Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 2699-2710.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202212026 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 二氧化碳虚拟合辑
廖旭a,b, 王泽宇b, 唐武飞a,*( ), 林金清b,*(
), 林金清b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-20
修回日期:2023-03-28
发布日期:2023-04-21
基金资助:
Xu Liaoa,b, Zeyu Wangb, Wufei Tanga( ), Jinqing Linb(
), Jinqing Linb( )
)
Received:2022-12-20
Revised:2023-03-28
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:Share
Xu Liao, Zeyu Wang, Wufei Tang, Jinqing Lin. Progress in Porous Organic Polymer for Chemical Fixation of Carnbon Dioxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2699-2710.

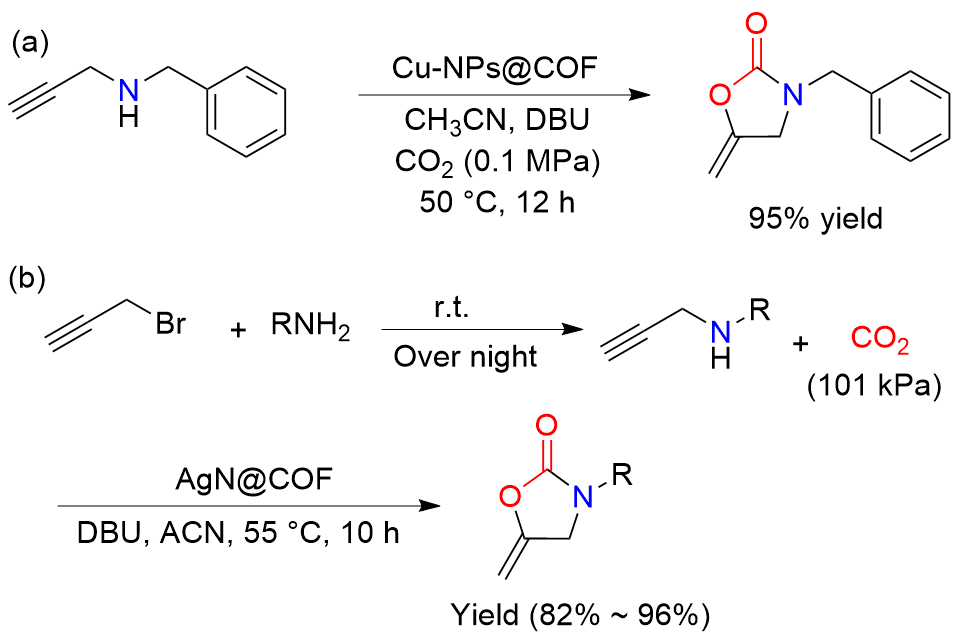
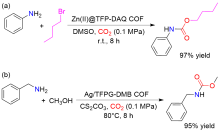
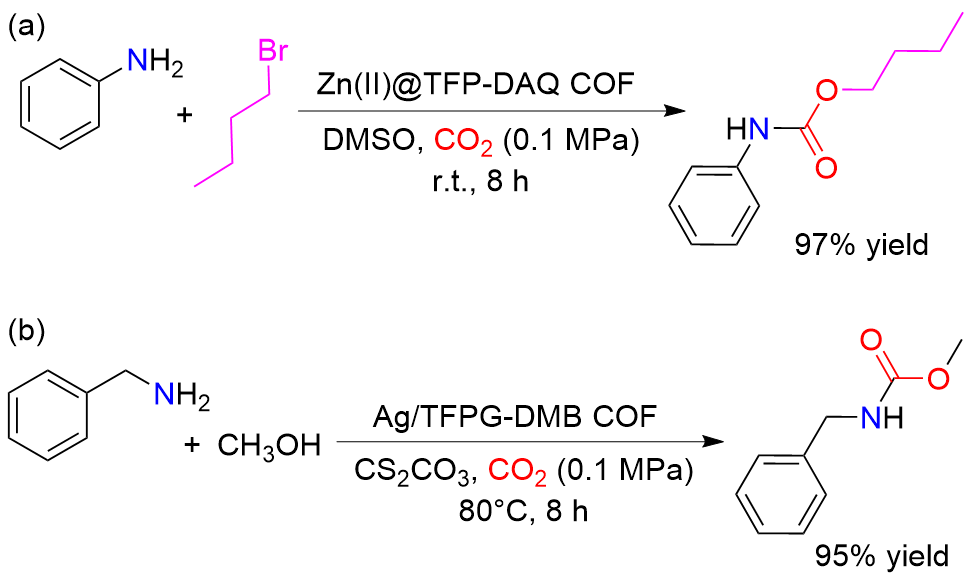
| [1] |
Tortajada, A.; Julia-Hernandez, F.; Borjesson, M.; Moragas, T.; Martin, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15948.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.49 |
| [2] |
Tyne, R. L.; Barry, P. H.; Lawson, M.; Byrne, D. J.; Warr, O.; Xie, H.; Hillegonds, D. J.; Formolo, M.; Summers, Z. M.; Skinner, B.; Eiler, J. M.; Ballentine, C. J. Nature 2021, 600, 670.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04153-3 |
| [3] |
Li, M.; Yang, K.; Abdinejad, M.; Zhao, C.; Burdyny, T. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11892.
doi: 10.1039/D2NR03310K |
| [4] |
Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, S.; Cheng, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 2221. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003039 |
|
( 周聪, 李渺, 于金涛, 孙松, 成江, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2221.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003039 |
|
| [5] |
Du, J.; Huang, O.; Tan, B. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 3833.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v16.23 |
| [6] |
Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Q.; Li, Y.; He, H. J. Environ Sci. 2023, 125, 811.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.02.025 |
| [7] |
Desgagnes, A.; Iliuta, M. C. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140214.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140214 |
| [8] |
Thubsuang, U.; Manmuanpom, N.; Chokaksornsan, N.; Sommut, C.; Singhawat, K.; Payaka, A.; Wongkasemjit, S.; Chaisuwan, T. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 155120.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155120 |
| [9] |
Wang, H.; Chuai, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1376.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c19502 |
| [10] |
Liang, J.; Chen, R. P.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, T. T.; Wang, X. S.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1570.
doi: 10.1039/c6sc04357g pmid: 28451286 |
| [11] |
Wu, Q. J.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2978.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00326 |
| [12] |
He, C.; Liang, J.; Zou, Y. H.; Yi, J. D.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab157.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab157 |
| [13] |
Liang, J.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. EnergyChem 2021, 3, 100064.
doi: 10.1016/j.enchem.2021.100064 |
| [14] |
Ebadi A, A.; Sanaeepur, H.; Luque, R.; Garcia, H.; Chen, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7427.
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00442A |
| [15] |
Lu, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, J. P.; Yang, M. Y.; Cai, Y. P.; Li, S. L.; Lan, Y. Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200003.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.15 |
| [16] |
Yang, Y. L.; Wang, Y. R.; Gao, G. K.; Liu, M.; Miao, C.; Li, L. Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, Z. Y.; Chen, Y.; Xin, Z.; Li, S. L.; Li, D. S.; Lan, Y. Q. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1439.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.08.063 |
| [17] |
Cai, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Liu, F.; Zhao, T.; Tao, D. J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138946.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138946 |
| [18] |
Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. N. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 42, 91.
|
| [19] |
Yang, D. H.; Tao, Y.; Ding, X.; Han, B. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 761.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00887K |
| [20] |
He, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, S.; Liu, Z. Q.; Zhu, M. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 1306.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63936-0 |
| [21] |
Song, K. S.; Fritz, P. W.; Coskun, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 9831.
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00727D |
| [22] |
Xu, Z. Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D. W.; Li, Z. T. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3777. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003070 |
|
( 徐子悦, 罗驿, 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3777.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003070 |
|
| [23] |
Lee, J. S. M.; Cooper, A. I. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 2171.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00399 |
| [24] |
Cote, A. P.; Yaghi, O. M. Science 2005, 310, 1166.
doi: 10.1126/science.1120411 |
| [25] |
Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Jin, S. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2856.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.065 |
| [26] |
Tan, L. X.; Tan, B. E. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3322.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00851H |
| [27] |
Kuhn, P.; Antonietti, M.; Thomas, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3450.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
| [28] |
Jiang, J. X.; Su, F.; Trewin, A.; Wood, C. D.; Campbell, N. L.; Niu, H.; Dickinson, C.; Ganin, A. Y.; Rosseinsky, M. J.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Cooper, A. I. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8574.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v46:45 |
| [29] |
Ben, T.; Ren, H.; Ma, S.; Cao, D.; Lan, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, F.; Simmons, J. M.; Qiu, S. L.; Zhu, G. S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9457.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200904637 |
| [30] |
Chen, J.; Longo, M.; Fuoco, A.; Esposito, E.; Monteleone, M.; Comesana, G. B.; Carolus, J. J.; McKeown, N. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215250.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.8 |
| [31] |
Guan, Q.; Zhou, L. L.; Dong, Y. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1475.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c11071 pmid: 36646043 |
| [32] |
Geng, K.; He, T.; Liu, R.; Dalapati, S.; Tan, K. T.; Li, Z.; Tao, S.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, D. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00550 |
| [33] |
Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chenm, Y. ; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 708.
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00827F |
| [34] |
Asokan, K.; Patil, M. K.; Mukherjee, S. P.; Sukumaran, S. B.; Nandakumar, T. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202201012.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v17.24 |
| [35] |
Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107201.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.007 |
| [36] |
Fu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Ai, S. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140154.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140154 |
| [37] |
Zhang, Z.; Kang, C.; Peh, S. B.; Shi, D.; Yang, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14992.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05309 |
| [38] |
Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, Q. Energy Stor. Mater. 2023, 55, 498.
|
| [39] |
Cui, B.; Fu, G. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1679.
doi: 10.1039/D1NR07614K |
| [40] |
Yao, S.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Xi, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202212466.
|
| [41] |
Yu, G.; Wang, C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 1437. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 于歌, 汪成, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 1437.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003018 |
|
| [42] |
Yue, J. Y.; Song, L.-P.; Wang, Y. T.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y.; Tang, B. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14419.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03179 |
| [43] |
Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3826. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202107030 |
|
( 陈育萱, 陈奇, 张占辉, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3826.)
|
|
| [44] |
Wu, C.; Li, X.; Shao, M.; Kan, J.; Wang, G.; Geng, Y.; Dong, Y. B. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4559.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.01.065 |
| [45] |
Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ju, J.; Yan, Q.; Arumugam, V.; Jing, X.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 485.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63487-X |
| [46] |
Li, W. Y.; Wan, J. J.; Kan, J. L.; Wang, B.; Song, T.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, L. L.; Li, Y. A.; Dong, Y. B. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 1453.
doi: 10.1039/D2SC05732H |
| [47] |
Saptal, V.; Shinde, D. B.; Banerjee, R.; Bhanage, B. M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 6152.
doi: 10.1039/C6CY00362A |
| [48] |
Yin, M.; Wang, L.; Tang, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55674.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c18226 |
| [49] |
Khatun, R.; Biswasa, S.; Biswas, I. H.; Riyajuddin, S.; Haque, N.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. M. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 40, 101180.
|
| [50] |
Cao, Q.; Zhang, L. L.; Zhou, C.; He, J. H.; Marcomini, A.; Lu, J. M. Appl. Catal. B. 2021, 294, 120238.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120238 |
| [51] |
He, C.; Si, D. H.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207478.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.40 |
| [52] |
Mu, Z. J.; Ding, X. S.; Chen, Z. Y.; Han, B. H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41350.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b14671 |
| [53] |
Sarkar, P.; Hazra, A.; Riyajuddin, C. S.; Biswas, S.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. M. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 744.
doi: 10.1039/C9NJ04673A |
| [54] |
Chowdhury, A. H.; Chowdhury, I. H.; Biswas, S.; Islam, S. M. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111050.
|
| [55] |
Ghosh, S.; Molla, R. A.; Kayal, U.; Bhaumik, A.; Islam, S. M. Dalton. Trans. 2019, 48, 4657.
doi: 10.1039/C9DT00017H |
| [56] |
Chakraborty, D.; Shekhar, P.; Singh, H. D.; Kushwaha, R.; Vinod, C. P.; Vaidhyanathan, R. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 4767.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v14.24 |
| [57] |
Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kan, J. L.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y. B. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 7363.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02721 |
| [58] |
Zhang, L.; Bu, R.; Liu, X.-Y.; Mu, P.-F.; Gao, E. Q. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 7620.
doi: 10.1039/D1GC02118D |
| [59] |
Toland, W. G. US US3060179, 1962.
|
| [60] |
Miller, G. H. US 3775380, 1973.
|
| [61] |
Ren, S.; Bojdys, M. J.; Dawson, R.; Laybourn, A.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Adams, D. J.; Cooper, A. I. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2357.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201200751 |
| [62] |
Meier, C. B.; Sprick, R. S.; Monti, A.; Guiglion, P.; Lee, J. M.; Zwijnenburg, M. A.; Cooper, A. I. Polymer 2017, 126, 283.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.04.017 |
| [63] |
Wang, K. W.; Yang, L. M.; Wang, X.; Guo, L. P.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S. B.; Tan, B.; Cooper, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14149.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201708548 |
| [64] |
Zhao, Y.; Huang, H. L.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, C. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 329, 111526.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111526 |
| [65] |
Dai, W.; Li, Q.; Long, J.; Mao, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zou, J.; Luo, X. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 62, 102101.
|
| [66] |
Roeser, J.; Kailasam, K.; Thomas, A. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1793.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v5.9 |
| [67] |
Lan, X. W.; Du, C.; Cao, L. L.; She, T. T.; Li, Y. M.; Bai, G. Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 38953.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b14743 |
| [68] |
Lan, X. W.; Li, Y. M.; Du, C.; She, T. T.; Li, Q.; Bai, G. Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 8560.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v25.36 |
| [69] |
Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhao, R.; Yang, S. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 3119.
doi: 10.1039/D0CY02473B |
| [70] |
Singh, G.; Nagaraja, C. M. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 63, 102132.
|
| [71] |
Tan, L. X.; Tan, B. E. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 530. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15020096 |
|
( 谭良骁, 谭必恩, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 530.)
doi: 10.6023/A15020096 |
|
| [72] |
Davankov, V. A.; Rogozhin, S. V.; Tsyurupa, M. P. US 3729457, 1971
|
|
[Chem. Abstr. 1971, 75, 6841.]
|
|
| [73] |
Liao, X.; Pei, B.; Ma, R.; Kong, L.; Gao, X.; He, J.; Luo, X.; Lin, J. Q. Catalysts 2022, 12, 62.
doi: 10.3390/catal12010062 |
| [74] |
Liao, X.; Xiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Kong, L.; Gao, X.; He, J.; Hou, W.; Peng, C.; Lin, J. Q. Sustainable Energy Fuels 2022, 6, 2846.
doi: 10.1039/D2SE00143H |
| [75] |
Ren, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tao, L.; Ji, H. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 2919.
doi: 10.1007/s10562-020-03527-y |
| [76] |
Molla, R. A.; Bhanja, P.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. S.; Bhaumik, A.; Islam, S. M. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1939.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201700069 |
| [77] |
Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A.; Riyajuddin, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chowdhury, A. H.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. K. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 1055.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v12.4 |
| [78] |
Xie, Y.; Wang, T. T.; Liu, X. H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W. Q. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1960.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2960 |
| [79] |
Xie, Y.; Wang, T. T.; Liu, X. H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W. Q. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2110.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201402162 |
| [80] |
Zhou, F.; Deng, Q.; Huang, N.; Zhou, W.; Deng, W. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10516.
doi: 10.1002/slct.v5.34 |
| [81] |
Zhang, X.; Qiu, B.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Mai, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 110758.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110758 |
| [82] |
Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Bian, Y.; Lv, H.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, R.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Mai, W.; Li, Y.; Li, T. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 58, 101924.
|
| [83] |
Ma, D. X.; Liu, K.; Li, J. X.; Shi, Z. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15050.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03517 |
| [84] |
Pan, Y.; Zhai, X. F.; Yin, J.; Zhang, T. Q.; Ma, L. J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Meng, J. Q. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 2231.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v12.10 |
| [1] | Jiyu Liu, Shengyu Li, Kuan Chen, Yin Zhu, Yuan Zhang. Triphenylamine-Based Ordered Mesoporous Polymer as a Metal-Free Photocatalyst for Oxidation of Thiols to Disulfide [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(2): 605-612. |
| [2] | Shiguo Ou, Ruirui Chai, Jiahao Li, Dawei Wang, Xinxin Sang. Metal-Organic Framework Derived Phytate-Iron for Efficient Synthesis of 2-Arylbenzoxazole via Hydrogen Transfer Strategy [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2934-2945. |
| [3] | Baichuan Mo, Chunxia Chen, Jinsong Peng. Research Progress in Application of Lignin and Its Derivatives Supported Metal Catalysts in Organic Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1215-1240. |
| [4] | Rui Bai, Xujuan Liu, Wenyu Luo, Shanshan Liu, Linyu Jiao. Research Progress of Chan-Lam Coupling Reaction in Heterogeneous Catalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(8): 2342-2354. |
| [5] | JIan Xiao, Zhiying Wu, Ziyi Chen, Pengfei Zhao. Tetraethylenepentamine Functionalized Phenolic Resin as Highly Active Acid-Base Bifunctional Catalyst for Knoevenagel Condensation Reaction [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(4): 1179-1187. |
| [6] | Qiang Huang, Tingting Deng, Jiayun Zhu, Jun Li, Feifei Li. Study on the Green Synthesis of β-Hydroxy-1,2,3-triazoles Catalyzed by An Amino-Functionalized Graphene-Supported Ag-Cu Composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(2): 534-542. |
| [7] | Yaoyao Zhang, Lijie Zhou, Biao Han, Weishuang Li, Bojie Li, Lei Zhu. Research Progress of Chitosan Supported Copper Catalyst in Organic Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(1): 33-53. |
| [8] | Xin Chen, Chunxia Chen, Jinsong Peng. Research Progress of Cellulose and Its Derivatives Supported Copper Catalyst Catalyzed Organic Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(4): 1319-1336. |
| [9] | Yuxuan Chen, Qi Chen, Zhanhui Zhang. Application of Covalent Organic Framework Materials as Heterogeneous Ligands in Organic Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(10): 3826-3843. |
| [10] | Feiyu Wang, Zhipeng Zhang, Fei Huang. Research Progress of O—H Insertion Reaction Based on Diazo Ester [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(1): 144-157. |
| [11] | Xu Zi-Yue, Luo Yi, Wang Hui, Zhang Dan-Wei, Li Zhan-Ting. Porous Organic Polymers as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Visible Light-Induced Organic Transformations [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(11): 3777-3793. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoling, Chen Jingwen, Bao Zongbi, Yang Qiwei, Yang Yiwen, Ren Qilong, Zhang Zhiguo. MIL-101(Cr)-SO3H Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation of 2-Substituted Quinoline Derivatives [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 39(6): 1681-1687. |
| [13] | Xu Peng, Duan Xinhong. Recent Progress in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions in Water [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019, 39(12): 3315-3327. |
| [14] | Zhong Wenwu, Tang Qian, Yang Zongfa, Zeng Xue, Gan Linling, Lan Zuoping, Yang Yuanjuan. Decarboxylative Oxyphosphorylation of Alkynyl Carboxylic Acids with H-Phosphonates Catalyzed by Cu-Cu2O/GO-NH2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019, 39(12): 3467-3474. |
| [15] | Xu Huan, Zhang Maoyuan, Huang Xiang, Shi Dabin. Palladium Nanoparticles Supported on MIL-101 as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for Selective C2 Arylation of Benzofuran [J]. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 38(4): 832-839. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||