有机化学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2554-2562.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403057 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
欧彦a, 蓝琳b, 王正雄b, 王志明a,b,*( ), 唐本忠a,b
), 唐本忠a,b
收稿日期:2024-03-31
修回日期:2024-05-17
发布日期:2024-06-07
基金资助:
Yan Oua, Lin Lanb, Zhengxiong Wangb, Zhiming Wanga,b( ), BenZhong Tanga,b
), BenZhong Tanga,b
Received:2024-03-31
Revised:2024-05-17
Published:2024-06-07
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
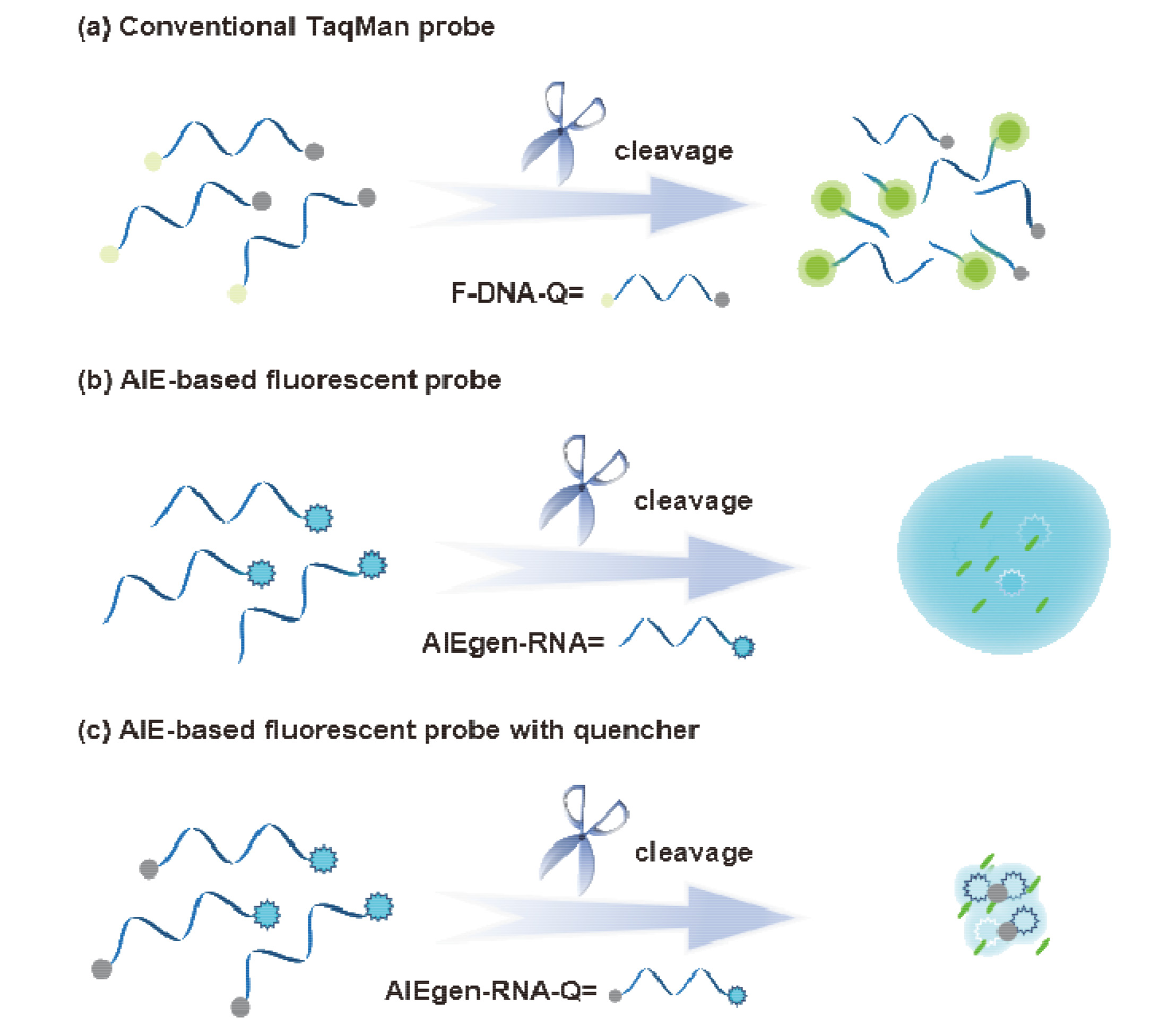
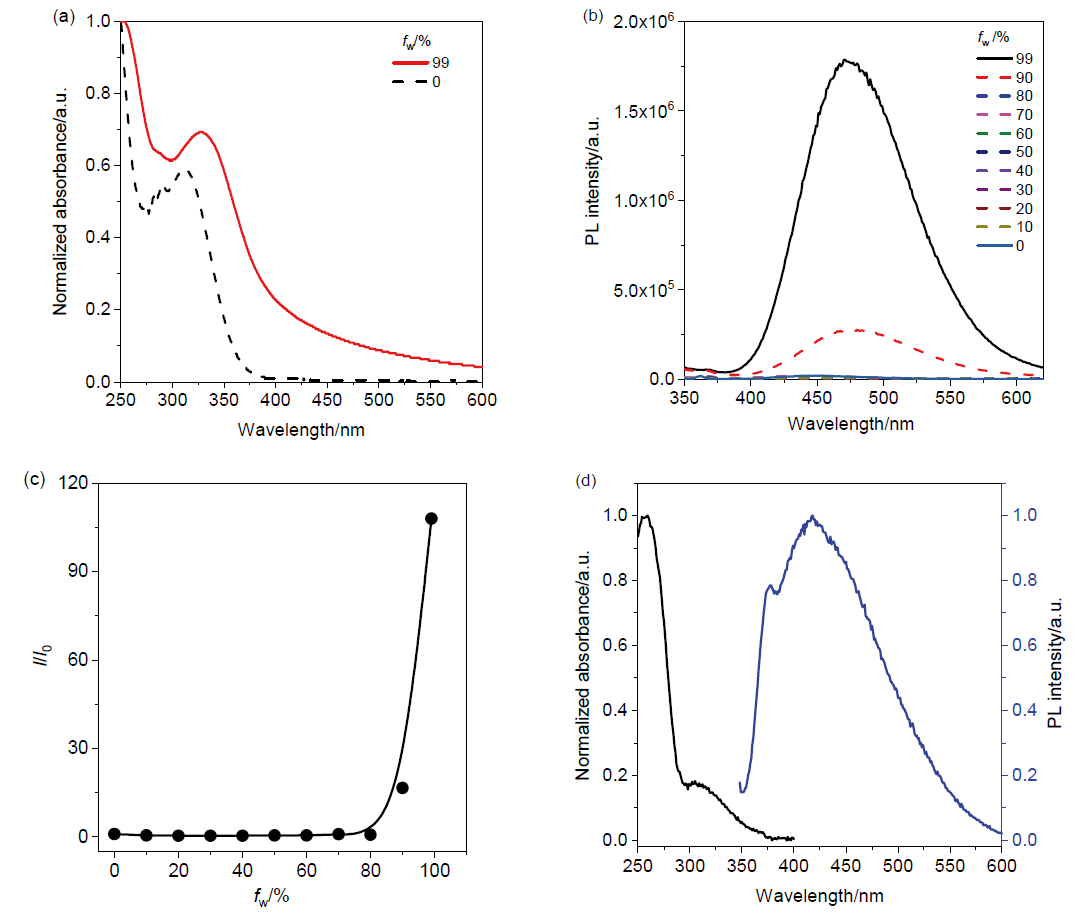
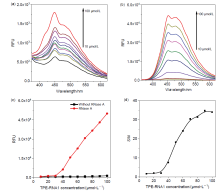
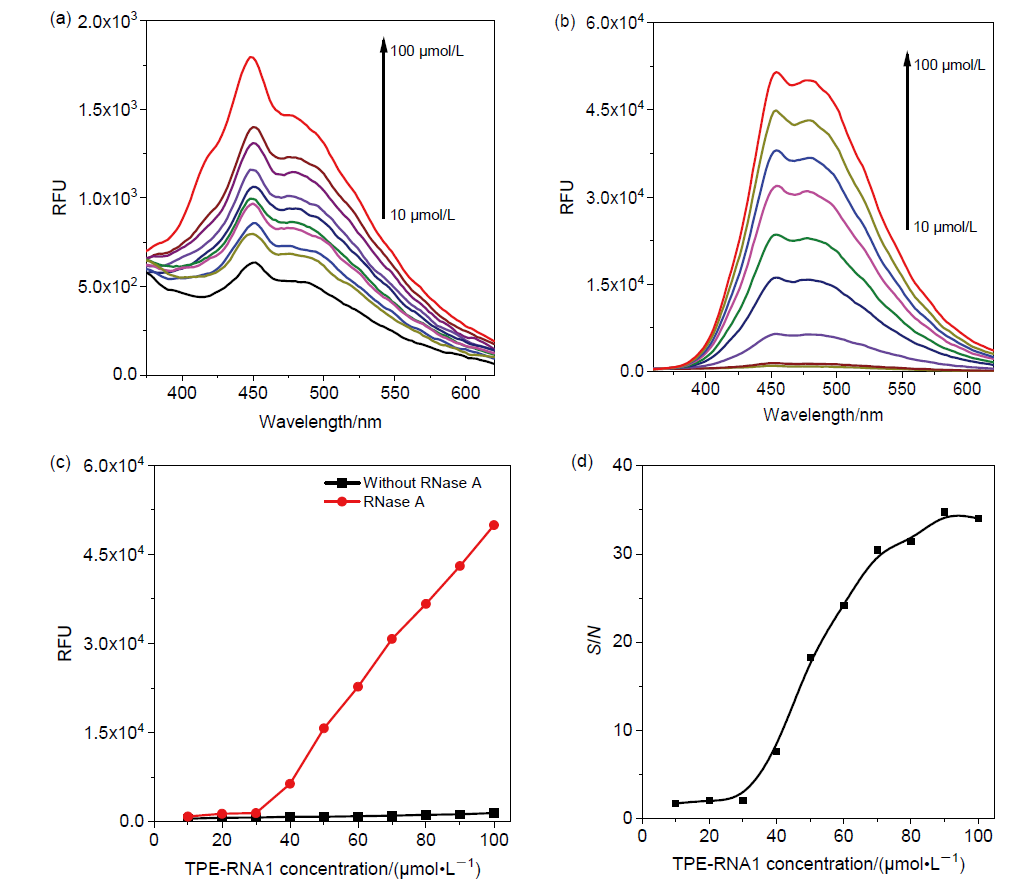
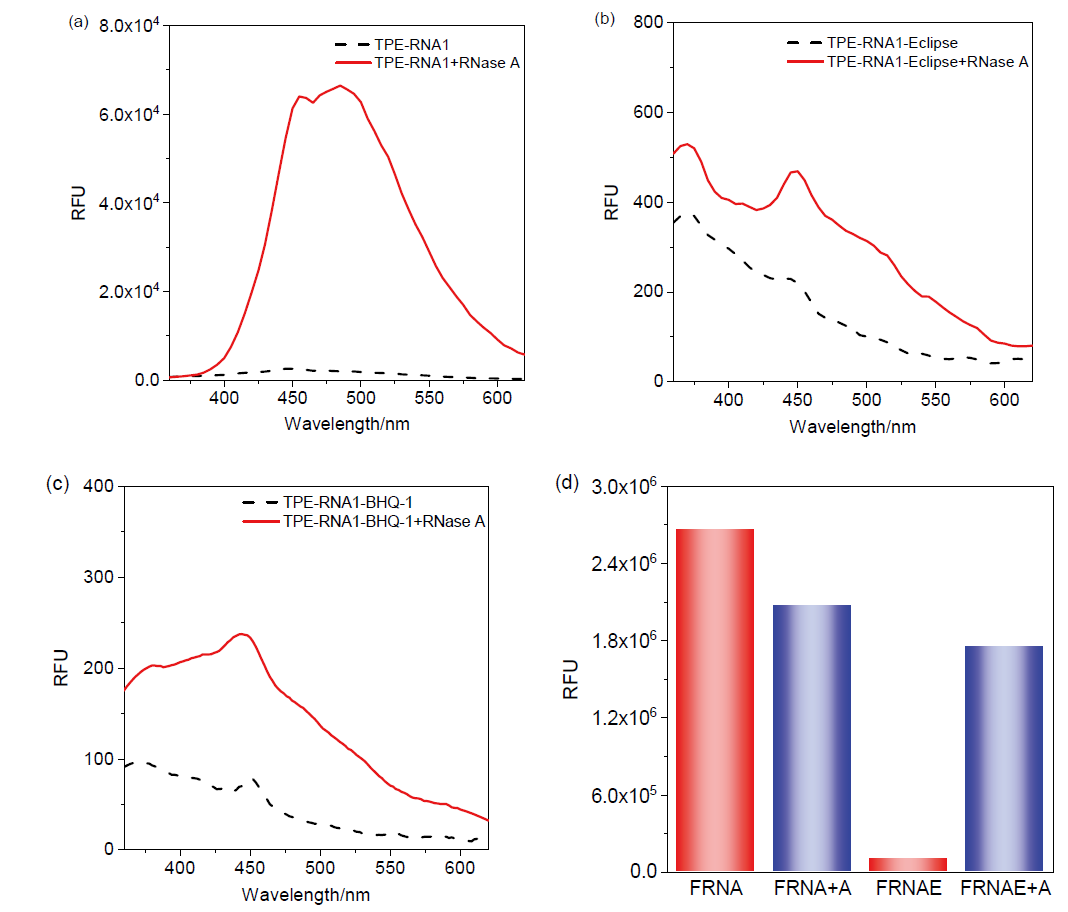
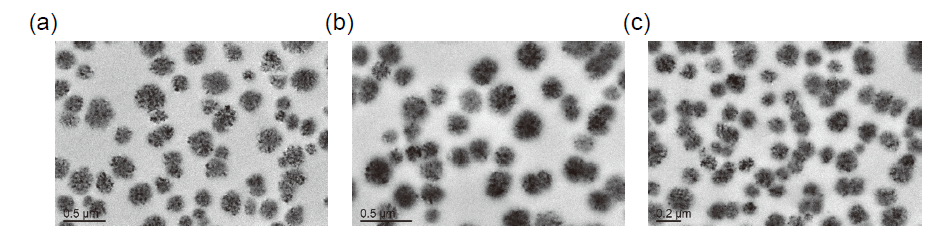
核酸检测是目前生物诊疗及医学分析领域最为精准的方法之一. 其中, 广泛应用的聚合酶链式反应(PCR)技术利用TaqMan探针的荧光信号输出, 可实现对微量目标序列的高灵敏定量分析. 本工作系统性地完成聚集诱导发光(AIE)基元——四苯乙烯(TPE)的亚磷酰胺修饰, 并将其设计和制备成一系列单标记特定RNA的核酸探针, 为后续高效率利用全自动核酸合成仪制备各类AIE探针奠定基础; 利用RNase A酶特异性切割TPE-RNA1探针中水溶性的RNA部分, 通过透射电镜、荧光光谱、质谱等表征证明酶切作用诱发的探针溶解能力变化且伴随着疏水聚集; 通过优化探针浓度、反应时间、序列长度等多个参数, 实现了AIE效应下荧光增强34.7倍. 采用AIE原理取代传统探针中荧光-淬灭基团的双标记策略, 扩展了核酸探针的设计策略, 并系统表征和探讨AIE型核酸探针的聚集过程, 旨在推动更高效、更灵敏的核酸检测探针, 拓展其在生物化学检测领域的应用.
欧彦, 蓝琳, 王正雄, 王志明, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光型核酸探针的制备及其核酸传感原理研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562.
Yan Ou, Lin Lan, Zhengxiong Wang, Zhiming Wang, BenZhong Tang. Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562.
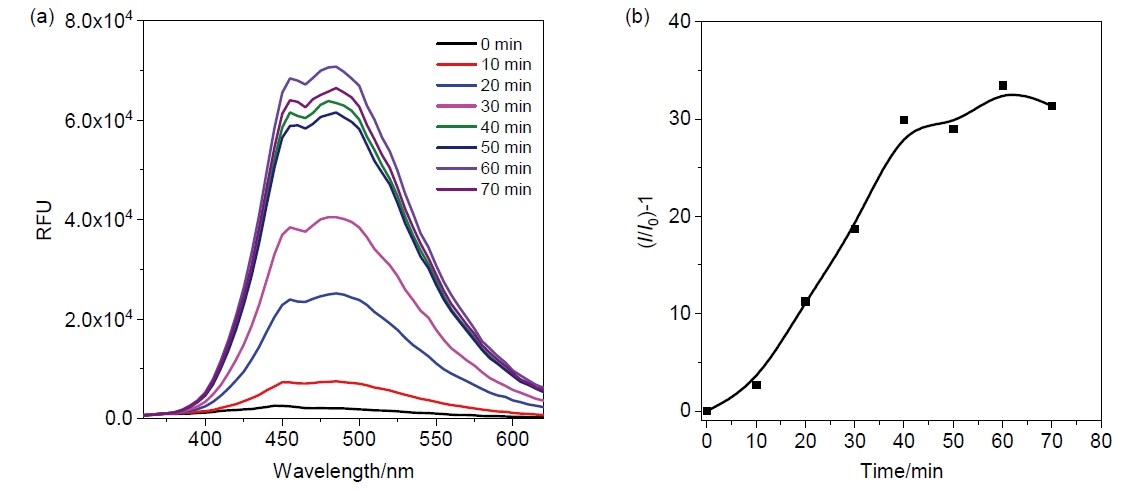
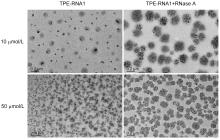

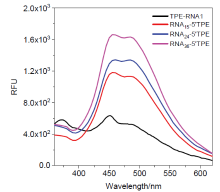
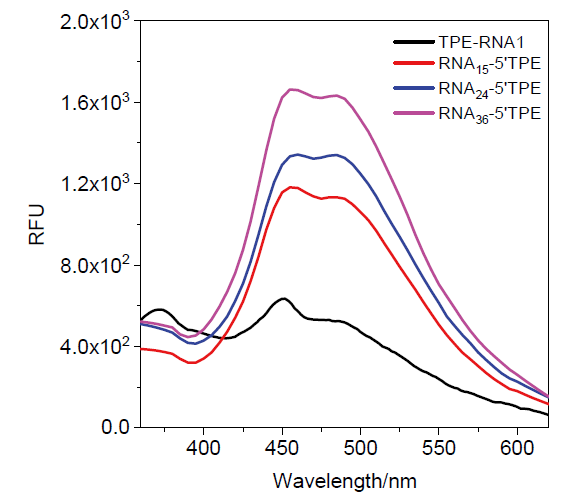

| [1] |
Hua, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, D.; Wang, R. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 183.
|
| [2] |
Samanta, D.; Ebrahimi, S. B.; Mirkin, C. A. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901743.
|
| [3] |
Tian, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B. Aggregat. 2021, 2, 133.
|
| [4] |
Quan, K.; Yi, C.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, K. TrA., Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115784.
|
| [5] |
Saccà, B.; Niemeyer, C. M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5910.
|
| [6] |
Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Innovatio. 2024, 5, 100538.
|
| [7] |
Fei, X.; Gu, Y. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1.
|
| [8] |
Tyagi, S.; Kramer, F. R. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 303.
doi: 10.1038/nbt0396-303 pmid: 9630890 |
| [9] |
Gibson, U. E.; Heid, C. A.; Williams, P. M. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 995.
doi: 10.1101/gr.6.10.995 pmid: 8908519 |
| [10] |
Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9736.
|
| [11] |
Tran, T.; Kostecki, R.; Catton, M.; Druce, J. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00360-18.
|
| [12] |
Tabatabaei, M. S.; Islam, R.; Ahmed, M. Anal. Chim. Act. 2021, 1143, 250.
|
| [13] |
Oxnard, G. R.; Paweletz, C. P.; Kuang, Y.; Mach, S. L.; O'Connell, A.; Messineo, M. M.; Luke, J. J.; Butaney, M.; Kirschmeier, P.; Jackman, D. M.; Jänne, P. A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1698.
|
| [14] |
Venkatesan, N.; Jun Seo, Y.; Hyean Kim, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 648.
doi: 10.1039/b705468h pmid: 18362974 |
| [15] |
Hwang, G. T.; Seo, Y. J.; Kim, B. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6528.
pmid: 15161261 |
| [16] |
Heinlein, T.; Knemeyer, J.-P.; Piestert, O.; Sauer, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7957.
|
| [17] |
Nazarenko, I.; Lowe, B.; Darfler, M.; Ikonomi, P.; Schuster, D.; Rashtchian, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e37.
|
| [18] |
Yang, C.; Abbas, F.; Rhouati, A.; Sun, Y.; Chu, X.; Cui, S.; Sun, B.; Xue, C. Biosensor. 2022, 12, 297.
|
| [19] |
Nikiforov, T. T. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 461, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.05.027 pmid: 24907506 |
| [20] |
Knemeyer, J.-P.; Marmé, N.; Sauer, M. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3717.
pmid: 10959954 |
| [21] |
Sobek, J.; Schlapbach, R. Molecule. 2020, 25, 5369.
|
| [22] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [23] |
Gui, Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249.
|
| [24] |
Lu, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 4075 (in Chinese).
|
|
(鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4075.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202305010 |
|
| [25] |
Xu, H.; Han, P.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050232 |
|
| [26] |
Feng, X.; Zhu, L.; Yue, B. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 647 (in Chinese).
|
|
(冯锡成, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 647.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010015 |
|
| [27] |
Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, G.; Niu, Z.; Wang, E. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2156 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵洋, 陈盼盼, 李高楠, 钮智刚, 王恩举, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2156.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210002 |
|
| [28] |
Zhang, Y.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202303022 |
|
| [29] |
Zhu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Ling, P.; Liu, B.; Ju, H.; Lei, J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2559.
|
| [30] |
Ma, K.; Zhang, F.; Sayyadi, N.; Chen, W.; Anwer, A. G.; Care, A.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.; Goldys, E. M.; Liu, G. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 320.
|
| [31] |
Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Min, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, J.; Yi, X.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8162.
|
| [32] |
Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Niu, N.; Shahzad, S. A.; Yu, C. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2398.
|
| [33] |
Lu, D.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Hu, M.; Liang, H.; Huan, S.; Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, W. Talant. 2017, 167, 550.
|
| [34] |
Min, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Hakeem, A.; Zheng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, B. Z.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2015, 7, 16813.
|
| [35] |
Li, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10135.
|
| [36] |
Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, F.; Chao, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207845.
|
| [37] |
Beaucage, S. L.; Caruthers, M. H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 1859.
|
| [38] |
Krotz, A. H.; Rentel, C.; Gorman, D.; Olsen, P.; Gaus, H. J.; McArdle, J. V.; Scozzari, A. N. Nucleoside., Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 767.
|
| [39] |
Takamoto, K.; He, Q.; Morris, S.; Chance, M. R.; Brenowitz, M. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2002, 9, 928.
|
| [1] | 沈钇灼, 罗康为, 徐清洋, 张鉴予, 孙景志, 张浩可, 唐本忠. 弱作用基有机发光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [2] | 何俊初, 伍俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金. 以二苯基硅杂吖啶为电子给体的蓝色聚集诱导延迟荧光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [3] | 谢志鑫, 黎少玲, 刘威, 严楷, 蒋涛, 刘一苇, Md. Monarul Islam, 冯星. 窄化芘基发光分子半峰宽的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [4] | 孟子翔, 田秀梅, 张天富. 聚集诱导发光材料在肿瘤光治疗应用中的最新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [5] | 黄伟庚, 高翼亭, 孙妍, 燕鼎元, 王东, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光材料用于肿瘤光学诊疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [6] | 唐子然, 孙浩, 朱亮亮. 光刺激响应型聚集诱导发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [7] | 张洁, 李楠, 赵娜. 聚集诱导发光分子纳米酶复合材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| [8] | 黄凯航, 尹理, 姜青云, 汪乾, 石光, 许炳佳. 具有聚集诱导发光性质的高效热激活延迟荧光材料用于脂滴成像[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [9] | 杨玉杰, 曹微, 于际凯, 张志霞, 徐莉, 王华. 给体-受体(D-A)型苯基环八四噻吩的合成及其聚集诱导发光与高压发光性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [10] | 苏小龙, 李健鹏, 刘孟鑫, 邹莉, 杨得锁, 冯海涛. 四苯乙烯酰胺类化合物的合成及其高灵敏度、高选择性识别Cu2+[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [11] | 胡甲松, 李春娟, 徐斌, 田文晶. 固态荧光光开关分子研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [12] | 宫清宝, 吕翔, 于长江, 李婉婉, 赵全胜, 焦莉娟, 郝二红. 聚集诱导发光活性氟硼吡啶肼醛腙染料的合成、晶体结构及光学性质[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [13] | 王源浩, 孙钰凯, 刘昱迒, 张照明, 颜徐州. 基于四苯乙烯的柔性发光材料的构筑及性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544. |
| [14] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [15] | 张继东, 杨垚, 张杰, 厍伟. 基于聚集诱导效应(AIE)-激发态分子内质子转移(ESIPT)效应的四苯乙烯荧光探针对Zn(II)检测研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1337-1342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||