化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (2): 152-169.DOI: 10.6023/A24090289 上一篇 下一篇
综述
张宇a,b, 张睿a,b, 王子健a,b, 汪啸a,b,*( ), 宋术岩a,b,*(
), 宋术岩a,b,*( ), 张洪杰a,b,c
), 张洪杰a,b,c
投稿日期:2024-09-24
发布日期:2024-11-12
作者简介: |
张宇, 男, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所2024级硕士研究生, 研究方向为稀土基催化纳米材料在非均相催化反应中的应用. |
 |
张睿, 男, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所2022级博士研究生, 研究方向为稀土基催化纳米材料在非均相催化反应中的应用. |
 |
汪啸, 男, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员. 2008年毕业于吉林大学化学系, 获理学学士学位. 随后, 他加入了中国科学院长春应用化学研究所张洪杰研究员的课题组, 并于2013年获得无机化学博士学位. 主要从事制备用于异相催化反应和能源相关应用的功能无机材料. |
 |
宋术岩, 男, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员. 2003年毕业于东北师范大学化学系, 获理学学士学位; 2006年毕业于东北师范大学无机化学系, 获理学硕士学位. 他加入了中国科学院长春应用化学研究所张洪杰教授的研究组, 并于 2009年获得无机化学博士学位. 主要从事开发用于异相催化、质子传导、化学传感和检测的多孔功能材料. |
 |
张洪杰, 男, 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所研究员. 于1978年获得北京大学理学学士学位. 之后, 他在长春应用化学研究所担任研究助理, 并于1985年获得无机化学硕士学位, 并在该研究所担任助教至1989年. 之后, 他在波尔多第一大学、法国国家科学研究中心固体化学实验室学习, 并于1993年获得固体化学和材料科学博士学位. 1994年, 他加入中国科学院长春应用化学研究所, 担任研究员. 他目前的研究方向主要集中在镧系元素功能纳米材料方面. |
基金资助:
Yu Zhanga,b, Rui Zhanga,b, Zijian Wanga,b, Xiao Wanga,b( ), Shuyan Songa,b(
), Shuyan Songa,b( ), Hongjie Zhanga,b,c
), Hongjie Zhanga,b,c
Received:2024-09-24
Published:2024-11-12
Contact:
About author:Supported by:文章分享

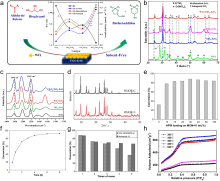
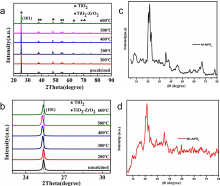
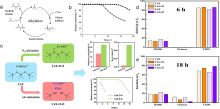
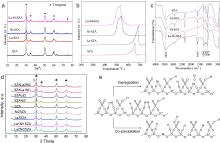
固体酸是一类制备过程简单、环境污染小且催化活性高的催化材料, 在烷基化、异构化和酯化反应等多种化学过程中表现出卓越的催化活性. 然而, 其稳定性不足和再生活性低下的问题, 很大程度上制约了其在大规模工业生产中的应用. 因此, 开发兼具高活性和高稳定性的新型固体酸催化剂具有极其重要的研究价值和意义. 本综述介绍了常用固体酸催化剂的概念、分类、合成方法以及表征技术, 并引入一些经过稀土改性的固体酸催化剂的应用研究进展. 本综述主要着重于研究固体酸催化剂酸性质对于催化性能的影响(如酸强度、酸含量、酸位点种类等), 而不是传统的物化性质(如比表面积、晶相、表面形貌等). 最后, 对固体酸催化剂的发展前景进行了展望.
张宇, 张睿, 王子健, 汪啸, 宋术岩, 张洪杰. 固体酸催化剂的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(2): 152-169.
Yu Zhang, Rui Zhang, Zijian Wang, Xiao Wang, Shuyan Song, Hongjie Zhang. Current Advances of Solid Acid Catalysts[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(2): 152-169.
| Acid type | Example |
|---|---|
| Oxide | Simple: SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, etc. |
| Composite: SiO2-Al2O3, MoO3-SiO2, etc. | |
| Sulfide | ZnS, CdS, etc. |
| Molecular sieve | Zeolite: X zeolite, Y zeolite, ZSM-5 zeolite, etc. |
| Non zeolitic molecular sieve: SAPO series, AlPO series, etc. | |
| Metal salt | Phosphates: FePO4, AlPO4, etc. |
| Sulfate: CuSO4, FeSO4, etc. | |
| Heteropoly acid | H3PW12O40, H4SiW12O40, etc. |
| Natural clay mine | Kaolin, bentonite, activated white clay, montmorillonite, etc. |
| Solid superacid | SO42−/ZrO2, WO3/ZrO2, MoO3/ZrO2, etc. |
| Supported catalyst | H3PO4/diatomite, BF3/Al2O3, etc. |
| Cation exchange resin | Nafion-H, etc. |
| Acid type | Example |
|---|---|
| Oxide | Simple: SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, etc. |
| Composite: SiO2-Al2O3, MoO3-SiO2, etc. | |
| Sulfide | ZnS, CdS, etc. |
| Molecular sieve | Zeolite: X zeolite, Y zeolite, ZSM-5 zeolite, etc. |
| Non zeolitic molecular sieve: SAPO series, AlPO series, etc. | |
| Metal salt | Phosphates: FePO4, AlPO4, etc. |
| Sulfate: CuSO4, FeSO4, etc. | |
| Heteropoly acid | H3PW12O40, H4SiW12O40, etc. |
| Natural clay mine | Kaolin, bentonite, activated white clay, montmorillonite, etc. |
| Solid superacid | SO42−/ZrO2, WO3/ZrO2, MoO3/ZrO2, etc. |
| Supported catalyst | H3PO4/diatomite, BF3/Al2O3, etc. |
| Cation exchange resin | Nafion-H, etc. |




| Indicator | Colour | pKa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkalinity | Acidity | ||
| Methyl red | Yellow | Red | +4.8 |
| Crystal violet | Blue | Yellow | +0.8 |
| Anthraquinone | Colourless | Yellow | -8.2 |
| p-nitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -11.35 |
| m-nitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -11.99 |
| p-nitrofluorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -12.44 |
| p-nitrochlorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -12.70 |
| m-nitrochlorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -13.16 |
| 2,4-dinitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -13.75 |
| 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -14.52 |
| 1,3,5-trinitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -16.04 |
| Indicator | Colour | pKa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkalinity | Acidity | ||
| Methyl red | Yellow | Red | +4.8 |
| Crystal violet | Blue | Yellow | +0.8 |
| Anthraquinone | Colourless | Yellow | -8.2 |
| p-nitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -11.35 |
| m-nitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -11.99 |
| p-nitrofluorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -12.44 |
| p-nitrochlorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -12.70 |
| m-nitrochlorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -13.16 |
| 2,4-dinitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -13.75 |
| 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene | Colourless | Yellow | -14.52 |
| 1,3,5-trinitrotoluene | Colourless | Yellow | -16.04 |









| [1] |
Qin, R. Z.; Zeng, H. C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903264.
|
| [2] |
Ly, I.; Layan, E.; Picheau, E.; Chanut, N.; Nallet, F.; Bentaleb, A.; Dourges, M.-A.; Pellenq, R.; Hillard, E.; Toupance, T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 13305.
|
| [3] |
Brzeski, J.; Skurski, P. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02133.
|
| [4] |
Kirdant, S. P.; Biradar Tamboli, A. T.; Jadhav, V. H. Helv. Chim. Acta 2022, 105, e202200032.
|
| [5] |
Kore, R.; Scurto, A. M.; Shiflett, M. B. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 15811.
|
| [6] |
Zhang, L.; Long, B. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18996.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01864 pmid: 31763521 |
| [7] |
Singhal, S.; Agarwal, S.; Singh, M.; Rana, S.; Arora, S.; Singhal, N. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 299.
|
| [8] |
Bayat, M.; Gheidari, D. Chemistryselect 2022, 7, e202200774.
|
| [9] |
Höpfl, V. B.; Schachtl, T.; Liu, Y.; Lercher, J. A. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 330.
|
| [10] |
Mu, J. L.; Liang, M. F.; Huang, H.; Meng, J.; Xu, L. L.; Song, Z. L.; Wu, M.; Miao, Z. C.; Zhuo, S. P.; Zhou, J. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9310.
|
| [11] |
Jiang, L.; Fan, Y. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Pei, Y.; Yan, S. R.; Qiao, M. H.; Fan, K. N.; Zong, B. N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 231 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A22120509 |
|
(姜兰, 范义秋, 张晓昕, 裴燕, 闫世润, 乔明华, 范康年, 宗保宁, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 231.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120509 |
|
| [12] |
Cai, X. L. M.S. Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2016 (in Chinese).
|
|
(蔡晓兰, 硕士论文,广东工业大学, 广州, 2016.)
|
|
| [13] |
Munyentwali, A.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. H. Appl. Catal., A 2022, 633, 118525.
|
| [14] |
İnan, B.; Koçer, A. T.; Özçimen, D. B. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 173, 106095.
|
| [15] |
Zhang, Q. F.; Xie, W. L.; Li, J. B.; Guo, L. H. Renewable Energy 2023, 217, 119144.
|
| [16] |
Duan, X. X.; Wang, H. Y.; Pan, D. H.; Chen, S. W.; Yu, F.; Yan, X. L.; Li, R. F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 755 (in Chinese).
|
|
(段晓宣, 王恒燕, 潘大海, 陈树伟, 于峰, 闫晓亮, 李瑞丰, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 755.)
doi: 10.6023/A24030095 |
|
| [17] |
Esmi, F.; Borugadda, V. B.; Dalai, A. K. Catal. Today 2022, 404, 19.
|
| [18] |
Tang, S. Y.; Duan, X. L.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Wang, C. W.; Wang, W. G.; Feng, W. L.; Wang, T. L. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 14, 2311.
|
| [19] |
Pasupulety, N.; Al-zahrani, A. A.; Daous, M. A.; Driss, H.; Alhumade, H. Fuel 2022, 324, 124513.
|
| [20] |
Changmai, B.; Vanlalveni, C.; Ingle, A. P.; Bhagat, R.; Rokhum, L. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41625.
|
| [21] |
Álvarez, M.; Cueto, J.; Serrano, D. P.; Marín, P.; Ordóñez, S. Catal. Today 2024, 428, 114464.
|
| [22] |
Lani, N. S.; Ngadi, N. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 3755.
|
| [23] |
Oishi, R.; Li, D. X.; Okazaki, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Ochiai, N.; Yamauchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Wakihara, T.; Okubo, T.; Tada, S.; Iyoki, K. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 72, 102491.
|
| [24] |
Wang, Y.; Dai, Y. N.; Wang, T. H.; Li, M. L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L. P. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 237, 107472.
|
| [25] |
Xing, X. Y.; Shi, X.; Ruan, M. Y.; Wei, Q. C.; Guan, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, S. Q. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125037.
|
| [26] |
Gromov, N. V.; Ogorodnikova, O. L.; Medvedeva, T. B.; Panchenko, V. N.; Yakovleva, I. S.; Isupova, L. A.; Timofeeva, M. N.; Taran, O. P.; Aymonier, C.; Parmon, V. N. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1298.
|
| [27] |
Huang, H.; Mu, J. L.; Liang, M. F.; Qi, R. R.; Wu, M.; Xu, L. L.; Xu, H. M.; Zhao, J. P.; Zhou, J.; Miao, Z. C. Mol. Catal. 2024, 552, 113682.
|
| [28] |
Ishitani, H.; Takeno, K.; Sasaya, M.; Kobayashi, S. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 5536.
|
| [29] |
Matsuhashi, H. Catal. Surv. Asia 2023, 27, 132.
|
| [30] |
Ren, Q. H.; Ma, H.; Wang, W. B.; Chen, C. C.; Xiao, J. B.; Che, P. H.; Nie, X.; Huang, Y. Z.; Rao, K. T. V.; Xu, C. B. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 174, 106860.
|
| [31] |
Sievers, C.; Zuazo, I.; Guzman, A.; Olindo, R.; Syska, H.; Lercher, J. A. J. Catal. 2007, 246, 315.
|
| [32] |
Feller, A.; Lercher, J. A. Adv. Catal. 2004, 48, 229.
|
| [33] |
Guzman, A.; Zuazo, I.; Feller, A.; Olindo, R.; Sievers, C.; Lercher, J. A. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 83, 309.
|
| [34] |
Song, H.; Zhao, L. L.; Wang, N.; Li, F. Appl. Catal., A 2016, 526, 37.
|
| [35] |
Zhao, H. Q.; Song, H.; Zhao, L. L.; Li, F. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 2020, 45, 1.
|
| [36] |
Li, Y.; Zhang, X. D.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. P. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 156.
|
| [37] |
Shu, Q.; Liu, X. Y.; Huo, Y. T.; Tan, Y. H.; Zhang, C. X.; Zou, L. X. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 44, 351.
|
| [38] |
Wang, K.; Jiang, J. C.; Si, Z.; Liang, X. Y. J. Renewable Sustainable Energy 2013, 5, 052001.
|
| [39] |
Zhang, Y. M.S. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, 2007 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张轶, 硕士论文,合肥工业大学, 合肥, 2007.)
|
|
| [40] |
Song, X. M.; Sayari, A. Catal. Rev. 1996, 38, 329.
|
| [41] |
Baithy, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Rangaswamy, A.; Reddy, B. M. Catal. Lett. 2022, 152, 1428.
|
| [42] |
Amrute, A. P.; Sahoo, S.; Bordoloi, A.; Hwang, Y. K.; Hwang, J.-S.; Halligudi, S. B. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1404.
|
| [43] |
Xu, X. P.; Fan, K.; Zhao, S. Z.; Li, J.; Gao, S.; Wu, Z. B.; Meng, X. J.; Xiao, F.-S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1108 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐续盼, 范凯, 赵胜泽, 李健, 高珊, 吴忠标, 孟祥举, 肖丰收, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1108.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040175 |
|
| [44] |
Ma, T. L.; Yun, Z.; Xu, W.; Chen, L. G.; Li, L.; Ding, J. F.; Shao, R. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 343.
|
| [45] |
Miao, K. K.; Luo, X. L.; Wang, W.; Guo, J. L.; Guo, S. F.; Cao, F. J.; Hu, Y. Q.; Chang, P. M.; Feng, G. D. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 289, 109640.
|
| [46] |
Zhang, G. X.; Song, A. K.; Duan, Y. W.; Zheng, S. L. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 255, 61.
|
| [47] |
Prasomsri, T.; Jiao, W. Q.; Weng, S. Z.; Garcia Martinez, J. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8900.
|
| [48] |
Gao, B. B.; Yang, M.; Qiao, Y. Y.; Li, J. Z.; Xiang, X.; Wu, P. F.; Wei, Y. X.; Xu, S. T.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7569.
|
| [49] |
Li, Y.; Yu, J. H. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1156.
|
| [50] |
Upham, D. C.; Orazov, M.; Jaramillo, T. F. J. Catal. 2021, 399, 132.
|
| [51] |
Xue, H. F.; Huang, X. M.; Ditzel, E.; Zhan, E. S.; Ma, M.; Shen, W. J. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1496.
|
| [52] |
Li, J. R.; Yang, Z.; Li, S. W.; Jin, Q. P.; Zhao, J. S. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 1.
|
| [53] |
Juan, J. C.; Zhang, J. C.; Yarmo, M. A. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2007, 267, 265.
|
| [54] |
Kim, H.-J.; Shul, Y.-G.; Han, H. Appl. Catal., A 2006, 299, 46.
|
| [55] |
Chen, L.; Nohair, B.; Zhao, D. Y.; Kaliaguine, S. Appl. Catal., A 2018, 549, 207.
|
| [56] |
Marcì, G.; García-López, E.; Bellardita, M.; Parisi, F.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Sorgues, S.; Liotta, L. F.; Palmisano, L. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13329.
doi: 10.1039/c3cp51142a pmid: 23703460 |
| [57] |
Yue, D.; Lei, J. H.; Zhou, L. N.; Du, X. D.; Guo, Z. R.; Li, J. S. Arabian J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2649.
|
| [58] |
Zhao, J. Ph.D. Dissertation, Fudan University, Shanghai, 2008 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵杰, 博士论文, 复旦大学, 上海, 2008.)
|
|
| [59] |
Hino, M.; Arata, K. Chem. Lett. 1979, 8, 477.
|
| [60] |
Li, L.; Yan, B.; Li, H. X.; Yu, S. T.; Liu, S. W.; Yu, H. L.; Ge, X. P. Fuel 2018, 226, 190.
|
| [61] |
Ji, X. B.; Chen, Y. X.; Shen, Z. Y. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 5769.
|
| [62] |
Singh, R. P.; Shiwankar, M. M.; Maurya, A. K.; Talmale, A. S.; Gaikwad, G. S.; Wankhade, A. V. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2024, 452, 115537.
|
| [63] |
Zou, R.; Shen, C. Y.; Sun, K. H.; Ma, X. B.; Li, Z. S.; Li, M. S.; Liu, C.-J. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 93, 135.
|
| [64] |
Jiao, Y.; Li, S. S.; Liu, B.; Du, Y. M.; Wang, J. L.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y. Q. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 91, 417.
|
| [65] |
Jiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, S. S.; Guo, C. H.; Yao, P.; Wang, J. L. Fuel 2018, 233, 724.
|
| [66] |
Wei, X. L.; Cheng, Q. W.; Sun, T. G.; Tong, S.; Meng, L. L. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6063.
|
| [67] |
Feng, J. Y.; Wang, Q. S.; Wu, T.; Gao, S. J.; Zhu, K.; Ye, D.; Guo, R. T. Fuel 2024, 363, 130989.
|
| [68] |
Masula, K.; Kore, R.; Bhongiri, Y.; Pola, S.; Basude, M. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1305, 137750.
|
| [69] |
Song, W. X.; Liu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhou, L. Q.; Zhang, L. H. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2024, 451, 115482.
|
| [70] |
Yaseen, M.; Khan, A.; Humayun, M.; Bibi, S.; Farooq, S.; Bououdina, M.; Ahmad, S. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2024, 17, 2321251.
|
| [71] |
Kignelman, G.; Thielemans, W. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16877.
|
| [72] |
Chen, C. C.; Chen, H. R.; Yu, J. C.; Ye, Z. Q.; Shi, J. L. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 647 (in Chinese).
|
|
(陈崇城, 陈航榕, 俞建长, 叶争青, 施剑林, 催化学报, 2011, 32, 647.)
|
|
| [73] |
Huang, Y. C.; Zhang, G. C.; Zhang, Q. H. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3875.
|
| [74] |
Freitas, E. F.; Paiva, M. F.; Dias, S. C. L.; Dias, J. A. Catal. Today 2017, 289, 70.
|
| [75] |
Devi, K. K.; Chellapandiankannan J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 1055.
|
| [76] |
Mateos, P. S.; Ruscitti, C. B.; Casell, M. L.; Matkovic, S. R.; Briand, L. E. Catalysts 2023, 130, 1253.
|
| [77] |
Ahmad, M. Y.; Saleh, S. N. M.; Abdullah, A. Z. Appl. Catal., A 2024, 670, 119534.
|
| [78] |
Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Z. Catal. Lett. 2021, 152, 2756.
|
| [79] |
Yuan, H.; He, J.; Li, R.; Ma, X. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 4353.
|
| [80] |
Zhang, M.; Cheng, Q. W.; Chen, T.; We, X. L.; Meng, L. L. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2022, 36, e6617.
|
| [81] |
Zhou, X.; He, P.; Zhang, C. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11529.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00693 pmid: 32478242 |
| [82] |
Peng, Q. P.; Zhao, X. G.; Li, D. F.; Chen, M. Y.; Wei, X. J.; Fang, J.; Cui, K.; Ma, Y.; Hou, Z. S. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 214, 106705.
|
| [83] |
Wang, A. Q.; Wang, J. X.; Lu, C.; Xu, M. L.; Lv, J. H.; Wu, X. L. Fuel 2018, 234, 430.
|
| [84] |
Thimmaraju, N.; Mohamed Shamshuddin, S. Z.; Pratap, S. R.; Shyam Prasad, K. Arabian J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1860.
|
| [85] |
Meng, C.; Cao, G. P.; Li, X. K.; Yan, Y. Z.; Zhao, E. Y.; Hou, L. Y.; Shi, H. Y. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 121, 719.
|
| [86] |
Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, N. W.; Shi, L. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122731.
|
| [87] |
Wang, Y. H.; Wang, J. J.; Liang, J. H.; Wang, J. G.; Cheng, J.; Ding, Z. X.; Liu, Z.; Ren, X. Q. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 2277 (in Chinese).
|
|
(王跃桦, 王俊杰, 梁金花, 王俊格, 成静, 丁中协, 刘振, 任晓乾, 物理化学学报, 2017, 33, 2277.)
|
|
| [88] |
Wang, T. T.; Dai, Q. G.; Yan, F. W. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 664.
|
| [89] |
Miao, L.; Hong, Z.; Wang, X. X.; Jia, W. Z.; Zhao, G. Q.; Huan, Y. Q.; Zhu, Z. R. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 332, 111718.
|
| [90] |
Liu, R. Z.; Bian, Y. K.; Dai, W. L. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2024, 43, 100250.
|
| [91] |
Yi, X. F.; Liu, K. Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J. J.; Xu, S. T.; Li, C. B.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H. C.; Guo, X. W.; Liu, S.-B.; Zheng, A. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10764.
|
| [92] |
Gao, N. B.; Salisu, J.; Quan, C.; Williams, P. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111023.
|
| [93] |
Zheng, B. Z.; Fan, J. Y.; Chen, B.; Qin, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Deng, R. R.; Liu, X. G. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5519.
|
| [94] |
Zhang, S.; Saji, S. E.; Yin, Z. Y.; Zhang, H. B.; Du, Y. P.; Yan, C.-H. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005988.
|
| [95] |
Bhattar, S.; Abedin, M. A.; Kanitkar, S.; Spivey, J. J. Catal. Today 2021, 365, 2.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.10.041 |
| [96] |
Liu, Y.; Wang, L. H.; Li, R.; Hu, R. S. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2016, 421, 29.
|
| [97] |
Li, H.; Gui, Z. Y.; Yang, S.; Qi, Z. W.; Saravanamurugan, S.; Riisager, A. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 1060.
|
| [98] |
Wang, H. Y.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Z. M.; Li, M. J.; Wang, H. Fuel 2020, 269, 117419.
|
| [99] |
Sievers, C.; Liebert, J. S.; Stratmann, M. M.; Olindo, R.; Lercher, J. A. Appl. Catal., A 2008, 336, 89.
|
| [100] |
Yang, Z. Q.; Zhang, R. R.; Zhang, H. H.; Tang, H. G.; Liu, R. X.; Zhang, S. J. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 46, 173.
|
| [101] |
Zhang, H. H.; Xu, J. K.; Tang, H. G.; Yang, Z. Q.; Liu, R. X.; Zhang, S. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 9690.
|
| [102] |
Gerzeliev, I. M.; Temnikova, V. A.; Deniskin, O. V.; Baskhanova, M. N.; Khusaimova, D. O.; Maksimov, A. L. Pet. Chem. 2019, 59, 706.
|
| [103] |
Thakur, R.; Halder, G.; Barman, S. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2020, 18, 20200032.
|
| [104] |
Wei, W. Q.; Wu, S. B. Fuel 2018, 225, 311.
|
| [105] |
Yan, G. X.; Wang, A. Q.; Wachs, I. E.; Baltrusaitis, J. Appl.Catal., A 2019, 572, 210.
|
| [106] |
Yang, L. M.; Xing, S. Y.; Sun, H. Z.; Miao, C. L.; Li, M.; Lv, P.; Wang, Z. M.; Yuan, Z. H. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 187, 52.
|
| [107] |
Song, H.; Wang, N.; Song, H. L.; Li, F. Catal. Commun. 2015, 59, 61.
|
| [108] |
Wang, P. Z.; Zhang, J. Y.; Han, C. Y.; Yang, C. H.; Li, C. Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 489.
|
| [109] |
Li, L. R. M.S. Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, 2012 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李丽蓉, 硕士论文,东北石油大学, 大庆, 2012.)
|
|
| [110] |
Suo, Y. H. Ph.D. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 2014 (in Chinese).
|
|
(所艳华, 博士论文,哈尔滨工业大学, 哈尔滨, 2014.)
|
|
| [111] |
Ebadinezhad, B.; Haghighi, M. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 125146.
|
| [112] |
Li, X. P. M.S. Thesis, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, 2020 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李兴鹏, 硕士论文,江西理工大学, 赣州, 2020.)
|
|
| [113] |
Li, Y.; Huang, S. Y.; Cheng, Z. Z.; Cai, K.; Li, L. D.; Milan, E.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ma, X. B. Appl. Catal., B 2019, 256, 117777.
|
| [114] |
Khezri, H.; Izadbakhsh, A.; Izadpanah, A. A. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106253.
|
| [115] |
Aghaei, E.; Haghighi, M. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 270, 227.
|
| [116] |
Zhao, Z. K.; Ran, J. Appl. Catal., A 2015, 503, 77.
|
| [117] |
Wang, X. M.; Wu, X. T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z. J.; Li, Y. O.; Zhang, L. L.; Wang, X.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 5645.
|
| [118] |
Wu, X. T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. L.; Wang, X. M.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202317594.
|
| [119] |
Fan, J.; Ning, P.; Song, Z. X.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. M.; Long, K. X.; Zhang, Q. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 855.
|
| [120] |
Gardy, J.; Osatiashtiani, A.; Céspedes, O.; Hassanpour, A.; Lai, X. J.; Lee, A. F.; Wilson, K.; Rehan, M. Appl. Catal., B 2018, 234, 268.
|
| [121] |
Wang, J.; Yang, P. P.; Fan, M. Q.; Yu, W.; Jing, X. Y.; Zhang, M. L.; Duan, X. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2235.
|
| [122] |
Zeng, M. J.; Pan, X. J. Catal. Rev. 2022, 64, 445.
|
| [123] |
Wu, L. H.; Zhou, Y. F.; Nie, W. Y.; Song, L. Y.; Chen, P. P. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 320.
|
| [124] |
Han, X. X.; Zhang, L. L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Tao, Z. P.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 3290.
|
| [125] |
Xu, J. H.; Li, L. L.; Pan, J.; Cui, W. J.; Liang, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2022, 6, 2100439.
|
| [126] |
Zhang, S. S.; Zhang, L. L.; Liu, L.; Chu, X.; Wang, X.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 6282.
|
| [127] |
Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Cui, W. J.; Liu, L.; Bootharaju, M. S.; Kim, J. H.; Hyeon, T.; Zhang, H. J.; Wang, Y.; Song, S. Y.; Wang, X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302877.
|
| [128] |
Liang, X.; Zhang, L. L.; Wang, X.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2023, 42, 100101.
|
| [129] |
Wang, H. L.; Bootharaju, M. S.; Kim, J. H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Hyeon, T.; Wang, X.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2264.
|
| [130] |
Winoto, H. P.; Fikri, Z. A.; Ha, J.-M.; Park, Y.-K.; Lee, H.; Suh, D. J.; Jae, J. Appl. Catal., B 2019, 241, 588.
|
| [1] | 王帅, 宋华. 氮修饰Ni2P-Nx/SiO2催化剂设计合成及间甲酚加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 979-986. |
| [2] | 热孜古丽•玉努斯, 卡迪尔亚•阿布都外力, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木. 电化学条件下由二苄胺合成N-亚苄基苄胺及衍生化研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 843-848. |
| [3] | 段晓宣, 王恒燕, 潘大海, 陈树伟, 于峰, 闫晓亮, 李瑞丰. SBA-15负载硫酸化氧化锆固体酸材料的设计合成及其酯交换反应催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(7): 755-762. |
| [4] | 付祎帅, 王文亮, 苗晖, 陈育彤, 崔洋怡, 王紫薇, 潘佳文, 肖国伟. 微波响应型CMF@CoS2/MoS2催化剂的制备及其用于木质素蒸气的催化重整[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 596-603. |
| [5] | 郑灏宁, 刘金宇. 有机催化吲哚碳环官能团化研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 641-657. |
| [6] | 李小贞, 孙庆福. 稀土圆偏振发光材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 707-730. |
| [7] | 李万红, 穆应红, 王新, 李星, 刘海洋, 彭素红. N-错位卟啉锰、铁和钴配合物的合成及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 541-550. |
| [8] | 刘浩, 徐旭莉, 郭勇, 刘晓晖, 王艳芹. Ru/NiPOx高效电催化醛还原胺化反应的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 477-485. |
| [9] | 谷琪, 刘夏夏, 周鑫宇, 李江, 林秀婧, 马延文. 用于锂金属电池的聚合物固态电解质的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 449-457. |
| [10] | 王国景, 陈永辉, 张秀芹, 张俊笙, 徐俊敏, 王静. 氧空位控制BiVO4晶面异质结的磁性和光电催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 409-415. |
| [11] | 张强, 王欢, 王帅, 王园园, 张梅, 宋华. NiCe(x)/FLRC-TiO2催化剂的制备及其加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 287-294. |
| [12] | 韩晶, 廖润华, 邓文强, 梁博宇, 周雨晴, 任帅, 洪燕. 铜掺杂氮化碳电催化硝酸盐产氨性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 295-302. |
| [13] | 杨铃悦, 李赟婷, 舒超. 亚磺酸内酯研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 171-189. |
| [14] | 李雅宁, 王晓艳, 唐勇. 自由基聚合的立体选择性调控★[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 213-225. |
| [15] | 陈博文, 徐克, 陈琪, 陈立桅. 原位电势表征揭示聚合物固态锂电池界面降解机理[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(12): 1209-1215. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||