Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 4143-4151.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202503024 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
白雪a, 谢祎黎b, 李君缘a, 莫梓华a, 万清a,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-24
修回日期:2025-06-07
发布日期:2025-08-18
基金资助:
Xue Baia, Yili Xieb, Junyuan Lia, Zihua Moa, Qing Wana,c,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-06-07
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
*E-mail: wanqingwork@nchu.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Xue Bai, Yili Xie, Junyuan Li, Zihua Mo, Qing Wan. Design of High Efficiency Cationic Photosensitizer and Its Application in Low Irradiation Dose Photodynamic Antibacterial[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(11): 4143-4151.

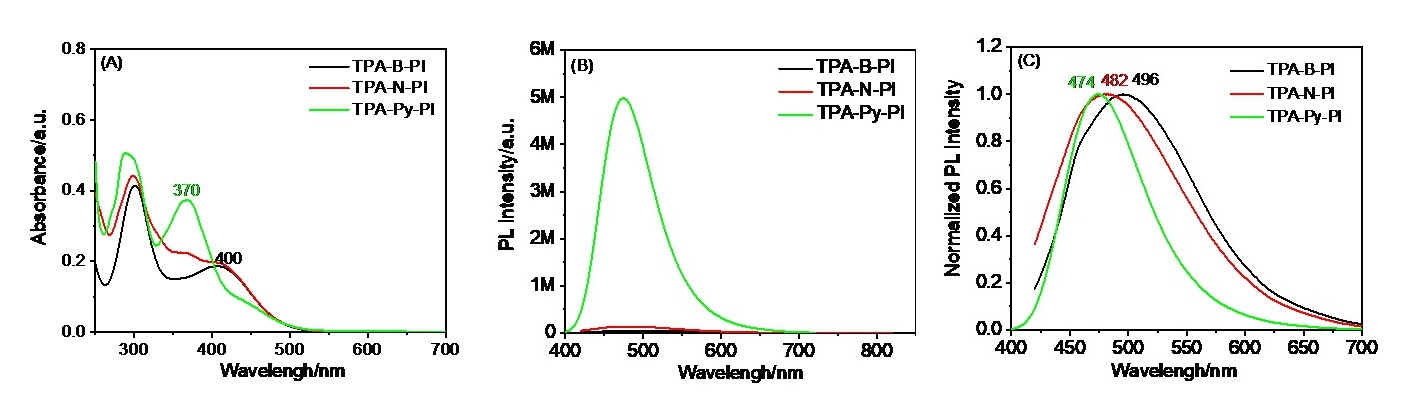
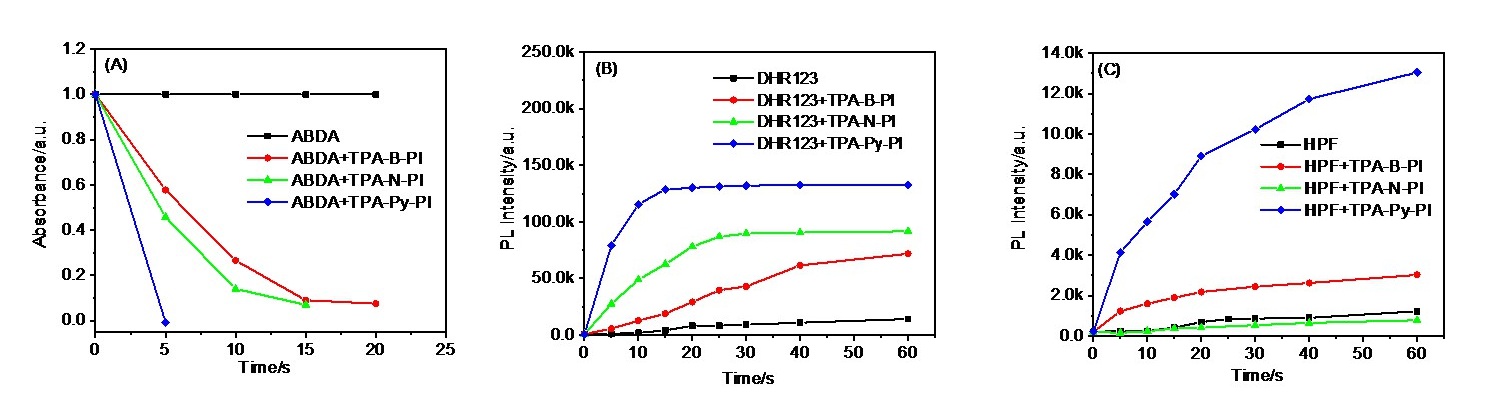

| [1] |
doi: 10.1039/D1NP00053E |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00794-x |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1186/s13613-022-01097-3 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.3390/medicina58091257 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.4161/gmic.28027 pmid: 24637595 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1111/nyas.2019.1435.issue-1 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00895 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138531 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.6023/A23050243 |
|
(闫英红, 梁平兆, 邹杨, 袁林, 彭孝军, 樊江莉, 张晓兵, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1642.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050243 |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1039/C2CS35216H |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1039/D3TB00545C |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.6023/A24040115 |
|
(黄艳琴, 罗集文, 李佳启, 张瑞, 刘兴奋, 范曲立, 黄维, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 903.)
doi: 10.6023/A24040115 |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.6023/A24010035 |
|
(李燕, 王玮, 张毓婷, 肖述章, 兰海闯, 耿鹏, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 443.)
doi: 10.6023/A24010035 |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.6023/A22120487 |
|
(吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 359.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120487 |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.33 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c09210 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101620 |
| [25] |
|
|
(郭玲香, 李菊平, 刘志洋, 李全, 化学进展, 2022, 34, 2489.)
doi: 10.7536/PC220335 |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v36.4 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [1] | Hua-Nan Wang, He Wu, Ye Zhao, Yi Gu, Gang Chen. Advances in the Process Chemistry of Semisynthetic Antibiotics Based on Complex Natural Products★ [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3045-3074. |
| [2] | Shutian Bu, Yong Wang, Wenjian Yin, Qingyun Wen, Pei Wang, Weiming Zhu. Staurosporine Natural Products Derived from Marine Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-5522 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(7): 2486-2500. |
| [3] | Jiaqiang Yang, Xurong Zhou, Yangmi Chen, Huixian She. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of Osthole Derivatives Containing Phosphonateptide Fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(4): 1306-1314. |
| [4] | Jianye Yang, Pei Zhou, Qifei Shen, Peijuan Zhang, Yanzi Xu, Bingjie Zhao, Dongfeng Dang. Progress of Organic Radical Materials in Biomedical Applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(11): 4013-4025. |
| [5] | Yixuan Chen, Zheng Zhao. Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Antimicrobial Therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(11): 3998-4012. |
| [6] | Hanyu Jia, Yuewen Yu, Guangxue Feng, BenZhong Tang. Construction of Type I Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy via Photoinduced Electron Transfer Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [7] | Limin Wang, Xiaoyu Song, Senxiang Cheng, Tong Chen, Deyun Cui. Synthesis and Activity Study of 1,2-Benzisothiazol-3-one Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(6): 1897-1906. |
| [8] | Lingdong Li, Weilun Zhang, Pengfei Liu, Zijie Zhou, Hao Zhou, Zhongtian Du. Synthesis of Gemini-Quaternary Ammonium N-Chloramine Biocides for Antibacterial Applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(6): 2041-2048. |
| [9] | Jiaqiang Yang, Xuejiao Wu, Zicong Lu, Yangmi Chen, Huixian She, Haijun Liu. Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of Osthole Derivatives Containing Thiazole Fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(11): 3541-3549. |
| [10] | Haibo Huo, Guixia Li, Shijun Wang, Chun Han, Baojun Shi, Jian Li. Novel γ-Carboline Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents: Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 204-215. |
| [11] | Ran Zhou, Chunmei Yuan, Tao Zhang, Piao Mao, Yi Liu, Kaini Meng, Hui Xin, Wei Xue. Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity of Chalcone Derivative Containing Quinazolinone [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3196-3209. |
| [12] | Weizhong Ding, Bingwen Zhang, Yanqing Xue, Yuqi Lin, Zhijun Tang, Jing Wang, Wenchao Yang, Xiaofeng Wang, Wen Liu. A New Polyketide from Fusarium graminearum [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3319-3322. |
| [13] | Yifang Chen, Xin Luo, Yu Wang, Zhifu Xing, Ju Peng, Jixiang Chen. Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Sufones Containing Sulfonamide Structure [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 274-284. |
| [14] | Dan Huang, Xuhua Nong, Jianni Yang, Chen Li, Changri Han, Guangying Chen, Xiaoping Song, Zhenfan Sun, Yang Hui, Wenhao Chen. Study on the Secondary Metabolites of the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus terreus HQ100X-1 in Scutellaria formosana [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2961-2966. |
| [15] | Huanhuan Wang, Pu Yang, Hongjin Zhai, Shuo Zhang, Yaquan Cao, Yingxue Yang, Chunli Wu. Design, Synthesis and Activity Evaluation of New Tylosin Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(2): 557-572. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||