有机化学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2413-2424.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403059 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
黄伟庚a, 高翼亭a,b, 孙妍a,b, 燕鼎元a,*( ), 王东a,*(
), 王东a,*( ), 唐本忠a,c,*(
), 唐本忠a,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-31
修回日期:2024-06-19
发布日期:2024-07-02
作者简介:基金资助:
Weigeng Huanga, Yiting Gaoa,b, Yan Suna,b, Dingyuan Yana( ), Dong Wanga(
), Dong Wanga( ), BenZhong Tanga,c(
), BenZhong Tanga,c( )
)
Received:2024-03-31
Revised:2024-06-19
Published:2024-07-02
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

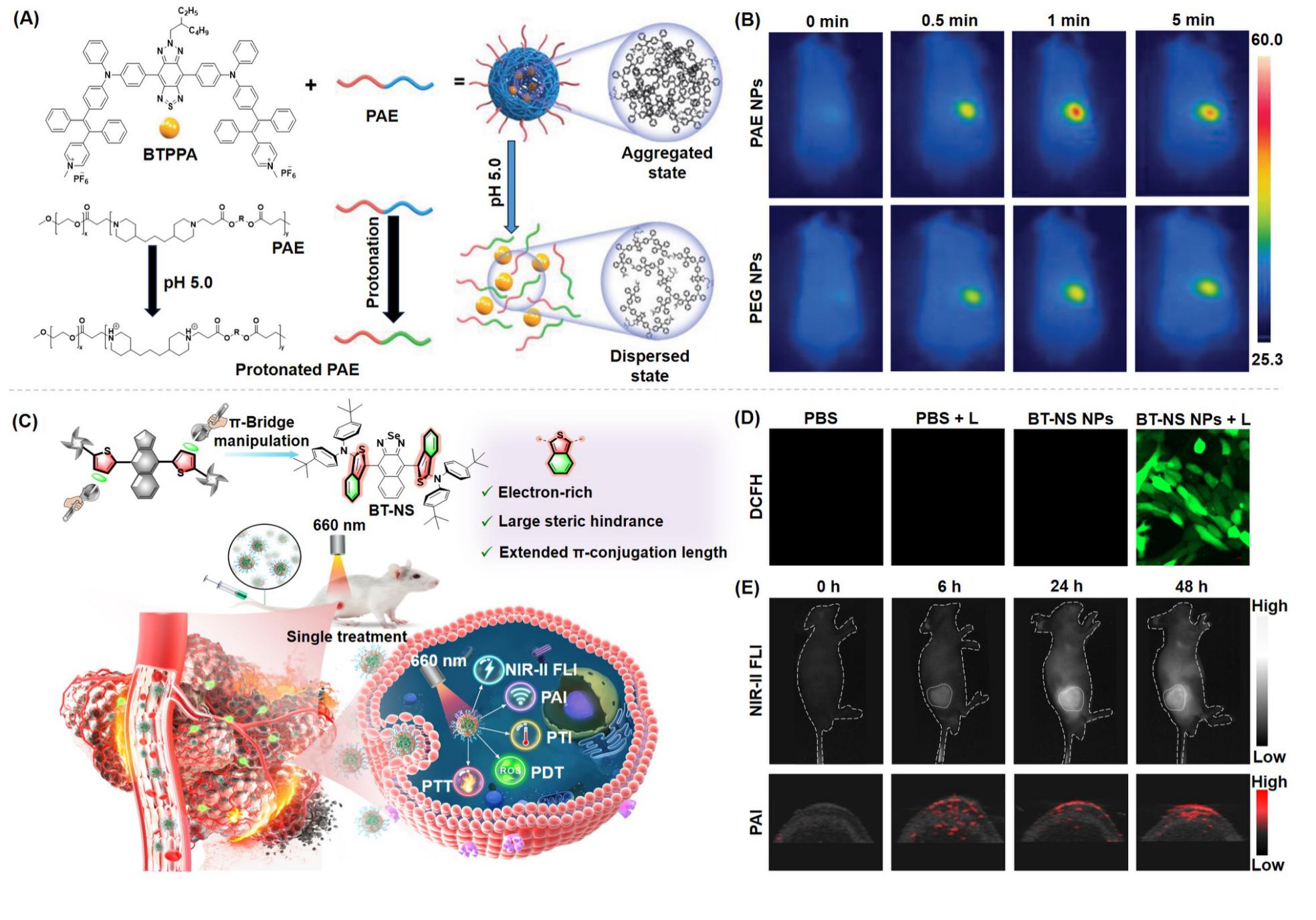
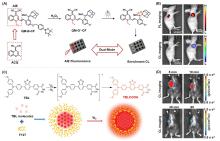
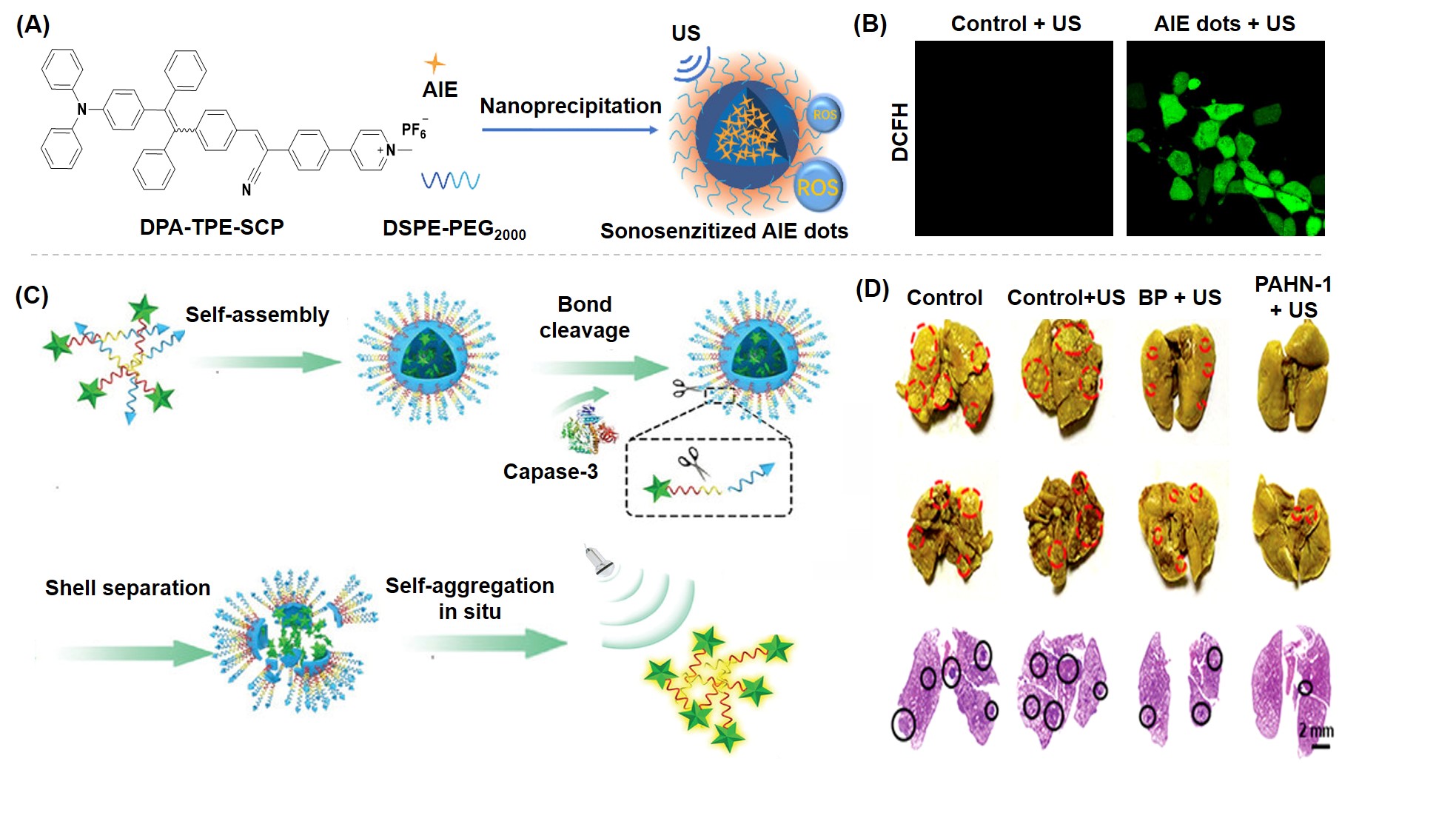
近年来, 聚集诱导发光(AIE)材料因其优异的聚集态增强诊疗特性在肿瘤诊疗领域备受关注. 激发后的AIE材料可以通过不同的能量弛豫途径耗散激发态能量, 产生活性氧或光热, 用于成像导航下的肿瘤一体化诊疗. 根据激发方式的不同, 系统地总结了AIE材料用于肿瘤诊疗的研究进展, 具体包括光致激发(包含使用白光、660、808、980或1064 nm激光器)、化学激发、超声激发和X射线激发. 此外, 简要讨论了每种激发方式的优势和局限性.
黄伟庚, 高翼亭, 孙妍, 燕鼎元, 王东, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光材料用于肿瘤光学诊疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424.
Weigeng Huang, Yiting Gao, Yan Sun, Dingyuan Yan, Dong Wang, BenZhong Tang. Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials for Tumor Phototheranostics[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424.


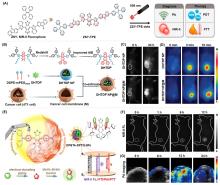
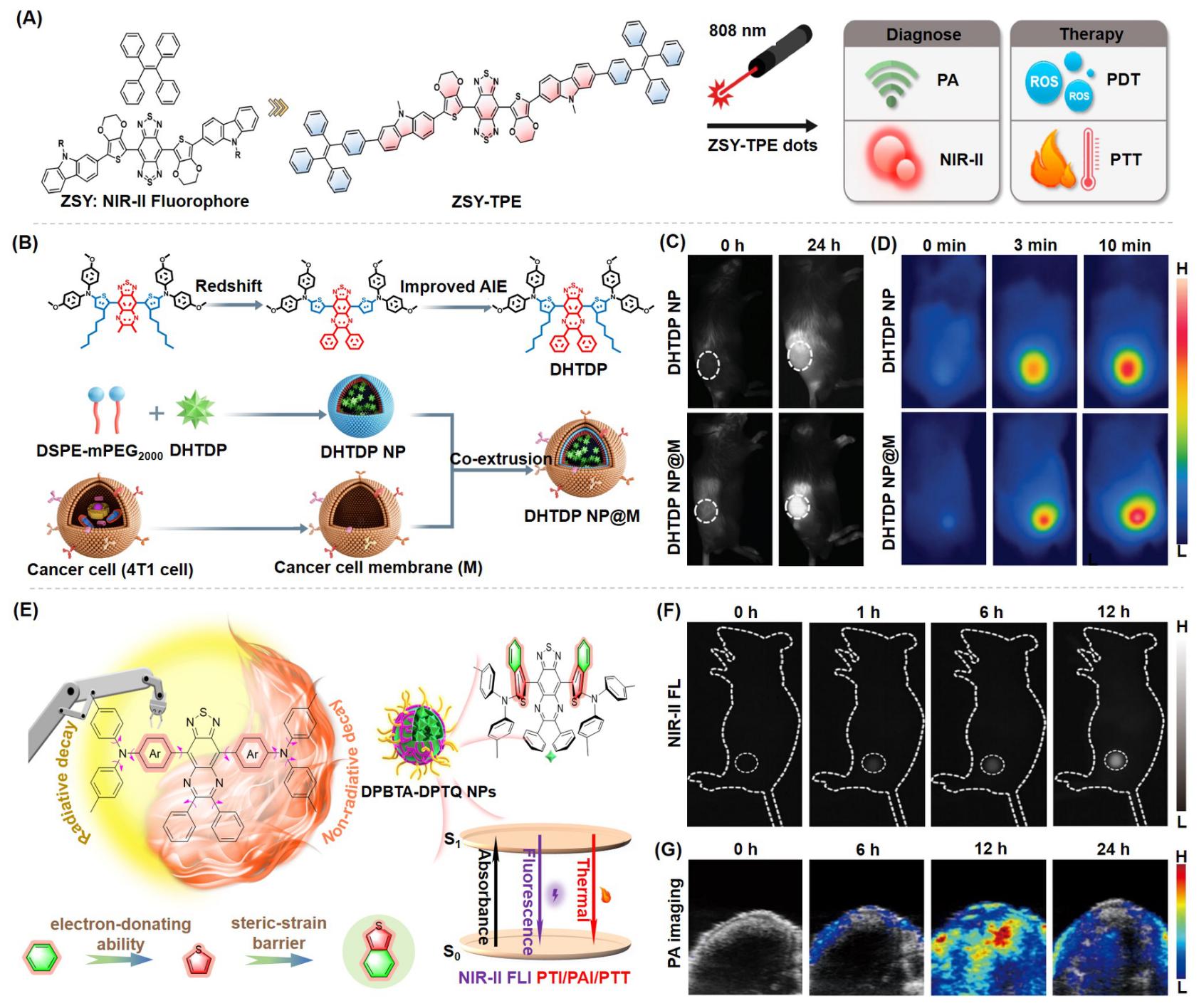
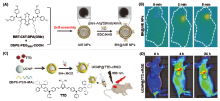

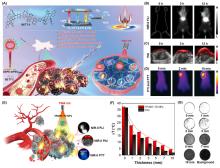

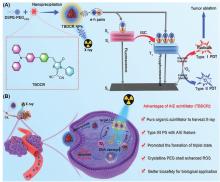

| [1] |
Siegel, R. L.; Miller, K. D.; Wagle, N. S.; Jemal, A. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17.
|
| [2] |
Lammers, T.; Aime, S.; Hennink, W. E.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1029.
|
| [3] |
Kumar, R.; Shin, W. S.; Sunwoo, K.; Kim, W. Y.; Koo, S.; Bhuniya, S.; Kim, J. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6670.
|
| [4] |
Tiwari, S. P. Int. J. Healthcare Med. Sci. 2022, 6, 12114.
|
| [5] |
Cai, X.; Liu, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9868.
|
| [6] |
Feng, G.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Ding, D. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8179.
|
| [7] |
Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Elsayed, M.; Nan, F.; Liang, W.; Valley, J. K.; Liu, L.; Huang, Q.; Wu, M. C.; Wheeler, A. R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 9203.
|
| [8] |
Xu, H.; Han, P.-B.; Qin, A.-J.; Tan, B.-Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050232 |
|
| [9] |
Chen, C.; Ou, H.; Liu, R.; Ding, D. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1806331.
|
| [10] |
Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004.
|
| [11] |
Gui, Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249.
|
| [12] |
Pratihar, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Prasad, E. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2020, 396, 112458.
|
| [13] |
Wang, D.; Lee, M. M. S.; Xu, W.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Theranostic. 2018, 8, 4925.
|
| [14] |
Zhan, R.; Pan, Y.; Manghnani, P. N.; Liu, B. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600433.
|
| [15] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Tang, B. Z.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [16] |
Tu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa260.
|
| [17] |
Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.-P.; Li, G.-N.; Niu, Z.-G.; Wang, E.-J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2156 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵洋, 陈盼盼, 李高楠, 钮智刚, 王恩举, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2156.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210002 |
|
| [18] |
Li, P.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Wang, C. C.; Xia, L. G.; Tang, B. Z. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imagin. 2022, 49, 2560.
|
| [19] |
Kang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, N.; Li, M.; Sun, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregat. 2020, 1, 80.
|
| [20] |
Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, J. Nanoscal. 2016, 8, 17422.
|
| [21] |
Lu, B.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Cao, D. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 4600.
|
| [22] |
Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Cui, P.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, P.; Wang, J. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100264.
|
| [23] |
Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Kang, M.; Wen, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, P.; Xi, L.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003210.
|
| [24] |
Feng, G.; Liu, B. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1404.
|
| [25] |
Zhang, Z.; Kang, M.; Tan, H.; Song, N.; Li, M.; Xiao, P.; Yan, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1983.
|
| [26] |
Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. M.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hao, X.; Lee, C. S.; Cheng, Y.; Tsang, S. W. Small Method. 2023, 8, 2300899.
|
| [27] |
Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.-R.; Zhu, L.-P.; Zhou, Y. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2024, 82, 265 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵玉强, 张霞, 杨芸如, 朱立平, 周莹, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 265.)
doi: 10.6023/A23100457 |
|
| [28] |
Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Yan, D.; Gui, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 15, e1906.
|
| [29] |
Zhang, T.; Pan, Y.; Suo, M.; Lyu, M.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Jin, Z.; Ning, S.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304042.
|
| [30] |
Hananya, N.; Shabat, D. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 949.
|
| [31] |
Liang, S.; Hu, D.; Li, G.; Gao, D.; Li, F.; Zheng, H.; Pan, M.; Sheng, Z. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2316.
|
| [32] |
Pei, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1011.
|
| [33] |
Gui, C.; Zhao, E.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Leung, A. C. S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Jiang, M.; Deng, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Su, H.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1822.
|
| [34] |
Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lu, G.; Dong, X.; Dai, J.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6607.
|
| [35] |
Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P.; Kang, M.; Yan, D.; Wen, H.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Nan. 2021, 15, 10689.
|
| [36] |
Xiong, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Tang, H.; Cao, D.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5234.
doi: 10.1039/d0tb00888e pmid: 32432307 |
| [37] |
Wang, D.; Lee, M. M. S.; Shan, G.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Su, H.; Cai, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802105.
|
| [38] |
Chen, X.; Niu, N.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Yan, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2211571.
|
| [39] |
Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Fu, S.; Li, Y.; Wen, H.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107545.
|
| [40] |
Chen, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 293.
|
| [41] |
Wen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, M.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wu, Q.; Huang, J.; Xi, L.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Biomaterial. 2021, 274, 120892.
|
| [42] |
Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, T.; Hu, X.; Lee, M. M. S.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105999.
|
| [43] |
Gui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Qin, Y.; Song, G.; Yan, D.; Tang, B. Z.; Wang, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318609.
|
| [44] |
Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; An, J.; Li, C.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; Deng, G.; Kim, J. S.; Sun, Y. Biomaterial. 2020, 259, 120315.
|
| [45] |
Zhu, J.; Sevencan, C.; Zhang, M.; McCoy, R. S. A.; Ding, X.; Ye, J.; Xie, J.; Ariga, K.; Feng, J.; Bay, B. H.; Leong, D. T. ACS Nan. 2020, 14, 3259.
|
| [46] |
Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Yan, D.; Han, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2302639.
|
| [47] |
Yan, D.; Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26769.
|
| [48] |
Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 60.
|
| [49] |
Tao, W.; Farokhzad, O. C. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5405.
|
| [50] |
Wu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Rommelfanger, N. J.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, R.; Liu, J.; Cai, S.; Ren, W.; Shin, A.; Ong, K. S.; Pu, K.; Hong, G. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 754.
|
| [51] |
Fan, C.-H.; Chang, E.-L.; Ting, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Liao, E.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chan, H.-L.; Wei, K.-C.; Yeh, C.-K. Biomaterial. 2016, 106, 46.
|
| [52] |
Guo, B.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, D.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Liu, B. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802591.
|
| [53] |
Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ashley, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008802.
|
| [54] |
Jin, G.; He, R.; Liu, Q.; Lin, M.; Dong, Y.; Li, K.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B.; Xu, F. Theranostic. 2019, 9, 246.
|
| [55] |
Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, M.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Niu, N.; Yang, H.; Wen, H.; Fu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, B. Z.; Wang, D. Adv. Mater. 2024, 2309748.
|
| [56] |
Yan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Gui, Y.; Zhu, J.; Kang, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, B. Z.; Wang, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2024, e202401877.
|
| [57] |
Chen, Z.; Su, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Song, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2023, 120, e2205186120.
|
| [58] |
Sun, J.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10, 2101177.
|
| [59] |
Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, W. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9059-9066.
|
| [60] |
Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Yue, Q.; Chen, S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Luo, L.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004685.
|
| [61] |
Deng, K.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhao, H.; Wu, M.; Huang, S. Nanoscal. 2023, 15, 8006.
|
| [62] |
Zeng, W.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; Bian, K.; Zhang, B. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2000560.
|
| [63] |
Zhao, W.; Fu, C.; Gao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, C.; Yin, Y.; Hu, R.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 6229.
|
| [64] |
Pandey, N. K.; Xiong, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Bui, B.; Yang, J.; Amador, E.; Chen, M.; Xing, C.; Athavale, A. A.; Hao, Y.; Feizi, W.; Lumata, L. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 7, 112.
|
| [65] |
Jia, S.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Ou, H.; Ding, D. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 501.
|
| [66] |
Jiang, W.; Cheng, C.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Ran, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, J. Adv. Sci. 2022, 10, 2204989.
|
| [67] |
He, L.; Yu, X.; Li, W. ACS Nan. 2022, 16, 19691.
|
| [68] |
Yu, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, Z. H.; Liu, Y.; Lan, J.; Liu, W.; Xie, G.; Feng, G.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2302395.
|
| [1] | 沈钇灼, 罗康为, 徐清洋, 张鉴予, 孙景志, 张浩可, 唐本忠. 弱作用基有机发光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [2] | 何俊初, 伍俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金. 以二苯基硅杂吖啶为电子给体的蓝色聚集诱导延迟荧光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [3] | 谢志鑫, 黎少玲, 刘威, 严楷, 蒋涛, 刘一苇, Md. Monarul Islam, 冯星. 窄化芘基发光分子半峰宽的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [4] | 孟子翔, 田秀梅, 张天富. 聚集诱导发光材料在肿瘤光治疗应用中的最新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [5] | 唐子然, 孙浩, 朱亮亮. 光刺激响应型聚集诱导发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [6] | 张洁, 李楠, 赵娜. 聚集诱导发光分子纳米酶复合材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| [7] | 黄凯航, 尹理, 姜青云, 汪乾, 石光, 许炳佳. 具有聚集诱导发光性质的高效热激活延迟荧光材料用于脂滴成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [8] | 杨玉杰, 曹微, 于际凯, 张志霞, 徐莉, 王华. 给体-受体(D-A)型苯基环八四噻吩的合成及其聚集诱导发光与高压发光性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [9] | 苏小龙, 李健鹏, 刘孟鑫, 邹莉, 杨得锁, 冯海涛. 四苯乙烯酰胺类化合物的合成及其高灵敏度、高选择性识别Cu2+[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [10] | 欧彦, 蓝琳, 王正雄, 王志明, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光型核酸探针的制备及其核酸传感原理研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562. |
| [11] | 胡甲松, 李春娟, 徐斌, 田文晶. 固态荧光光开关分子研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [12] | 宫清宝, 吕翔, 于长江, 李婉婉, 赵全胜, 焦莉娟, 郝二红. 聚集诱导发光活性氟硼吡啶肼醛腙染料的合成、晶体结构及光学性质[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [13] | 王源浩, 孙钰凯, 刘昱迒, 张照明, 颜徐州. 基于四苯乙烯的柔性发光材料的构筑及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544. |
| [14] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [15] | 张继东, 杨垚, 张杰, 厍伟. 基于聚集诱导效应(AIE)-激发态分子内质子转移(ESIPT)效应的四苯乙烯荧光探针对Zn(II)检测研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1337-1342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||