有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (7): 2192-2200.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202203017 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
闫法超a,b, 李洋a,b, 李玉东a, Mohamed Makhaa, 李跃辉a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-06
修回日期:2022-03-22
发布日期:2022-08-09
通讯作者:
李跃辉
作者简介:基金资助:
Fachao Yana,b, Yang Lia,b, Yudong Lia, Mohamed Makhaa, Yuehui Lia( )
)
Received:2022-03-06
Revised:2022-03-22
Published:2022-08-09
Contact:
Yuehui Li
About author:Supported by:文章分享
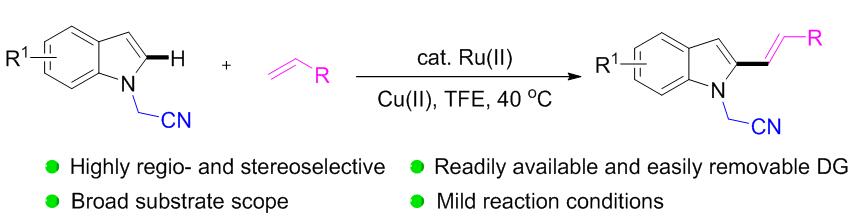
首次利用氰甲基作为导向基团, 在钌(II)催化下实现了吲哚及其衍生物C(2)位C—H的选择性烯基化反应, 制备得到了一系列具有潜在应用价值的吲哚C(2)-烯基化产物. 该反应条件温和, 并表现出较好的底物普适性和官能团兼容性, 酯基、氰基、碘、溴、氟和三氟甲基等均被较好地兼容. 该导向基团可以在相对温和的条件下方便地移除, 生成 N—H吲哚类化合物.
闫法超, 李洋, 李玉东, Mohamed Makha, 李跃辉. 氰甲基导向的吲哚选择性C—H烯基化[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 2192-2200.
Fachao Yan, Yang Li, Yudong Li, Mohamed Makha, Yuehui Li. Ru(II)-Catalyzed Regioselective C—H Alkenylation of Indoles Using Cyanomethyl Directing Group[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2192-2200.
| Entry | Catalyst | [Ag] | Additive | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | — | 30 |
| 2 | Ru(OAc)2(p-cymene) | AgSbF6 | — | 11 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgSbF6 | — | 2 |
| 4 | [Rh(COD)Cl]2 | AgSbF6 | — | Trace |
| 5 | [Cp*Co(CO)I2] | AgSbF6 | — | n.d. |
| 6 | Mn(CO)5Br | AgSbF6 | — | n.d. |
| 7 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | KOAc | 24 |
| 8 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 52 |
| 9 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgPF6 | DABCO | 31 |
| 10 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgOTf | DABCO | 35 |
| 11c | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 58 |
| 12c,d | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 80 |
| 13c,d,e | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 26 |
| 14c,d,f | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 3 |
| 15c,d,g | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | n.d. |
| 16c | — | AgSbF6 | DABCO | n.d. |
| Entry | Catalyst | [Ag] | Additive | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | — | 30 |
| 2 | Ru(OAc)2(p-cymene) | AgSbF6 | — | 11 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgSbF6 | — | 2 |
| 4 | [Rh(COD)Cl]2 | AgSbF6 | — | Trace |
| 5 | [Cp*Co(CO)I2] | AgSbF6 | — | n.d. |
| 6 | Mn(CO)5Br | AgSbF6 | — | n.d. |
| 7 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | KOAc | 24 |
| 8 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 52 |
| 9 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgPF6 | DABCO | 31 |
| 10 | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgOTf | DABCO | 35 |
| 11c | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 58 |
| 12c,d | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 80 |
| 13c,d,e | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 26 |
| 14c,d,f | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | 3 |
| 15c,d,g | [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | AgSbF6 | DABCO | n.d. |
| 16c | — | AgSbF6 | DABCO | n.d. |
| [1] |
(a) Zhang, M.-Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.-F. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 421.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.065 pmid: 20380420 |
|
(b) Somei, M.; Yamada, F. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 73.
doi: 10.1039/b316241a pmid: 20380420 |
|
|
(c) Kochanowska-Karamyan, A. J.; Hamann, M. T. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4489.
doi: 10.1021/cr900211p pmid: 20380420 |
|
|
(d) Kaushik, N. K.; Kaushik, N.; Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Kim, C. H.; Verma, A. K.; Choi, E. H. Molecules 2013, 18, 6620.
doi: 10.3390/molecules18066620 pmid: 20380420 |
|
|
(e) Liu, X.-Y.; Qin, Y. Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 25.
pmid: 20380420 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Xie, W.; Zuo, Z.; Zi, W.; Ma, D. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 869. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201301035 |
|
( 谢卫青, 左智伟, 资伟伟, 马大为, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 869.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201301035 |
|
|
(b) Zhang, D.; Qin, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 147. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12121037 |
|
|
( 张丹, 秦勇, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 147.)
doi: 10.6023/A12121037 |
|
|
(c) Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Yang, X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 75. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202107012 |
|
|
( 王弯弯, 张明明, 杨文超, 杨小虎, 有机化学, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 75.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202107012 |
|
|
(d) Hegedus, L. S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1988, 27, 1113.
doi: 10.1002/anie.198811133 |
|
|
(e) Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2873.
doi: 10.1021/cr040639b |
|
|
(f) Ackermann, L. Synlett 2007, 4, 507.
|
|
|
(g) Ma, W.; Gandeepan, P.; Li, J.; Ackermann, L. Org. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1435.
doi: 10.1039/C7QO00134G |
|
|
(h) Kumar, P.; Nagtilak, P. J.; Kapur, M. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 13692.
doi: 10.1039/D1NJ01696B |
|
|
(i) Rago, A. J.; Dong, G. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 216.
|
|
|
(j) Cerveria, A.; Bandini, M. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 287.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201900446 |
|
|
(k) Yang, P.; Xu, R.-Q.; Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 235.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201900509 |
|
|
(l) Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F. Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 84.
|
|
|
(m) Li, R.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, H.; Lei, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S.; Deng, G.-J. Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 95.
|
|
| [3] |
(a) Moritani, I.; Fujiwara, Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967, 8, 1119.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)90648-8 pmid: 17973536 |
|
(b) Danno, S.; Asano, R.; Teranishi, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 7166.
doi: 10.1021/ja01053a047 pmid: 17973536 |
|
|
(c) Jia, C.; Kitamura, T.; Fujiwara, Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 633.
doi: 10.1021/ar000209h pmid: 17973536 |
|
|
(d) Beccalli, E. M.; Broggini, G.; Martinelli, M.; Sottocornola, S. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5318.
pmid: 17973536 |
|
|
(e) Wang, Z.-T.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Wang, S.-C.; Xia, D.-H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 27, 143. (in Chinese)
pmid: 17973536 |
|
|
( 王宗廷, 张云山, 王书超, 夏道宏, 有机化学, 2007, 27, 143.)
pmid: 17973536 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Gai, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 2111.
doi: 10.1021/jo4028177 pmid: 26629889 |
|
(b) Basceken, S.; Kaya, S.; Balci, M. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12552.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02419 pmid: 26629889 |
|
|
(c) Yan, J.; Ni, T.; Yan, F. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1096.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.01.080 pmid: 26629889 |
|
| [5] |
(a) Lyons, T. W.; Sanford, M. S. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1147.
doi: 10.1021/cr900184e |
|
(b) Rousseau, G.; Breit, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2450.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201006139 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Su, W. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 843.
doi: 10.1039/C4QO00068D |
|
|
(d) Huang, Z.; Lim, H. N.; Mo, F.; Young, M. C. Dong, G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7764.
|
|
| [6] |
(a) Zhang, L.-Q.; Yang, S.; Huang, X.; You, J.; Song, F. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8830.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc44787a pmid: 33417465 |
|
(b) Li, B.; Ma, J.; Xie, W.; Song, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 19, 11863.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201301987 pmid: 33417465 |
|
|
(c) Ikemoto, H.; Yoshino, T.; Sakata, K.; Matsunaga, S.; Kanai, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5424.
doi: 10.1021/ja5008432 pmid: 33417465 |
|
|
(d) Ikemoto, H.; Tanaka, R.; Sakata, K.; Kanai, M.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7156.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201703193 pmid: 33417465 |
|
|
(e) Li, M.; Yao, T.-Y.; Sun, S.-Z.; Yan, T.-X.; Wen, L.-R.; Zhang, L.-B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 3158.
doi: 10.1039/D0OB00508H pmid: 33417465 |
|
|
(f) Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Dai, W.; Jia, X.; Ni, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, F. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 9163.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03077 pmid: 33417465 |
|
|
(g) Zhao, F.; Gong, X.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Jia, X.; Ni, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 727.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03950 pmid: 33417465 |
|
| [7] |
Lanke, V.; Prabhu, K. R. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2818.
doi: 10.1021/ol4011486 |
| [8] |
(a) Ding, Z.; Yoshikai, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4698.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201200019 pmid: 25575183 |
|
(b) Liang, L.; Fu, S.; Lin, D.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, W. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 9472.
doi: 10.1021/jo501460h pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(c) Wong, M. Y.; Yamakawa, T.; Yoshikai, N. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 442.
doi: 10.1021/ol503395g pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(d) Tian, P.; Feng, C.; Loh, T.-P. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7472.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8472 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(e) Kong, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, X. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6320.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03203 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(f) Cai, S.-H.; Ye, L.; Wang, D.-X.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Lai, L.-J.; Zhu, C.; Feng, C.; Loh, T.-P. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8731.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC04131D pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(g) Nakanowatari, S.; Mei, R.; Feldt, M.; Ackermann, L. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2511.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00207 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(h) Zhou, C.-N.; Xie, H.-H.; Zheng, Z.-A.; Xiao, Y.-C.; Li, G.; Shen, Y.-H.; Peng, W.-M.; Wang, L. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 5469.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201706025 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(i) Jagtap, R. A.; Vinod, C. P.; Punji, B. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 431.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b04267 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(j) Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Huang, H. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1509.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201301107 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(k) Zhou, X.; Luo, Y.; Kong, L.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Lan, Y.; Li, X. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 7296.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b02248 pmid: 25575183 |
|
|
(l) Wang, Z.-T.; Zheng, Z.-A.; Li, P.-J.; Zhou, C.-N.; Cai, S.-J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, L. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2823.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202100221 pmid: 25575183 |
|
| [9] |
(a) Garc, A.; Ram, R.; Mez, G.; Array, S.; Carretero, J. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 121, 6633.
|
|
(b) Yan, Z.-L.; Chen, W.-L.; Gao, Y.-R.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1085.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201300811 |
|
| [10] |
Sharma, S.; Han, S.; Kim, M.; Mishra, N. K.; Park, J.; Shin, Y.; Ha, J.; Kwak, J. H.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1703.
doi: 10.1039/C3OB42605J |
| [11] |
(a) Anbarasan, P.; Schareina, T.; Beller, M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5049.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15004a pmid: 20804202 |
|
(b) Fleming, F. F.; Yao, L.; Ravikumar, P. C.; Funk, L.; Shook, B. C. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7902.
doi: 10.1021/jm100762r pmid: 20804202 |
|
| [12] |
(a) Ping, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, Q.; Peng, Y. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 3274.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201700684 |
|
(b) Sinha, S. K.; Guin, S.; Maiti, S.; Biswas, J. P.; Porey, S.; Maiti, D. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5682.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00220 |
|
| [13] |
(a) Gandeepan, P.; Cheng, C.-H. Chem.-Asian J. 2015, 10, 824.
doi: 10.1002/asia.201403224 |
|
(b) Gandeepan, P.; Cheng, C.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5738.
doi: 10.1021/ja300168m |
|
|
(c) Reddy, M. C.; Jeganmohan, M. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10738.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC03112E |
|
| [14] |
(a) Leow, D.; Li, G.; Mei, T.-S.; Yu, J.-Q. Nature 2012, 486, 518.
doi: 10.1038/nature11158 |
|
(b) Yang, Y.-F.; Cheng, G.-J.; Liu, P.; Leow, D.; Sun, T.-Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.-Q.; Wu, Y.-D.; Houk, K. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 344.
doi: 10.1021/ja410485g |
|
|
(c) Tang, R.-Y.; Li, G.; Yu, J.-Q. Nature 2014, 507, 215.
doi: 10.1038/nature12963 |
|
|
(d) Yang, G.; Lindovska, P.; Zhu, D; Kim, J.; Wang, P.; Tang, R.-Y.; Movassaghi, M.; Yu, J.-Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10807.
doi: 10.1021/ja505737x |
|
|
(e) Deng, Y.; Yu, J.-Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 888.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201409860 |
|
|
(f) Xu, H.-J.; Lu, Y.; Farmer, M. E.; Wang, H.-W.; Zhao, D.; Kang, Y.-S.; Sun, W.-Y.; Yu, J.-Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2200.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b13269 |
|
|
(g) Fan, Z.; Bay, K. L.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Park, H. S.; Yeung, K.-S.; Houk, K. N.; Yu, J.-Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4770.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201915624 |
|
|
(h) Lam, N. Y. S.; Fan, Z.; Wu, K.; Park, H. S.; Shim, S. Y.; Strassfeld, D. A.; Yu, J.-Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2793.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c12654 |
|
| [15] |
(a) Bera, M.; Modak, A.; Patra, T.; Maji, A.; Maiti, D. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5760.
doi: 10.1021/ol502823c |
|
(b) Bag, S.; Patra, T.; Modak, A.; Deb, A.; Maity, S.; Dutta, U.; Dey, A.; Kancherla, R.; Maji, A.; Hazra, A.; Bera, M.; Maiti, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11888.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b06793 |
|
|
(c) Bera, M.; Maji, A.; Sahoo, S. K.; Maiti, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8515.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201503112 |
|
|
(d) Dey, A.; Maity, S.; Maiti, D. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12398.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC05235E |
|
| [16] |
Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Tan, K. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18778.
doi: 10.1021/ja4107034 |
| [17] |
Ramesh, P.; Sreenivasulu, C.; Kishore, D. R.; Srinivas, D.; Gorantla, K. R.; Mallik, B. S.; Satyanarayana, G. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 2204.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c02865 pmid: 35143206 |
| [18] |
(a) Li, S.; Ji, H.; Cai, L.; Li, G. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5595.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC01737H |
|
(b) Li, S.; Cai, L.; Ji, H.; Yang, L.; Li, G. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10443.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms10443 |
|
| [19] |
Ping, L.; Chung, D. S.; Bouffard, J.; Lee, S. G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4299.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00064B |
| [20] |
Yan, F.; Huang, Z.; Du, C.-X.; Bai, J.-F.; Li, Y. J. Catal. 2021, 395, 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2021.01.003 |
| [21] |
(a) Enders, D.; Shilvock, J. P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 359.
doi: 10.1039/a908290e |
|
(b) Otto, N.; Opatz, T. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 13064.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201403956 |
|
| [22] |
Donald, J. R.; Berrell, S. L. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5832.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc01370a pmid: 31293772 |
| [23] |
(a) Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, T.-T.; Yao, L.; Wang, Q.-L.; Zhao, L.-M. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 9514.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00249 |
|
(b) Jambu, S.; Tamizmani, M.; Jeganmohan, M. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1982.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00533 |
|
|
(c) Chen, W.; Li, H.-J.; Li, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 500.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB02421B |
|
|
(d) Leitch, J. A.; Wilson, P. B.; McMullin, C. L.; Mahon, M. F.; Bhonoah, Y.; Williams, I. H.; Frost, C. G. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5520.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01370 |
| [1] | 梅青刚, 李清寒. 可见光促进C(3)(杂)芳硫基吲哚化合物的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 398-408. |
| [2] | 贝文峰, 潘健, 冉冬梅, 刘伊琳, 杨震, 冯若昆. 基于钴催化吲哚酰胺与二炔和单炔的[4+2]环化反应合成γ-咔啉酮[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3226-3238. |
| [3] | 岁丹丹, 岑南楠, 龚若蕖, 陈阳, 陈文博. 无支持电解质条件下连续流电化学合成三氟甲基化氧化吲哚[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3239-3245. |
| [4] | 王熠, 张键, 刘飏子, 罗晓燕, 邓卫平. 钯催化不对称[3+4]环加成构建吲哚并环庚烷[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2864-2877. |
| [5] | 周章涛, 王杨, 程冰心, 叶伟平. [RuCl(p-cymene)-(S)-BINAP]Cl催化不对称合成反式-3-氨基-双环[2.2.2]辛烷-2-甲酸乙酯[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2961-2967. |
| [6] | 冯莹珂, 王贺, 崔梦行, 孙然, 王欣, 陈阳, 李蕾. 可见光诱导的新型官能化芳基异腈化合物的二氟烷基化环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2913-2925. |
| [7] | 张彦波, 孙萌. 铑催化碳酸亚乙烯酯与吲哚啉C(7)位C—H甲酰甲基化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2905-2912. |
| [8] | 孙李星, 孙婷婷, 王海清, 吴淑芳, 王小烨, 刘天雅, 张宇辰. Lewis酸催化下3-烷基-2-吲哚烯与α,β-不饱和N-磺酰基亚胺的[2+4]环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2178-2188. |
| [9] | 任志军, 罗维纬, 周俊. 银介导的N-芳基丙烯酰胺串联环化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2026-2039. |
| [10] | 孙泽人, 翟冰新, 何光超, 沈慧, 陈琳雅, 张杉, 邹毅, 朱启华, 徐云根. 新型1,2,3-三氮唑类衍生物的合成及抗炎活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2143-2155. |
| [11] | 南江, 黄冠杰, 胡岩, 王波. 钌催化喹唑啉酮与碳酸亚乙烯酯的C—H [4+2]环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1537-1549. |
| [12] | 庞明杨, 常宏宏, 冯璋, 张娟. 过渡金属催化吲哚的串联去芳构化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1271-1291. |
| [13] | 黄华, 李鑫, 苏建科, 宋秋玲. 二氟卡宾参与下从邻乙烯基苯胺出发构建3-取代吲哚酮类化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1146-1156. |
| [14] | 赵金晓, 魏彤辉, 柯森, 李毅. 可见光催化合成二氟烷基取代的多环吲哚化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1102-1114. |
| [15] | 杜昌远, 唐裕才, 段京林, 杨碧玉, 何宇鹏, 周谦, 刘学文. 可见光促进有机染料催化2-芳基吲哚自由基烷氧羰基化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4268-4276. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||