有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1375-1386.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202112022 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2021-12-17
修回日期:2022-01-22
发布日期:2022-02-10
通讯作者:
谭啸峰, 杨晴来
基金资助:
Na Li, Xiaofeng Tan( ), Qinglai Yang(
), Qinglai Yang( )
)
Received:2021-12-17
Revised:2022-01-22
Published:2022-02-10
Contact:
Xiaofeng Tan, Qinglai Yang
Supported by:文章分享

哺乳动物肠道中的微生物菌群在维持宿主生理状态和病理改变中起着非常重要的作用, 因此肠道微生物菌群的检测对宿主健康有着重要意义. 传统的染色标记方法存在着特异性差、与活菌不相容、受其他影响因素多等问题, 因此限制了对肠道微生物形态以及功能方面的深入研究. 在众多的成像技术中, 荧光成像技术可以显示肠道中共生菌、致病菌以及机会性致病菌的位置, 还可以提供有关细菌活力、代谢交换以及宿主和微生物之间的免疫相互作用等信息, 且荧光成像检测技术具有无创、对组织损伤小、特异性高、灵敏度高等优点, 所以在肠道微生物检测中得到了广泛的应用. 荧光成像技术在肠道微生物菌群成像研究方面发挥着重要作用, 而性能优越的荧光标记探针是肠道微生物菌群荧光成像的关键因素. 本篇综述主要总结了针对不同的肠道菌群而设计的标记策略, 主要包括荧光探针和同位素探针, 分别就代谢标记、非代谢标记以及代谢产物的特异性标记等方法进行了总结讨论, 最后对该研究方向的发展前景进行了展望.
李娜, 谭啸峰, 杨晴来. 肠道微生物菌群成像标记策略及其应用的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1375-1386.
Na Li, Xiaofeng Tan, Qinglai Yang. Recent Progress on Strategies and Applications of Imaging for Intestinal Microflora[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(5): 1375-1386.


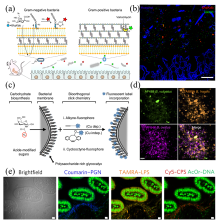

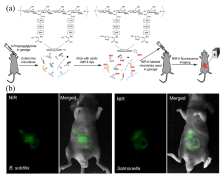



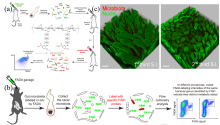

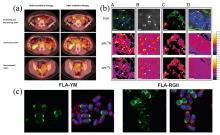

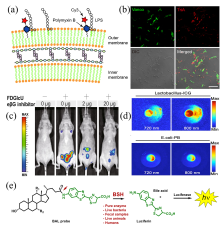

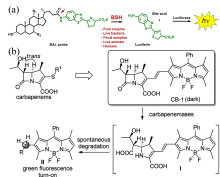
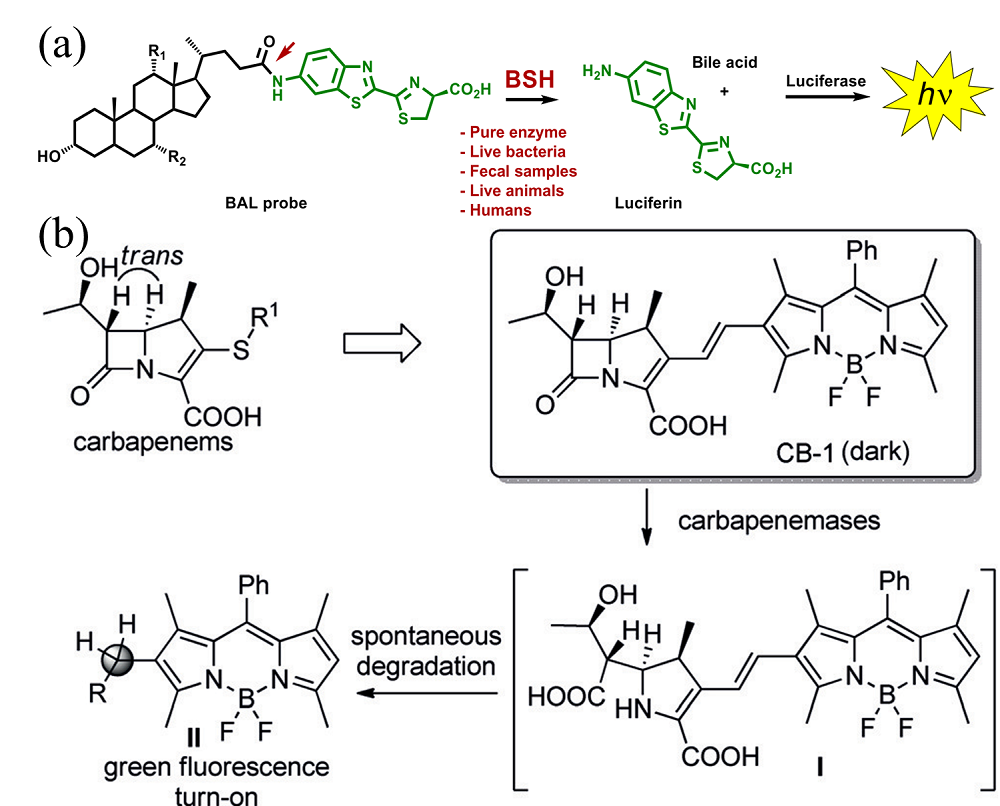
| [1] |
Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R. E.; Sonnenburg, J. L.; Peterson, D. A.; Gordon, J. I. Science 2005, 307, 1915.
doi: 10.1126/science.1104816 |
| [2] |
Borody, T. J.; Khoruts, A. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011, 9, 88.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.244 |
| [3] |
Dethlefsen, L.; McFall-Ngai, M.; Relman, D. A. Nature 2007, 449, 811.
doi: 10.1038/nature06245 |
| [4] |
Boulange, C. L.; Neves, A. L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J. K.; Dumas, M. E. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 42.
doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0303-2 |
| [5] |
Clemente, J. C.; Ursell, L. K.; Parfrey, L. W.; Knight, R. Cell 2012, 148, 1258.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035 pmid: 22424233 |
| [6] |
Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F. Nature 2012, 489, 242.
doi: 10.1038/nature11552 |
| [7] |
Lozupone, C. A.; Stombaugh, J. I.; Gordon, J. I.; Jansson, J. K.; Knight, R. Nature 2012, 489, 220.
doi: 10.1038/nature11550 |
| [8] |
Jacobson, W. J. Infect. 1983, 7, 97.
pmid: 6196416 |
| [9] |
Beveridge, T. J. Biotech. Histochem. 2001, 76, 111.
pmid: 11475313 |
| [10] |
Mason, D. J.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Mortimer, F. C.; Gant, V. A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2681.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.7.2681-2685.1998 |
| [11] |
Holm, C.; Jespersen, L. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2857.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.5.2857-2863.2003 |
| [12] |
Loy, A.; Maixner, F.; Wagner, M.; Horn, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D800.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl856 |
| [13] |
Johansson, M. E.; Hansson, G. C. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 842, 229.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-513-8_13 pmid: 22259139 |
| [14] |
Tropini, C.; Earle, K. A.; Huang, K. C.; Sonnenburg, J. L. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 433.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.03.010 |
| [15] |
Chen, S.-H.; Chen, Q.; Luo, S.-H.; Cao, X.-Y.; Yang, G.-X.; Zeng, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 919. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009012 |
|
(陈思鸿, 陈淇, 罗时荷, 曹西颖, 杨国贤, 曾晓晴, 汪朝阳, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 919.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009012 |
|
| [16] |
Chen, L.; Li, J.-B.; Chen, D.-G. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 611. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202006046 |
|
(陈莉, 黎俊波, 陈杜刚, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 611.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202006046 |
|
| [17] |
Wang, Y.-B.; Zhao, B.-X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1539. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 |
|
(王延宝, 赵宝祥, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1539.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 |
|
| [18] |
Wang, Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Jia, N. Q. Prog. Chem. 2020, 32, 204. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王阳, 黄楚森, 贾能勤, 化学进展, 2020, 32, 204.)
doi: 10.7536/PC190513 |
|
| [19] |
Dumont, A.; Malleron, A.; Awwad, M.; Dukan, S.; Vauzeilles, B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3143.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201108127 |
| [20] |
Wang, W.; Zhu, Y. T.; Chen, X. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3889.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00539 pmid: 28682052 |
| [21] |
Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Du, Y.; Zhou, X.; Du, X.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.; Song, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Tan, W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2628.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201910555 pmid: 31793153 |
| [22] |
Wang, W.; Chen, X. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 792.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-018-9236-5 |
| [23] |
Siegrist, M. S.; Swarts, B. M.; Fox, D. M.; Lim, S. A.; Bertozzi, C. R. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 184.
doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuu012 pmid: 25725012 |
| [24] |
Sletten, E. M.; Bertozzi, C. R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6974.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200900942 pmid: 19714693 |
| [25] |
Cipolla, L.; Gabrielli, L.; Bini, D.; Russo, L.; Shaikh, N. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1618.
doi: 10.1039/c004750n pmid: 20877901 |
| [26] |
Meredith, T. C.; Aggarwal, P.; Mamat, U.; Lindner, B.; Woodard, R. W. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 33.
pmid: 17163638 |
| [27] |
Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Alvarez, D.; Hudak, J. E.; Reading, N. C.; Erturk-Hasdemir, D.; Dasgupta, S.; von Andrian, U. H.; Kasper, D. L. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1091.
doi: 10.1038/nm.3929 pmid: 26280120 |
| [28] |
Hudak, J. E.; Alvarez, D.; Skelly, A.; von Andrian, U. H.; Kasper, D. L. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17099.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.99 |
| [29] |
Dube, D. H.; Prescher, J. A.; Quang, C. N.; Bertozzi, C. R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 4819.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506855103 |
| [30] |
Li, C.; Wang, Q. ACS Nano. 2018, 12, 9654.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b07536 |
| [31] |
Luo, X.-R.; Chen, M.-W.; Yang, Q.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 373. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20020045 |
|
(罗兴蕊, 陈敏文, 杨晴来, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 373.)
doi: 10.6023/A20020045 |
|
| [32] |
Sang, R.-Y.; Xu, X.-P.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Q.-L.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 901. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20050190 |
|
(桑若愚, 许兴鹏, 王其, 范曲立, 黄维, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 901.)
doi: 10.6023/A20050190 |
|
| [33] |
Robinson, J. T.; Hong, G.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yaghi, O. K.; Dai, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10664.
doi: 10.1021/ja303737a pmid: 22667448 |
| [34] |
Cai, Y.; Wei, Z.; Song, C.; Tang, C.; Han, W.; Dong, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 22.
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00494c pmid: 30444505 |
| [35] |
He, S.; Song, J.; Qu, J.; Cheng, Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4258.
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00234G |
| [36] |
Wang, W.; Lin, L.; Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, C. J. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1317.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09267-x pmid: 30899006 |
| [37] |
Hell, S. W. Science 2007, 316, 1153.
doi: 10.1126/science.1137395 |
| [38] |
Praveschotinunt, P.; Dorval Courchesne, N. M.; den Hartog, I.; Lu, C.; Kim, J. J.; Nguyen, P. Q.; Joshi, N. S. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1640.
doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00135 pmid: 29791796 |
| [39] |
Lin, L.; Song, J.; Du, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gao, J.; Song, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11923.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202004703 |
| [40] |
Carmody, R. N.; Turnbaugh, P. J. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 4173.
doi: 10.1172/JCI72335 pmid: 25105361 |
| [41] |
Hehemann, J. H.; Reintjes, G.; Klassen, L.; Smith, A. D.; Ndeh, D.; Arnosti, C.; Amann, R.; Abbott, D. W. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1883.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0406-z |
| [42] |
Chen, M.; Cheng, K. W.; Chen, Y. J.; Wang, C. H.; Cheng, T. C.; Chang, K. C.; Kao, A. P.; Chuang, K. H. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3142.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03252-4 |
| [43] |
Whidbey, C.; Sadler, N. C.; Nair, R. N.; Volk, R. F.; DeLeon, A. J.; Bramer, L. M.; Fansler, S. J.; Hansen, J. R.; Shukla, A. K.; Jansson, J. K.; Thrall, B. D.; Wright, A. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 42.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b09668 |
| [44] |
Meng, L.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Huang, R.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 12566.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1111 |
| [45] |
Li, H.-M.; Luo, H.-J.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, L.-Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 577.. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20040109 |
|
(李海梅, 罗华健, 肖琦, 杨立云, 黄珊, 刘义, 化学学报, 2017, 78, 577.)
|
|
| [46] |
Yang, L.-B.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1047. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17080353 |
|
(杨立敏, 刘波, 李娜, 唐波, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1047.)
doi: 10.6023/A17080353 |
|
| [47] |
Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Lemaitre, B. J. Endotoxin Res. 2005, 11, 105.
pmid: 15949137 |
| [48] |
Dramsi, S.; Magnet, S.; Davison, S.; Arthur, M. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 307.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00102.x |
| [49] |
Neuhaus, F. C.; Struve, W. G. Biochemistry 1965, 4, 120.
doi: 10.1021/bi00877a020 |
| [50] |
Typas, A.; Banzhaf, M.; Gross, C. A.; Vollmer, W. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 10, 123.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2677 |
| [51] |
Kajiwara, H.; Toda, M.; Mine, T.; Nakada, H.; Wariishi, H.; Yamamoto, T. Microbes Environ. 2010, 25, 152.
pmid: 21576867 |
| [52] |
Sizemore, R. K.; Caldwell, J. J.; Kendrick, A. S. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2245.
doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2245-2247.1990 |
| [53] |
Kuru, E.; Hughes, H. V.; Brown, P. J.; Hall, E.; Tekkam, S.; Cava, F.; de Pedro, M. A.; Brun, Y. V.; VanNieuwenhze, M. S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12519.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201206749 |
| [54] |
Kuru, E.; Lambert, C.; Rittichier, J.; Till, R.; Ducret, A.; Derouaux, A.; Gray, J.; Biboy, J.; Vollmer, W.; VanNieuwenhze, M.; Brun, Y. V.; Sockett, R. E. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 254.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0087-1 |
| [55] |
Brandt, L. J.; Aroniadis, O. C. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 240.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.03.1329 |
| [56] |
Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Du, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, M.; Lin, L.; Czajkowsky, D. M.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Shao, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3055.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202010921 pmid: 33084179 |
| [57] |
Susaki, E. A.; Tainaka, K.; Perrin, D.; Kishino, F.; Tawara, T.; Watanabe, T. M.; Yokoyama, C.; Onoe, H.; Eguchi, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Abe, T.; Kiyonari, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Miyawaki, A.; Yokota, H.; Ueda, H. R. Cell 2014, 157, 726.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.042 pmid: 24746791 |
| [58] |
Susaki, E. A.; Tainaka, K.; Perrin, D.; Yukinaga, H.; Kuno, A.; Ueda, H. R. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1709.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.085 pmid: 26448360 |
| [59] |
Gallamini, A.; Zwarthoed, C.; Borra, A. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1821.
doi: 10.3390/cancers6041821 pmid: 25268160 |
| [60] |
Boursi, B.; Werner, T. J.; Gholami, S.; Houshmand, S.; Mamtani, R.; Lewis, J. D.; Wu, G. D.; Alavi, A.; Yang, Y. X. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0192747.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192747 |
| [61] |
Donohoe, D. R.; Wali, A.; Brylawski, B. P.; Bultman, S. J. PLoS One 2012, 7, e46589.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046589 |
| [62] |
Oberbach, A.; Haange, S. B.; Schlichting, N.; Heinrich, M.; Lehmann, S.; Till, H.; Hugenholtz, F.; Kullnick, Y.; Smidt, H.; Frank, K.; Seifert, J.; Jehmlich, N.; von Bergen, M. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1593.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00973 pmid: 28252966 |
| [63] |
Berry, D.; Loy, A. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 999.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.06.004 |
| [64] |
Berry, D.; Stecher, B.; Schintlmeister, A.; Reichert, J.; Brugiroux, S.; Wild, B.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A.; Rauch, I.; Decker, T.; Loy, A.; Wagner, M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 4720.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219247110 |
| [65] |
Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Song, Y.; Yang, C. J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4017.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1465-0 pmid: 30415405 |
| [66] |
Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Ren, J.; Nie, L. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2938.
doi: 10.1364/OL.42.002938 |
| [67] |
Khodakivskyi, P. V.; Lauber, C. L.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Bazhin, A. A.; Bruce, S.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Ringel, Y.; Bétrisey, B.; Torres, J.; Hu, J.; Chou, C. J.; Goun, E. A. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7.
|
| [68] |
Stein, A.; Voigt, W.; Jordan, K. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2010, 2, 51.
doi: 10.1177/1758834009355164 |
| [69] |
Kehrer, D. F.; Sparreboom, A.; Verweij, J.; de Bruijn, P.; Nierop, C. A.; van de Schraaf, J.; Ruijgrok, E. J.; de Jonge, M. J. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1136.
pmid: 11350876 |
| [70] |
Cai, D.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, S. L. Opt. Express. 2017, 25, 1421.
doi: 10.1364/OE.25.001421 pmid: 28158024 |
| [71] |
Kang, D.; Lashkari, B.; Mandelis, A. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 655.
doi: 10.1364/OL.42.000655 |
| [72] |
Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Goel, S.; Sun, B.; Chitgupi, U.; Geng, J.; Sun, H.; Barnhart, T. E.; Cai, W.; Xia, J.; Lovell, J. F. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8524.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201602373 |
| [73] |
Whittam, T. S.; Wolfe, M. L.; Wachsmuth, I. K.; Orskov, F.; Orskov, I.; Wilson, R. A. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 1619.
doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1619-1629.1993 pmid: 7682992 |
| [74] |
Yu, S. Z.; Lu, L. G.; Zhang, Y. C.; Wu, G. R. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 46. (in Chinese)
|
|
(俞顺章, 卢林耿, 张幼辰, 卫国荣, 中华流行病学杂志, 1999, 46.)
|
|
| [75] |
Moseley, S. L.; Echeverria, P.; Seriwatana, J.; Tirapat, C.; Chaicumpa, W.; Sakuldaipeara, T.; Falkow, S. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 145, 863.
pmid: 7045250 |
| [76] |
Reardon, S. Nature 2014, 509, 141.
doi: 10.1038/509141a |
| [77] |
Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791.
doi: 10.3201/eid1710.110655 |
|
Mao, W.; Xia, L.; Xie, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4468.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201612495 |
| [1] | 张莹珍, 江丹丹, 李娟华, 王菁菁, 刘昆明, 刘晋彪. 高选择性硒代半胱氨酸荧光探针的构建策略及成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 41-53. |
| [2] | 杨维清, 葛宴兵, 陈元元, 刘萍, 付海燕, 马梦林. 1,8-萘酰亚胺衍生物的设计、合成及其对半胱氨酸的识别研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 180-194. |
| [3] | 李焕清, 陈兆华, 陈祖佳, 邱琪雯, 张又才, 陈思鸿, 汪朝阳. 基于有机小分子的汞离子荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3067-3077. |
| [4] | 丁炳辉, 韩少辉, 熊海青, 王本花, 左伯军, 宋相志. 高选择性比率型荧光探针用于急性肺损伤中次氯酸的检测[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2878-2884. |
| [5] | 刘飞冉, 敬静, 张小玲. 细胞器靶向型半胱氨酸荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2053-2067. |
| [6] | 刘甜甜, 张鸿鹏, 焦晓梦, 白银娟. 多信号同时检测生物硫醇荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2081-2095. |
| [7] | 李宜芳, 王耀, 牛华伟, 陈秀金, 李兆周, 王永国. 线粒体靶向的二氧化硫荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 1952-1962. |
| [8] | 陈志华, 胡艳, 马丽丽, 张子怡, 刘传祥. 基于氢化吡啶辅助氨基氧化策略的次氯酸根荧光探针的设计、合成及其性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 718-724. |
| [9] | 唐宏伟, 王超, 钟克利, 侯淑华, 汤立军, 边延江. 一种裸眼和荧光双通道快速检测Hg2+的探针及其多种应用[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 712-717. |
| [10] | 周五, 彭敏, 梁庆祥, 吴爱斌, 舒文明, 余维初. 高选择和高灵敏检测溶液和气相中硫化氢的新型萘酰亚胺类开启型荧光探针[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4277-4283. |
| [11] | 刘梦, 黄延茹, 孙小飞, 汤立军. 一种基于“聚集诱导发光+激发态分子内质子转移”机制的苯并噻唑衍生物荧光探针及其对次氯酸根的识别[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 345-351. |
| [12] | 李阳阳, 孙小飞, 胡晓玲, 任源远, 钟克利, 燕小梅, 汤立军. 三苯胺衍生物的合成及其基于聚集诱导发光(AIE)机理对汞离子“OFF-ON”荧光识别[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 320-325. |
| [13] | 张继东, 颜婉琳, 胡文强, 郭典, 张大龙, 权校昕, 卜贤盼, 陈思宇. 一种具有聚集诱导发光性能的Zn2+荧光探针的设计合成[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 326-331. |
| [14] | 马延慧, 武宇乾, 王晓旭, 高贵, 周欣. 基于1,3-二氯-7-羟基-9,9-二甲基-2(9H)-吖啶酮(DDAO)的近红外荧光探针研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 94-111. |
| [15] | 杨雅馨, 陈琳, 胡晓玲, 钟克利, 李世迪, 燕小梅, 张璟琳, 汤立军. 一种点亮型硫化氢荧光探针的合成及其在红酒和细胞中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 308-312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||