有机化学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2538-2544.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403051 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
王源浩a, 孙钰凯a, 刘昱迒a,b, 张照明a,*( ), 颜徐州a,b,*(
), 颜徐州a,b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-30
修回日期:2024-05-23
发布日期:2024-06-13
作者简介:基金资助:
Yuanhao Wanga, Yukai Suna, Yuhang Liua,b, Zhaoming Zhanga( ), Xuzhou Yana,b(
), Xuzhou Yana,b( )
)
Received:2024-03-30
Revised:2024-05-23
Published:2024-06-13
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

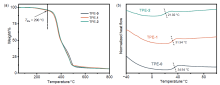
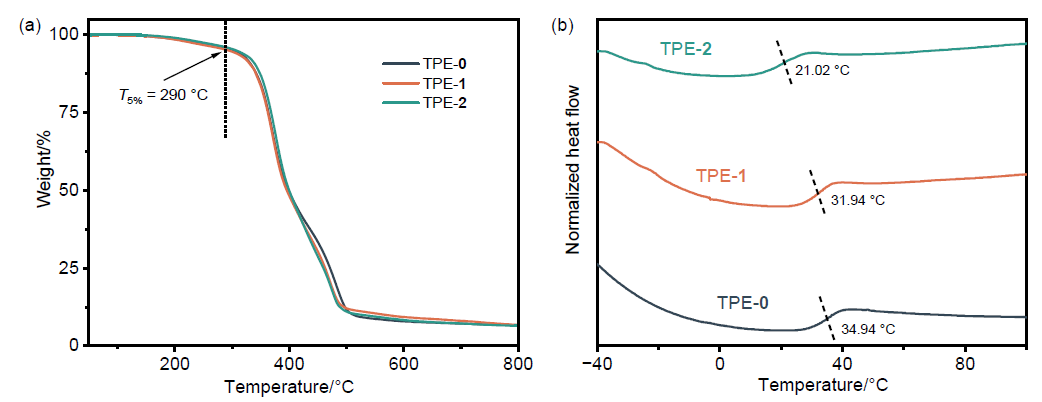
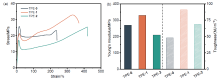
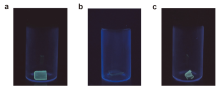
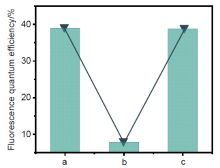
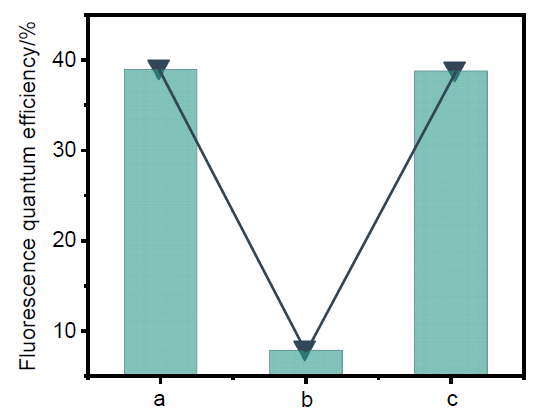
柔性发光材料凭借在不同外力作用下仍能保持形状完整和发光性能的特点, 在技术生产的多个领域有着广泛的应用. 利用四苯基乙烯作为发色基团, 利用硫醇与双键高效点击聚合的方法, 构筑了一系列荧光强度可调的柔性发光材料. 通过调节参与聚合的不同官能度硫醇单体的比例, 制备了机械性能优异的聚合物网络, 其断裂伸长率为377%, 断裂应力为33.0 MPa, 韧性可达90.6 MJ/m3. 通过外力诱导分子构象变化, 发现材料的荧光量子产率会随着拉伸程度的增加而升高. 同时, 该材料在溶胀后会发生荧光淬灭, 挥发溶剂后荧光重新出现, 符合聚集诱导发光的规律. 基于以上研究, 该柔性发光材料的机械性能优秀且荧光强度可调, 因此有望在发光传感器、信号探测器等方向开展实际应用.
王源浩, 孙钰凯, 刘昱迒, 张照明, 颜徐州. 基于四苯乙烯的柔性发光材料的构筑及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544.
Yuanhao Wang, Yukai Sun, Yuhang Liu, Zhaoming Zhang, Xuzhou Yan. Construction and Properties of Flexible Light-Emitting Materials Based on Tetraphenylethylene[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544.


| [1] |
Jeon, K. H.; Park, J. W. Macromolecule. 2022, 55, 8311.
|
| [2] |
Jang, B.; Won, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113299.
|
| [3] |
Lee, Y.; Chung, J. W.; Lee, G. H.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Bae, C.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, S.; Cho, H.; Kang, S.-G.; Jung, J. Y.; Lee, D.-W.; Gam, S.; Hahm, S. G.; Kuzumoto, Y.; Kim, S. J.; Bao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yun, Y.; Kim, S. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9180. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg9180
|
| [4] |
Zhang, P.; Lei, I. M.; Chen, G. D.; Lin, J. S.; Chen, X. M.; Zhang, J. J.; Cai, C. C.; Liang, X. Y.; Liu, J. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4775.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32126-1 pmid: 35999212 |
| [5] |
Lee, Y.; Kim, D. S.; Jin, S. W.; Lee, H.; Jeong, Y. R.; You, I.; Zi, G.; Ha, J. S. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130858.
|
| [6] |
Hong, S. Y.; Lee, Y. H.; Park, H.; Jin, S. W.; Jeong, Y. R.; Yun, J.; You, I.; Zi, G.; Ha, J. S. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 930.
|
| [7] |
Xu, H.; Han, P. B.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050232 |
|
| [8] |
Liu, B.; Chen, B. K. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 929 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘斌, 陈磅宽, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 929.)
doi: 10.6023/A22030122 |
|
| [9] |
Ou, X. Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, B. L.; Zan, J.; Wu, Q. X.; Hong, Z. Z.; Xie, L. L.; Bian, H. Y.; Yi, Z. G.; Chen, X. F.; Wu, Y. M.; Song, X. R.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. S.; Yang, H. H.; Liu, X. G. Natur. 2021, 590, 410.
|
| [10] |
Xie, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. L.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, S. T.; Yun, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, C. B.; Tian, F.; Su, M.; Li, F. Y. ACS Nan. 2022, 16, 20094.
|
| [11] |
Zhao, R. Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Fan, W. R.; Zhu, Q. X.; Ma, H. H.; Wang, X. W.; Wang, Z. H.; Huang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 26532.
|
| [12] |
Zhang, H. Y.; Jia, S. X.; Yin, D.; Feng, J. Chin. J. Lumin. 2023, 44, 1606 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张浩洋, 贾士鑫, 银达, 冯晶, 发光学报, 2023, 44, 1606.)
|
|
| [13] |
Liu, S. J.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Polym. Sinic. 2021, 52, 456 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘顺杰, 唐本忠, 高分子学报, 2021, 52, 456.)
|
|
| [14] |
Han, P. B.; Qin, A. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2254 (in Chinese).
|
|
(韩鹏博, 秦安军, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2254.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202300032 |
|
| [15] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [16] |
Hong, Y. N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4332.
|
| [17] |
Liu, L.; Hao, T. T.; Wu, W. H.; Yang, C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2189 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘铃, 浩涛涛, 伍晚花, 杨成, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2189.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210020 |
|
| [18] |
Wu, J. S.; Liu, W. M.; Ge, J. C.; Zhang, H. Y.; Wang, P. F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3483.
|
| [19] |
Mei, J.; Hong, Y. N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, Y. H.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429.
|
| [20] |
Cai, Y.; Du, L.; Samedov, K.; Gu, X.; Qi, F.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Patrick, B. O.; Yan, Z. P.; Jiang, X. F., Zhang, H. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Phillips, D. L.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4662.
|
| [21] |
Qiu, Z.; Chu, E. K. K.; Jiang, M.; Gui, C.; Xie, N.; Qin, W.; Alam, P.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2017, 50, 7620.
|
| [22] |
Han, T.; Gui, C.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Jiang, M. J.; Xie, N.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2017, 50, 5807.
|
| [23] |
Chi, W. W.; Yuan, W.; Du, J.; Han, T.; Li, H. K.; Li, Y. F.; Tang, B. Z. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800604
|
| [24] |
Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, X.; Albouy, P. A.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, M. H. Mater. Chem. Fron.. 2018, 2, 2245.
|
| [25] |
Lu, H. M.; Ma, L. M. C.; Ma, H. C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 4075 (in Chinese).
|
|
(鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4075.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202305010 |
|
| [26] |
Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Q.; Gao, L. C.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3165.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11144-6 pmid: 31320646 |
| [27] |
Khorloo, M.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhu, M.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Nan. 2021, 15, 1397.
|
| [28] |
Liu, G. J.; Feng, G. L.; Li, X. F.; Liu, Y. C.; Zhou, W.; Ji, Y. M.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, G. W. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 52, 880 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘广建, 冯改丽, 李夏芬, 刘怡晨, 周微, 及燕铭, 张媛, 邢国文, 中国科学:化学, 2022, 52, 880.)
|
|
| [29] |
Zhao, Y. Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. R.; Zhu, L. P.; Zhou, Y. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2024, 82, 265 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵玉强, 张霞, 杨芸如, 朱立平, 周莹, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 265.)
doi: 10.6023/A23100457 |
|
| [30] |
Zeng, C. Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, B. Q.; Fang, W. Y.; Zhao, K. Q.; Donnio, B. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 469 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曾崇洋, 胡平, 汪必琴, 方文彦, 赵可清, Donnio, B. 化学学报, 2023, 81, 469.)
doi: 10.6023/A23010006 |
|
| [31] |
Feng, X. C.; Zhu, L. L.; Yue, B. B. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 80, 647 (in Chinese).
|
|
(冯锡成, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 647.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010015 |
|
| [32] |
Zeng, C. Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, B. Q.; Fang, W. Y.; Zhao, K. Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3287 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曾崇洋, 胡平, 汪必琴, 方文彦, 赵可清, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3287.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202302025 |
|
| [33] |
Zhang, L. L.; Wang, Y. Y.; Zhu, G. N.; Dai, W. B.; Zhao, Z. X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhi, J. G.; Dong, Y. P. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 282 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张璐璐, 王媛媛, 朱贵楠, 戴文博, 赵紫璇, 赵盈, 支俊格, 董宇平, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 282.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120556 |
|
| [34] |
Wang, Y. T.; Liu, X. Q.; Li, H. K.; Liu, X. D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2393.
|
| [35] |
Guo, X. M.; Yuan, P. S.; Qiao, X. F.; Yang, D. Z.; Dai, Y. F.; Sun, Q.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z.; Ma, D. G. Adv. Funct. Mate.. 2020, 30, 1908704.
|
| [36] |
Liu, Y. H.; Guo, Z. W.; Guo, Y. C.; Li, G. F.; Yang, S. B.; Yan, X. Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. B. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108531.
|
| [37] |
Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. M.; Zhang, J. Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 870.
|
| [38] |
Jiang, Y.; Ma, J. H.; Ran, Z. Y.; Zhong, H. Q.; Zhang, D. H.; Hadjichristidis, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208516.
|
| [39] |
Jiang, Y.; Ran, Z. Y.; Wu, Y. F.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, D. H. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 12423.
|
| [40] |
Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. M.; Wang, C. Y.; Yan, X. Z. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 41.
|
| [41] |
Yu, P.; Huang, Q. R.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W.; Jia, Z. C.; Wang, H. Y.; Ma, J. J.; Wang, C. Y.; Yan, X. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 516.
|
| [42] |
Ma, S. Y.; Zhang, X. L.; Gong, L.; Zhan, S. P.; Hou, W. M.; Lu, C. L. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 566 (in Chinese).
|
|
(马思阳, 张晓琳, 宫蕾, 詹世平, 侯维敏, 卢春兰, 材料导报, 2021, 35, 566.)
|
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Y. H.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. F.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y. P.; Chen, W. C.; Zhao, Z. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202303022 |
|
| [44] |
Gui, Y. X.; Chen, K. Y.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y. H.; Luo, W. S.; Zhu, D. X.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D. Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249.
|
| [45] |
Chen, Y. J.; Pu, M. Q.; Wu, L. T.; Sun, X. L.; Wan, W. M. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1705.
|
| [46] |
Zhang, Z. M.; Zhao, J.; Yan, X. Z. Acta Polym. Sinic. 2022, 53, 691 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张照明, 赵骏, 颜徐州, 高分子学报, 2022, 53, 691.)
|
|
| [47] |
Wang, Y. M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. M.; Zhao, J.; Bai, R. X.; Liu, Y. H.; Zhang, X. H.; Yan, X. Z. Aggregat. 2022, 3, e206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.206.
|
| [1] | 宫清宝, 吕翔, 于长江, 李婉婉, 赵全胜, 焦莉娟, 郝二红. 聚集诱导发光活性氟硼吡啶肼醛腙染料的合成、晶体结构及光学性质[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [2] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [3] | 沈钇灼, 罗康为, 徐清洋, 张鉴予, 孙景志, 张浩可, 唐本忠. 弱作用基有机发光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [4] | 何俊初, 伍俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金. 以二苯基硅杂吖啶为电子给体的蓝色聚集诱导延迟荧光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [5] | 谢志鑫, 黎少玲, 刘威, 严楷, 蒋涛, 刘一苇, Md. Monarul Islam, 冯星. 窄化芘基发光分子半峰宽的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [6] | 孟子翔, 田秀梅, 张天富. 聚集诱导发光材料在肿瘤光治疗应用中的最新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [7] | 黄伟庚, 高翼亭, 孙妍, 燕鼎元, 王东, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光材料用于肿瘤光学诊疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [8] | 黄凯航, 尹理, 姜青云, 汪乾, 石光, 许炳佳. 具有聚集诱导发光性质的高效热激活延迟荧光材料用于脂滴成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [9] | 杨玉杰, 曹微, 于际凯, 张志霞, 徐莉, 王华. 给体-受体(D-A)型苯基环八四噻吩的合成及其聚集诱导发光与高压发光性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [10] | 苏小龙, 李健鹏, 刘孟鑫, 邹莉, 杨得锁, 冯海涛. 四苯乙烯酰胺类化合物的合成及其高灵敏度、高选择性识别Cu2+[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [11] | 欧彦, 蓝琳, 王正雄, 王志明, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光型核酸探针的制备及其核酸传感原理研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562. |
| [12] | 胡甲松, 李春娟, 徐斌, 田文晶. 固态荧光光开关分子研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [13] | 唐子然, 孙浩, 朱亮亮. 光刺激响应型聚集诱导发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [14] | 张洁, 李楠, 赵娜. 聚集诱导发光分子纳米酶复合材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| [15] | 张继东, 杨垚, 张杰, 厍伟. 基于聚集诱导效应(AIE)-激发态分子内质子转移(ESIPT)效应的四苯乙烯荧光探针对Zn(II)检测研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1337-1342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||