Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2538-2544.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202403051 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
王源浩a, 孙钰凯a, 刘昱迒a,b, 张照明a,*( ), 颜徐州a,b,*(
), 颜徐州a,b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-30
修回日期:2024-05-23
发布日期:2024-06-13
作者简介:基金资助:
Yuanhao Wanga, Yukai Suna, Yuhang Liua,b, Zhaoming Zhanga( ), Xuzhou Yana,b(
), Xuzhou Yana,b( )
)
Received:2024-03-30
Revised:2024-05-23
Published:2024-06-13
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:Share
Yuanhao Wang, Yukai Sun, Yuhang Liu, Zhaoming Zhang, Xuzhou Yan. Construction and Properties of Flexible Light-Emitting Materials Based on Tetraphenylethylene[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544.
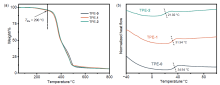
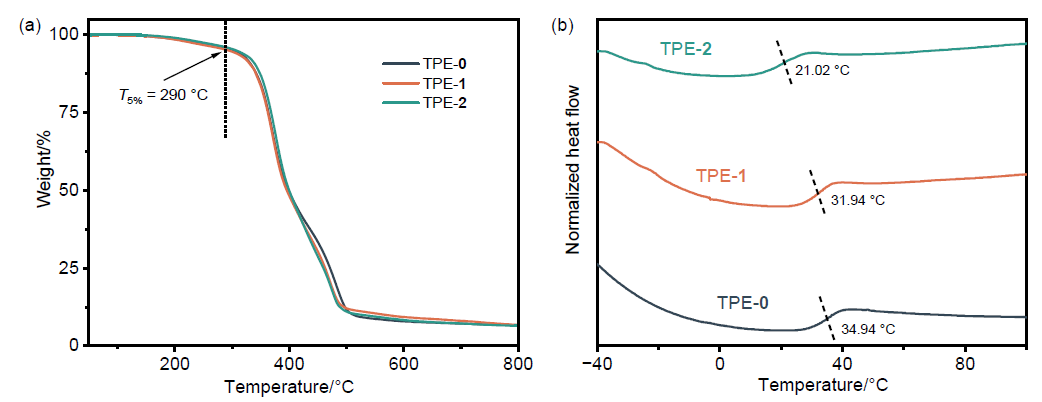
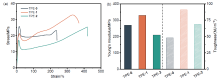

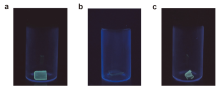

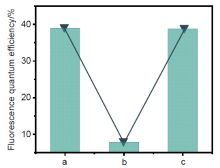
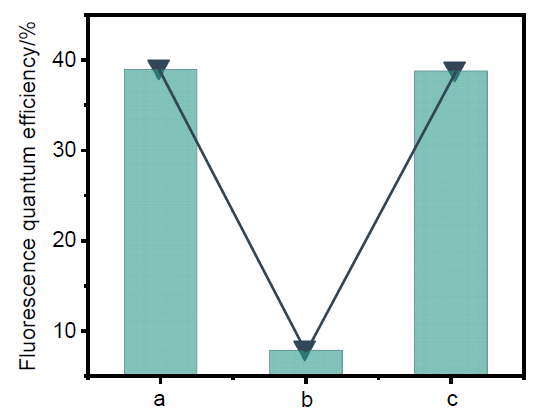
| [1] |
Jeon, K. H.; Park, J. W. Macromolecule. 2022, 55, 8311.
|
| [2] |
Jang, B.; Won, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113299.
|
| [3] |
Lee, Y.; Chung, J. W.; Lee, G. H.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Bae, C.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, S.; Cho, H.; Kang, S.-G.; Jung, J. Y.; Lee, D.-W.; Gam, S.; Hahm, S. G.; Kuzumoto, Y.; Kim, S. J.; Bao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yun, Y.; Kim, S. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9180. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg9180
|
| [4] |
Zhang, P.; Lei, I. M.; Chen, G. D.; Lin, J. S.; Chen, X. M.; Zhang, J. J.; Cai, C. C.; Liang, X. Y.; Liu, J. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4775.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32126-1 pmid: 35999212 |
| [5] |
Lee, Y.; Kim, D. S.; Jin, S. W.; Lee, H.; Jeong, Y. R.; You, I.; Zi, G.; Ha, J. S. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130858.
|
| [6] |
Hong, S. Y.; Lee, Y. H.; Park, H.; Jin, S. W.; Jeong, Y. R.; Yun, J.; You, I.; Zi, G.; Ha, J. S. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 930.
|
| [7] |
Xu, H.; Han, P. B.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 1420 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1420.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050232 |
|
| [8] |
Liu, B.; Chen, B. K. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 929 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘斌, 陈磅宽, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 929.)
doi: 10.6023/A22030122 |
|
| [9] |
Ou, X. Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, B. L.; Zan, J.; Wu, Q. X.; Hong, Z. Z.; Xie, L. L.; Bian, H. Y.; Yi, Z. G.; Chen, X. F.; Wu, Y. M.; Song, X. R.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. S.; Yang, H. H.; Liu, X. G. Natur. 2021, 590, 410.
|
| [10] |
Xie, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. L.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, S. T.; Yun, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, C. B.; Tian, F.; Su, M.; Li, F. Y. ACS Nan. 2022, 16, 20094.
|
| [11] |
Zhao, R. Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Fan, W. R.; Zhu, Q. X.; Ma, H. H.; Wang, X. W.; Wang, Z. H.; Huang, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 26532.
|
| [12] |
Zhang, H. Y.; Jia, S. X.; Yin, D.; Feng, J. Chin. J. Lumin. 2023, 44, 1606 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张浩洋, 贾士鑫, 银达, 冯晶, 发光学报, 2023, 44, 1606.)
|
|
| [13] |
Liu, S. J.; Tang, B. Z. Acta Polym. Sinic. 2021, 52, 456 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘顺杰, 唐本忠, 高分子学报, 2021, 52, 456.)
|
|
| [14] |
Han, P. B.; Qin, A. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2254 (in Chinese).
|
|
(韩鹏博, 秦安军, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2254.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202300032 |
|
| [15] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [16] |
Hong, Y. N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4332.
|
| [17] |
Liu, L.; Hao, T. T.; Wu, W. H.; Yang, C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2189 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘铃, 浩涛涛, 伍晚花, 杨成, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2189.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210020 |
|
| [18] |
Wu, J. S.; Liu, W. M.; Ge, J. C.; Zhang, H. Y.; Wang, P. F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3483.
|
| [19] |
Mei, J.; Hong, Y. N.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, Y. H.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429.
|
| [20] |
Cai, Y.; Du, L.; Samedov, K.; Gu, X.; Qi, F.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Patrick, B. O.; Yan, Z. P.; Jiang, X. F., Zhang, H. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Phillips, D. L.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4662.
|
| [21] |
Qiu, Z.; Chu, E. K. K.; Jiang, M.; Gui, C.; Xie, N.; Qin, W.; Alam, P.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2017, 50, 7620.
|
| [22] |
Han, T.; Gui, C.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Jiang, M. J.; Xie, N.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2017, 50, 5807.
|
| [23] |
Chi, W. W.; Yuan, W.; Du, J.; Han, T.; Li, H. K.; Li, Y. F.; Tang, B. Z. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800604
|
| [24] |
Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, X.; Albouy, P. A.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, M. H. Mater. Chem. Fron.. 2018, 2, 2245.
|
| [25] |
Lu, H. M.; Ma, L. M. C.; Ma, H. C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 4075 (in Chinese).
|
|
(鲁会名, 马拉毛草, 马恒昌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4075.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202305010 |
|
| [26] |
Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Q.; Gao, L. C.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3165.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11144-6 pmid: 31320646 |
| [27] |
Khorloo, M.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, S.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhu, M.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Nan. 2021, 15, 1397.
|
| [28] |
Liu, G. J.; Feng, G. L.; Li, X. F.; Liu, Y. C.; Zhou, W.; Ji, Y. M.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, G. W. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 52, 880 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘广建, 冯改丽, 李夏芬, 刘怡晨, 周微, 及燕铭, 张媛, 邢国文, 中国科学:化学, 2022, 52, 880.)
|
|
| [29] |
Zhao, Y. Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. R.; Zhu, L. P.; Zhou, Y. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2024, 82, 265 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵玉强, 张霞, 杨芸如, 朱立平, 周莹, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 265.)
doi: 10.6023/A23100457 |
|
| [30] |
Zeng, C. Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, B. Q.; Fang, W. Y.; Zhao, K. Q.; Donnio, B. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2023, 81, 469 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曾崇洋, 胡平, 汪必琴, 方文彦, 赵可清, Donnio, B. 化学学报, 2023, 81, 469.)
doi: 10.6023/A23010006 |
|
| [31] |
Feng, X. C.; Zhu, L. L.; Yue, B. B. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 80, 647 (in Chinese).
|
|
(冯锡成, 朱亮亮, 岳兵兵, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 647.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010015 |
|
| [32] |
Zeng, C. Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, B. Q.; Fang, W. Y.; Zhao, K. Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3287 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曾崇洋, 胡平, 汪必琴, 方文彦, 赵可清, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3287.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202302025 |
|
| [33] |
Zhang, L. L.; Wang, Y. Y.; Zhu, G. N.; Dai, W. B.; Zhao, Z. X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhi, J. G.; Dong, Y. P. Acta Chim. Sinic. 2022, 80, 282 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张璐璐, 王媛媛, 朱贵楠, 戴文博, 赵紫璇, 赵盈, 支俊格, 董宇平, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 282.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120556 |
|
| [34] |
Wang, Y. T.; Liu, X. Q.; Li, H. K.; Liu, X. D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2393.
|
| [35] |
Guo, X. M.; Yuan, P. S.; Qiao, X. F.; Yang, D. Z.; Dai, Y. F.; Sun, Q.; Qin, A. J.; Tang, B. Z.; Ma, D. G. Adv. Funct. Mate.. 2020, 30, 1908704.
|
| [36] |
Liu, Y. H.; Guo, Z. W.; Guo, Y. C.; Li, G. F.; Yang, S. B.; Yan, X. Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. B. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108531.
|
| [37] |
Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. M.; Zhang, J. Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 870.
|
| [38] |
Jiang, Y.; Ma, J. H.; Ran, Z. Y.; Zhong, H. Q.; Zhang, D. H.; Hadjichristidis, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208516.
|
| [39] |
Jiang, Y.; Ran, Z. Y.; Wu, Y. F.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, D. H. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 12423.
|
| [40] |
Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. M.; Wang, C. Y.; Yan, X. Z. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 41.
|
| [41] |
Yu, P.; Huang, Q. R.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W.; Jia, Z. C.; Wang, H. Y.; Ma, J. J.; Wang, C. Y.; Yan, X. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 516.
|
| [42] |
Ma, S. Y.; Zhang, X. L.; Gong, L.; Zhan, S. P.; Hou, W. M.; Lu, C. L. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 566 (in Chinese).
|
|
(马思阳, 张晓琳, 宫蕾, 詹世平, 侯维敏, 卢春兰, 材料导报, 2021, 35, 566.)
|
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Y. H.; Nie, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. F.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Y. P.; Chen, W. C.; Zhao, Z. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 3876 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张越华, 聂飞, 周路, 王晓烽, 刘源, 霍延平, 陈文铖, 赵祖金, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 3876.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202303022 |
|
| [44] |
Gui, Y. X.; Chen, K. Y.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y. H.; Luo, W. S.; Zhu, D. X.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, D. Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1249.
|
| [45] |
Chen, Y. J.; Pu, M. Q.; Wu, L. T.; Sun, X. L.; Wan, W. M. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1705.
|
| [46] |
Zhang, Z. M.; Zhao, J.; Yan, X. Z. Acta Polym. Sinic. 2022, 53, 691 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张照明, 赵骏, 颜徐州, 高分子学报, 2022, 53, 691.)
|
|
| [47] |
Wang, Y. M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. M.; Zhao, J.; Bai, R. X.; Liu, Y. H.; Zhang, X. H.; Yan, X. Z. Aggregat. 2022, 3, e206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.206.
|
| [1] | Yizhuo Shen, Kangwei Luo, Qingyang Xu, Jianyu Zhang, JingZhi Sun, Haoke Zhang, BenZhong Tang. Weak Interaction-Based Organic Luminescent Materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [2] | Junchu He, Junqi Wu, Jianghui Wang, Jingwen Xu, BenZhong Tang, Zujin Zhao. Blue Aggregation-Induced Delayed Fluorescence Materials with 5,10-Dihydrodibenzo[b,e][1,4]azasiline as Donor [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [3] | Zhixin Xie, Shaoling Li, Wei Liu, Kai Yan, Tao Jiang, Yiwei Liu, Md. Monarul Islam, Xing Feng. An Efficient Approach to Narrow the Emission Band of Pyrene-Based Emitters [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [4] | Zixiang Meng, Xiumei Tian, Tianfu Zhang. Recent Progress of Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials in Tumor Phototherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [5] | Weigeng Huang, Yiting Gao, Yan Sun, Dingyuan Yan, Dong Wang, BenZhong Tang. Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials for Tumor Phototheranostics [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [6] | Qingbao Gong, Xiang Lü, Changjiang Yu, Wanwan Li, Quansheng Zhao, Lijuan Jiao, Erhong Hao. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Active Fluoroboronated Pyridylhydrazinyl Aldehyde Hydrozone Dyes: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Optical Properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [7] | Hanyu Jia, Yuewen Yu, Guangxue Feng, BenZhong Tang. Construction of Type I Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy via Photoinduced Electron Transfer Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [8] | Kaihang Huang, Li Yin, Qingyun Jiang, Qian Wang, Guang Shi, Bingjia Xu. Efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission for Lipid Droplet Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [9] | Yujie Yang, Wei Cao, Jikai Yu, Zhixia Zhang, Li Xu, Hua Wang. Synthesis of Donor-Acceptor (D-A) Typed Phenylcyclooctatetrathiophenes and Their Performances on Aggregation Induced Emission and High Pressure Luminescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [10] | Xiaolong Su, Jianpeng Li, Mengxin Liu, Li Zou, Desuo Yang, Haitao Feng. Synthesis of Tetraphenylethylene Based Amides for Detection of Copper(II) Ion with High Sensitivity and Selectivity [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [11] | Haosen Chang, Liming Yang, Guan Wang, Xinggui Gu. Synthesis of Anthraquinone Derivate with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristic for Fingerprint Development [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2571-2580. |
| [12] | Yan Ou, Lin Lan, Zhengxiong Wang, Zhiming Wang, BenZhong Tang. Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562. |
| [13] | Ziran Tang, Hao Sun, Liangliang Zhu. Research Progress of Photoresponsive Photoluminescent Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [14] | Jie Zhang, Nan Li, Na Zhao. Recent Progress of Aggregation-Induced Emission Molecule Nanozyme Composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| [15] | Jidong Zhang, Yao Yang, Jie Zhang, Wei She. Detection of Zn(II) by Tetraphenylethyene Fluorescent Probe Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE)-Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(4): 1337-1342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||