有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (10): 3322-3334.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202205037 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 不对称催化专辑
综述与进展
收稿日期:2022-05-22
修回日期:2022-06-25
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
王春江
基金资助:
Huachao Liua, Chong Shena, Xin Changa, Chunjiang Wanga,b( )
)
Received:2022-05-22
Revised:2022-06-25
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
Chunjiang Wang
Supported by:文章分享

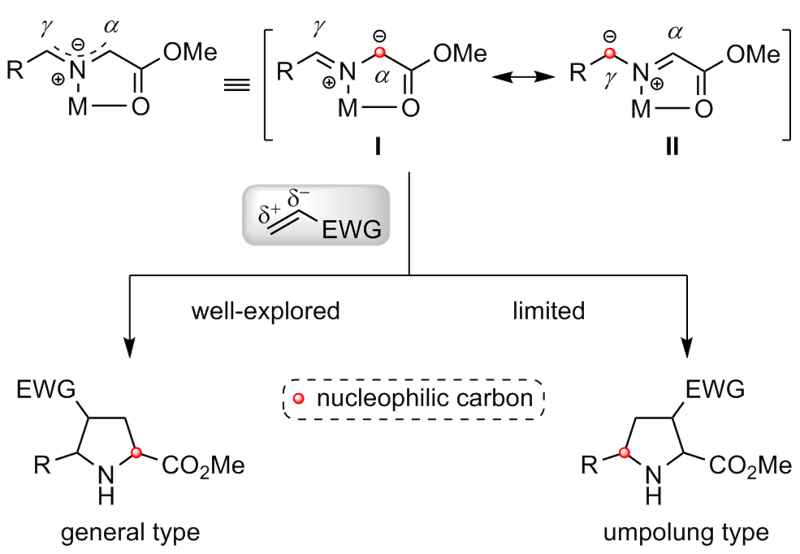
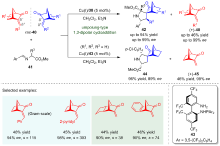
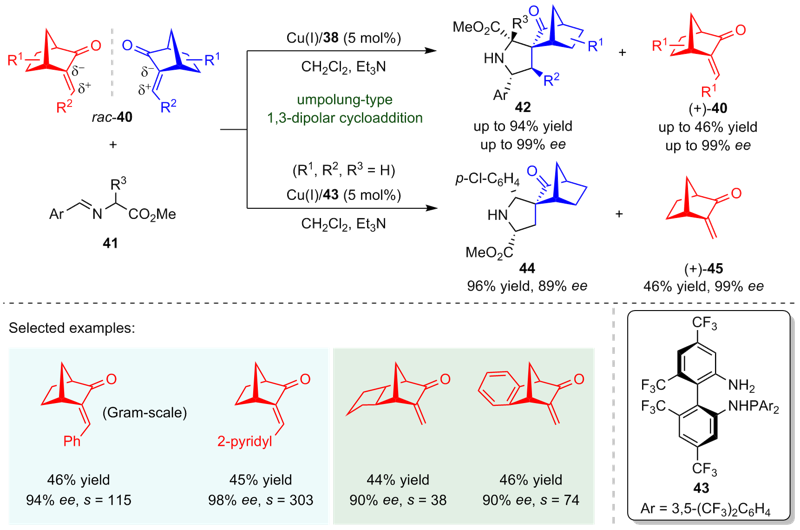
动力学拆分是一类高效且应用广泛的不对称有机合成策略, 可将外消旋化合物转化成高光学活性的构筑模块, 是现代不对称合成领域的重要组成部分. 尽管多年前就已被报道, 但涉及不对称催化的动力学拆分过程在实际运用中往往拆分效率较低或者底物适用范围较窄, 这极大地阻碍了该策略的发展. 过去的二十年里, 随着不对称催化领域中手性催化剂和手性配体的快速发展, 动力学拆分策略开始广泛运用于外消旋底物的高效分离, 进而获得优异光学纯度的手性分子. 自2005年亚甲胺亚胺通过催化不对称1,3-偶极环加成反应实现动力学拆分的案例被首次报道以来, 利用1,3-偶极环加成反应以实现高效动力学拆分获取手性氮杂环化合物或高对映选择性片段的相关研究已得到较好发展. 根据参与的1,3-偶极子的不同, 总结了近年来动力学拆分策略在亚甲胺亚胺和亚甲胺叶立德参的催化不对称1,3-偶极环加成反应中的研究进展, 并讨论了相关局限性和发展前景.
刘华超, 沈冲, 常鑫, 王春江. 动力学拆分在催化不对称1,3-偶极环加成反应中的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3322-3334.
Huachao Liu, Chong Shen, Xin Chang, Chunjiang Wang. Recent Advances in Catalytic Asymmetric 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reactions with Kinetic Resolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(10): 3322-3334.
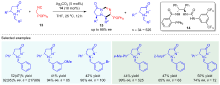
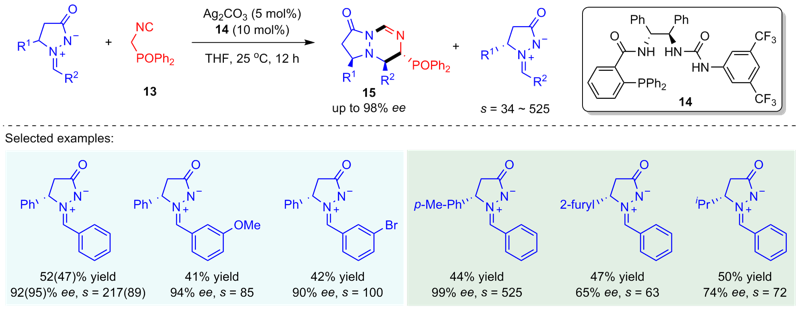
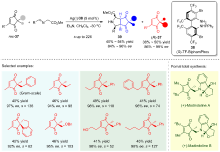
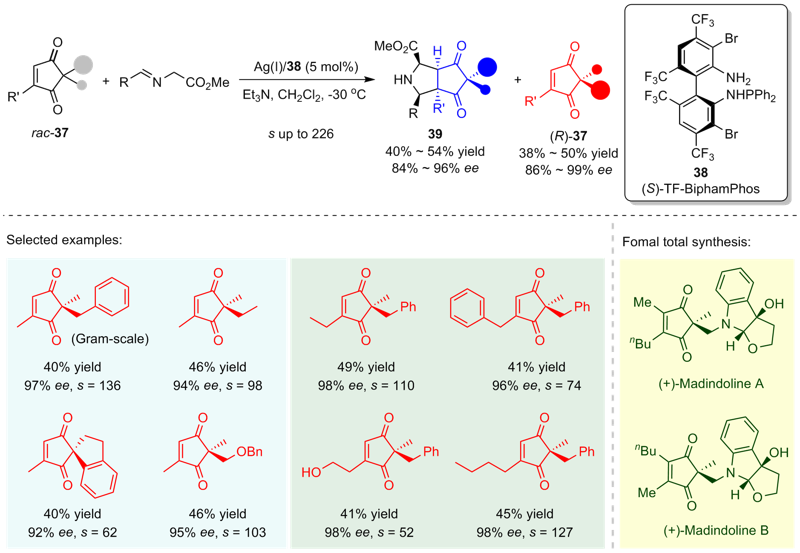

| [1] |
(a) Kagan, H. B.; Fiaud, J. C. Top. Stereochem. 1988, 18, 249.
|
|
(b) Keith, J. M.; Larrow, J. F.; Jacobsen, E. N. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 5.
|
|
|
(c) Robinson, D. E. J. E.; Bull, S. D. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2003, 14, 1407.
|
|
|
(d) Vedejs, E.; Jure, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3974.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200460842 |
|
|
(e) Pellissier, H. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1613.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201100111 |
|
|
(f) Ding, B.; Xue, Q.; Jia, S.; Cheng, H.-G.; Zhou, Q. Synthesis 2022, 54, 1721.
doi: 10.1055/a-1712-0912 |
|
|
(g) Chang, X.; Che, C.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wang, C.-J. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 1484.
|
|
|
(h) Wang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.-B.; Tian, Z.; Qu, X. Green. Synth. Catal. 2020, 1, 60.
|
|
| [2] |
Pasteur, M. L. C. R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1858, 46, 615.
|
| [3] |
For earlier reviews on 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions, see: (a) Huisgen, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1963, 2, 565.
pmid: 18613728 |
|
(b) Padwa, A.; Pearson, W. H. Synthetic Applications of 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Chemistry Toward Heterocycles and Natural Products, Wiley-VCH, New York, 2002.
pmid: 18613728 |
|
|
(c) Gothelf, K. V.; Jørgensen, K. A. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 863.
pmid: 18613728 |
|
|
(d) Stanley, L.M.; Sibi, M. P. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2887.
doi: 10.1021/cr078371m pmid: 18613728 |
|
| [4] |
For recent reviews on 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions, see: (a) Adrio, J.; Carretero, J. C. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12434.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC04381B pmid: 25961125 |
|
(b) Hashimoto, T.; Maruoka, K. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5366.
doi: 10.1021/cr5007182 pmid: 25961125 |
|
|
(c) Adrio, J.; Carretero, J. C. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11979.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC05238K pmid: 25961125 |
|
|
(d) Wei, L.; Chang, X.; Wang, C.-J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1084.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00113 pmid: 25961125 |
|
|
(e) Tang, Q.; Zhang, K. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3093.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202100305 pmid: 25961125 |
|
|
(f) Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 1123.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201800373 pmid: 25961125 |
|
| [5] |
(a) Breugst, M.; Reissig, H.-U. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12293.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202003115 |
|
(b) Heusgen, R. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 2291.
doi: 10.1021/jo01270a024 |
|
|
(c) Firestone, R. A. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 2285.
doi: 10.1021/jo01270a023 |
|
|
(d) Poppinger, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 7486.
doi: 10.1021/ja00859a017 |
|
|
(e) Huisgen, R. Chemistry and Biological Applications of Oxygen- and Sulfur-Containing Heterocycles, Eds.: Kartsev, V. G., IBX Press, Moscow, 2003, p. 83.
|
|
| [6] |
For a review, see: Cardona, F.; Goti, A.; Brandi, A. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 2999.
|
| [7] |
For reviews on the studies of azomethine imines, see: (a) Schantl, J. G. Sci. Synth. 2004, 27, 731.
|
|
(b) Grashey, R. In 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Chemistry, Vol. 1, Eds.: Padwa, A., Wiley, New York, 1984, p. 733.
|
|
| [8] |
For reviews on the chemistry and biology of pyrazolidinones, see: (a) Claramunt, R. M.; Elguero, J. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 1991, 23, 273.
doi: 10.1080/00304949109458208 |
|
(b) Konaklieva, M. I.; Plotkin, B. J. Curr. Med. Chem.: Anti-Infect. Agents 2003, 2, 287, and references cited therein.
|
|
| [9] |
(a) Bongers, A.; Moon, P. J.; Beauchemin, A. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15516.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201507548 |
|
(b) Wang, H.-Y.; Zheng, C.-W.; Chai, Z.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhao, G. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12720.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12720 |
|
| [10] |
(a) Shintani, R.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10778.
pmid: 12952444 |
|
(b) Suarez, A.; Downey, C. W.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11244.
doi: 10.1021/ja052876h pmid: 12952444 |
|
| [11] |
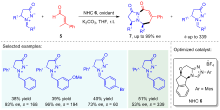
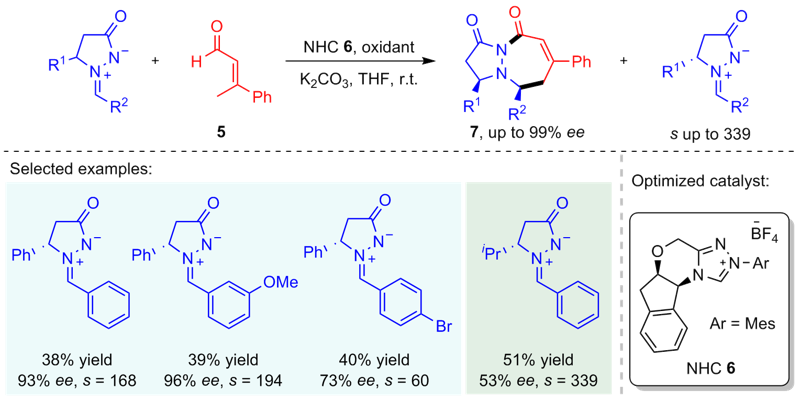
Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Chi, Y. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1214.
doi: 10.1021/ja411110f |
| [12] |
Wei, L. Wang, Z.-F.; Yao, L.; Qiu, G.; Tao, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.-J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 3955.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201600961 |
| [13] |
(a) Evans, D. A.; Rovis, T.; Kozlowski, M. C.; Tedrow, J. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1994.
doi: 10.1021/ja983864h |
|
(b) Evans, D. A.; Miller, S. J.; Lectka, T.; von Matt, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 7559.
doi: 10.1021/ja991190k |
|
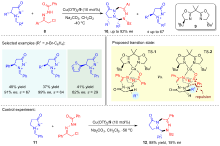
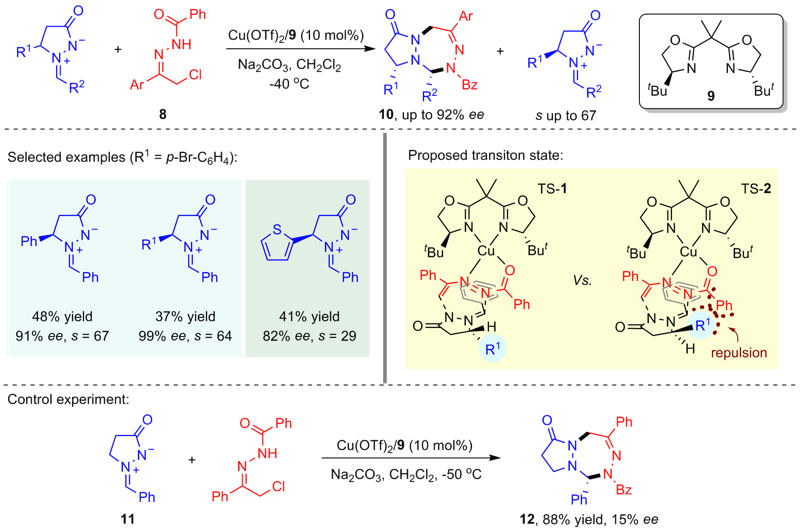
| [14] |
Tao, L.-F; Zhang, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, W.-T.; Luo, Z.-H.; Qin, L.; Liao, J.-Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202679.
|
| [15] |
(a) Xie, J.; Yoshida, K.; Takasu, K.; Takemoto, Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6910.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.09.113 |
|
(b) Xie, J.-W.; Fan, L.-P.; Su, H.; Li, X.-S.; Xu, D.-C. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2117.
doi: 10.1039/b922668k |
|
| [16] |
(a) Zeni, G.; Larock, R. C. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2285.
doi: 10.1021/cr020085h |
|
(b) Bonsignore, L.; Loy, G.; Secci, D.; Calignano, A. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 28, 517.
doi: 10.1016/0223-5234(93)90020-F |
|
|
(c) Machlin, L. J. α-Tocopherol, Eds.: Dekker, M., New York, 1980, p. 345.
|
|
| [17] |
Yu, J.; Chen, W.-J.; Gong, L.-Z. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4050.
doi: 10.1021/ol101544c |
| [18] |
(a) Krause, N. Modern Allene Chemistry, Eds.: Hashmi, A. S. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004.
pmid: 24676356 |
|
(b) Hoffmann-Roder, A.; Krause, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1196.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200300628 pmid: 24676356 |
|
|
(c) Alcaide, B.; Almendros, P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2886, and references cited therein.
doi: 10.1039/c4cs90020k pmid: 24676356 |
|
| [19] |
Takayama, H.; Jia, Z.-J.; Kremer, L.; Bauer, J. O.; Strohmann, C.; Ziegler, S.; Antonchick, A. P.; Waldmann, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12404.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201306948 |
| [20] |
Xu, H.; Golz, C.; Strohmann, C.; Antonchick, A. P.; Waldmann, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7761.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201602084 |
| [21] |
Yuan, Y.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Li, L.; Bai, X.-F.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Y.-M.; Cao, J.; Yang, K.-F.; Xu, L.-W. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 3002.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201800220 |
| [22] |
(a) Liu, H.-C.; Liu, K.; Xue, Z.-Y.; He, Z.-L.; Wang, C.-J. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5440.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02810 pmid: 29846076 |
|
(b) Liu, H.-C.; Wei, L.; Huang, R.; Tao, H.-Y.; Cong, H.; Wang, C.-J. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3482.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01254 pmid: 29846076 |
|
|
(a) Aikawa, K.; Okamoto, T.; Mikami, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10329.
doi: 10.1021/ja3032345 pmid: 29846076 |
|
|
(b) Hirose, T.; Sunazuka, T.; Yamamoto, D.; Kojima, N.; Shirahata, T.; Harigaya, Y.; Kuwajima, I.; Ōmura, S. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 6015.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2005.04.056 pmid: 29846076 |
|
| [23] |
(a) Liu, X.; Zhang, L.-N.; Leng, Y. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1013.
doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.75 pmid: 20092908 |
|
(b) Zhao, C.; Sun, M.-H.; Cowart, M. D. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5423.
doi: 10.1021/jm8003625 pmid: 20092908 |
|
|
(c) Doebele, R. C.; Oton, A. B.; Peled, N.; Camidge, D. R.; Bunn, P. A., Jr. Lung Cancer 2010, 69, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.12.009 pmid: 20092908 |
|
| [24] |
(a) Barr, D. A.; Grigg, R.; Sridharan, V. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 4727.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)80786-3 pmid: 19736987 |
|
(b) Kanemasa, S.; Uchida, O.; Wada, E.; Yamamoto, H. Chem. Lett. 1990, 19, 105.
doi: 10.1246/cl.1990.105 pmid: 19736987 |
|
|
(c) Chen, X.-H.; Wei, Q.; Luo, S.-W.; Xiao, H.; Gong, L.-Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13819.
doi: 10.1021/ja905302f pmid: 19736987 |
|
|
(d) Feng, B.; Lu, L.-Q.; Chen, J.-R.; Feng, G.; He, B.-Q.; Lu, B.; Xiao, W.-J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5888.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201802492 pmid: 19736987 |
|
|
(e) Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Xu, B.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2272.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12137 pmid: 19736987 |
|
|
(f) Stohler, R.; Wahl, F.; Pfaltz, A. Synthesis 2005, 1431.
pmid: 19736987 |
|
| [25] |
Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Wei, L.; Dong, W.-W.; Chung, L. W.; Wang, C.-J. iScience 2019, 11, 146.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.010 |
| [26] |
Wang, M.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, Z. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7870.
doi: 10.1021/om300435s |
| [27] |
Krotz, A.; Helmchen, G. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1994, 6, 601.
|
| [28] |
Chang, X.; Sun, X.-S.; Che, C.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Tao, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-J. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 1191.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00136 pmid: 30707591 |
| [29] |
Vázquez-Romero, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Lledó, A.; Verdaguer, X.; Riera, A. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4509.
doi: 10.1021/ol8017352 pmid: 18798645 |
| [30] |
Deng, H.; Liu, T.-T.; Ding, Z.-D.; Yang, W.-L.; Luo, X.; Deng, W.-P. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3247.
doi: 10.1039/D0QO00789G |
| [1] | 杨爽, 房新强. 氮杂环卡宾催化实现的动力学拆分近期研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 448-480. |
| [2] | 胡慧娟, 闫巧丽, 卢晓刚, 杨启帆, 裴承新, 王红梅, 高润利. 猪胰脂肪酶催化外消旋P-手性α-羟基磷酸酯类化合物的动力学拆分[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2815-2825. |
| [3] | 褚杨杨, 韩召斌, 丁奎岭. 动力学拆分在过渡金属催化的不对称(转移)氢化中的应用研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1934-1951. |
| [4] | 罗诚, 尹艳丽, 江智勇. P-手性膦氧化物的不对称合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1963-1976. |
| [5] | 陈宇亮, 贺凤开, 王思云, 贾鼎成, 刘亚群, 黄毅勇. 手性磷酸催化α-全碳季碳醛的不对称烯丙基化动力学拆分[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4294-4302. |
| [6] | 陈运荣, 刘炜, 杨晓瑜. 叔醇的动力学拆分研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 679-697. |
| [7] | 任红霞, 马萌萌, 黄有. 手性膦催化的氮杂环合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3129-3142. |
| [8] | 李晖, 殷亮. P-手性化合物的不对称催化合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3183-3200. |
| [9] | 范铃洁, 周涛, 杨旭, 江梦雪, 胡信全, 史炳锋. 钯催化的不对称碳氢键烯基化动力学拆分2-(芳基亚磺酰基)吡啶[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(10): 3405-3418. |
| [10] | 唐亮, 李雪薇, 谢芳, 张万斌. 胺及其衍生物的非酰基化动力学拆分[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(3): 575-588. |
| [11] | 张齐英, 张一铭, 郝二军, 白娟, 渠桂荣, 郭海明. 通过不对称氢转移/动态动力学拆分合成碳环N3-嘌呤核苷[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(2): 376-383. |
| [12] | 王才, 周锋, 周剑. 铜催化的不对称叠氮和炔烃的环加成反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(10): 3065-3077. |
| [13] | 乐贵洲, 刘波. 1,3-偶极子[3+n](n≥3)环加成反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(10): 3132-3153. |
| [14] | 卫亮, 肖露, 胡远征, 汪昨非, 陶海燕, 王春江. 金属化亚甲胺叶立德在手性非天然α-氨基酸合成中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(8): 2119-2130. |
| [15] | 倪国伟, 汤佳伟, 邹杰, 陈少欣, 鞠佃文, 张福利. 羰基还原酶在动态动力学拆分中的应用进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(2): 339-349. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||