Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 1974-1981.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202101038 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
赵云1,*( ), 李艳芳1, 李蓉晓1, 王雅卿1, 樊晓霞1
), 李艳芳1, 李蓉晓1, 王雅卿1, 樊晓霞1
收稿日期:2021-01-22
修回日期:2021-03-15
发布日期:2021-04-06
通讯作者:
赵云
基金资助:
Yun Zhao1,*( ), Yanfang Li1, Rongxiao Li1, Yaqing Wang1, Xiaoxia Fan1
), Yanfang Li1, Rongxiao Li1, Yaqing Wang1, Xiaoxia Fan1
Received:2021-01-22
Revised:2021-03-15
Published:2021-04-06
Contact:
Yun Zhao
About author:Supported by:Share
Yun Zhao, Yanfang Li, Rongxiao Li, Yaqing Wang, Xiaoxia Fan. A New Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorous Acid Based on Chlorinium Ions Recognition Mechanism and Its Bioimaging Research in Living Cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(5): 1974-1981.

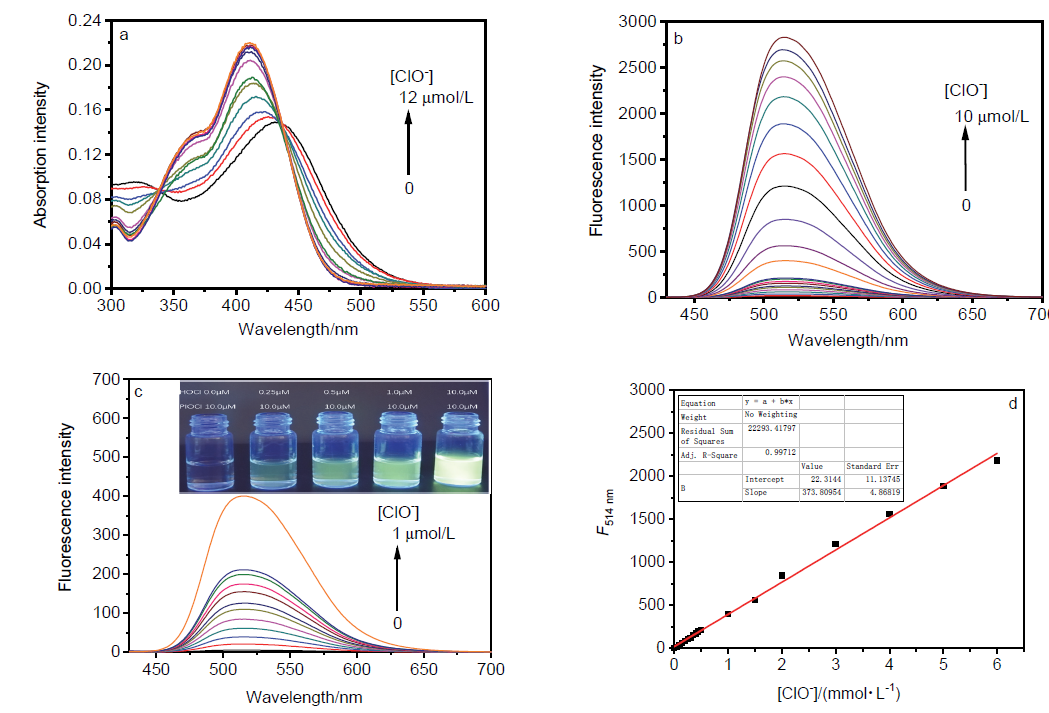
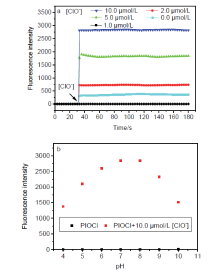



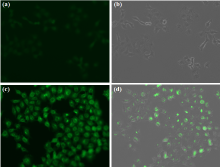

| [1] |
Zielonka, J.; Joseph, J.; Sikora, A.; Hardy, M.; Ouari, O.; Vasquez-Vivar, J.; Cheng, G.; Lopez, M.; Kalyanaraman, B. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10043.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00042 |
| [2] |
Wu, D.; Chen, L. Y.; Xu, Q. L.; Chen, X. Q.; Yoon, J. Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2158.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00307 |
| [3] |
Wang Y. B.; Zhao B. X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1539. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 |
|
(王延宝, 赵宝祥, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1539.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 |
|
| [4] |
Yuan, L.; Wang, L.; Agrawalla, B. K.; Park, S. J.; Zhu, H.; Sivaraman, B.; Peng, J.; Xu, Q. H.; Chang, Y. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5930.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00042 |
| [5] |
Pattison, D. I.; Davies, M. J. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1453.
pmid: 11599938 |
| [6] |
Wei, P.; Liu, L.; Yuan, W.; Yang, J.; Li, R.; Yi, T. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1153.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9737-y |
| [7] |
Nathan, C.; Cunningham-Bussel, A. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 349.
doi: 10.1038/nri3423 |
| [8] |
Ma, C.; Zhong, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Shen, B. Spectrochim. Acta A 2020, 240, 118545.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118545 |
| [9] |
Yue, Y.; Huo, F.; Yin, C.; Escobedo, J. O.; Strongin, R. M. Analyst 2016, 141, 1859.
doi: 10.1039/C6AN00158K |
| [10] |
Zhang, Y. R.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhao, B. X. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 240, 18.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.066 |
| [11] |
Yu Q., Chen X. L., Liu H., Zhang Q. L. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 1206. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201911004 |
|
(余青, 陈晓丽, 刘华, 张奇龙, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 1206.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201911004 |
|
| [12] |
Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Peng, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12820,.
doi: 10.1021/ja505988g |
| [13] |
He, L.; Xiong, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Song, X. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11029,.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00030 |
| [14] |
Radi, R.; Beckman, J. S.; Bush, K. M.; Freeman, B. A. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4244,.
pmid: 1847917 |
| [15] |
Koide, Y.; Urano, Y.; Kenmoku, S.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10324,.
doi: 10.1021/ja073220m |
| [16] |
Lou, Z.; Li, P.; Han, K. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1358,.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00009 |
| [17] |
Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, P.; Sun, M.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.-P.; Guo, W. Biomaterials 2017, 133, 60,.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.023 |
| [18] |
Jiao C. P., Liu Y. Y., Lu W. J., Zhang P. P., Wang Y. F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 591. (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201810013 |
|
(矫春鹏, 刘媛媛, 路文娟, 张平平, 王延风, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 591.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201810013 |
|
| [19] |
Xie, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Jiao, X.; Tang, B. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11965.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC07312K |
| [20] |
Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Hyun, J. Y.; Wei, T.; Qiang, J.; Ren, X.; Shin, I.; Yoon, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2976.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00192K |
| [21] |
de la Mare, P. B. D.; Hilton, I. C.; Vernon, C. A. J. Chem. Soc. (Resumed) 1960,4039.
|
| [22] |
Ren, T.-B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-X.; Wen, S.-Y.; Yi, H.-B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7473.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201800293 |
| [23] |
Wu, M. Y.; Li, K.; Hou, J. T.; Huang, Z.; Yu, X. Q. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8342.
doi: 10.1039/c2ob26235e |
| [24] |
Weng, J.; Mei, Q.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Tong, B.; Fan, Q.; Ling, Q.; Huang, W. Analyst 2013, 138, 6607.
doi: 10.1039/c3an01214j |
| [25] |
Xiao, H.; Xin, K.; Dou, H.; Yin, G.; Quan, Y.; Wang, R. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1442.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC07411D |
| [26] |
Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, C.; Guo, B.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3377.
doi: 10.1039/C6TB03345H |
| [27] |
Zhi, X.; Qian, Y. Talanta 2021, 222, 121503.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121503 |
| [28] |
Ma, J.; Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Duo, H.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Guo, Y. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 7168.
|
| [29] |
Lu, P.; Zhang, X.; Ren, T.; Yuan, L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2980.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.08.016 |
| [30] |
Hileman, E. O.; Liu, J.; Albitar, M.; Keating, M. J.; Huang, P. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2004, 53, 209.
doi: 10.1007/s00280-003-0726-5 |
| [31] |
Toşa, M.; Paizs, C.; Majdik, C.; Moldovan, P.; Novák, L.; Kolonits, P.; Szabó, É.; Poppe, L.; Irimie, F.-D. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2002, 17, 241.
doi: 10.1016/S1381-1177(02)00015-2 |
| [32] |
Yu, F.; Song, P.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Han, K. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7735.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc33264g |
| [33] |
Jia, P.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Tian, B.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, W.; Huang, S.; Zhu, B. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 305, 127460.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127460 |
| [34] |
Liu, F.; Du, J.; Song, D.; Xu, M.; Sun, G. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4636.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC10658C |
| [35] |
Xiao, H. D.; Li, J. H.; Zhao, J.; Yin, G.; Quan, Y. W.; Wang, J.; Wang, R. Y. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1633.
doi: 10.1039/C4TB02003K |
| [36] |
Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, R. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3909.
doi: 10.1039/C9TB00551J |
| [1] | Yingzhen Zhang, Dandan Jiang, Juanhua Li, Jingjing Wang, Kunming Liu, Jinbiao Liu. Construction Strategy and Imaging of Highly Selective Selenocysteine Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 41-53. |
| [2] | Huanqing Li, Zhaohua Chen, Zujia Chen, Qiwen Qiu, Youcai Zhang, Sihong Chen, Zhaoyang Wang. Research Progress in Mercury Ion Fluorescence Probes Based on Organic Small Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3067-3077. |
| [3] | Binghui Ding, Shaohui Han, Haiqing Xiong, Benhua Wang, Bojun Zuo, Xiangzhi Song. A Highly Selective Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Hypochlorite in Acute Lung Injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2878-2884. |
| [4] | Yifang Li, Yao Wang, Huawei Niu, Xiujin Chen, Zhaozhou Li, Yongguo Wang. Research Progress of Sulfur Dioxide Fluorescent Probe Targeting Mitochondria [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(6): 1952-1962. |
| [5] | Feiran Liu, Jing Jing, Xiaoling Zhang. Research Progress of Fluorescent Probes for Cysteine Targeting Cellular Organelles [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(6): 2053-2067. |
| [6] | Jiao Qin, Jie Chen, Yan Su. Synthesis of 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl-2-(2-cyanophenyl)-acetate by Transition Metal-Free Radical Cleavage Reaction from α-Bromoindanone [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(6): 2171-2177. |
| [7] | Tiantian Liu, Hongpeng Zhang, Xiaomeng Jiao, Yinjuan Bai. Research Progress of Multi-signal Fluorescent Probes for Simultaneous Detection of Biothiols [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(6): 2081-2095. |
| [8] | Zhihua Chen, Yan Hu, Lili Ma, Ziyi Zhang, Chuanxiang Liu. Rational Design of ortho-Vinylhydropyridine-Assisted Amino-fluorophore as Hypochlorite Fluorescent Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 718-724. |
| [9] | Hongwei Tang, Chao Wang, Keli Zhong, Shuhua Hou, Lijun Tang, Yanjiang Bian. A Naked-Eye and Fluorescent Dual-Channel Probe for Rapid Detection of Hg2+ and Its Multiple Applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(2): 712-717. |
| [10] | Meng Liu, Yanru Huang, Xiaofei Sun, Lijun Tang. An “Aggregation-Induced Emission+Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer” Mechanisms-Based Benzothiazole Derived Fluorescent Probe and Its ClO– Recognition [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 345-351. |
| [11] | Yangyang Li, Xiaofei Sun, Xiaoling Hu, Yuanyuan Ren, Keli Zhong, Xiaomei Yan, Lijun Tang. Synthesis of Triphenylamine Derivative and Its Recognition for Hg2+ with “OFF-ON” Fluorescence Response Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 320-325. |
| [12] | Jidong Zhang, Wanlin Yan, Wenqiang Hu, Dian Guo, Dalong Zhang, Xiaoxin Quan, Xianpan Bu, Siyu Chen. Design and Synthesis of a Zn2+ Fluorescent Probe Based on Aggregation Induced Luminescence Properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 326-331. |
| [13] | Yanhui Ma, Yuqian Wu, Xiaoxu Wang, Gui Gao, Xin Zhou. Research Progress of Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probes Based on 1,3-Dichloro-7-hydroxy-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone (DDAO) [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 94-111. |
| [14] | Yaxin Yang, Lin Chen, Xiaoling Hu, Keli Zhong, Shidi Li, Xiaomei Yan, Jinglin Zhang, Lijun Tang. Synthesis of a Turn-On Fluorescent Probe for Hydrogen Sulfide and Its Application in Red Wine and Living Cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 308-312. |
| [15] | Yanqin Lai, Xue Chen, Fang Chen, Linchen Ni, Ting Wang, Ziping Zhu, Ju Man, Chunxiao Jiang, Zhenda Xie. A Lysosome-Targeted Far-Red to Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Viscosity Change During the Ferroptosis Process [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2850-2856. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||