化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (12): 1695-1700.DOI: 10.6023/A23070344 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-30
Xuan Zhang, Jun Xiong, Wang Zhang( )
)
Received:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-30
Contact:
*E-mail: 文章分享

金属卤化物钙钛矿材料因其独特的光电特性, 在光电器件领域引起了相当大的关注和研究. 特别是近年来, 绿色和红色钙钛矿发光二极管(PeLEDs)研究取得了显著进展. 然而, 蓝色PeLEDs的发展落后于绿光和红光PeLEDs, 效率也要低得多. 其中一个主要原因是空穴传输层与蓝色钙钛矿材料的能级不匹配. 在这项研究中, 通过使用聚(4-苯乙烯磺酸钠)(PSS-Na)和溴化钾(KBr)改性空穴传输层材料聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)-聚苯乙烯磺酸(PEDOT:PSS), 抑制PEDOT:PSS与钙钛矿材料界面之间的非辐射复合. 并通过降低膜的粗糙度来提高钙钛矿膜的质量. 结果表明, PSS-Na和KBr有效地提高了空穴传输能力, 从而提高了PeLEDs器件的整体性能. 通过PSS-Na改性PEDOT:PSS制备的蓝色PeLEDs具有低启亮电压(仅为3.3 V)和高外量子效率(EQE)(达到4.12%). 随着PEDOT:PSS中进一步加入KBr, 蓝色PeLEDs最大EQE达到6.25%, 启亮电压降至3 V. 此外, 与其他蓝光钙钛矿器件相比, 该器件在不同电压下也表现出了良好的光谱稳定性. 说明通过改性空穴传输层, 可以提高钙钛矿发光器件的效率和稳定性, 显示出钙钛矿发光二极管在彩色显示器和固态照明中的潜力.
张璇, 熊军, 张旺. 通过聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)-聚苯乙烯磺酸改性实现高性能蓝色钙钛矿发光二极管[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1695-1700.
Xuan Zhang, Jun Xiong, Wang Zhang. High Performance Blue Perovskite Light Emitting Diode Realized by Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) Modification[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(12): 1695-1700.
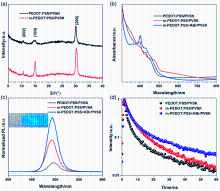


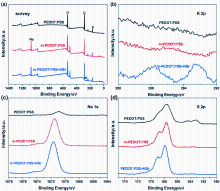

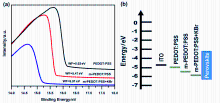
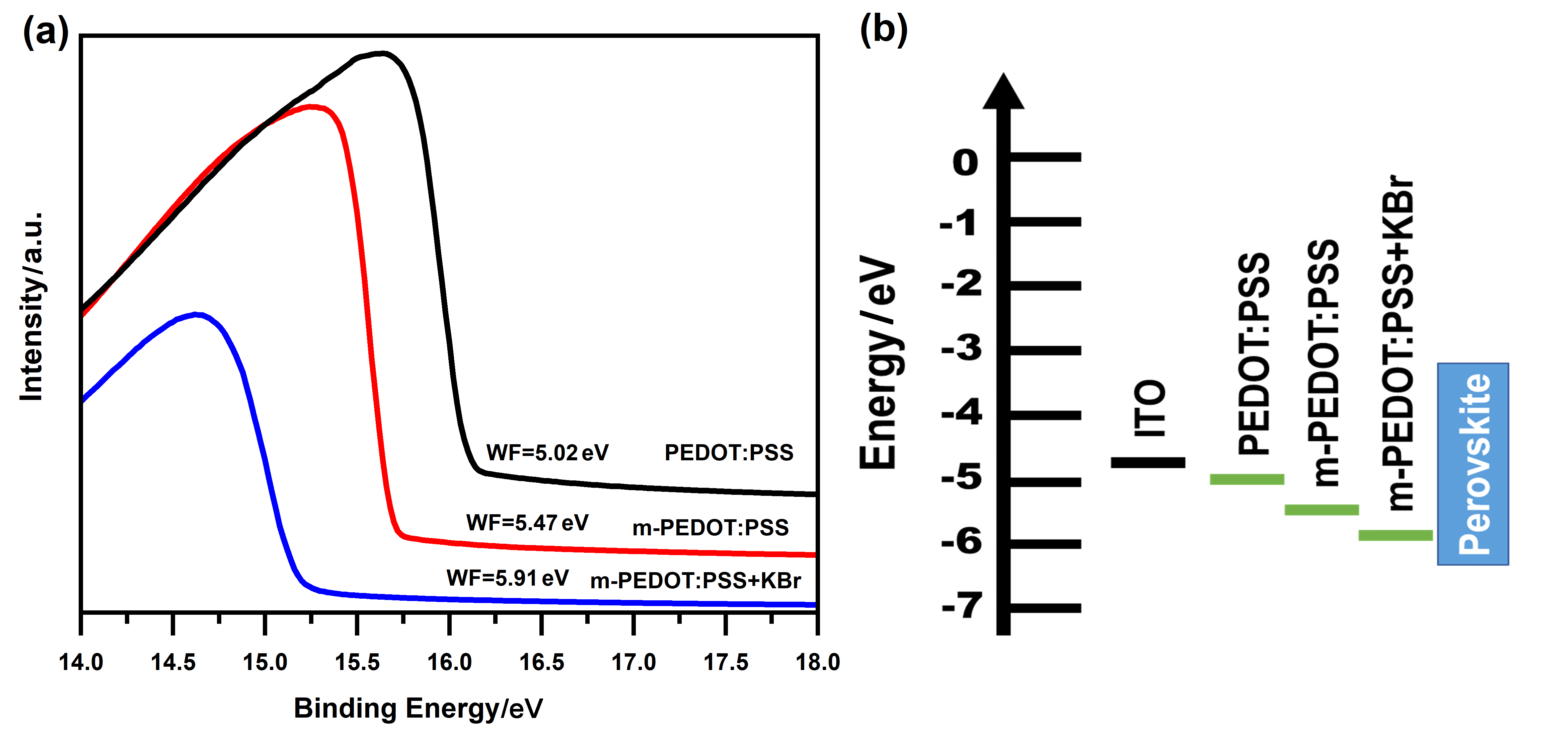
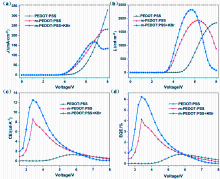
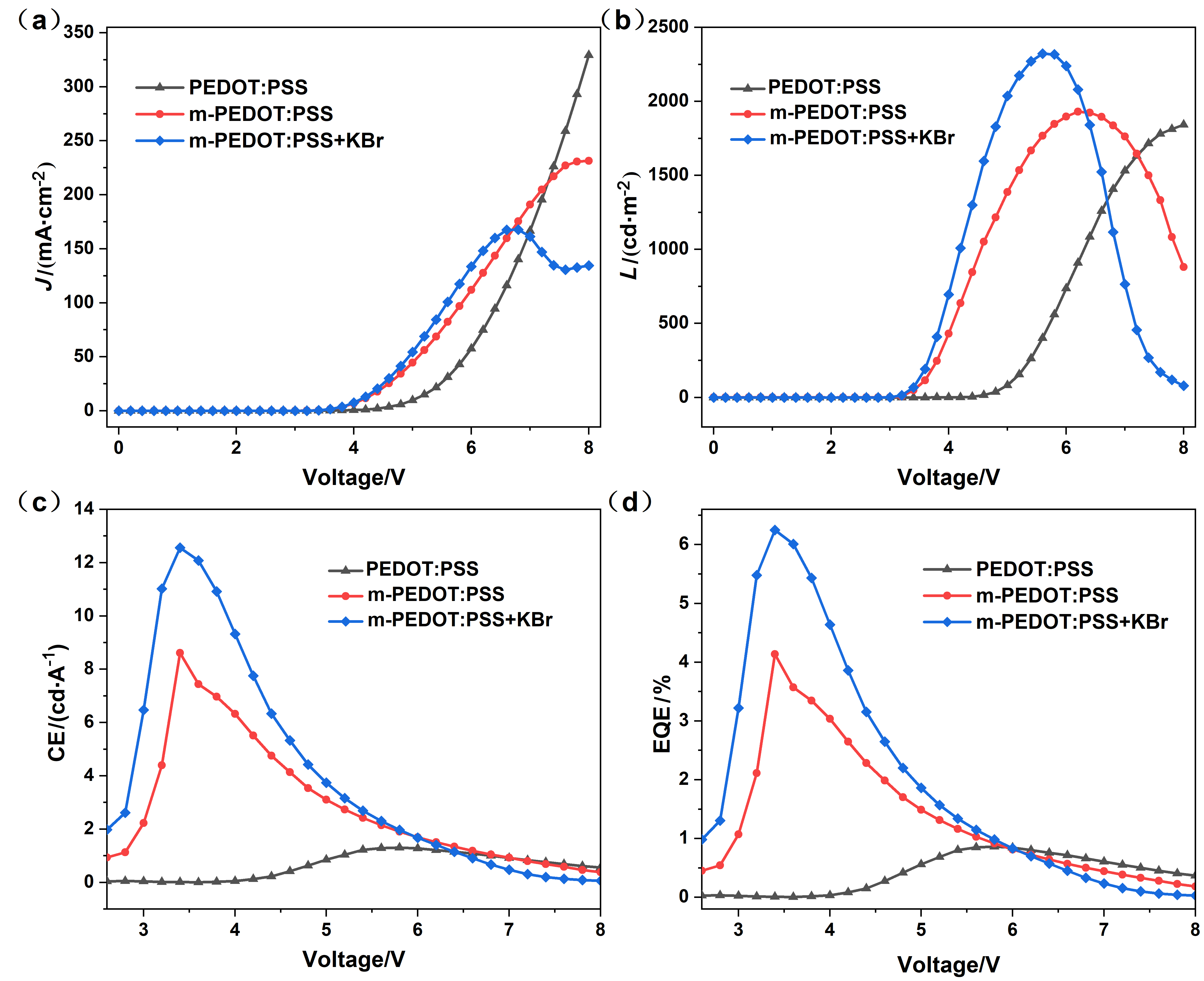
| HTL层材料 | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m−2) | EQEmax/% | CEmax/(cd•A−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | 4.1 | 1843 | 0.86 | 1.30 |
| m-PEDOT:PSS | 3.3 | 1930 | 4.14 | 8.62 |
| m-PEDOT:PSS+KBr | 3 | 2322 | 6.25 | 12.56 |
| HTL层材料 | Von/V | Lmax/(cd•m−2) | EQEmax/% | CEmax/(cd•A−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | 4.1 | 1843 | 0.86 | 1.30 |
| m-PEDOT:PSS | 3.3 | 1930 | 4.14 | 8.62 |
| m-PEDOT:PSS+KBr | 3 | 2322 | 6.25 | 12.56 |

| [1] |
Quan, L. N.; García de Arquer, F. P.; Sabatini, R. P.; Sargent, E. H. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801996.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.45 |
| [2] |
Liu, X.-K.; Xu, W.; Bai, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Friend, R. H.; Gao, F. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 10.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-0784-7 |
| [3] |
Fakharuddin, A.; Gangishetty, M. K.; Abdi-Jalebi, M.; Chin, S.-H.; bin Mohd Yusoff, A. R.; Congreve, D. N.; Tress, W.; Deschler, F.; Vasilopoulou, M.; Bolink, H. J. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 203.
doi: 10.1038/s41928-022-00745-7 |
| [4] |
Guo, Z.; Zhou, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 223 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20100463 |
|
(郭镇域, 周欢萍, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 223.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100463 |
|
| [5] |
Gong, C.; Cheng, S.; Meng, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 853 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21030106 |
|
(龚陈祥, 程书平, 孟祥川, 胡笑添, 陈义旺, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 853.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030106 |
|
| [6] |
Liu, Z.; Qiu, W.; Peng, X.; Sun, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; He, F.; Shen, C.; Gu, Q. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103268.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.43 |
| [7] |
Jiang, J.; Chu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; You, J.; Zhang, X. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2204460.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.36 |
| [8] |
Guo, B.; Lai, R.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, L.; Ren, Z.; Lian, Y.; Li, P.; Cao, X.; Xing, S.; Wang, Y. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 637.
doi: 10.1038/s41566-022-01046-3 |
| [9] |
Tan, Z.; Luo, J.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Gao, L.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Du, P.; Niu, G. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1901094.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v8.2 |
| [10] |
Protesescu, L.; Yakunin, S.; Bodnarchuk, M. I.; Krieg, F.; Caputo, R.; Hendon, C. H.; Yang, R. X.; Walsh, A.; Kovalenko, M. V. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692.
doi: 10.1021/nl5048779 pmid: 25633588 |
| [11] |
Draguta, S.; Sharia, O.; Yoon, S. J.; Brennan, M. C.; Morozov, Y. V.; Manser, J. S.; Kamat, P. V.; Schneider, W. F.; Kuno, M. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 200.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00284-2 pmid: 28779144 |
| [12] |
Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W. W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1088.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09047-7 |
| [13] |
Li, J.; Gan, L.; Fang, Z.; He, H.; Ye, Z. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 6002.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b02786 |
| [14] |
Gong, X.; Voznyy, O.; Jain, A.; Liu, W.; Sabatini, R.; Piontkowski, Z.; Walters, G.; Bappi, G.; Nokhrin, S.; Bushuyev, O. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 550.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-018-0081-x |
| [15] |
Kim, H.; Park, J. H.; Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Song, M. H.; Park, J. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104660.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v9.5 |
| [16] |
Cheng, L.; Cao, Y.; Ge, R.; Wei, Y.-Q.; Wang, N.-N.; Wang, J.-P.; Huang, W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2016.07.001 |
| [17] |
Vashishtha, P.; Ng, M.; Shivarudraiah, S. B.; Halpert, J. E. Chem. Mater. 2018, 31, 83.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b02999 |
| [18] |
Congreve, D. N.; Weidman, M. C.; Seitz, M.; Paritmongkol, W.; Dahod, N. S.; Tisdale, W. A. ACS Photonics 2017, 4, 476.
doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00963 |
| [19] |
Hou, S.; Gangishetty, M. K.; Quan, Q.; Congreve, D. N. Joule 2018, 2, 2421.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.08.005 |
| [20] |
Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ji, C.; Chuai, Y.; Wang, P.; Wen, S.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W. W. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 4602.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02073 |
| [21] |
Kim, Y.-H.; Wolf, C.; Kim, Y.-T.; Cho, H.; Kwon, W.; Do, S.; Sadhanala, A.; Park, C. G.; Rhee, S.-W.; Im, S. H. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6586.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07617 |
| [22] |
Zou, Y.; Ban, M.; Yang, Y.; Bai, S.; Wu, C.; Han, Y.; Wu, T.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24320.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b07438 |
| [23] |
Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Tu, B.; Yu, B.; Liu, F.; Tam, H. W.; Wang, G.; Djurišić, A. B. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800515.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.20 |
| [24] |
Gangishetty, M. K.; Hou, S.; Quan, Q.; Congreve, D. N. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706226.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.20 |
| [25] |
Chu, Z. M.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, F.; Zhang, C. X.; Deng, H. X.; Gao, F.; Ye, Q. F.; Meng, J. H.; Yin, Z. G.; Zhang, X. W.; You, J. B. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4165.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17943-6 |
| [26] |
Alahbakhshi, M.; Mishra, A.; Verkhogliadov, G.; Turner, E. E.; Haroldson, R.; Adams, A. C.; Gu, Q.; Rack, J. J.; Slinker, J. D.; Zakhidov, A. A. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214315.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.28 |
| [27] |
Ren, Z.; Wang, K.; Sun, X. W.; Choy, W. C. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100516.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.30 |
| [28] |
Zhang, D.; Fu, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, L. Small 2023, 19, 2206927.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v19.11 |
| [29] |
Mao, C.; Ju, S.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, L.; Hu, H.; Yang, K.; Guo, T.; Li, F. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 11, 2202058.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v11.4 |
| [30] |
Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Gao, L.; Yan, X.; Li, L.; Yu, J. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 34.
doi: 10.1186/s11671-020-3260-z |
| [31] |
Li, Y. Q.; Wang, W.; Dong, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, X. F.; Niu, Y.; Qiao, B.; Zhao, S. L.; Xu, Z.; Smirnov, A.; Song, D. D. Org. Electron. 2022, 108, 106579.
doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2022.106579 |
| [32] |
He, B. C.; Liu, T. H.; Wang, B. Z.; Wen, Z. R.; Yu, X. C.; Xing, G. C.; Chen, S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152692.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152692 |
| [33] |
Wu, Y. H.; Duan, G. F. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 025005.
doi: 10.1149/2162-8777/ac4d81 |
| [1] | 杨娜, 马建中, 石佳博, 郭旭. 层状复合氢氧化物的有机改性方法及应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 207-216. |
| [2] | 伏成玉, 周星宇, 杨鹏. 基于蛋白质类淀粉样聚集的表面功能化★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1566-1576. |
| [3] | 何新蕊, 蔡丽娜, 陈汉生, 尹攀, 尹志刚, 郑庆东. 表面双重后处理方法提升三元NiMgO半导体界面层及其有机太阳能电池的性能※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 581-589. |
| [4] | 张桢焱, 刘琳, 许东华, 张若愚, 石恒冲, 栾世方, 殷敬华. 功能化医用聚氨酯弹性体制备及生物医用研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1436-1447. |
| [5] | 陈锋, 程晓琴, 赵振新, 王晓敏. 分级多孔N, P共掺杂rGO改性隔膜增强锂硫电池的循环稳定性[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 941-947. |
| [6] | 余梦, 张子俊, 朱国委, 谷振华, 段玉霖, 余良翀, 高冠斌, 孙涛垒. Ag2S基近红外II区荧光量子点的水相合成优化探究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1281-1285. |
| [7] | 陈杨, 杜亚丹, 王勇, 刘普旭, 李立博, 李晋平. UTSA-280的氨改性以及C2H4/C2H6分离性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 534-539. |
| [8] | 李钊, 王忠, 班丽卿, 王建涛, 卢世刚. 富锂锰基正极材料的表面改性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1115-1128. |
| [9] | 崔素珍, 杨汉培, 孙慧华, 聂坤, 吴俊明. Fe对NaNbO3的晶格掺杂和同步异质结改性及其光催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(12): 995-1002. |
| [10] | 黄国家, 陈志刚, 李茂东, 杨波, 辛明亮, 李仕平, 尹宗杰. 石墨烯和氧化石墨烯的表面功能化改性[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(10): 789-799. |
| [11] | 马春燕, 傅伟飞, 黄国伟, 陈红征, 徐明生. 高性能的二维层状材料硫化钨界面层的有机太阳能电池[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 949-953. |
| [12] | 钮东方, 丁勇, 马智兴, 王明辉, 刘洲, 张博文, 张新胜. 纳米碳纤维的表面改性对水电解析氢反应催化活性的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(7): 729-734. |
| [13] | 邱振平, 张英杰, 夏书标, 董鹏. 无机全固态锂离子电池界面性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(10): 992-1001. |
| [14] | 郝威, 邵正中. 尼龙表面的超疏水及高度疏油改性[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(9): 1023-1028. |
| [15] | 万洋, 郑荞佶, 赁敦敏. 锂离子电池正极材料磷酸锰锂研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(5): 537-551. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||