有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (7): 2236-2242.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202202038 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
王泽坤a, 徐子悦a, 李娟娟b, 余尚博c, 王辉a, 郭东升b, 张丹维a, 黎占亭a,c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-28
修回日期:2022-03-13
发布日期:2022-08-09
通讯作者:
黎占亭
基金资助:
Ze-Kun Wanga, Zi-Yue Xua, Juan-Juan Lib, Shang-Bo Yuc, Hui Wanga, Dong-Sheng Guob, Dan-Wei Zhanga, Zhan-Ting Lia,c( )
)
Received:2022-02-28
Revised:2022-03-13
Published:2022-08-09
Contact:
Zhan-Ting Li
Supported by:文章分享

很多功能性有机分子在水中溶解度很小, 限制了它们的实际应用. 水溶性主体的包结是提高有机分子水溶性的重要手段, 但要获得显著的增溶效果, 一般需要主体分子具有很高的浓度. 报道了一种梯度增溶新策略, 即利用一种高水溶性多孔聚合物富集另一个具有增溶作用的主体分子, 提高其局部有效浓度, 实现其增溶作用增强的目的. 为此利用一个水溶性正离子型超分子有机框架, 吸收富集负离子型杯[5]芳烃, 实现了杯[5]芳烃对C60、C70、二茂铁、1,1'-二甲二茂铁及1,1°-二溴二茂铁的增溶作用的进一步提高, 通过吸收富集开环葫芦脲, 实现了后者对紫杉醇, 多西他赛和卡巴他赛的水溶性的进一步提高.
王泽坤, 徐子悦, 李娟娟, 余尚博, 王辉, 郭东升, 张丹维, 黎占亭. 超分子有机框架对分子容器的水相增溶的梯度增强效应[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 2236-2242.
Ze-Kun Wang, Zi-Yue Xu, Juan-Juan Li, Shang-Bo Yu, Hui Wang, Dong-Sheng Guo, Dan-Wei Zhang, Zhan-Ting Li. Gradient Enhancement of Supramolecular Organic Framework for Solubilization of Hydrophobic Molecules by Two Molecular Containers in Water[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2236-2242.
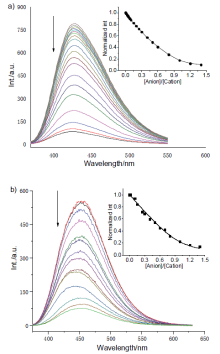
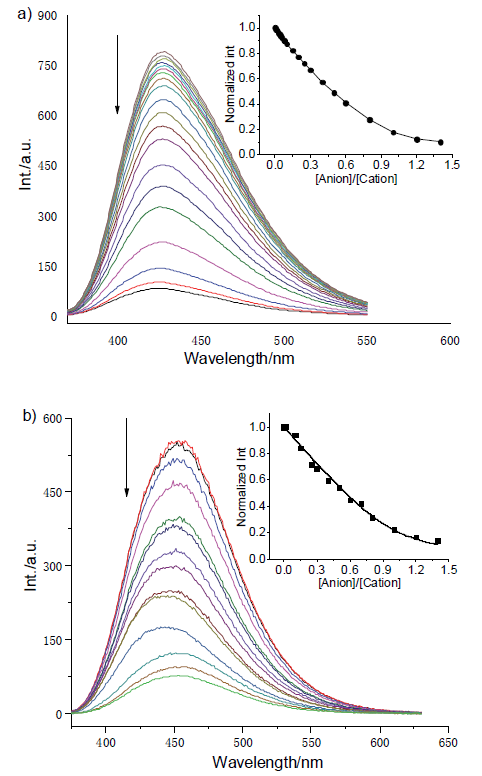
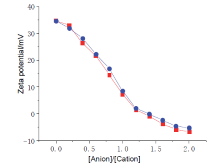
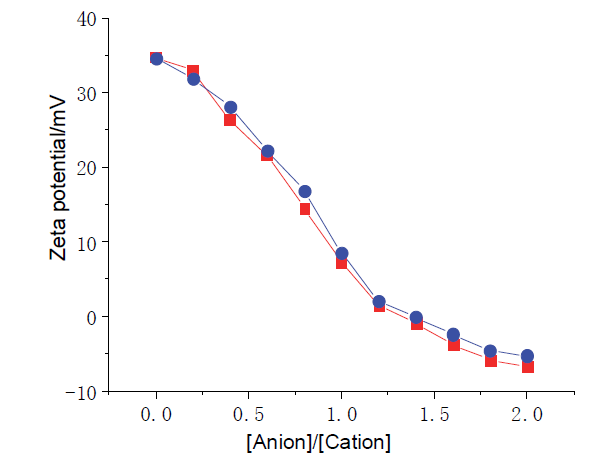
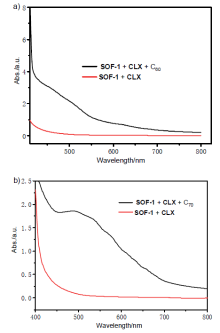
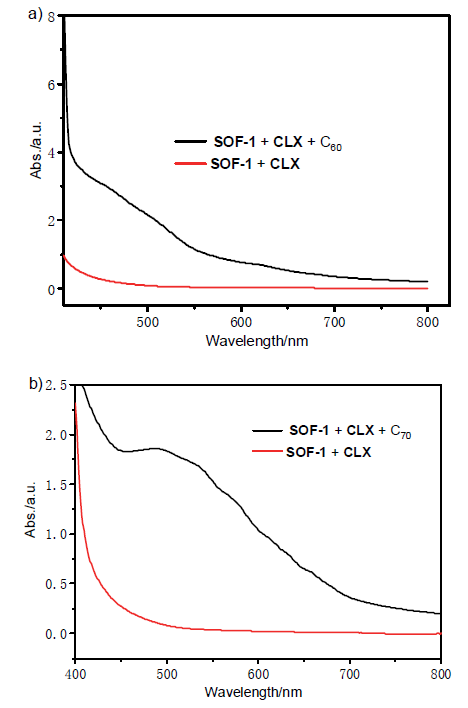


| [1] |
(a) Brewster, M. E.; Loftsson, T. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2007, 59, 645.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012 |
|
(b) Rao, V. M.; Stella, V. J. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 927.
doi: 10.1002/jps.10341 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Fan, L. Wang, J.; Jin, Z. Trend. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 398.
doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.023 |
|
(b) Jambhekar, S. S.; Breen, P. Drug Delivery Today 2016, 21, 363.
|
|
|
(c) Qie, S.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Xi, J. Acta Chim. Sin. 2020, 78, 232. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
( 郄淑燕, 郝莹, 刘宗建, 王锦, 席家宁, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 232.)
doi: 10.6023/A20010006 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Nakahata, M.; Takashima, Y.; Harada, A. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 330.
doi: 10.1248/cpb.c16-00778 |
|
(b) Qi, W.; Ma, C.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101526.
doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101526 |
|
|
(c) Xu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Chu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 635507.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.635507 |
|
|
(d) Zhou, W.-L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Acta Chim. Sin. 2020, 78, 1164. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
( 周维磊, 陈湧, 刘育, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1164.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100486 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Yu, Y.; Rebek, R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3031.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00269 |
|
(b) Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Khalil-Cruz, L. E.; Khashab, N. M.; Yu, G.; Huang, F. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 688.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9932-9 |
|
|
(c) Yin, H.; Wang, R. Isr. J. Chem. 2018, 58, 188.
doi: 10.1002/ijch.201700092 |
|
|
(d) Gu, A.; Wheate, N. J. J. Inclus. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 100, 55.
doi: 10.1007/s10847-021-01055-9 |
|
|
(e) Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Li, W.; Pei, Z. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5865.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC02001J |
|
|
(f) Zheng, Z.; Geng, W.-C.; Xu, Z.; Guo, D.-S. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 913.
doi: 10.1002/ijch.201900032 |
|
|
(g) Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Jin, X.-Y.; Cong, H.; Tao, Z. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2018, 15, 274.
doi: 10.2174/1570193X15666171228150315 |
|
|
(h) Sathiyajith, C.; Shaikh, R. R.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Meguellati, K.; Yang, Y.-W. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 677.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC08967D |
|
|
(i) Yin, H.; Bardelang, D.; Wang, R. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2020.08.008 |
|
|
(j) Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2020, 41, 1139. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
( 黎占亭, 王辉, 张丹维, 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41, 1139.)
|
|
|
(k) Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Qiao, P.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12379.
doi: 10.1039/D1CC04400A |
|
|
(l) Zhang, S.; Boussouar, I.; Li, H. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 642.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.06.035 |
|
|
(m) Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, A.; Tan, H. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 313.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.04.049 |
|
|
(n) Xiao, T.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X.-Q.; Huang, F.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.05.011 |
|
|
(o) Li, R.-H.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, H. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 3095.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.06.041 |
|
|
(p) Duan, Z.; Xu, F.; Huang, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, W. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, e2100775.
|
|
| [5] |
(a) Hussain, A. M.; Ashraf, U. M.; Muhammad, G.; Tahir, N. M.; Bukhari, N. A. S. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2377.
|
|
(b) Pan, Y. C.; X. Y. Hu, X. Y.; Guo, D.-S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2768.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201916380 |
|
|
(c) Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1190.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.03.035 |
|
|
(d) Guo, D.-S.; Liu, Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1925.
doi: 10.1021/ar500009g |
|
|
(e) Perret, F.; Coleman, A. W. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7303.
doi: 10.1039/c1cc11541c |
|
|
(f) Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.-W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 825.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2015.01.038 |
|
| [6] |
(a) Macartney, D. H. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 2075.
doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.164 pmid: 24215347 |
|
(b) Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Lu, S.; Bardelang, D.; Wang, R. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1513.
doi: 10.7150/thno.53459 pmid: 24215347 |
|
|
(c) Ma, D.; Hettiarachchi, G.; Nguyen, D.; Zhang, B.; Wittenberg, J. B.; Zavalij, P. Y.; Briken, V.; Isaacs, L. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 503.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1326 pmid: 24215347 |
|
|
(d) Mao, D.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, J.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.; Ma, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12614.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201707164 pmid: 24215347 |
|
|
(e) Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, P.; Liao, X.; Wang, B.; Yang, B. J. Inclus. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 100, 197.
doi: 10.1007/s10847-021-01073-7 pmid: 24215347 |
|
|
(f) Deng, C.-L.; Murkli, S. L.; Isaacs, L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7516-7532.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00454E pmid: 24215347 |
|
|
(g) Lu, X.; Isaacs, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8076-8080.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201602671 pmid: 24215347 |
|
| [7] |
(a) Lagona, J.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chakrabarti, S.; Isaacs, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4844.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200460675 |
|
(b) Barrow, S. J.; Kasera, S.; Rowland, M. J.; del Barrio, J.; Scherman, O. A. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12320.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00341 |
|
|
(c) Kim, K. Selvapalam, N.; Ko, Y. H.; Park, K. M.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 267.
doi: 10.1039/B603088M |
|
|
(d) Yao, Y. Q.; Chen, K.; Hua, Z. Y.; Zhu, Q. J.; Xue, S. F.; Tao, Z. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2017, 89, 1.
doi: 10.1007/s10847-017-0733-5 |
|
| [8] |
(a) Yu, S.-B.; Lin, F.; Tian, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 434.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00862E pmid: 25470406 |
|
(b) Tian, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-T. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6351.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC02331B pmid: 25470406 |
|
|
(c) Tian, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-T. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 426.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx030 pmid: 25470406 |
|
|
(d) Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 970.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202000085 pmid: 25470406 |
|
|
(e) Tian, J.; Zhou, T.-C.; Zhang, S.-C.; Aloni, S.; Altoe, M. V.; Xie, S.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-T. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5574.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6574 pmid: 25470406 |
|
|
(f) Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2020, 41, 1139. (in Chinese)
pmid: 25470406 |
|
|
( 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭, 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41, 1139.)
pmid: 25470406 |
|
| [9] |
(a) Xu, Z.-Y.; Mao, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.-K.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T.; Ma, D. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 899.
doi: 10.1039/D1TB02601A |
|
(b) Liu, Y.; Liu, C.-Z.; Wang, Z.-K.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhang, D.-W.; Ma, D.; Li, Z.-T. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121467.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121467 |
|
| [10] |
(a) Yao, C.; Tian, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.-T. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 893.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.01.005 |
|
(b) Tian, J.; Yao, C.; Yang, W.-L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.-W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-T. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 798.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.01.010 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, Y.-C.; Zeng, P.-Y.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.-K.; Guo, B.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.-T. Drug Delivery 2022, 29, 128.
doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2021325 |
|
| [11] |
Yang, B.; Zhang, X.-D.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Wu, Y.-P.; Yu, F.-X.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.-T. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 156.
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.019.20180011 |
| [12] |
(a) Guo, D.-S.; Jiang, B.-P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 720.
doi: 10.1039/C2OB06973C |
|
(b) Ma, D.; Zavalij, P. Y.; Isaacs, L. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 4786.
doi: 10.1021/jo100760g |
|
| [13] |
Yu, S.-B.; Qi, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.-T. Small 2018, 14, 1801037.
|
| [14] |
Haino, T.; Yanase, M.; Fukunaga, C.; Fukazawa, Y. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 2025.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2005.07.121 |
| [15] |
(a) Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zheng, L.; Fang, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 14667.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02674 |
|
(b) Han, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5165.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00802C |
|
| [16] |
Hardie, M. J. Supramol. Chem. 2002, 14, 7.
doi: 10.1080/10610270290006529 |
| [17] |
Lim, S.; Pang, Z.; Hweiyuin, T.; Shaikh, M.; Adinarayana, G.; Garg, S. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. Drug Develop. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1.
|
| [1] | 王化坤, 任晓龙, 宣宜宁. 卤盐催化的α,β-环氧羧酸酯与异氰酸酯[3+2]环加成反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 251-258. |
| [2] | 徐利军, 李宗军, 韩福社, 高翔. N,N-二甲基甲酰胺促进的富勒烯稠合噁唑啉衍生物的合成[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 242-250. |
| [3] | 戴力, 徐迪, 毛翼斐, 朱嘉琦, 杨梦娇. 手性噁唑啉二茂铁化合物结构与合成方法[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(8): 2364-2375. |
| [4] | 郭京京, 郭敏捷. 基于大环化合物与二氟硼二吡咯亚甲基的超分子荧光系统的设计及应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(8): 2946-2963. |
| [5] | 马志艳, 李云剑, 孙小强, 杨科, 李正义. 杯芳烃促进的过渡金属催化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(6): 2188-2201. |
| [6] | 吴赛, 陶吴晞, 王果, 赵斌, 陈华杰. 含靛红并苊醌二甲酰亚胺端基的A-D-A型小分子受体材料的合成及其光电性质研究[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(5): 2019-2028. |
| [7] | 朱三娥, 豆礼锋, 张建辉, 吴缨, 杨伟, 鲁红典, 卫春祥, 邓崇海, 董强. 钯催化烯烃杂环化反应制备[60]富勒烯二氢呋喃化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(5): 2082-2090. |
| [8] | 刘玉婷, 李洁, 尹大伟. 基于二茂铁的金属阳离子识别受体的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(1): 158-170. |
| [9] | 刘旭波, 林佳乐, 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭. 开环葫芦脲在水中对芳烃和芳醛的增溶和对腙大环形成的促进作用[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(3): 663-668. |
| [10] | 牛闯, 王官武. [60]富勒烯稠合杂环化合物的电化学反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(11): 3633-3645. |
| [11] | 闫萌, 彭文昶, 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭. 超分子有机框架对喜树碱类开环羧酸盐的负载及其内酯化动力学[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(9): 2567-2573. |
| [12] | 贾慧劼, 韩利民, 竺宁, 高媛媛, 王亚琦, 索全伶. 乙酰基二茂铁苯并噻唑探针对Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+识别性能的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(6): 1753-1760. |
| [13] | 盛家骏, 于雅楠, 王信, 钱宇, 符立梧, 赵芸, 马明亮, 胡文浩. 多组分反应合成紫杉醇侧链及其在合成紫杉醇衍生物中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(2): 377-389. |
| [14] | 孙卫东, 叶琳, 刘佳, 郑璐, 郭文彩, 韩森凯, 邵成园, 江华. 富勒烯作为模板剂的碗烯基分子笼构筑的自组装[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(10): 2867-2874. |
| [15] | 李四聪, 季绍聪, 赵亮, 廖晓雨, 刘传峰, 汤浩东, 舒正宁, 杨鹏, 裴月湖. N-水杨醛腙修饰11-氮杂青蒿素衍生物的合成及性质研究[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(10): 2860-2866. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||