Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2453-2468.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202404041 Previous Articles Next Articles
REVIEWS
沈钇灼a, 罗康为a, 徐清洋a,b,c, 张鉴予d, 孙景志a,c, 张浩可a,b,c,*( ), 唐本忠a,e,*(
), 唐本忠a,e,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-29
修回日期:2024-05-30
发布日期:2024-06-24
作者简介:基金资助:
Yizhuo Shena, Kangwei Luoa, Qingyang Xua,b,c, Jianyu Zhangd, JingZhi Suna,c, Haoke Zhanga,b,c( ), BenZhong Tanga,e(
), BenZhong Tanga,e( )
)
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-05-30
Published:2024-06-24
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:Share
Yizhuo Shen, Kangwei Luo, Qingyang Xu, Jianyu Zhang, JingZhi Sun, Haoke Zhang, BenZhong Tang. Weak Interaction-Based Organic Luminescent Materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468.


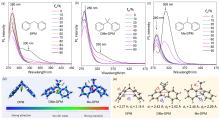

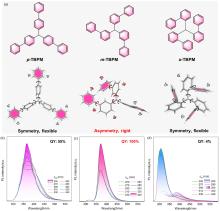

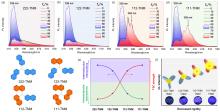

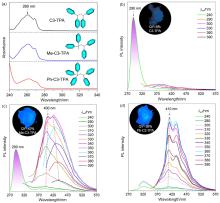

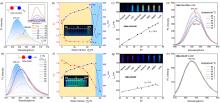

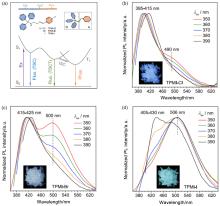



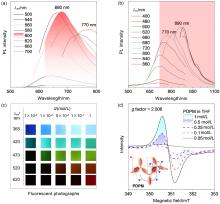

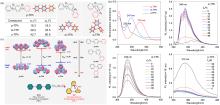

| [1] |
Hwang, J.; Nagaraju, P.; Cho, M. J.; Choi, D. H. Aggregat. 2023, 4, e199.
|
| [2] |
Bai, T.; Zhang, Y. S.; Wang, L.; Yan, H. X.; Zhou, W. H. Aggregat. 2023, 4, e267.
|
| [3] |
Wen, Q.; Cai, Q. Q.; Fu, P.; Chang, D.; Xu, X. Y.; Wen, T. J.; Wu, G. P.; Zhu, W. P.; Wan, L. S.; Zhang, C. J.; Zhang, X. H.; Jin, Q.; Wu, Z. L.; Gao, C.; Zhang, H. K.; Huang, N.; Li, C. Z.; Li, H. Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107592.
|
| [4] |
Zhang, J.; He, B.; Hu, Y.; Alam, P.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008071.
|
| [5] |
Yang, J.; Fang, M.; Li, Z. Aggregat. 2020, 1, 6.
|
| [6] |
Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Shen, H.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. J. A. P. Adv. Photonic. 2022, 4, 014001.
|
| [7] |
Saal, F.; Zhang, F.; Holzapfel, M.; Stolte, M.; Michail, E.; Moos, M.; Schmiedel, A.; Krause, A.-M.; Lambert, C.; Würthner, F.; Ravat, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21298.
|
| [8] |
Li, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Shen, P.; Song, S.; Tang, B. Z.; Zhao, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8073.
|
| [9] |
‘conjugated system’ in IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 3rd ed., International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2006, https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.C01267.
|
| [10] |
Wang, Y.; Bin, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W. Z. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, e1800528.
|
| [11] |
Lee, W. I.; Bae, Y.; Bard, A. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8358.
|
| [12] |
Larson, C. L.; Tucker, S. A. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 679.
|
| [13] |
Gong, Y.; Tan, Y.; Mei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 1178.
|
| [14] |
Dou, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Tan, Y.; He, X.; Lu, P.; Sui, K.; Tang, B. Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W. Z. Biomacromolecule. 2018, 19, 2014.
|
| [15] |
Gu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Su, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Niu, G.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Ni, X.-L.; Sun, J.; Qin, A.; Lam, Jacky, W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6497.
|
| [16] |
Cai, X.-M.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1773.
|
| [17] |
Liu, Y.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Carter, G. C.; Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Grainger, L. S.; Miao, K.; Fares, M.; Hoelzel, C. A.; Yennawar, H. P.; Ning, G.; Du, M.; Bai, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7381.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b02176 pmid: 29883112 |
| [18] |
Xing, C. M.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Qin, A.; Dong, Y.; Haussler, M.; Yang, W. T.; Tang, B. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 96, 418.
|
| [19] |
Chu, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, B.; Yu, Q.-L.; Zhang, C.-J.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.-H.; Tang, B. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 15286.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05948 pmid: 35796412 |
| [20] |
Chu, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114117.
|
| [21] |
Chu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J. Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 10889.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c01568 pmid: 38584517 |
| [22] |
Chu, B.; Liu, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z.; Zhang, X.-H. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 366.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44505-3 pmid: 38191597 |
| [23] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Kang, M.; Li, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1990.
|
| [24] |
He, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Kei, K. H. S.; Qin, A.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004299.
|
| [25] |
Chen, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Dong, W.; Qiao, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface. 2023, 15, 23824.
|
| [26] |
Guo, L.; Yan, L.; He, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, B. Z.; Yan, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204383.
|
| [27] |
Ji, X.; Tian, W.; Jin, K.; Diao, H.; Huang, X.; Song, G.; Zhang, J. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3717.
|
| [28] |
Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, H. Smal. 2023, 19, e2302095.
|
| [29] |
Deng, J. W.; Jia, H. Y.; Xie, W. D.; Wu, H. R.; Li, J. Y.; Wang, H. L. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2100425.
|
| [30] |
Shang, C.; Wei, N.; Zhuo, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8082.
|
| [31] |
Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; Kong, L.; Yu, S.; Zhao, C.; Chen, C. Biomacromolecule. 2024, 25, 1897.
|
| [32] |
Liu, K.; Han, P.; Yu, S.; Wu, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C. Macromolecule. 2022, 55, 8599.
|
| [33] |
Du, H.; Zhao, W.; Xia, Y.; Xie, S.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Y. Q.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X. Aggregat. 2022, 4, e276.
|
| [34] |
Li, C.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X. Polymer. 2022, 14, 4050.
|
| [35] |
Ren, Y.; Dai, W.; Guo, S.; Dong, L.; Huang, S.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Hao, N.; Li, L.; Cai, Z.; Dong, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1361.
|
| [36] |
Shi, C. Y.; He, D. D.; Wang, B. S.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Qu, D. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214422.
|
| [37] |
Zhang, Q.; Huang, C.; Huang, S.; Xie, H.; Huang, Q.; Guo, M. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 2522.
|
| [38] |
Xu, A.; Liu, H.; Yi, G.; Feng, N.; Li, H. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 3558.
|
| [39] |
Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhao, B.; Deng, J. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 530.
|
| [40] |
Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Shi, S.; Yuan, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Su, S.; Loos, J.; Liu, K.; Wen, T. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 2788.
|
| [41] |
Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.; Tang, B. Z.; Mao, S. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 409.
|
| [42] |
Zhou, M.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 126, 15485.
|
| [43] |
Wang, D.; Imae, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13204.
|
| [44] |
Zhao, E.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Meng, L. M.; Hong, Y.; Deng, H. Q.; Bai, G. X.; Huang, X. H.; Hao, J. H.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2015, 48, 64.
|
| [45] |
Zhang, H. K.; Zhao, Z.; McGonigal, P. R.; Ye, R. Q.; Liu, S. J.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Yuan, W. Z.; Xie, J. P.; Rogach, A. L.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Toda. 2020, 32, 275.
|
| [46] |
Liao, P. L.; Huang, J. B.; Yan, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 6693.
|
| [47] |
Tang, S.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, W.; Yuan, W. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12616.
|
| [48] |
Tomalia, D. A.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B.; Johnson, K. A. M.; Brinkman, H. F.; Janaszewska, A.; Hedstrand, D. M. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 35.
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.09.004 |
| [49] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Z.; Tang, B. Z. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2127.
|
| [50] |
Zhang, Z. M.; Yan, W.; Dang, D. F.; Zhang, H. K.; Sun, J. Z.; Tang, B. Z. Cell. Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100716.
|
| [51] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Z.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 713.
|
| [52] |
Bao, J.; Tong, C.; He, M.; Zhang, H. Luminescenc. 2024, 39, e4594.
|
| [53] |
Miller, G. R.; Yankowsky, A. W.; Grim, S. O. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 3185.
|
| [54] |
Gribble, G. W.; Douglas, J. R., Jr J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 5764.
|
| [55] |
Heilbronner, E.; Muszkat, K. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 3818.
|
| [56] |
Hoffmann, R. Acc. Chem. Res. 1971, 4, 1.
|
| [57] |
Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; Xie, N.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Leung, N. L. C.; Niu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wong, K. S.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Qin, A.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16264.
|
| [58] |
Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. JACS A. 2021, 1, 1805.
|
| [59] |
Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, S.; Wong, K. S.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4690.
|
| [60] |
Chen, L.; Wang, Y.-H.; He, B.; Nie, H.; Hu, R.; Huang, F.; Qin, A.; Zhou, X.S.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4231.
|
| [61] |
Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Matte. 2023, 6, 3702.
|
| [62] |
Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Turley, A. T.; Wang, L.; McGonigal, P. R.; Tu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001457.
|
| [63] |
Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9888.
|
| [64] |
Xu, S. D.; Duan, Y. K.; Liu, B. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903530.
|
| [65] |
Yamaguchi, Y.; Matsubara, Y.; Ochi, T.; Wakamiya, T.; Yoshida, Z.-i. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13867.
|
| [66] |
Braendle, A.; Perevedentsev, A.; Cheetham, N. J.; Stavrinou, P. N.; Schachner, J. A.; Mösch-Zanetti, N. C.; Niederberger, M.; Caseri, W. R. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 707.
|
| [67] |
Wang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, J. Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318245.
|
| [68] |
Tu, W.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Z.; Tang, B. Z. Smart Mol. 2023, 1, e20220006.
|
| [69] |
Taniguchi, M.; Lindsey, J. S. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 290.
doi: 10.1111/php.12860 pmid: 29166537 |
| [70] |
Zhang, H.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wan, Q.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Phillips, D. L.; Tang, B. Z. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 7077.
|
| [71] |
Sturala, J.; Etherington, M. K.; Bismillah, A. N.; Higginbotham, H. F.; Trewby, W.; Aguilar, J. A.; Bromley, E. H. C.; Avestro, A.-J.; Monkman, A. P.; McGonigal, P. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17882.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b08570 pmid: 29151342 |
| [72] |
Turley, A. T.; Saha, P. K.; Danos, A.; Bismillah, A. N.; Monkman, A. P.; Yufit, D. S.; Curchod, B. F. E.; Etherington, M. K.; McGonigal, P. R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202193.
|
| [73] |
Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tu, W.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Sun, J. Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. ChemRxi. 2024, 10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-692m1.
|
| [74] |
Hatakeyama, T.; Shiren, K.; Nakajima, K.; Nomura, S.; Nakatsuka, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Ni, J.; Ono, Y.; Ikuta, T. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2777.
|
| [75] |
Xu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. ChemRxi. 2023, 10.26434/chemrxiv-2023-pj5cn.
|
| [76] |
Najbar, J.; Turek, A. M. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 73, 536.
|
| [77] |
Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 21104.
|
| [78] |
Hestand, N. J.; Spano, F. C. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7069.
|
| [79] |
Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Z.; Huang, F.; Tang, B. Z. CCS Chem. 2023, 5, 2832.
|
| [80] |
Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 1.
|
| [81] |
Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Zeng, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 9565.
|
| [82] |
Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202381.
|
| [83] |
Lu, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 3012.
|
| [84] |
Xie, Y.; Tu, W.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Macromolecule. 2023, 56, 10082.
|
| [85] |
Shao, S. Y.; Wang, L. X. Aggregat. 2020, 1, 45.
|
| [86] |
Jiang, X.; Tao, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Wei, P. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 15928.
|
| [87] |
Hu, R.; Lager, E.; Aguilar-Aguilar, A.; Liu, J.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Zhong, Y.; Wong, K. S.; Peña-Cabrera, E.; Tang, B. Z. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 15845.
|
| [88] |
Tu, W.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 10.1007/s11426-024-2015-9.
|
| [89] |
Zhang, J.; Alam, P.; Zhang, S.; Shen, H.; Hu, L.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Sun, J.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3492.
|
| [90] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Chu, B.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. H.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306762.
|
| [91] |
Shi, Q.-X.; Xiao, H.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Li, D.-S.; Su, M.; Sun, X.-L.; Bao, H.; Wan, W.-M. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 4524.
|
| [92] |
Jing, Y.-N.; Li, S.-S.; Su, M.; Bao, H.; Wan, W.-M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 168398.
|
| [93] |
Ai, X.; Evans, E. W.; Dong, S.; Gillett, A. J.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Hele, T. J. H.; Friend, R. H.; Li, F. Natur. 2018, 563, 536.
|
| [94] |
Wang, Z.; Zou, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Chan, C. C. S.; Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Zeng, Z.; Wong, K. S.; Sherrill, C. D.; Ye, R.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 2564.
|
| [95] |
Montgomery, L. K.; Huffman, J. C.; Jurczak, E. A.; Grendze, M. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6004.
doi: 10.1021/ja00279a056 pmid: 22175364 |
| [96] |
Liu, Z.; Deeth, R. J.; Butler, J. S.; Habtemariam, A.; Newton, M. E.; Sadler, P. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4194.
|
| [97] |
Cook, A. R.; Curtiss, L. A.; Miller, J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 5729.
|
| [98] |
Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chu, B.; Liu, X.; Tu, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202403827.
|
| [99] |
Dixon, J. M.; Taniguchi, M.; Lindsey, J. S. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 81, 212.
|
| [100] |
Zhang, H. K.; Liu, J. K.; Du, L. L.; Ma, C.; Leung, N. L. C.; Niu, Y. L.; Qin, A. J.; Sun, J. Z.; Peng, Q.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Wong, K. S.; Phillip, D. L.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 1143.
|
| [101] |
Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Blancafort, L.; Tang, B. Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7901.
|
| [102] |
Zhao, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23726.
|
| [103] |
Han, Y. Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, S.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Z.; Sessler, J. L.; Huang, F. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 1739.
|
| [104] |
Zhang, Z. T.; Xiong, Z. P.; Chu, B.; Zhang, Z. M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, H. K.; Zhang, X. H.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregat. 2022, 3, e278.
|
| [105] |
Liu, X.; Chu, B.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, B.; Tu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 1579.
|
| [1] | Junchu He, Junqi Wu, Jianghui Wang, Jingwen Xu, BenZhong Tang, Zujin Zhao. Blue Aggregation-Induced Delayed Fluorescence Materials with 5,10-Dihydrodibenzo[b,e][1,4]azasiline as Donor [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [2] | Zhixin Xie, Shaoling Li, Wei Liu, Kai Yan, Tao Jiang, Yiwei Liu, Md. Monarul Islam, Xing Feng. An Efficient Approach to Narrow the Emission Band of Pyrene-Based Emitters [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [3] | Zixiang Meng, Xiumei Tian, Tianfu Zhang. Recent Progress of Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials in Tumor Phototherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [4] | Weigeng Huang, Yiting Gao, Yan Sun, Dingyuan Yan, Dong Wang, BenZhong Tang. Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials for Tumor Phototheranostics [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [5] | Kaihang Huang, Li Yin, Qingyun Jiang, Qian Wang, Guang Shi, Bingjia Xu. Efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission for Lipid Droplet Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2479-2486. |
| [6] | Yujie Yang, Wei Cao, Jikai Yu, Zhixia Zhang, Li Xu, Hua Wang. Synthesis of Donor-Acceptor (D-A) Typed Phenylcyclooctatetrathiophenes and Their Performances on Aggregation Induced Emission and High Pressure Luminescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2495-2503. |
| [7] | Xiaolong Su, Jianpeng Li, Mengxin Liu, Li Zou, Desuo Yang, Haitao Feng. Synthesis of Tetraphenylethylene Based Amides for Detection of Copper(II) Ion with High Sensitivity and Selectivity [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2581-2587. |
| [8] | Haosen Chang, Liming Yang, Guan Wang, Xinggui Gu. Synthesis of Anthraquinone Derivate with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristic for Fingerprint Development [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2571-2580. |
| [9] | Yan Ou, Lin Lan, Zhengxiong Wang, Zhiming Wang, BenZhong Tang. Preparation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Nucleic Acid Probes and Study of Their Nucleic Acid Sensing Principles [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2554-2562. |
| [10] | Jiasong Hu, Chunjuan Li, Bin Xu, Wenjing Tian. Research Progress of Solid-State Fluorescent Photoswitching Molecules [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [11] | Qingbao Gong, Xiang Lü, Changjiang Yu, Wanwan Li, Quansheng Zhao, Lijuan Jiao, Erhong Hao. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Active Fluoroboronated Pyridylhydrazinyl Aldehyde Hydrozone Dyes: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Optical Properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [12] | Yuanhao Wang, Yukai Sun, Yuhang Liu, Zhaoming Zhang, Xuzhou Yan. Construction and Properties of Flexible Light-Emitting Materials Based on Tetraphenylethylene [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2538-2544. |
| [13] | Hanyu Jia, Yuewen Yu, Guangxue Feng, BenZhong Tang. Construction of Type I Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy via Photoinduced Electron Transfer Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| [14] | Ziran Tang, Hao Sun, Liangliang Zhu. Research Progress of Photoresponsive Photoluminescent Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2412. |
| [15] | Jie Zhang, Nan Li, Na Zhao. Recent Progress of Aggregation-Induced Emission Molecule Nanozyme Composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(8): 2469-2478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||