化学学报 ›› 2012, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (17): 1798-1804.DOI: 10.6023/A12040115 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
祝海涛, 倪哲明, 薛继龙
Zhu Haitao, Ni Zheming, Xue Jilong
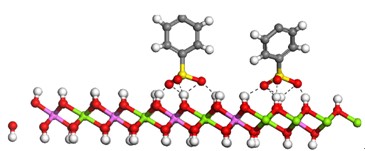
探讨了Mg/Al=3的水滑石焙烧产物(MgAl-LDO)对染料酸性湖蓝7(AB7)的吸附性能及其机理. 考察了不同因素对MgAl-LDO吸附AB7性能的影响, 并研究了吸附过程的热力学机理. 实验结果表明: MgAl-LDO对AB7具有优异的吸附性能, 在288 K, pH=6.74条件下, 0.33 g·L-1 MgAl-LDO对150 mg·L-1AB7溶液的吸附容量和去除率分别达到446.9 mg·g-1和99.31%. 热力学研究表明: MgAl-LDO对AB7的吸附过程同时符合Langmuir 和 Freundlich等温吸附方程, 并且是个放热、自发的过程. 计算所得的吉布斯自由能绝对值在8~10 kJ·mol-1, 这主要是由染料分子与水滑石层板的氢键作用产生, 结合Materials Studio 5.5软件模拟AB7染料分子在MgAl-LDHs上的排列分布, 推测MgAl-LDO对AB7的吸附机理是表面吸附作用. 同时, 经4次回收, LDO对AB7的去除率仍达到85%以上.