有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 2509-2519.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202411024 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
张威光a,†, 张国锋a,†, 李梦a, 李雪莲c, 包书红a, 葛李宵a, 施志平a, 申强强a, 姚李a,*( ), 朱三娥a,b,*(
), 朱三娥a,b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-29
修回日期:2025-01-06
发布日期:2025-02-07
作者简介:基金资助:
Weiguang Zhanga, Guofeng Zhanga, Meng Lia, Xuelian Lic, Shuhong Baoa, Lixiao Gea, Zhiping Shia, Qiangqiang Shena, Li Yaoa,*( ), San E Zhua,b,*(
), San E Zhua,b,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-29
Revised:2025-01-06
Published:2025-02-07
Contact:
*E-mail: yaoli@hfuu.edu.cn; zhuse@hfuu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:文章分享

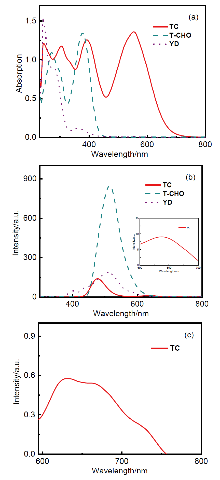
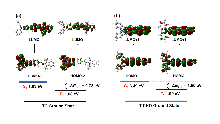
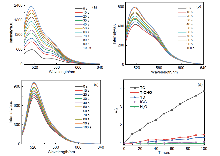
开发具有多种活性氧(ROS)生成能力的光敏剂(PSs)对于提升光动力治疗(PDT)的疗效具有重要意义. 在分子中引入电子供体(D)-共轭桥(π)-电子受体(A)结构, 能够拓展分子的共轭体系与光捕获范围, 有效分离最高占据分子轨道(HOMO)与最低未占分子轨道(LUMO)的电子云, 减小单重态与三重态能级差(ΔES-T), 促进系间窜跃(ISC), 提高ROS生成效率. 本研究以三苯胺为供体, 吲哚碘鎓为受体, 苯乙烯基为π桥, 成功合成了D-π-A结构的半花菁光敏剂(E)-2-(2- (4'-(二苯胺基)-[1,1'-联苯]-4-基)乙烯基)-1-乙基-3,3-二甲基-3H-吲哚-1-铵碘盐(TC). 与单体分子4'-(二苯基氨基)-[1,1'-联苯]-4-甲醛(T-CHO)和1-乙基-2,3,3-三甲基-3H-吲哚-1-铵碘盐(YD)相比(T-CHO: 400~456 nm; YD: 400~440 nm), TC的光捕获范围显著拓展至400~745 nm.. 稳态和瞬态荧光结果表明, 与T-CHO和YD相比, TC的荧光强度和寿命显著降低. 理论计算显示, TC的ΔES-T值为0.73 eV, 远低于T-CHO的1.50 eV. ROS生成研究表明, TC在Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型及总ROS的生成能力上均显著优于单体分子和吲哚菁绿(ICG). 本研究为新型PSs的设计提供了重要的理论依据与实验支持.
张威光, 张国锋, 李梦, 李雪莲, 包书红, 葛李宵, 施志平, 申强强, 姚李, 朱三娥. I型和II型D-π-A半花菁光敏剂的合成、光物理性质与活性氧生成机制[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(7): 2509-2519.
Weiguang Zhang, Guofeng Zhang, Meng Li, Xuelian Li, Shuhong Bao, Lixiao Ge, Zhiping Shi, Qiangqiang Shen, Li Yao, San E Zhu. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Mechanism of Type I and Type II D-π-A Hemicyanine Photosensitizers[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(7): 2509-2519.

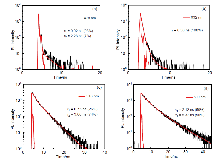




| Photosensitizer | kobsb/s-1 | vic | Φ∆d |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 1.760 | 0.1760 | 0.766 |
| T-CHO YD | 0.072 0.048 | 0.0072 0.0048 | 0.152 —e |
| ICG | 0.045 | 0.0045 | 0.002 |
| Photosensitizer | kobsb/s-1 | vic | Φ∆d |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 1.760 | 0.1760 | 0.766 |
| T-CHO YD | 0.072 0.048 | 0.0072 0.0048 | 0.152 —e |
| ICG | 0.045 | 0.0045 | 0.002 |





| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
( 张碧玮, 袁展翔, 徐建兴, 籍少敏, 霍延平, 梁亮, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2929.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202002027 |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4085-0 pmid: 35126878 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [1] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [2] | 徐茂财, 田佳壮, 杨艳华, 苟高章, 李福敏, 邵林, 池可心. 一种三苯胺基二氟硼发光化合物的力致可逆荧光变色及数据安全保护研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1824-1831. |
| [3] | 王妮, 郑姿君, 贾小苹, 赵梦圆, 王亚蕾, 周臣, 王志佳, 肖泽霖, 刘宏民, 可钰. 济源冬凌草甲素衍生物作为潜在抗肿瘤药物的合成及药理学活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 646-659. |
| [4] | 陈思鸿, 陈淇, 罗时荷, 曹西颖, 杨国贤, 曾晓晴, 汪朝阳. 基于三苯胺的荧光探针设计、合成与应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(3): 919-933. |
| [5] | 汪文源, 陈洪进, 张纲, 张蕤, 刘建. 基于给体-受体型三苯胺喹喔啉类电致变色材料的合成及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(8): 2513-2519. |
| [6] | 张燕, 王芸芸, 赵雨珣, 张成龙, 谷文, 王忠龙, 朱永强, 王石发. 樟脑基缩氨基硫脲衍生物通过活性氧(ROS)介导的线粒体途径诱导人乳腺癌细胞的G2期阻滞和凋亡[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(8): 2374-2386. |
| [7] | 周鑫云, 谢凌超, 吴凯乐, 谭松庭. 含树枝状和3D三苯胺衍生物有机染料的合成与光伏性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(9): 2589-2598. |
| [8] | 鄢剑锋, 张睿祺, 原野, 袁耀锋. 4,4'-二甲氧基三苯胺取代偶氮苯开关分子的设计合成、电化学及光化学性质研究[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(7): 2009-2017. |
| [9] | 矫春鹏, 刘媛媛, 路文娟, 张平平, 王延风. 检测活性氮/活性氧的分子荧光探针[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(3): 591-616. |
| [10] | 后际挺, 李坤, 覃彩芹, 余孝其. 活性氧簇的小分子荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(3): 612-628. |
| [11] | 王延宝, 赵宝祥. 次氯酸荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2016, 36(7): 1539-1554. |
| [12] | 毛利军, 谭青龙, 辛冠琼, 韩明亮, 张学俊. 不对称三苯胺-锌酞菁的合成及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2012, 32(12): 2315-2321. |
| [13] | 孟祥丽,黄玉东,牛海军, 雷作涛. 4,4'-二氨基三苯胺的合成与纯化[J]. 有机化学, 2007, 27(05): 682-684. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||