有机化学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (11): 3745-3760.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202303043 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
邱建文a, 刘梦a, 熊新怡a, 高勇a,b,*( ), 朱虎a,c,*(
), 朱虎a,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-29
修回日期:2023-06-18
发布日期:2023-07-05
基金资助:
Jianwen Qiua, Meng Liua, Xinyi Xionga, Yong Gaoa,b( ), Hu Zhua,c(
), Hu Zhua,c( )
)
Received:2023-03-29
Revised:2023-06-18
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

近红外光(650~1700 nm)在生物成像中具有组织穿透深度大、受生物体自身荧光干扰小和对生物体光损伤小等优点. 因此, 近红外染料已成为生物成像新的研究热点. 近红外荧光染料较窄的能量带隙使激发态非辐射跃迁几率增大, 导致荧光强度大幅降低. 同时较长的共轭疏水骨架及强大的分子电荷转移能力, 使他们容易与外部分子交互, 从而加剧非辐射能量损耗增加, 致使荧光强度降低. 为了获取高亮度近红外荧光染料, 研究人员针对近红外染料做了很多改进和修饰. 从荧光染料的结构-性质关系角度, 综述了目前主流的高亮度近红外染料的发展情况, 希望能为发展高亮度近红外荧光染料提供帮助和指导.
邱建文, 刘梦, 熊新怡, 高勇, 朱虎. 高亮度近红外荧光染料研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(11): 3745-3760.
Jianwen Qiu, Meng Liu, Xinyi Xiong, Yong Gao, Hu Zhu. Research Progress in High Brightness Near Infrared Fluorescent Dyes[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(11): 3745-3760.
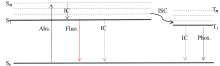

| [1] |
(a) Lei, Z.; Zhang, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16294.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.30 |
|
(b) Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, M.; Wang, P; Sun, P.; Ji, M. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2022, 11, 2201158.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v11.21 |
|
|
(c) Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213556.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213556 |
|
|
(d) Wang, Z.; Geng, H.; Nie, C.; Xing, C. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 759.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v40.6 |
|
|
(e) He, Y.; Liao, S.; Wang, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1435.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.6 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Beija, M.; Afonso, C. A. M.; Martinho, J. M. G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2410.
doi: 10.1039/b901612k pmid: 21796324 |
|
(b) Boens, N.; Leen, V.; Dehaen, W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1130.
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15132k pmid: 21796324 |
|
|
(c) Cavazos‐Elizondo, D.; Aguirre‐Soto, A. Analysis Sensing 2022, 2, e202200004.
doi: 10.1002/anse.v2.5 pmid: 21796324 |
|
|
(d) Karaman, O.; Alkan, G. A.; Kizilenis, C.; Akgul, C. C.; Gunbas, G. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214841.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214841 pmid: 21796324 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Khan, Z.; Sekar, N. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 110735.
|
|
(b) Wang, L.; Du, W.; Hu, Z.; Uvdal, K.; Lin, L.; Huang, W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14026.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.40 |
|
|
(c) Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, P.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhu, W.; Guo, Z. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 473, 214813.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214813 |
|
|
(d) Bumagina, N. A.; Antina, E. V.; Ksenofontov, A. A.; Antina, L. A.; Kalyagin, A. A.; Berezin, M. B. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 469, 214684.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214684 |
|
|
(e) Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80,1071. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22040141 |
|
|
(刘巴蒂, 王承俊, 钱鹰, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1071.)
doi: 10.6023/A22040141 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Poronik, Y. M.; Vygranenko, K. V.; Gryko, D.; Gryko, D. T. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5242.
doi: 10.1039/c9cs00166b pmid: 31549709 |
|
(b) Zhu, S.; Tian, R.; Antaris, A. L.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900321.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.24 pmid: 31549709 |
|
|
(c) Ni, Y.; Wu, J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 3774.
doi: 10.1039/c3ob42554a pmid: 31549709 |
|
| [5] |
(a) Mayerhöffer, U.; Fimmel, B.; Würthner, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 164.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v51.1 |
|
(b) Zhou, E. Y.; Knox, H. J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Chan, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17601.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b06694 |
|
| [6] |
(a) Umezawa, K.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Anal. Sci. 2014, 30, 327.
doi: 10.2116/analsci.30.327 |
|
(b) Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Xu, M.; Hao, S.; Fan, Y.; Shao, T.; Bai, H.; Peng, B.; Hu, W.; Liu, X.; Yao, C.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102514.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v10.8 |
|
| [7] |
Kowada, T.; Maeda, H.; Kikuchi, K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4953.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00030K |
| [8] |
Sun, W.; Guo, S.; Hu, C.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7768.
|
| [9] |
(a) Chen, X, Pradhan, T, Wang, F, Kim, J. S.; Yoon, J. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1910.
doi: 10.1021/cr200201z |
|
(b) Zhao, M.; Guo, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Guo, D. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115704.
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.115704 |
|
|
(c) Liu, D.; He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17136.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07711 |
|
| [10] |
(a) Wang, C.; Chi, W.; Qiao, Q.; Tan, D.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12656.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00239B |
|
(b) Lv, X.; Gao, C.; Han, T.; Shi, H.; Guo, W. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 715.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC09138F |
|
| [11] |
(a) Koide, Y.; Urano, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Terai, T.; Nagano, T. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 600.
doi: 10.1021/cb1002416 pmid: 30920803 |
|
(b) Ogasawara, A.; Kamiya, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Kuriki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Komatsu, T.; Ueno, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Onoyama, H.; Abe, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Fujishiro, M.; Koike, K.; Fukayama, M.; Seto, Y.; Urano, Y. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 1055.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00198 pmid: 30920803 |
|
|
(c) Tang, W.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gai, L.; Feng, X. J.; Tian, J.; Lu, H.; Guo, Z. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 2724.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v15.17 pmid: 30920803 |
|
| [12] |
Koide, Y.; Urano, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Piao, W.; Kusakabe, M.; Saito, N.; Terai, T.; Okabe, T.; Nagano, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5029.
doi: 10.1021/ja210375e |
| [13] |
Zhou, X.; Lai, R.; Beck, J. R.; Li, H.; Stains, C. I. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12290.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC05717A |
| [14] |
Ren, T.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 14, 7716.
|
| [15] |
Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Wei, R.; Jiang, G.; Yao, C.; Lv, M.; Wu, Y.; Gardner, S. H.; Zhang, F.; Lucero, M. Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Ge, H.; Chan, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Luo, X.; Qian, X.; Yang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14351.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05826 |
| [16] |
Jiang, G.; Ren, T-B.; Este, E. D.; Xiong, M.; Xiong, B.; Johnsson, K.; Zhang, X-B.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2264.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29547-3 |
| [17] |
Jiang, G.; Lou, X.-F.; Zuo, S.; Liu, X.; Ren, T.-B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.-B.; Yuan, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 135, e202218613.
doi: 10.1002/ange.v135.17 |
| [18] |
Grimm, J. B.; English, B. P.; Chen, J.; Slaughter, J. P.; Zhang, Z.; Revyakin, A.; Patel, R.; Macklin, J. J.; Normanno, D.; Singer, R. H.; Lionnet, T.; Lavis, L. D. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 244.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3256 |
| [19] |
Lv, X.; Gao, C.; Han, T.; Shi, H.; Guo, W. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 715.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC09138F |
| [20] |
Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Shi, Y.; Guo, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22953.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b08338 |
| [21] |
Grzybowski, M.; Taki, M.; Senda, K.; Sato, Y.; Ariyoshi, T.; Okada, Y.; Kawakami, R.; Imamura, T.; Yamaguchi, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10137.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.32 |
| [22] |
Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Yang, W.; Wei, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, B. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12137.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04926 |
| [23] |
Liu, D.; He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, X.; Ma. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17136.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07711 |
| [24] |
(a) Kamkaew, A.; Lim, S. H.; Lee, H. B.; Kiew, L. V.; Chung, L. Y.; Burgess, K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 77.
doi: 10.1039/C2CS35216H |
|
(b) Wu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiong, H. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 2039.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c01066 |
|
|
(c) Cheng, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, L.; Liang, X.; Yoon, J. Adv. Mater. 2022, 2207546.
|
|
| [25] |
Ziessel, R.; Rihn, S.; Harriman, A. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 11942.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v16:39 |
| [26] |
Li, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Li, T.; Zeika, O.; Leo, P. ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 1017.
doi: 10.1002/cptc.v2.12 |
| [27] |
Rappitsch, T.; Borisov, S. M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2021, 27, 10685.
doi: 10.1002/chem.202100965 pmid: 33950529 |
| [28] |
Chen, J.; Mizumura, M.; Shinokubo, H.; Osuka, A. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5942.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v15:24 |
| [29] |
Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y-Q.; Liu, M.; Guo, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17069.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06916 |
| [30] |
Taguchi, D.; Nakamura, T.; Horiuchi, H.; Saikawa, M.; Nabeshima, T. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 5331.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b00782 |
| [31] |
Deckers, J.; Cardeynaels, T.; Doria, S.; Tumanov, N.; Lapini, A.; Ethirajan, A.; Ameloot, M.; Wouters, J.; Donato, M. D.; Champagne, B.; Maes, W. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 9344.
doi: 10.1039/D2TC01526A |
| [32] |
Killoran, J.; Allen, L.; Gallagher, J. F.; Gallagherb, W. M.; O′Shea, D. F. Chem. Commun. 2002, 17, 1862.
|
| [33] |
Gorman, A.; Killoran, J.; O'Shea, C.; Kenna, T.; Gallagher, W. M.; O'Shea, D. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10619.
doi: 10.1021/ja047649e |
| [34] |
Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Yu, C.; Wei, Y.; Mu, X.; Hao, E. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 9, 805.
|
| [35] |
Lv, X.; Han, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Guo, W. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 9744.
doi: 10.1039/D1CC03360C |
| [36] |
Bai, L.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10920.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC03378E |
| [37] |
Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. P.; Fan, Y.; Sun, C.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3967.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.8 |
| [38] |
(a) Mustroph, H. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2020, 5(5), 20190145.
|
|
(b) Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, X.; Dai, Z. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2001327.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v9.22 |
|
| [39] |
Matikonda, S. S.; Hammersley, G.; Kumari, N.; Grabenhorst, L.; Glembockyte, V.; Tinnefeld, P.; Ivanic, J.; Levitus, M.; Schner- mann, M. J. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 5907.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00236 |
| [40] |
Ran, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Kun Li, K.; Yu, X. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2210179.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v35.12 |
| [41] |
Li, D. H.; Schreiber, C. L.; Smith, B. D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2020, 132, 2252.
|
| [42] |
Li, D.-H.; Gamage, R. S.; Oliver, A. G.; Patel, N. L.; Usama, S. M.; Kalen, J. D.; Schnermann, M. J.; Smith, B. D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, e202305062.
|
| [43] |
Cosco, E. D.; Caram, J. R.; Bruns, O. T.; Franke, D.; Day, R. A.; Farr, E. P.; Bawendi, G. M.; Sletten, E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13126.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.42 |
| [44] |
Cosco, E. D.; Arús, B. A.; Spearman, A. L.; Atallah, T. L.; Lim, I.; Leland, O. S.; Caram, J. R.; Bischof, T. S.; Bruns, O. T.; Sletten, E. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6836.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c11599 |
| [45] |
Ndaleh, D.; Smith, C.; Yaddehige, M. L.; Shaik, A. K.; Watkins, D. L.; Hammer, N. I.; Delcamp, J. H. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 15376.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c01908 pmid: 34647452 |
| [46] |
Mujumdar, S. R.; Mujumdar, R. B.; Grant, C. M.; Waggoner, A. S. Bioconjugate Chem. 1996, 7, 356.
pmid: 8816960 |
| [47] |
Cha, J.; Nani, R. R.; Luciano, M. P.; Kline, G.; Broch, A.; Kim, K.; Namgoong, J.-M.; Kulkarni, R. A.; Meier, J. L.; Kim, P.; Schner- mann, M. J. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2741.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.02.040 |
| [48] |
Luciano, M. P.; Crooke, S. N.; Nourian, S.; Dingle, I.; Nani, R. R.; Gabriel Kline, G.; Patel, N. L.; Robinson, C. M.; Difilippantonio, S.; Kalen, J. D.; Finn, M. G.; Schnermann, M. J. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 934.
|
| [49] |
(a) Anzalone, A. V.; Wang, T. Y.; Chen, Z.; Cornish V. W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 650.
|
|
(b) Pauff, S. M.; Miller, S. C. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 711.
doi: 10.1021/jo302065u |
|
| [50] |
(a) Shang, J.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.; Shen, S.; Liu, D.; Shi, W.; Ma, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e2022050.
|
|
(b) Li, W.; Yin, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 3736.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c13222 |
|
|
(c) Wei, P.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Yi, T. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 5211.
doi: 10.1039/D2TB00765G |
|
| [51] |
Wang, C.; Qiao, Q.; Chi, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Tan, D.; McKechnie, S.; Lyu, D.; Jiang, X.-F.; Zhou, W.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10160.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.25 |
| [52] |
Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wei, A.; Guo, W. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7718.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC02322A |
| [53] |
For the properties of ATTO dyes, see:
|
| [54] |
(a) Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1200.
doi: 10.1021/ja209292b pmid: 22816866 |
|
(b) Yuan, L.; Weiying Lin, W.; Zhao, S.; Gao, W.; Chen, B.; He, L.; Zhu, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13510.
doi: 10.1021/ja305802v pmid: 22816866 |
|
| [55] |
Chen, H.; Lin, W.; Cui, H.; Jiang, W. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 733.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201404718 pmid: 25388080 |
| [56] |
Ren, T.-B.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, P.; Lai, H.-H.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 800.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.2 |
| [57] |
Ong, M. J. H.; Debieu, S.; Moreau, M.; Romieu, A. Richard J. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 936.
|
| [58] |
Wang, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, F. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1302.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00544 |
| [59] |
Hara, D.; Uno, S.; Motoki, T.; Kazuta, Y.; Norimine, Y.; Suganuma, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Shimaoka, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Okada, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Amino, H.; Iwanaga, S. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 8703.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c03193 |
| [60] |
Li, N.; Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Fan, M.; Cui, X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, e202217326.
|
| [1] | 吴思敏, 唐嘉欣, 周于佳, 徐学涛, 张昊星, 王少华. 2β-Acetoxyferruginol去醋酸基骨架衍生物抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 613-621. |
| [2] | 徐利军, 李宗军, 韩福社, 高翔. N,N-二甲基甲酰胺促进的富勒烯稠合噁唑啉衍生物的合成[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 242-250. |
| [3] | 马翠云, 罗海澜, 张福华, 郭丹, 陈树兴, 王飞. 3-Pyrrolyl BODIPY的绿色生物合成、光物理性质及应用研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 216-223. |
| [4] | 张莹珍, 江丹丹, 李娟华, 王菁菁, 刘昆明, 刘晋彪. 高选择性硒代半胱氨酸荧光探针的构建策略及成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 41-53. |
| [5] | 杨维清, 葛宴兵, 陈元元, 刘萍, 付海燕, 马梦林. 1,8-萘酰亚胺衍生物的设计、合成及其对半胱氨酸的识别研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 180-194. |
| [6] | 李焕清, 陈兆华, 陈祖佳, 邱琪雯, 张又才, 陈思鸿, 汪朝阳. 基于有机小分子的汞离子荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3067-3077. |
| [7] | 丁炳辉, 韩少辉, 熊海青, 王本花, 左伯军, 宋相志. 高选择性比率型荧光探针用于急性肺损伤中次氯酸的检测[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2878-2884. |
| [8] | 关丽, 周艳艳, 毛永爆, 付恺森, 关文惠, 付义乐. 甲川链修饰菁染料的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2682-2698. |
| [9] | 赵小龙, 郭亮武, 李宇晴, 冉启元, 吴会慧, 张祯, 苏瀛鹏, 周鹏鑫, 燕娜. 大Stokes位移的近红外氟硼二吡咯(BODIPY)荧光探针应用于生物体中Na2S2O4的检测[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(7): 2484-2491. |
| [10] | 刘飞冉, 敬静, 张小玲. 细胞器靶向型半胱氨酸荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2053-2067. |
| [11] | 李宜芳, 王耀, 牛华伟, 陈秀金, 李兆周, 王永国. 线粒体靶向的二氧化硫荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1952-1962. |
| [12] | 刘甜甜, 张鸿鹏, 焦晓梦, 白银娟. 多信号同时检测生物硫醇荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2081-2095. |
| [13] | 张祎, 杜呈卓, 李继坤, 王小野. 基于硼氮杂稠环芳烃的多重共振热活化延迟荧光材料研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1645-1690. |
| [14] | 梁凯淳, 白科研, 戴雷, 刘源, 叶泽聪, 霍延平. 基于四氢喹啉的多重共振热活化延迟荧光材料的设计、合成及电致发光性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1799-1807. |
| [15] | 徐茂财, 田佳壮, 杨艳华, 苟高章, 李福敏, 邵林, 池可心. 一种三苯胺基二氟硼发光化合物的力致可逆荧光变色及数据安全保护研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1824-1831. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||