有机化学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2513-2522.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403047 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
何俊初a, 伍俊琪a, 王江辉a, 徐静文a, 唐本忠b, 赵祖金a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-28
修回日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-07-02
作者简介:基金资助:
Junchu Hea, Junqi Wua, Jianghui Wanga, Jingwen Xua, BenZhong Tangb, Zujin Zhaoa( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Revised:2024-06-20
Published:2024-07-02
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享
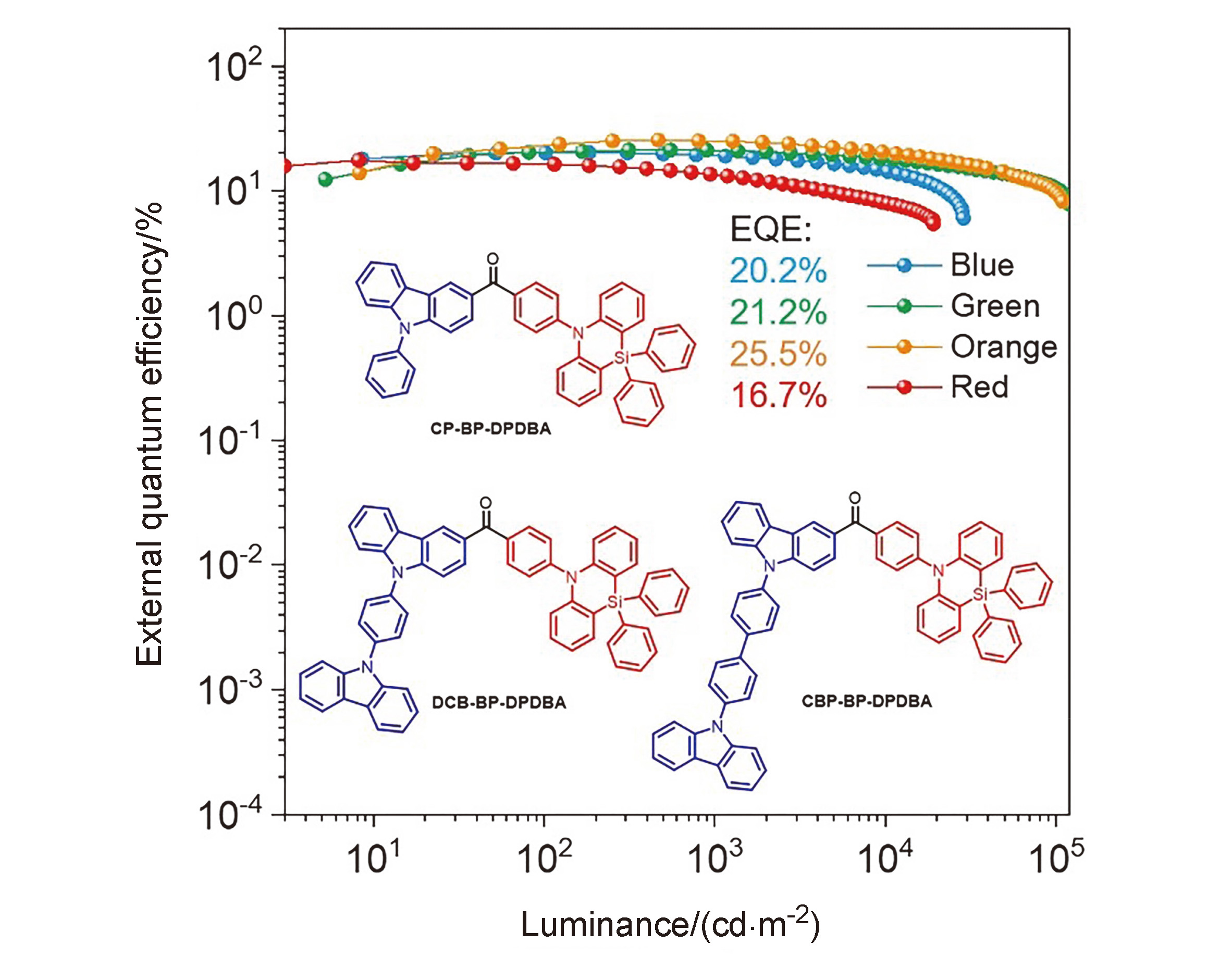
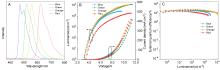
以硅杂吖啶(DPDBA)和咔唑衍生物作为电子给体、苯甲酮作为电子受体构筑给体-受体-给体(D-A-D')型分子, 开发了三个蓝光材料. 对材料的热稳定性、电化学性质、单晶结构、光物理性质和电致发光性能等进行了系统研究. 三个材料具有较小的单线态-三线态能级差以及微秒级别的延迟荧光寿命, 并表现出显著的聚集诱导延迟荧光(AIDF)特性. 以这些材料作为发光层制备的有机发光二极管(OLED)的最大外量子效率(EQE)达到14.8%, 发光峰在474~476 nm. 由于这些AIDF分子具有良好的双极载流子传输性能, 将这些材料作为主体材料制备了不同光色的磷光OLED器件, 器件表现出较为优秀的性能, 其中黄光和绿光器件的EQE分别为25.5%和21.2%, 在1000 cd•m−2亮度下效率滚降非常小. 因此, 所制备的这些AIDF分子可分别作为发光材料和主体材料用于高性能OLED器件的制备, 具有较好的应用前景.
何俊初, 伍俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金. 以二苯基硅杂吖啶为电子给体的蓝色聚集诱导延迟荧光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522.
Junchu He, Junqi Wu, Jianghui Wang, Jingwen Xu, BenZhong Tang, Zujin Zhao. Blue Aggregation-Induced Delayed Fluorescence Materials with 5,10-Dihydrodibenzo[b,e][1,4]azasiline as Donor[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522.



| Compd. | Solutiona | Neat film/doped filmb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λabs/nm | ФPLc/% | τd/ns | λem/nm | ФPLc/% | τd/ns | τe/μs | kRISCf/107 s-1 | ||
| CP-BP-DPDBA | 337 | 6.0 | 50 | 469/472 | 10.3/37.1 | 1.0/39.4 | 6.2/166.8 | —/0.98 | |
| DCB-BP-DPDBA | 339 | 6.7 | 10 | 467/468 | 7.8/44.6 | 0.6/13.4 | 4.8/160.8 | —/1.72 | |
| CBP-BP-DPDBA | 339 | 12.1 | 7 | 460/470 | 4.1/42.1 | 3.2/7.0 | 40.0/30.0 | —/5.50 | |
| Compd. | Solutiona | Neat film/doped filmb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λabs/nm | ФPLc/% | τd/ns | λem/nm | ФPLc/% | τd/ns | τe/μs | kRISCf/107 s-1 | ||
| CP-BP-DPDBA | 337 | 6.0 | 50 | 469/472 | 10.3/37.1 | 1.0/39.4 | 6.2/166.8 | —/0.98 | |
| DCB-BP-DPDBA | 339 | 6.7 | 10 | 467/468 | 7.8/44.6 | 0.6/13.4 | 4.8/160.8 | —/1.72 | |
| CBP-BP-DPDBA | 339 | 12.1 | 7 | 460/470 | 4.1/42.1 | 3.2/7.0 | 40.0/30.0 | —/5.50 | |
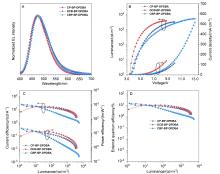

| EML | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m-2) | ηCb/(cd•A-1) | ηPb/(lm•W-1) | EQEb/% | λEL/nm | CIE/(x, y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-BP-DPDBA | 3.8 | 3170 | 23.6/7.8 | 19.5/3.4 | 13.2/4.4 | 474 | (0.164, 0.261) | ||
| DCB-BP-DPDBA | 3.4 | 3752 | 17.4/10.1 | 14.1/5.7 | 10.4/6.0 | 472 | (0.156, 0.254) | ||
| CBP-BP-DPDBA | 3.6 | 5168 | 25.7/2.6 | 22.4/1.0 | 14.8/1.5 | 476 | (0.159, 0.248) | ||
| EML | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m-2) | ηCb/(cd•A-1) | ηPb/(lm•W-1) | EQEb/% | λEL/nm | CIE/(x, y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-BP-DPDBA | 3.8 | 3170 | 23.6/7.8 | 19.5/3.4 | 13.2/4.4 | 474 | (0.164, 0.261) | ||
| DCB-BP-DPDBA | 3.4 | 3752 | 17.4/10.1 | 14.1/5.7 | 10.4/6.0 | 472 | (0.156, 0.254) | ||
| CBP-BP-DPDBA | 3.6 | 5168 | 25.7/2.6 | 22.4/1.0 | 14.8/1.5 | 476 | (0.159, 0.248) | ||

| EML | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m-2) | ηCb/(cd•A-1) | ηPb/(lm•W-1) | EQEb/% | λEL/nm | CIE/(x, y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FirPic:A | 3.2 | 28677 | 45.2/42.4 | 38.0/26.6 | 20.2/18.9 21.2/21.1 25.5/25.0 16.7/13.6 | 470 | (0.161, 0.373) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:A | 3.2 | 119911 | 78.8/78.5 | 59.3/51.4 | 520 | (0.313, 0.638) | |
| PO-01-TB:A | 3.2 | 109871 | 85.9/84.4 | 63.2/57.6 | 558 | (0.469, 0.526) | |
| Ir(piq)2acac:A | 3.4 | 19063 | 14.7/11.4 | 12.2/6.1 | 622 | (0.672, 0.323) | |
| FirPic:B | 3.2 | 6723 | 27.2/20.6 | 26.7/13.5 83.7/50.9 71.2/43.2 12.7/4.7 | 14.8/11.1 23.4/18.7 21.7/18.0 15.6/9.6 | 472 | (0.149, 0.349) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:B | 3.2 | 131771 | 85.3/68.0 | 520 | (0.298, 0.643) | ||
| PO-01-TB:B | 3.2 | 59680 | 72.6/60.4 | 558 | (0.463, 0.524) | ||
| Ir(piq)2acac:B | 3.4 | 17302 | 13.8/8.1 | 622 | (0.650, 0.320) | ||
| FirPic:C | 3.2 | 15190 | 22.7/22.7 | 20.9/16.2 | 12.0/12.0 | 470 | (0.149, 0.336) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:C | 3.0 | 106887 | 76.6/62.9 | 80.2/49.4 | 21.8/17.5 | 520 | (0.291, 0.644) |
| PO-01-TB:C | 3.2 | 36036 | 70.7/53.1 | 69.3/36.2 | 21.3/16.0 | 556 | (0.462, 0.527) |
| Ir(piq)2acac:C | 3.2 | 16444 | 12.9/8.2 | 12.7/5.2 | 14.8/9.4 | 622 | (0.650, 0.320) |
| EML | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m-2) | ηCb/(cd•A-1) | ηPb/(lm•W-1) | EQEb/% | λEL/nm | CIE/(x, y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FirPic:A | 3.2 | 28677 | 45.2/42.4 | 38.0/26.6 | 20.2/18.9 21.2/21.1 25.5/25.0 16.7/13.6 | 470 | (0.161, 0.373) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:A | 3.2 | 119911 | 78.8/78.5 | 59.3/51.4 | 520 | (0.313, 0.638) | |
| PO-01-TB:A | 3.2 | 109871 | 85.9/84.4 | 63.2/57.6 | 558 | (0.469, 0.526) | |
| Ir(piq)2acac:A | 3.4 | 19063 | 14.7/11.4 | 12.2/6.1 | 622 | (0.672, 0.323) | |
| FirPic:B | 3.2 | 6723 | 27.2/20.6 | 26.7/13.5 83.7/50.9 71.2/43.2 12.7/4.7 | 14.8/11.1 23.4/18.7 21.7/18.0 15.6/9.6 | 472 | (0.149, 0.349) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:B | 3.2 | 131771 | 85.3/68.0 | 520 | (0.298, 0.643) | ||
| PO-01-TB:B | 3.2 | 59680 | 72.6/60.4 | 558 | (0.463, 0.524) | ||
| Ir(piq)2acac:B | 3.4 | 17302 | 13.8/8.1 | 622 | (0.650, 0.320) | ||
| FirPic:C | 3.2 | 15190 | 22.7/22.7 | 20.9/16.2 | 12.0/12.0 | 470 | (0.149, 0.336) |
| Ir(ppy)2acac:C | 3.0 | 106887 | 76.6/62.9 | 80.2/49.4 | 21.8/17.5 | 520 | (0.291, 0.644) |
| PO-01-TB:C | 3.2 | 36036 | 70.7/53.1 | 69.3/36.2 | 21.3/16.0 | 556 | (0.462, 0.527) |
| Ir(piq)2acac:C | 3.2 | 16444 | 12.9/8.2 | 12.7/5.2 | 14.8/9.4 | 622 | (0.650, 0.320) |
| [1] |
Jong, H.; Yasuda, T. Adv. Opt. Mate.. 2022, 10, 2201714.
|
| [2] |
Yu, M. X.; Huang, R. S.; Guo, J. J.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Photoni. 2020, 1, 11.
|
| [3] |
Uoyama, H.; Goushi, K.; Shizu, K.; Nomura, H.; Adachi, C. Natur. 2012, 492, 234.
|
| [4] |
Liu, H.; Zeng, J.; Guo, J.; Nie, H.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9290.
|
| [5] |
Zhang, D.; Song, X.; Gillett, A. J.; Drummond, B. H.; Jones, S. T. E.; Li, G.; He, H.; Cai, M.; Credgington, D.; Duan, L. Adv. Mate.. 2020, 32, 1908355.
|
| [6] |
Huang, T.; Jiang, W.; Duan, L. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 5577.
|
| [7] |
Huang, C.; Qiu, Z. P.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W. W.; Ji, S. M.; Huo, Y. P. Chin. J. Org. Che.. 2021, 41, 3050 (in Chinese).
|
|
(黄酬, 邱志鹏, 高杨, 陈文铖, 籍少敏, 霍延平, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3050.)
|
|
| [8] |
Zhang, Y. H.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. F.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y. P.; Chen, W. C.; Zhao, Z. J. Chin. J. Org. Che.. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.)
|
|
| [9] |
Li, C.; Fan, X.; Han, C.; Xu, H. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6747.
|
| [10] |
Wang, T. T.; Hua, X. C.; Yu, Y. J.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, M. Q.; Jiang, Z. Q. Chin. J. Org. Che.. 2019, 39, 1436 (in Chinese).
|
|
(王彤彤, 华晓晨, 郁友军, 袁熠, 冯敏强, 蒋佐权, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1436.)
|
|
| [11] |
Ye, Z. H.; Yang, J. L.; Ling, Z. T.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, Y. Q.; Wei, B.; Shi, Y. Chin. J. Org. Che.. 2019, 39, 449 (in Chinese).
|
|
(叶中华, 杨佳丽, 凌志天, 赵艺, 陈果, 郑燕琼, 魏斌, 施鹰, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 449.)
|
|
| [12] |
Tan, J. H.; Huo, Y. P.; Cai, N.; Ji, S. M.; Li, Z. Z.; Zhang, L. Chin. J. Org. Che.. 2017, 37, 2457 (in Chinese).
|
|
(谭继华, 霍延平, 蔡宁, 籍少敏, 李宗植, 张力, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 2457.)
|
|
| [13] |
Song, W.; Lee, I.; Lee, J. Y. Adv. Mate.. 2015, 27, 4358.
|
| [14] |
Li, C.; Duan, L.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2015, 7, 15154.
|
| [15] |
Zhang, D.; Duan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Bin, Z.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, J.; Dong, G.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Y. Adv. Funct. Mate.. 2014, 24, 3551.
|
| [16] |
Zhang, D.; Duan, L.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, Y. Adv. Mate.. 2014, 26, 5050.
|
| [17] |
Guo, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Si, C.; Peng, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Wei, B. Chem. Sc.. 2017, 8, 1259.
|
| [18] |
Jeon, S. K.; Oh, C. S.; Kim, M.; Yook, K. S.; Lee, J. Y. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1606.
|
| [19] |
Yang, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S.; Zhao, Z. J.; Li, X.; Ji, S.; Huo, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2020, 12, 29528.
|
| [20] |
Song, S.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Dyes Pig.. 2021, 196, 109776.
|
| [21] |
Zeng, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Chem.-Asian J. 2019, 14, 828.
|
| [22] |
Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Opt. Mate.. 2022, 10, 2102568.
|
| [23] |
Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Guo, J.; Zeng, J.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Opt. Mate.. 2020, 8, 2001027
|
| [24] |
Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 9549.
|
| [25] |
Huang, R. S.; Yang, Z. G.; Wang, J. H.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Tang, B. Z.; Zhao, Z. J. Chin. J. Che.. 2023, 41, 527.
|
| [26] |
Woo, S.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, S; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2019, 11, 7199.
|
| [27] |
He, J. C.; Chen, H.; Li, J. S.; Wang, J. H.; Xu, J. W.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Cell Rep. Phys. Sc.. 2022, 3, 100733.
|
| [28] |
Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A. J. Chem. Phy.. 2010, 132, 154104.
|
| [29] |
Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. J. Comput. Che.. 2011, 32, 1456.
|
| [30] |
Yang, Z.; Ge, X.; Li, W.; Mao, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Long, G. F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chi, Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136219.
|
| [31] |
Zeng, J.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Redshaw, C.; Feng, X.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Opt. Mate.. 2022, 10, 2200917.
|
| [32] |
Wan, Q.; Dai, W.; Xie, Y.; Ke, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138529.
|
| [33] |
Guo, J.; Fan, J.; Lin, L.; Zeng, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. K.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Sc.. 2019, 6, 1801629.
|
| [34] |
Kim, H. J.; Kang, H.; Jeong, J. E.; Park, S. H.; Koh, C. W.; Kim, C. W.; Woo, H. Y.; Cho, M. J.; Park, S.; Choi, D. H. Adv. Funct. Mate.. 2021, 31, 2102588.
|
| [35] |
Cai, Z.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Front. Che.. 2020, 8, 193.
|
| [36] |
Matsuo, K.; Yasuda, T. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 10, 10687.
|
| [37] |
Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, D. Z.; Ma, D. G.; Zhao, Z. J.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. Ad.. 2021, 7, eabj2504.
|
| [38] |
Guo, J. J.; Li, X. L.; Nie, H.; Luo, W. W.; Gan, S. F.; Hu, S. M.; Hu, R. R.; Qin, A. J.; Zhao, Z. J.; Su, S. J.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606458.
|
| [39] |
An, Z.; Yu, J.; Jones, S. C.; Barlow, S.; Yoo, S.; Domercq, B.; Prins, P.; Siebbeles, L. D. A.; Kippelen, B.; Marder, S. R. Adv. Mate.. 2005, 17, 2580.
|
| [1] | 唐子然, 孙浩, 朱亮亮. 光刺激响应型聚集诱导发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [2] | 张洁, 李楠, 赵娜. 聚集诱导发光分子纳米酶复合材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| [3] | 宫清宝, 吕翔, 于长江, 李婉婉, 赵全胜, 焦莉娟, 郝二红. 聚集诱导发光活性氟硼吡啶肼醛腙染料的合成、晶体结构及光学性质[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [4] | 王源浩, 孙钰凯, 刘昱迒, 张照明, 颜徐州. 基于四苯乙烯的柔性发光材料的构筑及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544. |
| [5] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [6] | 沈钇灼, 罗康为, 徐清洋, 张鉴予, 孙景志, 张浩可, 唐本忠. 弱作用基有机发光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [7] | 谢志鑫, 黎少玲, 刘威, 严楷, 蒋涛, 刘一苇, Md. Monarul Islam, 冯星. 窄化芘基发光分子半峰宽的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [8] | 孟子翔, 田秀梅, 张天富. 聚集诱导发光材料在肿瘤光治疗应用中的最新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [9] | 黄伟庚, 高翼亭, 孙妍, 燕鼎元, 王东, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光材料用于肿瘤光学诊疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [10] | 黄凯航, 尹理, 姜青云, 汪乾, 石光, 许炳佳. 具有聚集诱导发光性质的高效热激活延迟荧光材料用于脂滴成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [11] | 杨玉杰, 曹微, 于际凯, 张志霞, 徐莉, 王华. 给体-受体(D-A)型苯基环八四噻吩的合成及其聚集诱导发光与高压发光性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [12] | 苏小龙, 李健鹏, 刘孟鑫, 邹莉, 杨得锁, 冯海涛. 四苯乙烯酰胺类化合物的合成及其高灵敏度、高选择性识别Cu2+[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [13] | 欧彦, 蓝琳, 王正雄, 王志明, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光型核酸探针的制备及其核酸传感原理研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562. |
| [14] | 胡甲松, 李春娟, 徐斌, 田文晶. 固态荧光光开关分子研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [15] | 李治, 李祯龙, 刘俊杰, 憨卫国, 游劲松, 宾正杨. 基于七元环三芳胺给体的蓝光热活化延迟荧光材料的构筑[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 2006-2013. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||