Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 204-215.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202307018 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
霍海波a, 李桂霞b, 王世军c, 韩春c, 师宝君d, 李健a,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-17
修回日期:2023-08-31
发布日期:2023-09-15
作者简介:基金资助:
Haibo Huoa, Guixia Lib, Shijun Wangc, Chun Hanc, Baojun Shid, Jian Lia,c( )
)
Received:2023-07-17
Revised:2023-08-31
Published:2023-09-15
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:Share
Haibo Huo, Guixia Li, Shijun Wang, Chun Han, Baojun Shi, Jian Li. Novel γ-Carboline Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 204-215.
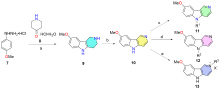
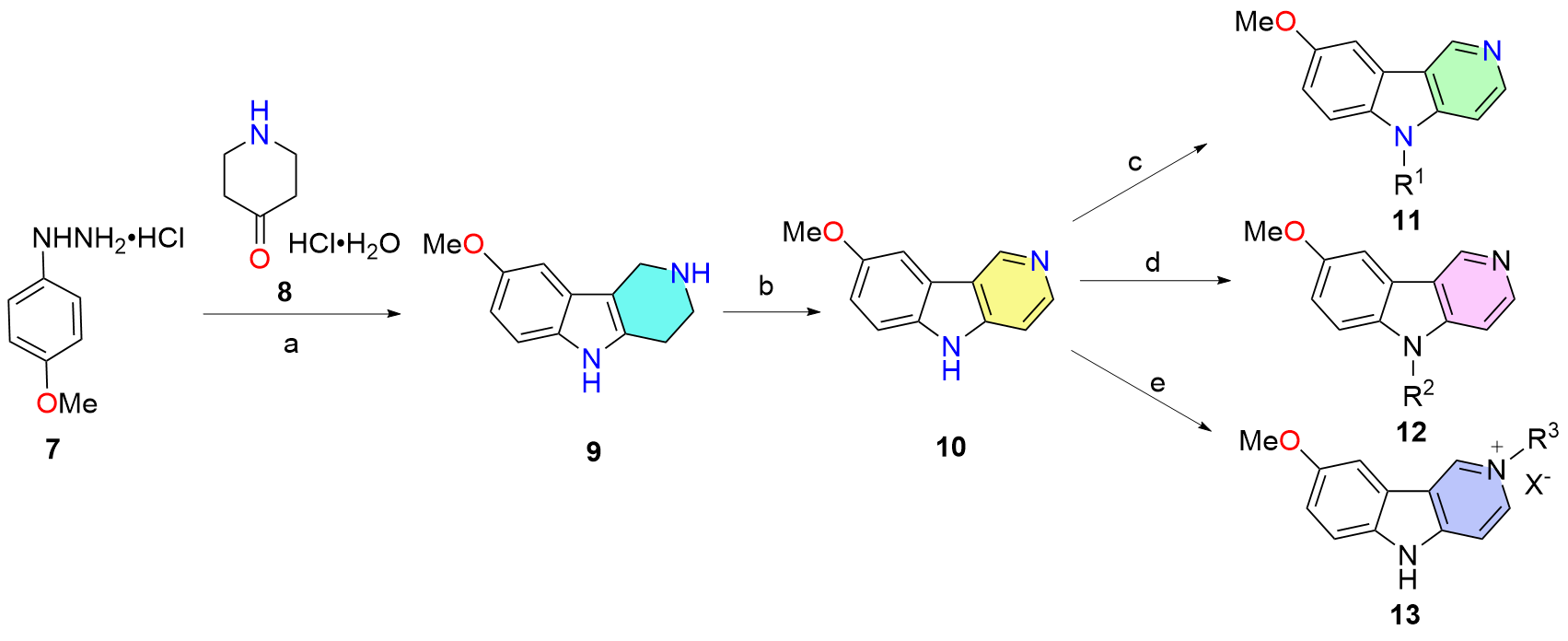
| Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11a | | 11b | | 11c | | 11d | | 11e | | |
| 11f | | 11g | | 11h | | 11i | | 11j | | |
| 11k | | 11l | | 11m | | 11n | | |||
| Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | |
| 12a | | 12b | | 12c | | 12d | | 12e | | |
| 12f | | 12g | | 12h | | 12i | | 12j | | |
| 12k | | |||||||||
| Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | |
| 13a | | 13b | | 13c | | 13d | | 13e | | |
| 13f | | 13g | | 13h | | 13i | | 13j | | |
| 13kb | | 13l | | 13m | | 13nb | | 13o | | |
| 13p | | 13q | | 13r | | 13s | | 13t | | |
| Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | Compd. | R1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11a | | 11b | | 11c | | 11d | | 11e | | |
| 11f | | 11g | | 11h | | 11i | | 11j | | |
| 11k | | 11l | | 11m | | 11n | | |||
| Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | Compd. | R2 | |
| 12a | | 12b | | 12c | | 12d | | 12e | | |
| 12f | | 12g | | 12h | | 12i | | 12j | | |
| 12k | | |||||||||
| Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | Compd. | R3 | |
| 13a | | 13b | | 13c | | 13d | | 13e | | |
| 13f | | 13g | | 13h | | 13i | | 13j | | |
| 13kb | | 13l | | 13m | | 13nb | | 13o | | |
| 13p | | 13q | | 13r | | 13s | | 13t | | |
| Compound | S.a | E.c | P.a | R.s | Compound | S.a | E.c | P.a | R.s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11a | — | — | 16 | 32 | 12g | 64 | — | — | 32 |
| 11b | — | 32 | 64 | 32 | 12h | 16 | — | 8 | 64 |
| 11c | — | — | 64 | 64 | 12i | 16 | — | 16 | 16 |
| 11d | — | — | 64 | 64 | 12k | 16 | 64 | 64 | 16 |
| 11e | — | — | — | 64 | 13a | — | 64 | ||
| 11f | — | — | — | 64 | 13b | — | 64 | ||
| 11g | 16 | — | 16 | 16 | 13c | 64 | 16 | ||
| 11h | — | — | 64 | — | 13e | 16 | — | 8 | |
| 11i | — | 16 | — | — | 13f | 16 | — | 32 | |
| 11j | 16 | — | — | 16 | 13j | 64 | |||
| 11k | — | — | — | 16 | 13k | 32 | 64 | 32 | |
| 11m | — | — | — | 16 | 13o | - | — | 64 | |
| 11n | — | 64 | 32 | — | 13p | 64 | — | 64 | |
| 12a | — | — | 64 | 32 | 13q | 64 | — | ||
| 12b | 64 | — | 64 | 16 | 13s | — | 64 | ||
| 12c | — | — | 32 | — | 13t | — | 64 | ||
| 12d | — | — | — | 64 | 13u | — | 64 | ||
| 12f | 8 | — | 64 | 8 | A.S.b | 8 | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Compound | S.a | E.c | P.a | R.s | Compound | S.a | E.c | P.a | R.s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11a | — | — | 16 | 32 | 12g | 64 | — | — | 32 |
| 11b | — | 32 | 64 | 32 | 12h | 16 | — | 8 | 64 |
| 11c | — | — | 64 | 64 | 12i | 16 | — | 16 | 16 |
| 11d | — | — | 64 | 64 | 12k | 16 | 64 | 64 | 16 |
| 11e | — | — | — | 64 | 13a | — | 64 | ||
| 11f | — | — | — | 64 | 13b | — | 64 | ||
| 11g | 16 | — | 16 | 16 | 13c | 64 | 16 | ||
| 11h | — | — | 64 | — | 13e | 16 | — | 8 | |
| 11i | — | 16 | — | — | 13f | 16 | — | 32 | |
| 11j | 16 | — | — | 16 | 13j | 64 | |||
| 11k | — | — | — | 16 | 13k | 32 | 64 | 32 | |
| 11m | — | — | — | 16 | 13o | - | — | 64 | |
| 11n | — | 64 | 32 | — | 13p | 64 | — | 64 | |
| 12a | — | — | 64 | 32 | 13q | 64 | — | ||
| 12b | 64 | — | 64 | 16 | 13s | — | 64 | ||
| 12c | — | — | 32 | — | 13t | — | 64 | ||
| 12d | — | — | — | 64 | 13u | — | 64 | ||
| 12f | 8 | — | 64 | 8 | A.S.b | 8 | 4 | 8 | 2 |


| [1] |
Fridkin; S. K.; Hageman; J. C.; Morrison; M.; Sanza; L. T.; Como-Sabetti; K.; Jernigan; J. A.; Harriman; K.; Harrison, L. H.; Lynfield, R.; Farley, M. M. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1436.
|
| [2] |
Song, F.; Shi, N.; Shan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Lu, H.; Ling, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y. Radiology 2020, 295, 210.
|
| [3] |
(a) Meganck, R. M.; Baric, R. S. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 401.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01282-0 |
|
(b) Genin, S. New Phytologist. 2010, 187, 920.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2010.187.issue-4 |
|
| [4] |
Walsh, C. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 65.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro727 |
| [5] |
Wohlleben, W.; Mast, Y.; Stegmann, E.; Ziemert, N. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 541.
doi: 10.1111/mbt2.2016.9.issue-5 |
| [6] |
Clardy, J.; Fischbach, M. A.; Currie, C. R. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 437.
|
| [7] |
Overbye, K. M.; Barrett, J. F. Drug Discovery Today 2005, 10, 45.
doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(04)03285-4 |
| [8] |
Tam, V. H.; Rogers, C. A.; Chang, K. T.; Weston, J. S.; Caeiro, J. P.; Garey, K. W. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3717.
|
| [9] |
Fischbach, M. A.; Walsh, C. T. Science 2009, 325, 1089.
|
| [10] |
Alanis, A. J. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 697.
doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2005.06.009 |
| [11] |
Theuretzbacher, U. J. Glob Antimicrob. Resist. 2013, 1, 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2013.03.010 |
| [12] |
Dai, J.; Dan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 447.
|
| [13] |
Bian, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Guo, R. Chem. Biodiversity 2020, 17, e2000186.
|
| [14] |
Nakamura, I.; Yamamoto, Y. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2127.
doi: 10.1021/cr020095i |
| [15] |
Li, J.; Huo, H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. S.; Ji, K. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4853.
doi: 10.1039/D1QO00821H |
| [16] |
Jiang, B.; Jia, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Bu, X.; Shi, L.; Sun, X.; Yang, X. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 13389.
|
| [17] |
Solé, D.; Bennasar, M. L.; Jiménez, I. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4535.
doi: 10.1039/c1ob05087g |
| [18] |
Yang, W. L.; Li, C. Y.; Qin, W. J.; Tang, F. F.; Yu, X. X.; Deng, W. P. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5685.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01596 |
| [19] |
Molina, A.; Vaquero, J. J.; García-Navio, J. L.; Alvarez-Builla, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 2673.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)77653-2 |
| [20] |
Heravi, M. M.; Rohani, S.; Zadsirjan, V.; Zahedi, N. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52852.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA10716A |
| [21] |
Snyder, S. A.; Vosburg, D. A.; Jarvis, M. G.; Markgraf, J. H. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 5329.
|
| [22] |
Tu, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, C.; Han, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Sheng, C. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2376.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01598 |
| [23] |
Bronovitsky, E. V.; Deikin, A. V.; Ermolkevich, T. G.; Elyakov, A. B.; Fedorov, E. N.; Sadchikova, E. R.; Goldman, I. L.; Ovchinnikov, R. K.; Roman, A. Y.; Khritankova, I. V.; Kukharsky, M. S.; Buchman, V. L.; Bachurin, S. O.; Ustyugov, A. A. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 462, 189.
doi: 10.1134/S1607672915030138 |
| [24] |
Otto, R.; Penzis, R.; Gaube, F.; Winckler, T.; Appenroth, D.; Fleck, C.; Tränkle, C.; Lehmann, J.; Enzensperger, C. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.09.048 |
| [25] |
Salim, M. T. A.; Goto, Y.; Hamasaki, T.; Okamoto, M.; Aoyama, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Musiu, S.; Paeshuyse, J.; Neyts, J.; Froeyen, M.; Herdewijn, P.; Baba, M. Antiviral Res. 2010, 88, 263.
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.09.013 |
| [26] |
Brindani, N.; Gianotti, A.; Giovani, S.; Giacomina, F.; Di Fruscia, P.; Sorana, F.; Bertozzi, S. M.; Ottonello, G.; Goldoni, L.; Penna, I.; Russo, D.; Summa, M.; Bertorelli, R.; Ferrera, L.; Pesce, E.; Sondo, E.; Galietta, L. J. V.; Bandiera, T.; Pedemonte, N.; Bertozzi, F. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11169.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01050 |
| [27] |
Bridoux, A.; Millet, R.; Pommery, J.; Pommery, N.; Henichart, J. P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3910.
|
| [28] |
Dai, J.; Dan, W.; Schneider, U.; Wang, J. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 622.
|
| [29] |
Bridoux, A.; Goossens, L.; Houssin, R.; Hénichart, J.-P. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2006, 43, 571
doi: 10.1002/jhet.v43:3 |
| [30] |
Dossetter, A. G.; Beeley, H.; Bowyer, J.; Cook, C. R.; Crawford, J. J.; Finlayson, J. E.; Heron, N. M.; Heyes, C.; Highton, A. J.; Hudson, J. A.; Jestel, A.; Kenny, P. W.; Krapp, S.; Martin, S.; MaCFaul, P. A.; McGuire, T. M.; Gutierrez, P. M.; Morley, A. D.; Morris, J. J.; Page, K. M.; Ribeiro, L. R.; Sawney, H.; Steinbacher, S.; Smith, C.; Vickers, M. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6363.
doi: 10.1021/jm3007257 |
| [31] |
Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5457.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b02377 |
| [32] |
Schwarthoff, S.; Tischer, N.; Sager, H.; Schätz, B.; Rohrbach, M. M.; Raztsou, I.; Robaa, D.; Gaube, F.; Arndt, H.; Winckler, T. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 46, 116355.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116355 |
| [1] | Qianfan Zhao, Yongzheng Chen, Shiming Zhang. Application and Mechanism Study of Carbon-Based Metal-Free Catalysts in Organic Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 137-147. |
| [2] | Huanqing Li, Zhaohua Chen, Zujia Chen, Qiwen Qiu, Youcai Zhang, Sihong Chen, Zhaoyang Wang. Research Progress in Mercury Ion Fluorescence Probes Based on Organic Small Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3067-3077. |
| [3] | Weizhong Ding, Bingwen Zhang, Yanqing Xue, Yuqi Lin, Zhijun Tang, Jing Wang, Wenchao Yang, Xiaofeng Wang, Wen Liu. A New Polyketide from Fusarium graminearum [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3319-3322. |
| [4] | Cunjing Miao, Jiaqi Yao. Recent Advances in the Transformation Reactions of Aromatic Nitriles via C—CN Bond Cleavage [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1341-1364. |
| [5] | Xingzhou Liu, Mingjia Yu, Jianhua Liang. Research Progress on the Synthesis of Protoberberine Skeleton and Its Anti-inflammatory Activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1325-1340. |
| [6] | Guanghui Shi, Yunzhe Du, Yuanyuan Gao, Huijie Jia, Hailong Hong, Limin Han, Ning Zhu. Reduction of Nitro Group by Sulfide and Its Applications in Amine Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 491-502. |
| [7] | Yueling Liu, Xinxin Zhong, Ganbing Zhang. Density Functional Theory Study for Exploring the Mechanisms of the [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions between 1-R-3-Phenylpropylidenecyclopropane (R=Me/H) and Furfural Catalyzed by Pd(0) [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 660-667. |
| [8] | Tingting Liu, Yucai Hu, An Shen. Mechanism of Carbon-Carbon Coupling Reactions Catalyzed by Imine-Ligand-Assisted N-Heterocyclic Carbene Palladium Complexes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 622-628. |
| [9] | Zehui Li, Haoyu Zou, Lincai Li, Yiling Zhao, Hongping Zhu. Synthesis and Propylene Oxide Carbonylation Hydroesterification Catalytic Property of N,O-Ligand Coordination Cobalt Compounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(11): 3907-3915. |
| [10] | Yifang Chen, Xin Luo, Yu Wang, Zhifu Xing, Ju Peng, Jixiang Chen. Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Sufones Containing Sulfonamide Structure [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 274-284. |
| [11] | Lin Ling, Jian Wang, Jing Li, Yuxue Li, Long Lu. Broken-Symmetry Density Functional Theory Study on Pyrolysis Mechanisms of 3-Nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO) [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 285-294. |
| [12] | Rong Zhang, Xiang Gao, Lingling Chen, Fajun Nan. Discovery and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Thiazole- Oxazole Tandem Heterocyclic RNA Splicing Inhibitors [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2925-2939. |
| [13] | Dan Huang, Xuhua Nong, Jianni Yang, Chen Li, Changri Han, Guangying Chen, Xiaoping Song, Zhenfan Sun, Yang Hui, Wenhao Chen. Study on the Secondary Metabolites of the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus terreus HQ100X-1 in Scutellaria formosana [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2961-2966. |
| [14] | Zhaohua Chen, Xiying Cao, Sihong Chen, Shiwei Yu, Yanlan Lin, Shuting Lin, Zhaoyang Wang. Design, Synthesis and Application of Trisubstituted Olefinic Aggregation-Induced Emission Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(8): 2355-2363. |
| [15] | Zexin Huang, Yuqiang Yin, Fengcheng Jia, Anxin Wu. Research Progress on C2—C3 Bond Cleavage of Indole and Its Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2028-2044. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||