-28
Revised:2020-08-04
Published:2020-09-16
Contact:
Yuhui Zhang
Supported by:文章分享

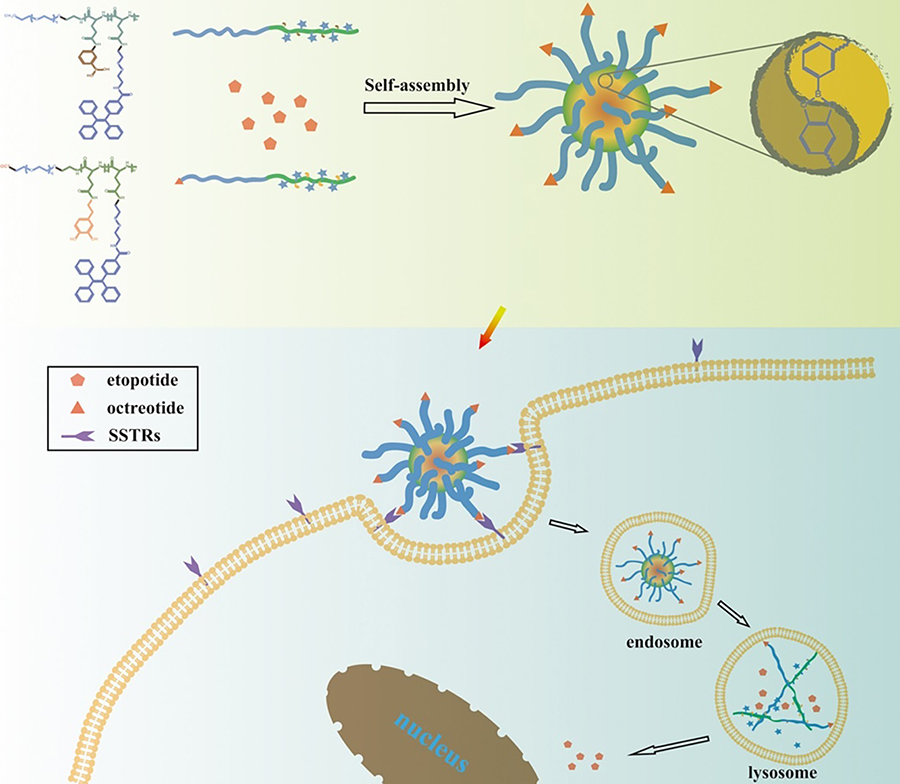
刺激响应性药物载体由于其优异的控释性能, 在生物医药领域引发了广泛的关注并得到了极为快速的发展. 硼酸酯键因构筑条件简单、生物相容性好以及能够响应生物体内pH、葡萄糖、三磷酸腺苷(ATP)等多种微环境变化的优势被广泛用于刺激响应性药物载体的构筑. 基于硼酸酯键的药物载体类型有药物-聚合物偶联、聚合物胶束、线性-超支化聚合物和介孔二氧化硅等, 它们既能负载抗癌药物, 又能递送胰岛素和基因. 药物通过共价或非共价作用负载到载体上, 并利用硼酸酯键在不同环境下的形成与断裂实现药物的可控释放. 从药物类型、载体类型、药物与载体的结合方式以及硼酸酯键的断裂机制四个方面综述了硼酸酯键在药物传递体系中的应用, 并对其当前面临的主要挑战和未来的发展趋势进行了总结和展望.
王李娟, 盛显良, 王杰, 张玉辉. 硼酸酯键在药物传递体系中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(2): 567-581.
Lijuan Wang, Xianliang Sheng, Jie Wang, Yuhui Zhang. Application of Boronate Bond in Drug Delivery System[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(2): 567-581.
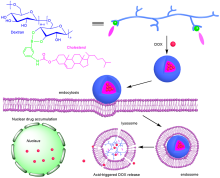
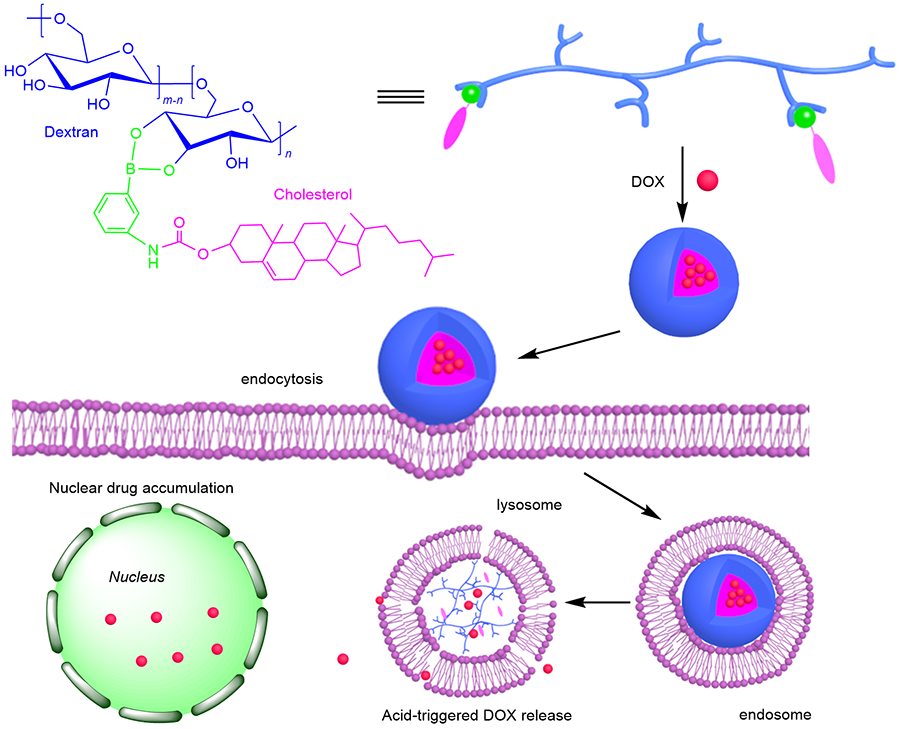
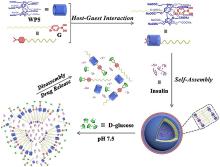
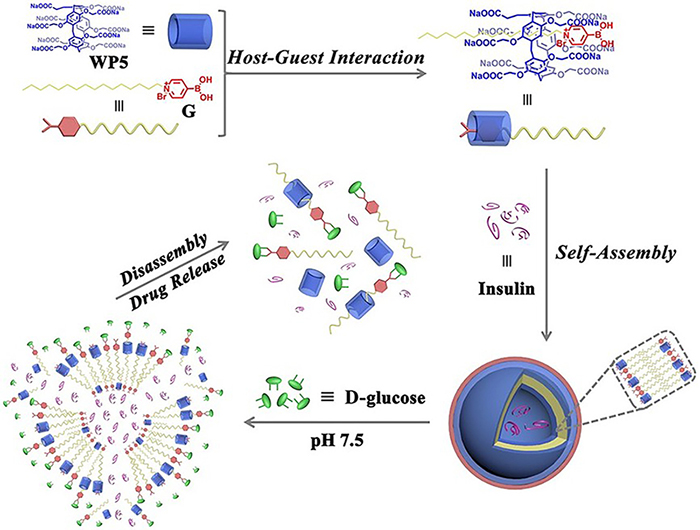
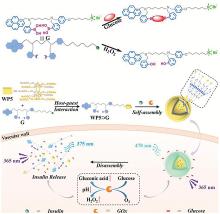
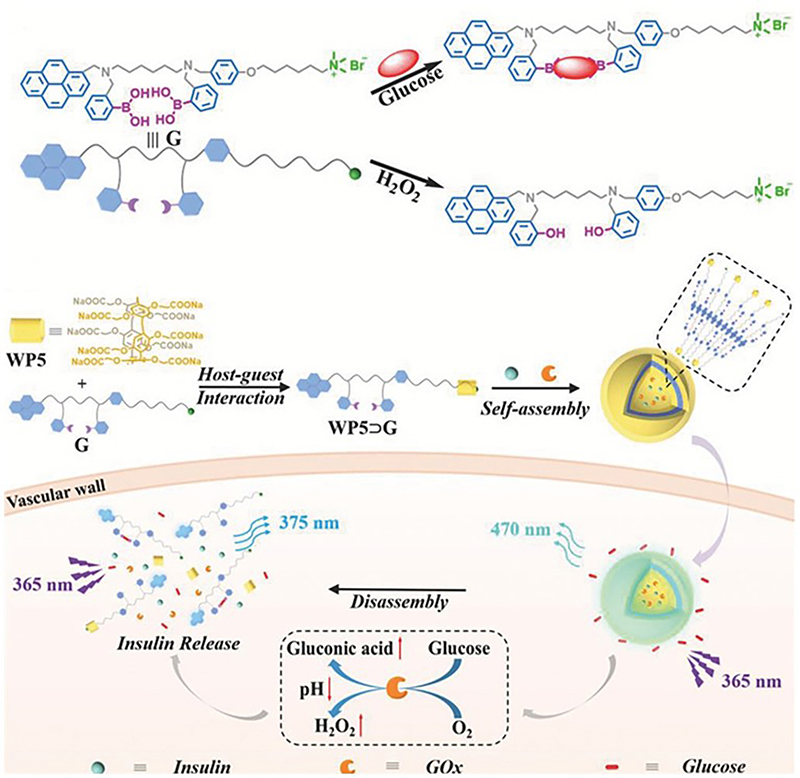
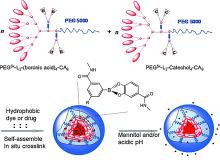
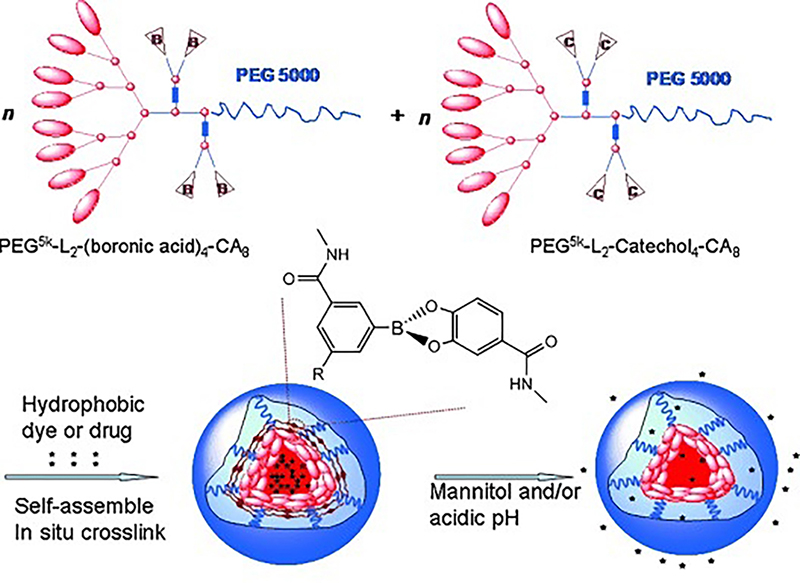
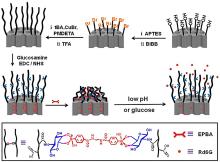
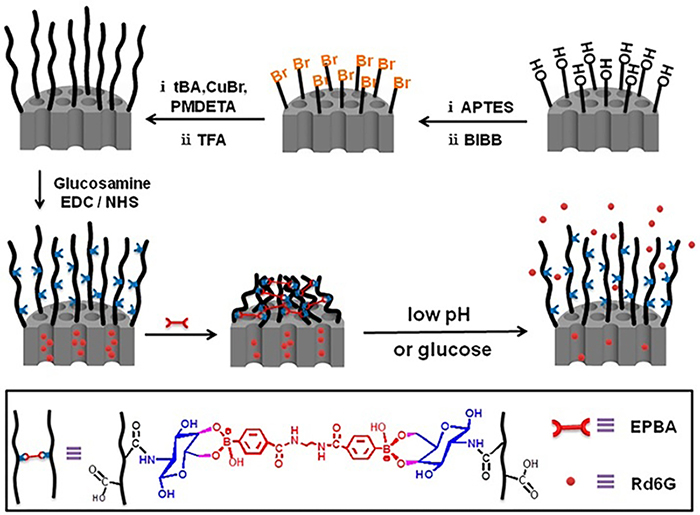
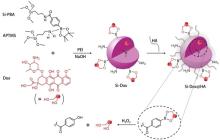
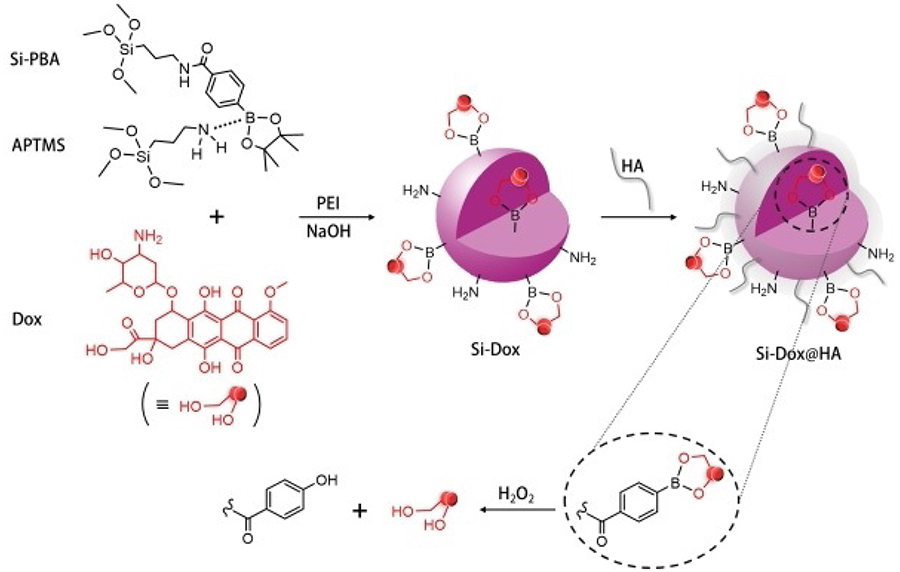

| [1] |
Sun Q.H.; Sun X.R.; Ma X.P.; Zhou Z.X.; Jin E.L.; Zhang B.; Shen Y.Q.; Van Kirk E.A.; Murdoch W.J.; Lott J.R.; Lodge T.P.; Radosz M.; Zhao Y.L. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7615.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.45 |
| [2] |
Peer D.; Karp J.M.; Hong S.; FaroKHzad O.C.; Margalit R.; Langer R. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.387 pmid: 18654426 |
| [3] |
Ma X.H.; Wang J.Y.; Guo J.J.; Wang Z.Y.; Zang S.Q. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1120.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v37.11 |
| [4] |
Meng F.D.; Sun J.; Li Z.B. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1137.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v37.11 |
| [5] |
Guan X.L.; Wang L.; Li Z.F.; Liu M.N.; Wang K.L.; Lin B.; Yang X.Q.; Lai S.J.; Lei Z.Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1036. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19060226 pmid: CC5BD6CA-FAA8-490E-921F-F2D7E5FB382A |
|
关晓琳, 王林, 李志飞, 刘美娜, 王凯龙, 林斌, 杨学琴, 来守军, 雷自强, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1036.).
doi: 10.6023/A19060226 pmid: CC5BD6CA-FAA8-490E-921F-F2D7E5FB382A |
|
| [6] |
Rowan S.J.; Cantrill S.J.; Cousins G. R. L.; Sanders J. K. M.; Stoddart J.F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 898.
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020315)41:6【-逻*辑*与-】amp;lt;【-逻*辑*与-】amp;gt;1.0.CO;2-R |
| [7] |
Zhang Y.L.; Yang B.; Xu L.X.; Zhang X.Y.; Tao L.; Wei Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 48. (in Chinese)
|
|
张亚玲, 杨斌, 许亮鑫, 张小勇, 陶磊, 危岩, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 48.).
|
|
| [8] |
Tang Q.Q.; Yuan L.; Yang D.; Hu J.H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 1925. (in Chinese)
pmid: 3CE6B69E-9EBA-4871-A18F-F71FDD646908 |
|
唐倩倩, 袁丽, 杨东, 胡建华, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 1925.).
pmid: 3CE6B69E-9EBA-4871-A18F-F71FDD646908 |
|
| [9] |
Xu H.P.; Cao W.; Zhang X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1647.
doi: 10.1021/ar4000339 |
| [10] |
Brooks W. L. A.; Sumerlin B.S. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1375.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00300 |
| [11] |
Vancoillie G.; Hoogenboom R. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5484.
doi: 10.1039/C6PY00775A |
| [12] |
Lorand J.P.; Edwards J.O. J. Org. Chem. 1959, 24, 769.
doi: 10.1021/jo01088a011 |
| [13] |
Bosch L.I.; Fyles T.M.; James T.D. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11175.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2004.08.046 |
| [14] |
Ma R.J.; Shi L.Q. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1503.
doi: 10.1039/C3PY01202F |
| [15] |
Djanashvili K.; Frullano L.; Peters J.A. Chem.-Eur. J. 2005, 11, 4010.
pmid: 15838860 |
| [16] |
Dick L.R.; Fleming P.E. Drug Discovery Today 2010, 15, 243.
doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.008 |
| [17] |
Kupperman E.; Lee E.C.; Cao Y.Y.; Bannerman B.; Fitzgerald M.; Berger A.; Yu J.; Yang Y.; Hales P.; Bruzzese F.; Liu J.; Blank J.; Garcia K.; Tsu C.; Dick L.; Fleming P.; Yu L.; Manfredi M.; Rolfe M.; Bolen J. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1970.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2766 |
| [18] |
Wang C.; Hou X.B.; Fang H. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2019, 54, 1940. (in Chinese)
|
|
王川, 侯旭奔, 方浩, 药学学报, 2019, 54, 1940.).
|
|
| [19] |
Zhu S.-S.; Chen X.; Yan Q.Y.; Lin Z. Chin. Mod. Doctor 2019, 57, 164. (in Chinese)
|
|
朱珊珊, 陈鑫, 颜巧妍, 林忠, 中国现代医生, 2019, 57, 164.).
|
|
| [20] |
Escalante J.; McQuade R.M.; Stojanovska V.; Nurgali K. Maturitas 2017, 105, 23.
doi: S0378-5122(17)30534-0 pmid: 28545907 |
| [21] |
Zhu J.Y.; Lei Q.; Yang B.; Jia H.Z.; Qiu W.X.; Wang X.L.; Zeng X.; Zhuo R.X.; Feng J.; Zhang X.Z. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 281.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.048 |
| [22] |
Hao Y.W.; Zheng C.X.; Wang L.; Hu Y.J.; Guo H.C.; Song Q.L.; Zhang H L.; Zhang Z.Z.; Zhang Y. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2133.
doi: 10.1039/C6TB02833K |
| [23] |
Zhu X.Y.; Wu C.H.; Qiu S.H.; Yuan X.L.; Li L. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 60.
doi: 10.1186/s12986-017-0217-z |
| [24] |
Xu Y.; Wang L.M.; He J.; Bi Y.F.; Li M.; Wang T.G.; Wang L.H.; Jiang Y.; Dai M.; Lu J.L.; Xu M.; Li Y.C.; Hu N.; Li J.H.; Mi S.Q.; Chen C.S.; Li G.W.; Mu Y.M.; Zhao J.J.; Kong L.Z.; Chen J.L.; Lai S.H.; Wang W.Q.; Zhao W.H.; Ning G. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 948.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.168118 |
| [25] |
Shah R.B.; Patel M.; Maahs D.M.; Shah V.N. Int. J. Pharm. Invest. 2016, 6, 1.
doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.176456 |
| [26] |
Wang Y.X.; Chai Z.H.; Ma L.Y.; Shi C.S.; Shen T.F.; Song J. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 53877.
doi: 10.1039/C4RA05034G |
| [27] |
Zhang Y.H.; Zhang Y.M.; Zhao Q.H.; Liu Y. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22654.
doi: 10.1038/srep22654 |
| [28] |
Gao L.; Wang T.T.; Jia K.K.; Xuan Wu X.; Yao C.H.; Shao W.; Zhang D.M.; Hu X.Y.; Wang L.Y. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6605.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v23.27 |
| [29] |
Zuo M.Z.; Qian W.R.; Xu Z.Q.; Shao W.; Hu X.Y.; Zhang D.M.; Jiang J.L.; Sun X.Q.; Wang L.Y. Small 2018, 14, 1801942.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v14.38 |
| [30] |
Wang J.Q.; Yu J.; Zhang Y.Q.; Zhang X.D.; Kahkoska A.R.; Chen G.J.; Wang Z.J.; Sun W.J.; Cai L.L.; Chen Z.W.; Qian C.G.; Shen Q.D.; Khademhosseini A.; Buse J.B.; Gu Z. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw4357.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4357 |
| [31] |
Yu J.C.; Wang J.Q.; Zhang Y.Q.; Chen G.J.; Mao W.W.; Ye Y.Q.; Kahkoska A.R.; Buse J.B.; Langer R.; Gu Z. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 499.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0508-y |
| [32] |
Akhtar N.; Akram M.; Asif H.M.; Usmanghani K.; Shah S. M. A.; Rao S.A.; Uzair M.; Shaheen G.; Ahmad K. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 1812.
|
| [33] |
Miyazawa H.; Hirai K.; Ookawara S.; Ishibashi K.; Morishita Y. Nano Rev. Exp. 2017, 8, 1331099.
doi: 10.1080/20022727.2017.1331099 |
| [34] |
Yang B.; Jia H.Z.; Wang X.L.; Chen S.; Zhang X.Z.; Zhuo R.X.; Feng J. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2014, 3, 596.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v3.4 |
| [35] |
Jeon J.H.; Park J.H.; Kim T. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.016 |
| [36] |
Liu X.; Xiang J.J.; Zhu D.C.; Jiang L.M.; Zhou Z.X.; Tang J.B.; Liu X.R.; Huang Y.Z.; Shen Y.Q. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1743.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201504288 |
| [37] |
Elvira C.; Gallardo A.; San Roman J.; Cifuentes A. Molecules 2005, 10, 114.
doi: 10.3390/10010114 |
| [38] |
Tan J. P. K.; Voo Z.X.; Lim S.; Venkataraman S.; Ng K.M.; Gao S.J.; Hedrick J.L.; Yang Y.Y. Nanomedicine 2019, 17, 236.
|
| [39] |
Kim J.; Lee J.; Lee Y.M.; Pramanick S.; Im S.; Kim W.J. J. Controlled Release 2017, 259, 203.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.10.029 |
| [40] |
Zhang Y.H.; Zhang Y.M.; Yu J.; Wang J.; Liu Y. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1164.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC09956A |
| [41] |
Chai Y.; Xu K.; Chang H.B.; Zhang P.Y. Chem. Res. 2018, 29, 522. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1021/ar950053z |
|
柴云, 许凯, 常海波, 张普玉, 化学研究, 2018, 29, 522.).
|
|
| [42] |
Li Y.P.; Xiao W.W.; Xiao K.; Berti L.; Luo J.T.; Tseng H.P.; Fung G.; Lam K.S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2864.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201107144 |
| [43] |
Han Y.; Yin W.; Li J.J.; Zhao H.; Zha Z.S.; Ke W.D.; Wang Y.H.; He C.X.; Ge Z.S. J. Controlled Release 2018, 273, 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.01.019 |
| [44] |
Mehta P.; Kadam S.; Pawar A.; Bothiraja C. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8396.
doi: 10.1039/C9NJ01591D |
| [45] |
Jiang W.F.; Zhou Y.F.; Yan D.Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3874.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00274A |
| [46] |
Jia H.Z.; Zhu J.Y.; Wang X.L.; Cheng H.; Chen G.; Zhao Y.F.; Zeng X.; Feng J.; Zhang X.Z.; Zhuo R.X. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5240.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.029 |
| [47] |
Long Z.; Liu M.Y.; Mao L.C.; Zeng G.J.; Wan Q.; Xu D.Z.; Deng F.J.; Huang H.Y.; Zhang X.Y.; Wei Y. Colloids Surf., B 2017, 150, 114.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.11.018 |
| [48] |
Liu C.Y.; Shao N.M.; Wang Y.T.; Cheng Y.Y. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2016, 5, 584.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v5.5 |
| [49] |
Hu Y.C.; Wang Y.Z.; Wang S.L. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ.. 2010, 27, 961. (in Chinese)
|
|
胡延臣, 王彦竹, 王思玲, 沈阳药科大学学报, 2010, 27, 961.).
|
|
| [50] |
Regi M.V.; Ramila A.; del Real R.P.; Pariente J.P. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308.
|
| [51] |
Wang H.G.; Liu X.H. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2019, 39, 1099. (in Chinese)
|
|
王海刚, 刘向红, 中国医院药学杂志, 2019, 39, 1099.).
|
|
| [52] |
Hu C.L.; Yu L.X.; Zheng Z.; Wang J.; Liu Y.; Jiang Y.F.; Tong G.Z.; Zhou Y.J.; Wang X.L. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 85436.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA12009H |
| [53] |
Tan L.; Yang M.Y.; Wu H.U.; Tang Z.W.; Xiao J.Y.; Liu C.J.; Zhuo R.X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6310.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b00631 |
| [54] |
Qiu X.L.; Li Q.L.; Zhou Y.; Jin X.Y.; Qi A.D.; Yang Y.W. Chem. Commun. 2015, 20, 4237.
|
| [55] |
Xu Y.H.; Shi W.; Li H.Y.; Li X.H.; Ma H.M. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1079.
doi: 10.1002/cmdc.v14.11 |
| [56] |
Aguirre-Chagala Y.E.; Santos J.L.; Aguilar-Castillo B.A.; Herrera-Alonso M. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 353.
doi: 10.1021/mz500047p |
| [57] |
Zhao Z.K.; Zhang Y.; Tian C.L.; Yin T.J.; Zhang C. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2605.
doi: 10.1039/C8BM00712H |
| [58] |
Bai J.A.; Tian Y.; Liu F.Z.; Li X.L.; Shao Y.; Lu X.T.; Wang J.T.; Zhu G.Q.; Xue B.Y.; Liu M.; Hu P.; He N.; Tang Q.Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18111.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b01827 |
| [59] |
Chen Y.J.; Han H.J.; Tong H.X.; Chen T.T.; Wang H.B.; Ji J.; Jin Q. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21185.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b06071 |
| [60] |
Fan B.; Kang L.; Chen L.P.; Sun P.; Jin M.J.; Wang Q.M.; Bea Y.H.; Huang W.; Gao Z.G. Theranostics 2017, 7, 357.
doi: 10.7150/thno.16855 pmid: 28042340 |
| [61] |
Kim J.; Lee Y.M.; Kim H.; Park D.; Kim J.; Kim W.J. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 102.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.022 |
| [62] |
Wang C.Y.; Qi P.L.; Lu Y.; Liu L.; Zhang Y.N.; Sheng Q.L; Wang T.S.; Zhang M.Y.; Wang R.; Song S.Y. Drug Delivery 2020, 27, 344.
doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1726526 |
| [63] |
Zhang P; Xu Q.N.; Li X.F.; Wang Y.X. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 2020, 108, 110396.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110396 |
| [64] |
Chen W.Z.; Zhen X.; Wu W.; Jiang X.Q. Sci. China : Chem. 2020, 63, 648.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-019-9699-3 |
| [65] |
Mansour O.; El Joukhar I.; Belbekhouche S. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 145, 104377.
doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.104377 |
| [66] |
Szatrowski T.P.; Nathan C.F. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 794.
pmid: 1846317 |
| [67] |
Li C.T.; Pan R.J.; Li P.Y.; Guan Q.H.; Ao J.P.; Wang K.; Xu L.; Liang X.F.; Jin X.; Zhang C.; Zhu X.Y. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5967.
|
| [68] |
Zhang Q.X.; Zhang F.Z.; Chen Y.; Dou Y.; Tao H.; Zhang D.L.; Wang R.B.; Li X.H.; Zhang J.X. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8221.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02412 |
| [69] |
Antunes F.; Cadenas E. Free Radicals Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1008.
doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00493-2 |
| [70] |
Ye M.Z.; Han Y.X.; Tang J.B.; Piao Y.; Liu X.R.; Zhou Z.X.; Gao J.Q.; Rao J.H.; Shen Y.Q. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702342.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201702342 |
| [71] |
Yin W.; Li J.J.; Ke W.D.; Zha Z.S.; Ge Z.S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29538.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b08347 |
| [72] |
Zhou J.; Yu G.C.; Yang J.; Shi B.B.; Ye B.Y.; Wang M.B.; Huang F.H.; Stang P.J. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 4564.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c00615 |
| [73] |
Qie S.Y.; Hao Y.; Liu Z.J.; Wang J.; Xi J.N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 232. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20010006 pmid: 0B5BD5DF-AE45-4D0D-BC88-82F43B17BE7B |
|
郄淑燕, 郝莹, 刘宗建, 王锦, 席家宁, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 232.).
doi: 10.6023/A20010006 pmid: 0B5BD5DF-AE45-4D0D-BC88-82F43B17BE7B |
|
| [74] |
Zhou J.Y.; Tang Q.J.; Zhong J.X.; Lei Z.T.; Luo H.P.; Tong Z.Z.; Jang G.H.; Liu X.D. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14063.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2622-8 |
| [1] | 曾崇洋, 胡平, 汪必琴, 方文彦, 赵可清. 氰基二苯乙烯桥联苯并菲二联体刺激响应盘状液晶: 合成、性质与应用[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3287-3296. |
| [2] | 路云乐, 王彦杰, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵. 多硫芳烃化合物的合成及聚集诱导磷光性质研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(11): 3549-3561. |
| [3] | 秦成远, 刘威, 聂永, 高迎, 苗金玲, 李天瑞, 蒋绪川. 聚集诱导发光有机氟化合物的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(8): 2232-2253. |
| [4] | 严子昂, 邹雷, 马骧. 纯有机超分子发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(7): 1814-1822. |
| [5] | 张依, 刘育. 多电荷环糊精的超分子组装[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(11): 3802-3811. |
| [6] | 唐雨平, 何艳梅, 范青华. 用于可切换不对称催化的人工刺激响应催化体系[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(11): 3672-3685. |
| [7] | 蔡晓冰, 胡薇, 陆国林, 黄晓宇. PPEGMEA-g-PBLG两亲性接枝共聚物的合成及其作为阿霉素输送载体的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2013, 33(12): 2520-2527. |
| [8] | 徐志远, 李永军, 史萍, 王博婵, 黄晓宇. 功能化石墨烯负载毛萼乙素抗肿瘤制剂的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2013, 33(10): 2162-2168. |
| [9] | 沈利英; 陈肖卓; 于海涛*; 梁 刚. 刺激响应型有机小分子凝胶的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2009, 29(03): 321-333. |
| [10] | 何 谷 , 郭 丽. 树枝状化合物作为药物载体的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2008, 28(08): 1326-1335. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||