Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 39-73.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202506020 Previous Articles Next Articles
REVIEWS
崔心怡a, 郭丽帆a, 马聪璇a,*( ), 李耘b,*(
), 李耘b,*( ), 梁建华a,*(
), 梁建华a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-08-08
修回日期:2025-09-05
发布日期:2025-09-17
基金资助:
Xinyi Cuia, Lifan Guoa, Congxuan Maa,*( ), Yun Lib,*(
), Yun Lib,*( ), Jianhua Lianga,*(
), Jianhua Lianga,*( )
)
Received:2025-08-08
Revised:2025-09-05
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
* E-mail: ljhbit@bit.edu.cn;
7520250060@bit.edu.cn;
liyun19702@sina.com
Supported by:Share
Xinyi Cui, Lifan Guo, Congxuan Ma, Yun Li, Jianhua Liang. Structural Modifications, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Total Synthesis Advances in Erythromycin Analogs against Resistant Pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2026, 46(1): 39-73.
| Macrolide | Species | Res/Å | Method | PDB No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 5JU8 | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 5JTE | [ |
| Telithromycin | B. subtilis | 3.10 | Electron microscopy | 6HA1 | [ |
| Telithromycin | E. coli | 3.50 | Electron microscopy | 6HA8 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.85 | X-Ray diffraction | 6ND6 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.42 | Electron microscopy | 6S0X | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.55 | X-Ray diffraction | 6XHX | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 6XHY | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 2.90 | Electron microscopy | 7NSO | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.50 | Electron microscopy | 7NSP | [ |
| Telithromycin | E. coli | 3.10 | Electron microscopy | 7NSQ | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.00 | Electron microscopy | 7Q4K | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.50 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC1 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.45 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC4 | [ |
| Azithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.50 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC2 | [ |
| Azithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.65 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC5 | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.35 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC6 | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC3 | [ |
| MCX-66 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTU | [ |
| MCX-128 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTX | [ |
| MCX-128 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.35 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTW | [ |
| MCX-91 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTV | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.58 | Electron microscopy | 8Y38 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 8Y39 | [ |
| Macrolide | Species | Res/Å | Method | PDB No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 5JU8 | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 5JTE | [ |
| Telithromycin | B. subtilis | 3.10 | Electron microscopy | 6HA1 | [ |
| Telithromycin | E. coli | 3.50 | Electron microscopy | 6HA8 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.85 | X-Ray diffraction | 6ND6 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.42 | Electron microscopy | 6S0X | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.55 | X-Ray diffraction | 6XHX | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 6XHY | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 2.90 | Electron microscopy | 7NSO | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.50 | Electron microscopy | 7NSP | [ |
| Telithromycin | E. coli | 3.10 | Electron microscopy | 7NSQ | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.00 | Electron microscopy | 7Q4K | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.50 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC1 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.45 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC4 | [ |
| Azithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.50 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC2 | [ |
| Azithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.65 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC5 | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.35 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC6 | [ |
| Telithromycin | Thermus thermophilus | 2.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 8FC3 | [ |
| MCX-66 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTU | [ |
| MCX-128 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTX | [ |
| MCX-128 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.35 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTW | [ |
| MCX-91 | Thermus thermophilus | 2.40 | X-Ray diffraction | 8VTV | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.58 | Electron microscopy | 8Y38 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 8Y39 | [ |
| Macrolide | Species | Res/Å | Method | PDB No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamolide 4d | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.20 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IO9 | [ |
| Carbamolide 4e | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.20 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IOA | [ |
| Carbamolide 4f | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IOC | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 6.60 | Cryo-electron microscopy | 3J5L | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.90 | Cryo-electron microscopy | 3J7Z | [ |
| Telithromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 3.43 | X-Ray diffraction | 4WF9 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.54 | X-Ray diffraction | 4WFN | [ |
| Erythromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.30 | Electron microscopy | 6S0Z | [ |
| Clarithromycin | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 3.30 | Electron microscopy | 7F0D | [ |
| Erythromycin | Mycobacterium smegmatis | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 8XZ3 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.65 | CElectron microscopy | 8Y36 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.53 | Electron microscopy | 8Y37 | [ |
| Macrolide | Species | Res/Å | Method | PDB No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamolide 4d | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.20 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IO9 | [ |
| Carbamolide 4e | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.20 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IOA | [ |
| Carbamolide 4f | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.60 | X-Ray diffraction | 4IOC | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 6.60 | Cryo-electron microscopy | 3J5L | [ |
| Erythromycin | E. coli | 3.90 | Cryo-electron microscopy | 3J7Z | [ |
| Telithromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 3.43 | X-Ray diffraction | 4WF9 | [ |
| Erythromycin | Deinococcus radiodurans | 3.54 | X-Ray diffraction | 4WFN | [ |
| Erythromycin | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.30 | Electron microscopy | 6S0Z | [ |
| Clarithromycin | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 3.30 | Electron microscopy | 7F0D | [ |
| Erythromycin | Mycobacterium smegmatis | 3.60 | Electron microscopy | 8XZ3 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.65 | CElectron microscopy | 8Y36 | [ |
| MCX-190 | Staphylococcus aureus | 2.53 | Electron microscopy | 8Y37 | [ |
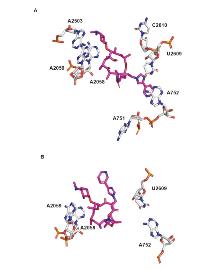
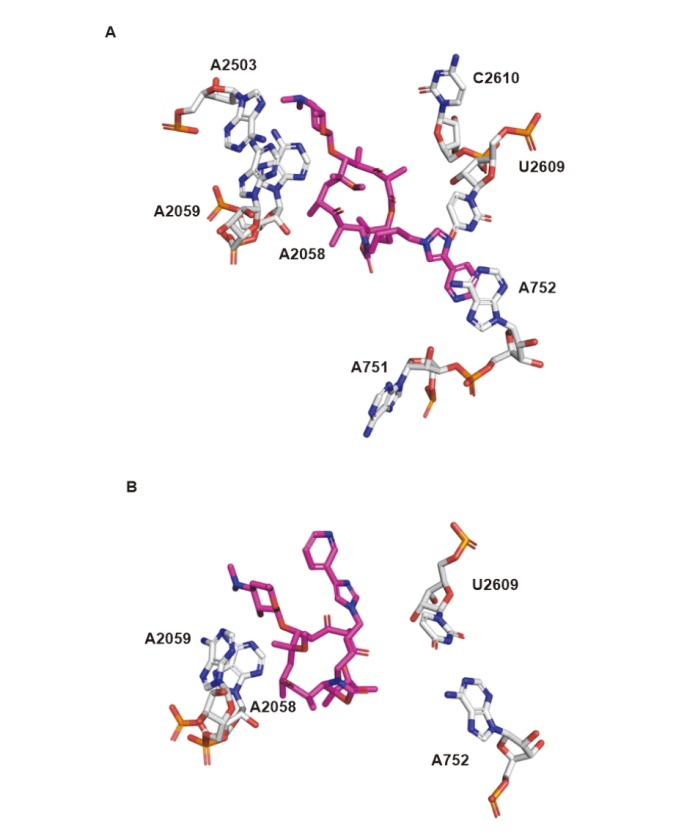
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes (genotypes) | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Clarithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae BAA1402 | M (mef) | 0.03 | 2 |
| Staphylococcus aureus BAA976 | M (mef) | 0.03 | 64 |
| Staphylococcus aureus BA977 | iMLS (erm) | 0.03 | >64 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes (genotypes) | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Clarithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae BAA1402 | M (mef) | 0.03 | 2 |
| Staphylococcus aureus BAA976 | M (mef) | 0.03 | 64 |
| Staphylococcus aureus BA977 | iMLS (erm) | 0.03 | >64 |
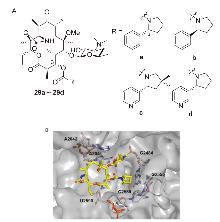
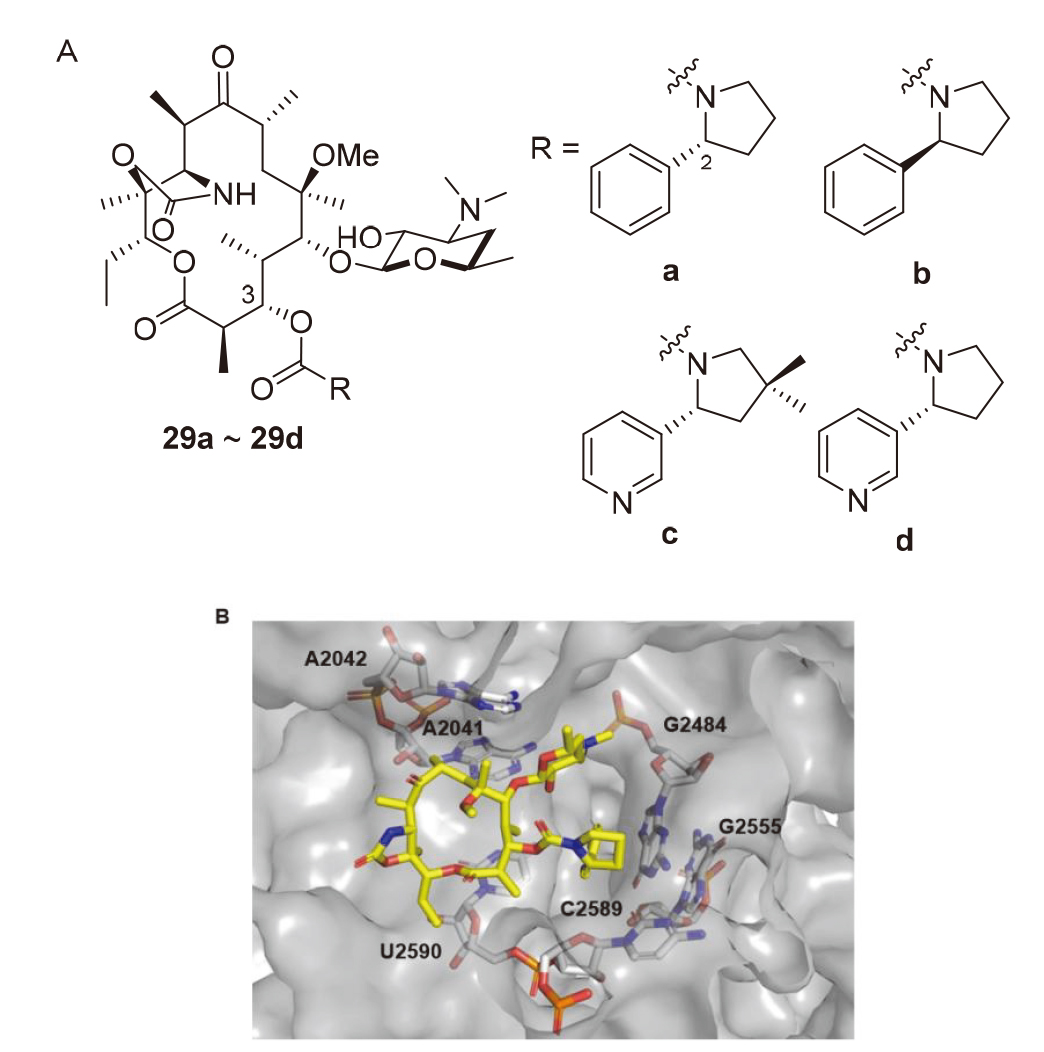
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(mg•L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29a | 29b | Clarithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 1243-00 | MLSB | 0.5 | 64 | >64 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 1304-00 | MLSB | 0.5 | 32 | >64 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(mg•L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29a | 29b | Clarithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 1243-00 | MLSB | 0.5 | 64 | >64 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 1304-00 | MLSB | 0.5 | 32 | >64 |
| Compd. | Clearance/(mL•h-1•kg-1) | t1/2/h | Mean resident time/h | cmax/(ng•mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 3034±600 | 2.9±0.4 | 4.5±0.6 | 1029±115 |
| Telithromycin | 21758±2748 | 1.2±0.3 | 3.3±0.5 | 204±20.5 |
| Compd. | Clearance/(mL•h-1•kg-1) | t1/2/h | Mean resident time/h | cmax/(ng•mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 3034±600 | 2.9±0.4 | 4.5±0.6 | 1029±115 |
| Telithromycin | 21758±2748 | 1.2±0.3 | 3.3±0.5 | 204±20.5 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | 42 | Telithromycin | Clarithromycin | ||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis 12-4 | MRSEa | 4 | 8 | ≤2 | 32 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis 12-11 | MRSE | 2 | ≤1 | ≤2 | 4 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | 42 | Telithromycin | Clarithromycin | ||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis 12-4 | MRSEa | 4 | 8 | ≤2 | 32 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis 12-11 | MRSE | 2 | ≤1 | ≤2 | 4 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | Azithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 943 | Sensitive | 1 | 4 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 746 | Sensitive | 2 | 8 |
| MRSA-1 | MRSAa | 16 | 16 |
| Strain | Resistance phenotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | Azithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 943 | Sensitive | 1 | 4 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 746 | Sensitive | 2 | 8 |
| MRSA-1 | MRSAa | 16 | 16 |
| Strain | Resistance genotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | Azithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae B1 | erm | 0.25 | 128 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae AB11 | mef, erm | 2 | 256 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae A22072 | mef | 0.03 | 4 |
| Strain | Resistance genotypes | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | Azithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae B1 | erm | 0.25 | 128 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae AB11 | mef, erm | 2 | 256 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae A22072 | mef | 0.03 | 4 |
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 66 | Telithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae PU09 | PSSP,a mef | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 01-968 | i-erm | 0.062 | 0.062 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-207 | mef | 0.031 | 0.5 |
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 66 | Telithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae PU09 | PSSP,a mef | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 01-968 | i-erm | 0.062 | 0.062 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-207 | mef | 0.031 | 0.5 |
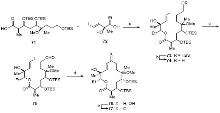
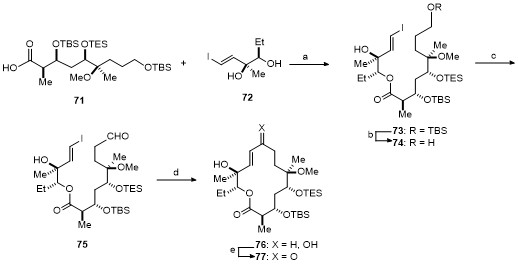
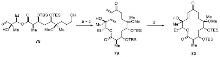
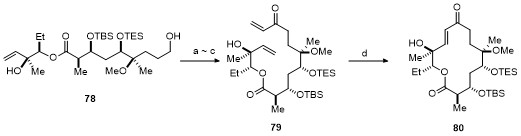
| Strain | Resistant determinant | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | Telithromycin | ||
| E. coli SQ171/2058G | A2058G | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | — |
| E. coli DK/PKK3535 | wt | 32 | 4 | 8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| E. coliDK/2058G | A2058G | 64 | 32 | 16 | 4 | 1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus UCN14 | A2058T | 32 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC33591 | ermA | >128 | >64 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| Strain | Resistant determinant | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | Telithromycin | ||
| E. coli SQ171/2058G | A2058G | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | — |
| E. coli DK/PKK3535 | wt | 32 | 4 | 8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| E. coliDK/2058G | A2058G | 64 | 32 | 16 | 4 | 1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus UCN14 | A2058T | 32 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC33591 | ermA | >128 | >64 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| Strain | Resistant determinant | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115 | Azithromycin | Telithromycin | Ciprofloxacin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 07P390 | c-ermB | ≤0.008 | 256 | 0.016 | — |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-206 | c-ermTR | 0.016 | >256 | 0.031 | 0.125 |
| Staphylococcus aureus PU32 | MRSA, i-ermA | 0.25 | 32 | 0.125 | 64 |
| Strain | Resistant determinant | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115 | Azithromycin | Telithromycin | Ciprofloxacin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae 07P390 | c-ermB | ≤0.008 | 256 | 0.016 | — |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-206 | c-ermTR | 0.016 | >256 | 0.031 | 0.125 |
| Staphylococcus aureus PU32 | MRSA, i-ermA | 0.25 | 32 | 0.125 | 64 |
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 119 | Telithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae PU09 | mef | ≤0.008 | 0.5 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-206 | c-ermTR | 0.06 | 0.25 |
| Haemophilus influenzae ATCC49247 | sensitive | 2 | 4 |
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 119 | Telithromycin | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae PU09 | mef | ≤0.008 | 0.5 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes 12-206 | c-ermTR | 0.06 | 0.25 |
| Haemophilus influenzae ATCC49247 | sensitive | 2 | 4 |
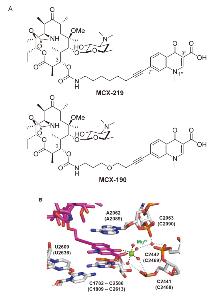
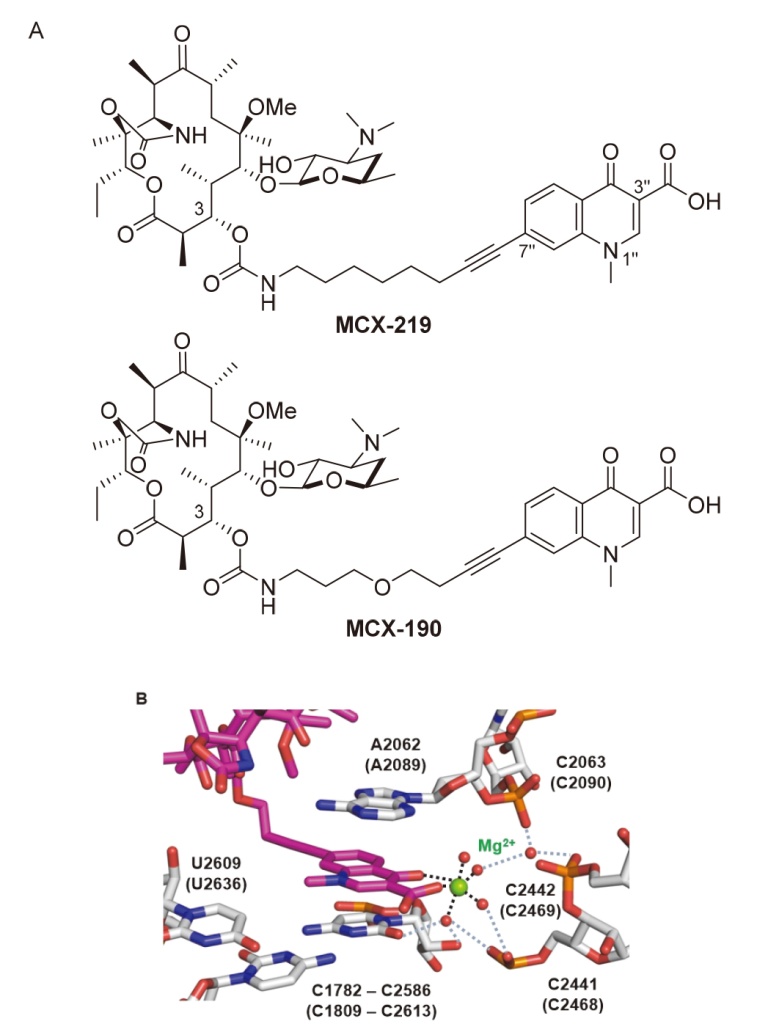
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCX-190 | MCX-219 | Telithromycin | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus 15B196 | c-ermB | 8 | 1 | 32~>256 |
| Staphylococcus aureus PU32 | i-ermA | 0.25~0.5 | 0.25 | 0.12~0.5 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2058G | 1 | 0.25 | 256 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2059G | 2 | 0.25 | 256 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2058T | 0.5 | 0.06 | 256 |
| Strain | Resistant determinants | MIC/(μg•mL-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCX-190 | MCX-219 | Telithromycin | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus 15B196 | c-ermB | 8 | 1 | 32~>256 |
| Staphylococcus aureus PU32 | i-ermA | 0.25~0.5 | 0.25 | 0.12~0.5 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2058G | 1 | 0.25 | 256 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2059G | 2 | 0.25 | 256 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | A2058T | 0.5 | 0.06 | 256 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.126850 |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.12.070 |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.10.054 |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.064 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.08.023 |
| [65] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.09.064 |
| [66] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2015.11.029 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.04.014 |
|
| [67] |
doi: 10.1080/10286020.2018.1451519 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.02.041 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2022.06.001 |
| [70] |
pmid: 11708904 |
| [71] |
pmid: 12801234 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02137246 |
| [3] |
pmid: 10377939 |
| [4] |
pmid: 15257629 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1002/ange.v69:1/2 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
pmid: 2656049 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-00715-0 pmid: 33462493 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics5030029 |
| [10] |
(a)
doi: S0968-0004(18)30128-2 pmid: 30054232 |
| [72] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.03.026 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.10.101 |
|
| [73] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.08.020 |
| [74] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.02.041 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.148 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.037 |
| [10] |
(b)
pmid: 30054232 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1111/bph.v174.18 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007988107 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2006.07.016 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.2174/1568026033452159 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1128/AAC.11.4.669 pmid: 856018 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3155 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.09.012 |
| [78] |
doi: S0223-5234(16)30936-9 pmid: 27836198 |
| [79] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128330 |
| [80] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.01.023 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.03.038 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1038/ja.2009.89 |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-3-1 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.07.016 |
| [22] |
(a)
pmid: 11036012 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.2999-3002.2000 pmid: 11036012 |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00702-y |
| [24] |
doi: 10.2174/15680266113136660223 |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106147 |
| [82] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.04.051 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/ardp.v343:8 |
|
| [83] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.09.083 pmid: 24139585 |
| [84] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.01.092 |
| [85] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.07.042 pmid: 23937982 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12026 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1261/rna.069260.118 pmid: 30733327 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48019-1 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24674-9 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39553-8 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39653-5 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01685-3 pmid: 39039256 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.01.067 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4501 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.014 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: S0969-2126(17)30184-3 pmid: 28689968 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2024.06.016 |
| [40] |
pmid: 4213128 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
(a)
pmid: 11592503 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.57.518 pmid: 11592503 |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262120-00006 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01841.x pmid: 10760175 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00060-11 pmid: 21537010 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70002-1 pmid: 18222155 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.08.035 |
| [48] |
pmid: 16194243 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.42 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.06.039 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03281-5 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1007/s11696-023-02725-3 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2022.100757 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2021.104889 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
doi: S0960-894X(17)30705-9 pmid: 28711353 |
| [58] |
doi: S0960-894X(18)30490-6 pmid: 29880401 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128110 |
| [86] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106020 |
| [87] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.09.020 pmid: 26402728 |
| [88] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.06.044 |
| [89] |
doi: 10.1038/s41429-018-0107-2 pmid: 30315257 |
| [90] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.11.028 |
| [91] |
doi: 10.1039/c7np00006e pmid: 28530279 |
| [92] |
doi: S0960-894X(18)30905-3 pmid: 30473176 |
| [93] |
doi: 10.3390/ph17020187 |
| [94] |
doi: 10.1002/cmdc.v15.16 |
| [95] |
doi: 10.1039/D3RA03168C |
| [96] |
doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0667-z |
| [97] |
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00860-10 pmid: 20855725 |
| [98] |
(a)
doi: 10.1128/AAC.02316-12 pmid: 23318809 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.08.021 pmid: 23318809 |
|
| [99] |
doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.200733 pmid: 23359665 |
| [100] |
doi: 10.1128/AAC.04652-14 pmid: 25870056 |
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
doi: 10.2146/ajhp160934 |
| [103] |
doi: 10.1128/AAC.01589-13 |
| [104] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.03.038 |
| [105] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114213 |
| [106] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.129115 |
| [107] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116181 |
| [108] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.005 |
| [109] |
pmid: 21643527 |
| [110] |
doi: 10.1039/D4NP00050A |
| [111] |
(a)
doi: 10.1039/D5SC00591D pmid: 21815685 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jo201319b pmid: 21815685 |
|
| [112] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c13304 pmid: 38241031 |
| [113] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ml300230h pmid: 25221660 |
|
(b)
pmid: 25221660 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/ml5002097 pmid: 25221660 |
|
| [114] |
doi: 10.1055/s-00000083 |
| [115] |
doi: 10.1038/nature17967 |
| [116] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.04.062 pmid: 20462754 |
| [117] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ml100253p pmid: 27353268 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00524-16 pmid: 27353268 |
|
| [118] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.02.019 |
| [119] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.01.055 |
| [120] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.10.024 |
| [121] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.073 |
| [122] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112222 |
| [123] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116630 |
| [124] |
doi: S0223-5234(16)30753-X pmid: 27657812 |
| [125] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107712 |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128761 |
| [127] |
doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01772-5 |
| [1] | Lilin Zhao, Zhaoqi Li, Liping Zhong, Long Min. Recent Progress in the Total Synthesis of abeo-Steroids [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2026, 46(1): 21-38. |
| [2] | Sai Hong, Fahong Yin, Minghui Chen, Bin Fu, Yumei Xiao, Zhaohai Qin. Study on the Synthesis and Fungicidal Activity of 1-Azolyl-1,1- diarylmethanes Containing Pyridine Ring [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2026, 46(1): 106-117. |
| [3] | Qianqian Zhao, Peiyao Wei, Sundian Liu, Boxin Zhang, Chengyuan Liang. Applications of Palladium-Catalyzed Cascade Reactions in Total Synthesis of Complex Natural Products with Quaternary Carbon Centers [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3289-3300. |
| [4] | Ying Xia, Chenlong Zhu, Bingfeng Sun. Progress in Total Synthesis of Entecavir, an Antiviral Drug for Hepatitis B★ [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3186-3202. |
| [5] | Xiaoyu Liu, Tingrui Xu, Yong Qin. Recent Progress in the Total Synthesis of Morphine Alkaloids★ [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3098-3112. |
| [6] | Youxue Zhao, Xiruo Li, Luobing Meng, Chunxiu Li, Guisheng Fan, Jianhe Xu. Advances in Understanding the Substrate Promiscuity of Alcohol Dehydrogenases/Carbonyl Reductases★ [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3175-3185. |
| [7] | Haozhe Guo, Yuyin Li, Peichen Tang, Jiangli Fan. Advances in Machine Learning-Based Design of Organic Fluorescent Theranostic Molecules★ [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(9): 3203-3212. |
| [8] | Baichuan Mo, Tingting Li, Fang Wang, Xiaojie Li, Darifu Ba. Recent Progress in the Synthesis of Carbazolequinone Natural Products [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(8): 2746-2766. |
| [9] | Yiming Ding, Tingrong Zhang, Jingwei Zhang, Jun Deng. Progress in the Total Synthesis of Cephalotane Diterpenoid Natural Products [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(6): 2048-2073. |
| [10] | Weigang He, Yadong Liu, Yingkai Deng, Xianyu Sun. Recent Progress in the Synthesis of the Malagasy Alkaloids [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(4): 1153-1165. |
| [11] | Jiuzhou Yi, Liang Huo, Jinyan Chen, Meng Liu, Huilin Li, Xuegong She. Protecting Group Effects on the Total Syntheses of Several Classes of Natural Products [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(3): 1030-1039. |
| [12] | Jie Chen, Jun Li, Xianwen Long, Haixiang Shen, Jun Deng. Recent Advances of Wagner-Meerwein Rearrangement in Natural Product Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(3): 896-912. |
| [13] | Chuang Li, Cheng Zhang, Xiaoyu Liu, Yong Qin. Recent Progress in the Total Synthesis of Diterpenoid Alkaloids [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(3): 881-895. |
| [14] | Qingxing Yang, Xuan Liu, Shuo Ma, Xinxin Li, Dongxu Ma, Tao Xu. Total Syntheses of Marine-Derived Polyhalogenated Natural Products [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(3): 764-803. |
| [15] | Yunbo Yang, Hanfeng Ding. Advances in the Total Syntheses of Tetraquinane and Tetraquinane-Type Terpenes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(3): 725-747. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||