有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 830-837.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202109022 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
李征a, 谷迎春a,*( ), 徐大振b, 费学宁a, 张磊a,*(
), 徐大振b, 费学宁a, 张磊a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-16
修回日期:2021-10-27
发布日期:2021-11-17
通讯作者:
谷迎春, 张磊
基金资助:
Zheng Lia, Yingchun Gua( ), Dazhen Xub, Xuening Feia, Lei Zhanga(
), Dazhen Xub, Xuening Feia, Lei Zhanga( )
)
Received:2021-09-16
Revised:2021-10-27
Published:2021-11-17
Contact:
Yingchun Gu, Lei Zhang
Supported by:文章分享

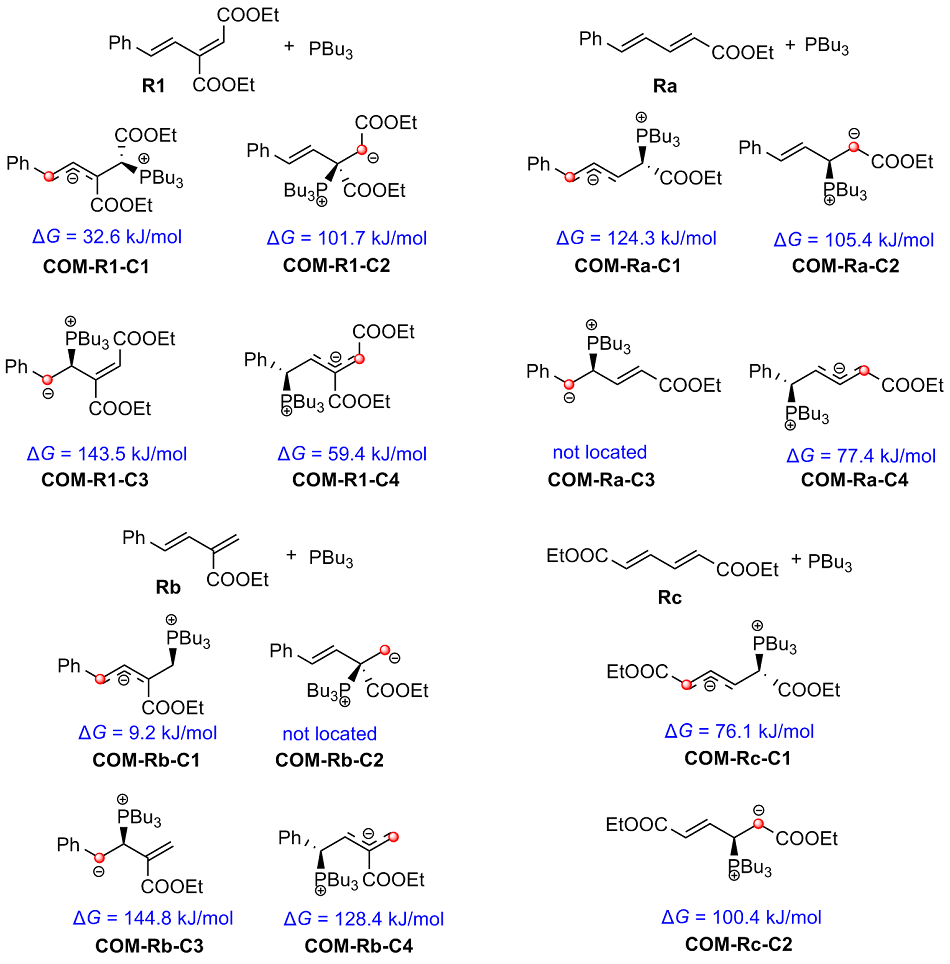
有机膦催化的环加成反应是构建重要杂环骨架的高效方法, 从文献报道中选取一个膦催化共轭二烯与α,β-不饱和酮的[4+2]环加成反应为研究对象, 通过密度泛函理论计算、表征反应的详细机制. 总反应包含的四个基元步骤依次为偶极离子形成、分子间亲核加成、分子内环化和膦配体解离. 活化自由能垒的计算值为84.4 kJ/mol, 总反应的自由能变的计算值为–18.8 kJ/mol. 当使用手性膦催化剂时, 计算出的反应机理和动力学参数与实验观测的对映异构选择性相符, 并且揭示了立体选择性的根源是空间位阻导致过渡态的扭转张力增大, 从而不利于次要对映异构体的形成. 最后, 设计了四种二烯底物, 分别考察了它们与膦催化剂形成的偶极离子中间体, 表明底物上的2-酯基对反应活性和位置选择性起至关重要的影响, 而1-酯基的作用可能不重要. 研究成果可以为优化实验条件和设计新反应提供理论指导.
李征, 谷迎春, 徐大振, 费学宁, 张磊. 有机膦催化的[4+2]环加成反应机理的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 830-837.
Zheng Li, Yingchun Gu, Dazhen Xu, Xuening Fei, Lei Zhang. Density Functional Theory Study on the Mechanism of Organophosphine-Catalyzed [4+2] Cycloaddition Reaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(3): 830-837.
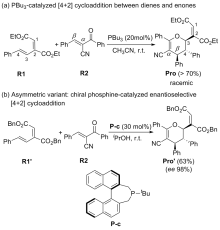

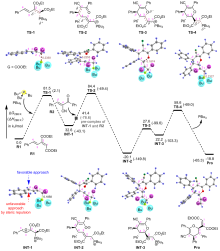
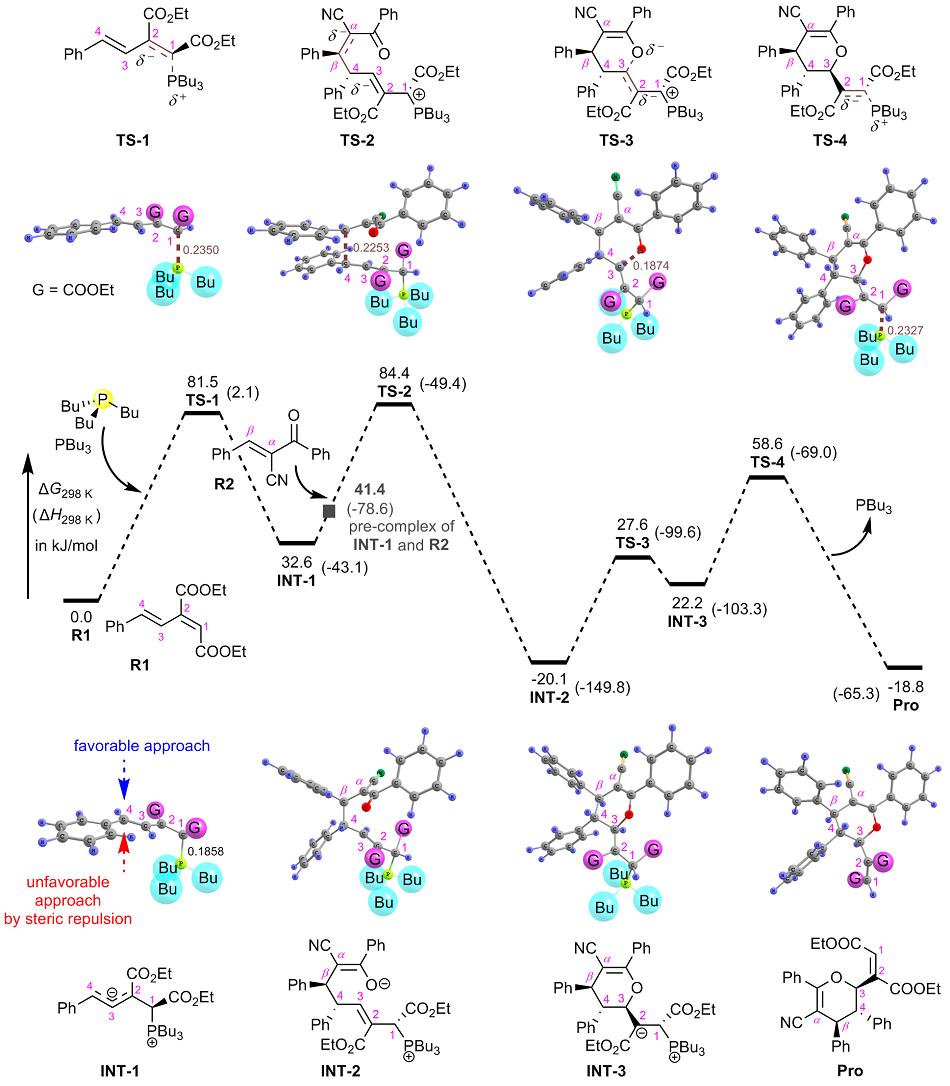
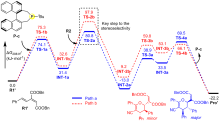


| [1] |
(a) Wang, N.-Z.; Wu, Z.-G.; Wang, J.-J.; Ullah, N.; Lu, Y.-X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 9766.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01124J |
|
(b) Cai, W.; Huang, Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3903. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202106004 |
|
|
(蔡卫, 黄有, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3903.)
|
|
| [2] |
(a) Huang, Y.-F.; Liao, J.-N.; Wang, W. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15235.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC05699E |
|
(b) Ni, H.-Z.; Chan, W.-L.; Lu, Y.-X. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9344.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00261 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Wang, H.-M.; Zhou, W.; Tao, M.-N.; Hu, A.-J.; Zhang, J.-L. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1710.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00489 |
|
(b) Tang, X.-D.; Tan, C.-X. A.; Chan, W.-L.; Zhang, F.-H.; Zheng, W.-R.; Lu, Y.-X. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 1361.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c05225 |
|
| [4] |
Ni, H.-Z.; Wong, Y.-L.; Wu, M.-Y.; Han, Z.-B.; Ding, K.-L.; Lu, Y.-X. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 2460.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00681 |
| [5] |
(a) Ziegler, D.-T.; Riesgo, L.; Ikeda, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Fu, G.-C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13183.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201405854 |
|
(b) Yang, M.; Cao, S.-X.; He, Z.-J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 2235. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201904041 |
|
|
(杨梅, 曹仕轩, 贺峥杰, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2235.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201904041 |
|
| [6] |
(a) Tran, Y.-S.; Kwon, O. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12632.
doi: 10.1021/ja0752181 |
|
(b) Gu, Y.-C.; Huang, Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 2251. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(谷迎春, 黄有, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2251.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201904017 |
|
| [7] |
Huang, G.-F.; Ren, X.-Y.; Jiang, C.-H.; Wu, H.-J.; Gao, G.-W.; Wang, T.-L. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 2872.
doi: 10.1039/C9QO00478E |
| [8] |
(a) Jin, Z.-X.; Ni, H.-Z.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, W.-R.; Lu, Y.-X. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5515.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b02519 |
|
(b) Zhang, X.-N.; Deng, H.-P.; Huang, L.; Wei, Y.; Shi, M. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8664.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc34619b |
|
| [9] |
(a) Schuler, M.; Duvvuru, D.; Retailleau, P.; Betzer, J.-F.; Marinett, A. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4406.
doi: 10.1021/ol901758k pmid: 19725549 |
|
(b) Li, N.; Jia, P.-H.; Huang, Y. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10976.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC05832J pmid: 19725549 |
|
| [10] |
(a) He, X.; Tang, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Chen, J.-B.; Xu, S.-L.; Dou, J.-W.; Li, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10698.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.31 |
|
(b) Wu, J.; Tang, Y.-H.; Wei, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Xu, S.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6284.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.21 |
|
| [11] |
(a) Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Peng, Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3995. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202102036 |
|
(张凯瑞, 王亚亚, 朱宏丹, 彭谦, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3995.)
|
|
|
(b) Li, S.-J.; Fang, D.-C. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 30815.
doi: 10.1039/C6CP05190A |
|
| [12] |
(a) Huang, G.-T.; Lankau, T.; Yu, C.-H. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 1700.
doi: 10.1021/jo402609v |
|
(b) Yu, Z.-Y.; Jin, Z.-J.; Duan, M.; Bai, R.-P.; Lu, Y.-X.; Lan, Y. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 9729.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b01259 |
|
|
(c) Wu, Y.; Li, M.-Z.; Jin, L.; Zhao, X. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2957.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03902 |
|
|
(d) Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Q. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13600.
doi: 10.1039/C9NJ01943J |
|
| [13] |
Li, K.; Gan, Z.-J.; Li, E.-Q.; Duan, Z. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 3094.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00780 |
| [14] |
Lu, T.; Chen, F. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580.
doi: 10.1002/jcc.v33.5 |
| [15] |
Johnson, E. R.; Keinan, S.; Mori-Sánchez, P.; Contreras-García, J.; Cohen, A. J.; Yang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6498.
doi: 10.1021/ja100936w pmid: 20394428 |
| [16] |
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgomery, J. A., Jr.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Cross, J. B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R. E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Voth, G. A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A. D.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2013.
|
| [17] |
Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194101.
doi: 10.1063/1.2370993 |
| [18] |
Scalmani, G.; Frisch, M. J. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 114110.
doi: 10.1063/1.3359469 |
| [19] |
Fukui, K. Acc. Chem. Res. 1981, 14, 363.
doi: 10.1021/ar00072a001 |
| [20] |
Marenich, A. V.; Cramer, C. J.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378.
doi: 10.1021/jp810292n |
| [21] |
(a) Mammen, M.; Shakhnovich, E. I.; Deutch, J. M.; Whitesides, G. M. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3821.
doi: 10.1021/jo970944f pmid: 25714789 |
|
(b) Besora, M.; Vidossich, P.; Lledós, A.; Ujaque, G.; Maseras, F. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 1392.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b11580 pmid: 25714789 |
|
|
(c) Liang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.-X. Chem.-Eur. J. 2008, 14, 4361.
doi: 10.1002/chem.200701725 pmid: 25714789 |
|
|
(d) Plata, R. E.; Singleton, D. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3811.
doi: 10.1021/ja5111392 pmid: 25714789 |
|
|
(e) Han, L.-L.; Li, S.-J.; Fang, D.-C. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 6182
doi: 10.1039/C5CP07803B pmid: 25714789 |
|
| [22] |
(a) Huang, F.; Lu, G.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.-X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12388.
doi: 10.1021/ja103531z pmid: 20707349 |
|
(b) Li, H.; Lu, G.; Jiang, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, Z.-X. Organometallics 2011, 30, 2349.
doi: 10.1021/om200089m pmid: 20707349 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, L.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lü, J.-F.; Feng, W.-C. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 6217.
pmid: 20707349 |
| [1] | 王兢睿, 冯永奎, 王能中, 黄年玉, 姚辉. 钯催化立体选择性合成硝基烷类β-碳糖苷[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3216-3225. |
| [2] | 向勋, 何照林, 董秀琴. 钯和手性磷酸协同催化高效构建手性分子的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 791-808. |
| [3] | 刘婷婷, 胡宇才, 沈安. 亚胺配体协同氮杂环卡宾钯配合物催化碳碳偶联反应的作用机制[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 622-628. |
| [4] | 钟绪琴, 刘振. 含过渡金属和柔性配体催化体系的构象搜索[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 734-741. |
| [5] | 刘悦灵, 钟欣欣, 张干兵. Pd(0)催化1-R-3-苯基亚丙基环丙烷(R=Me/H)与呋喃甲醛[3+2]环加成反应机理的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 660-667. |
| [6] | 潘康, 徐凡. 硅氨基镧化合物催化合成磷酸烯醇酯[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4261-4267. |
| [7] | 彭菊, 何晓倩, 廖黎丽, 白若鹏, 蓝宇. 取代基电性效应对碳硅还原消除区域选择性调控的理论研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(10): 3608-3613. |
| [8] | 田冲, 孙奇, 王俊锋, 陈俏, 温志国, Maxim Borzov, 聂万丽. 卤素阴离子催化的立体可控炔烃碳硼化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 338-344. |
| [9] | 孙奇, 孙泽颖, 俞泽, 王光伟. 镍催化炔烃的立体选择性芳基-二氟烷基化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(8): 2515-2520. |
| [10] | 黄泽鑫, 尹宇强, 贾丰成, 吴安心. 吲哚及其衍生物C2—C3键断裂的反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 2028-2044. |
| [11] | 来梦楠, 王秋圆, 华敏, 黄年玉, 姚辉. 开放体系中芳基岩藻糖/阿拉伯糖碳苷的立体选择性合成[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(6): 1694-1705. |
| [12] | 马丽文, 魏晓叶, 赵紫琳, 赵昂, 邓祥文, 霍丙南, 马刚, 张春芳. 端炔偶联反应中铜变价催化机制的理论研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(6): 1811-1819. |
| [13] | 石宇冰, 白文己, 母伟花, 李江平, 于嘉玮, 连冰. 钯催化C—H键官能团化形成C—X (X=O, N, F, I, ……)键的密度泛函理论研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1346-1374. |
| [14] | 朱有财, 丁欣欣, 孙莉, 刘振. CO2/C2H4耦合制备丙烯酸及其衍生物的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(4): 965-977. |
| [15] | 高娜, 初晓辉, 刘洋, 李家柱, 王进军. 焦脱镁叶绿酸的区域和立体选择性的芳(芳酰)亚甲基化及其叶绿素类二氢卟吩衍生物的合成[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(4): 1111-1122. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||