化学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (1): 53-63.DOI: 10.6023/A25060236 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-09-03
基金资助:
Ziyi Shui*( ), Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo
), Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo
Received:2025-06-25
Published:2025-09-03
Contact:
* E-mail: m18182696780@163.com
Supported by:文章分享
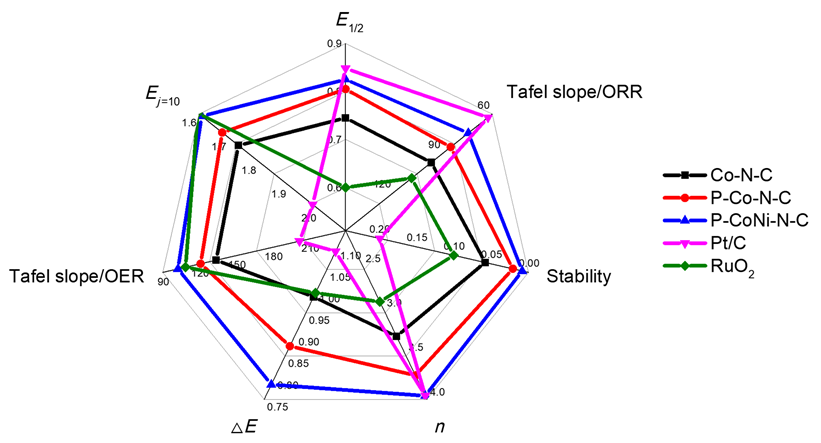
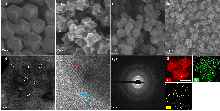
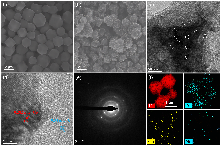
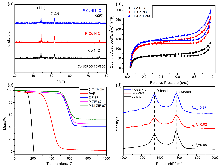
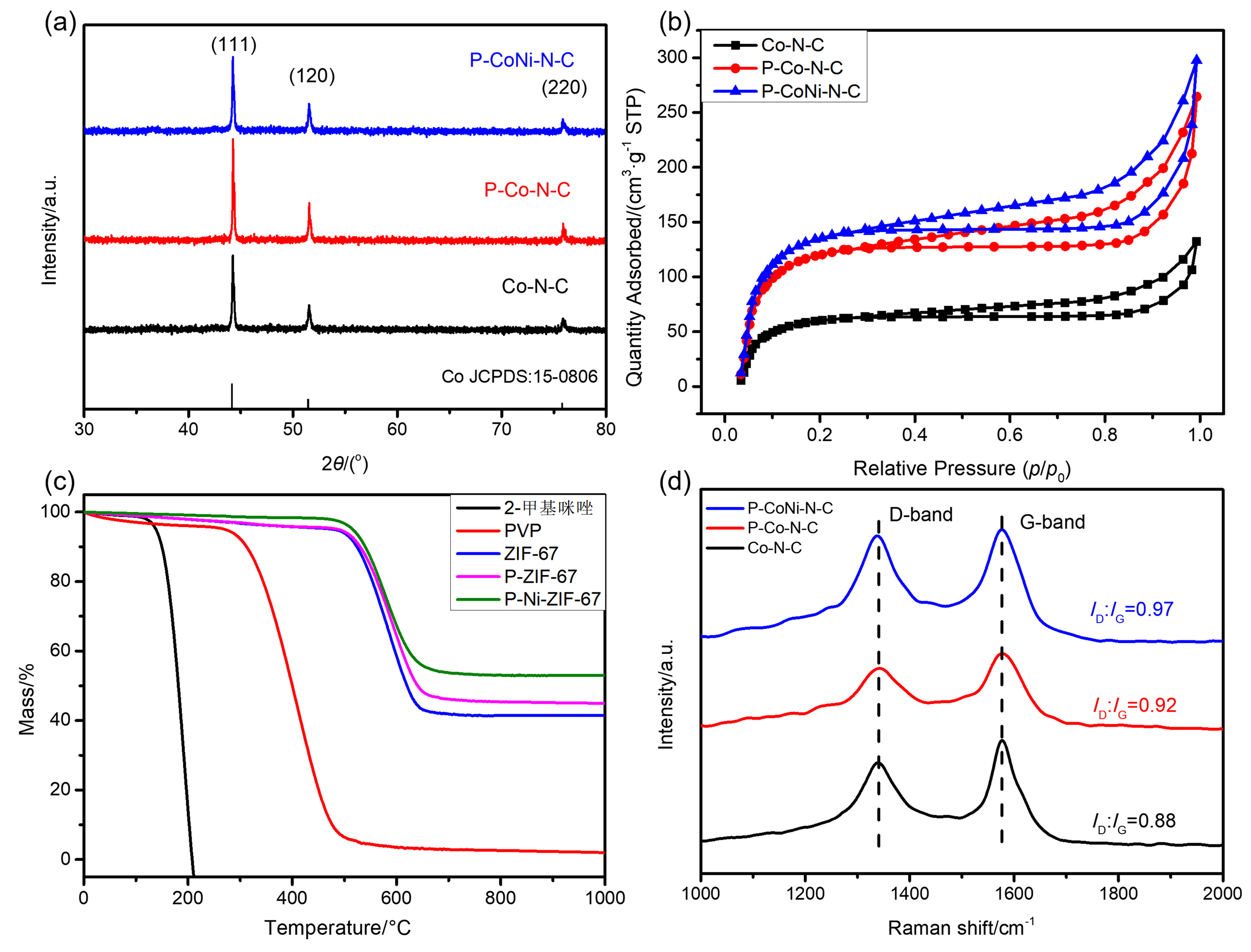
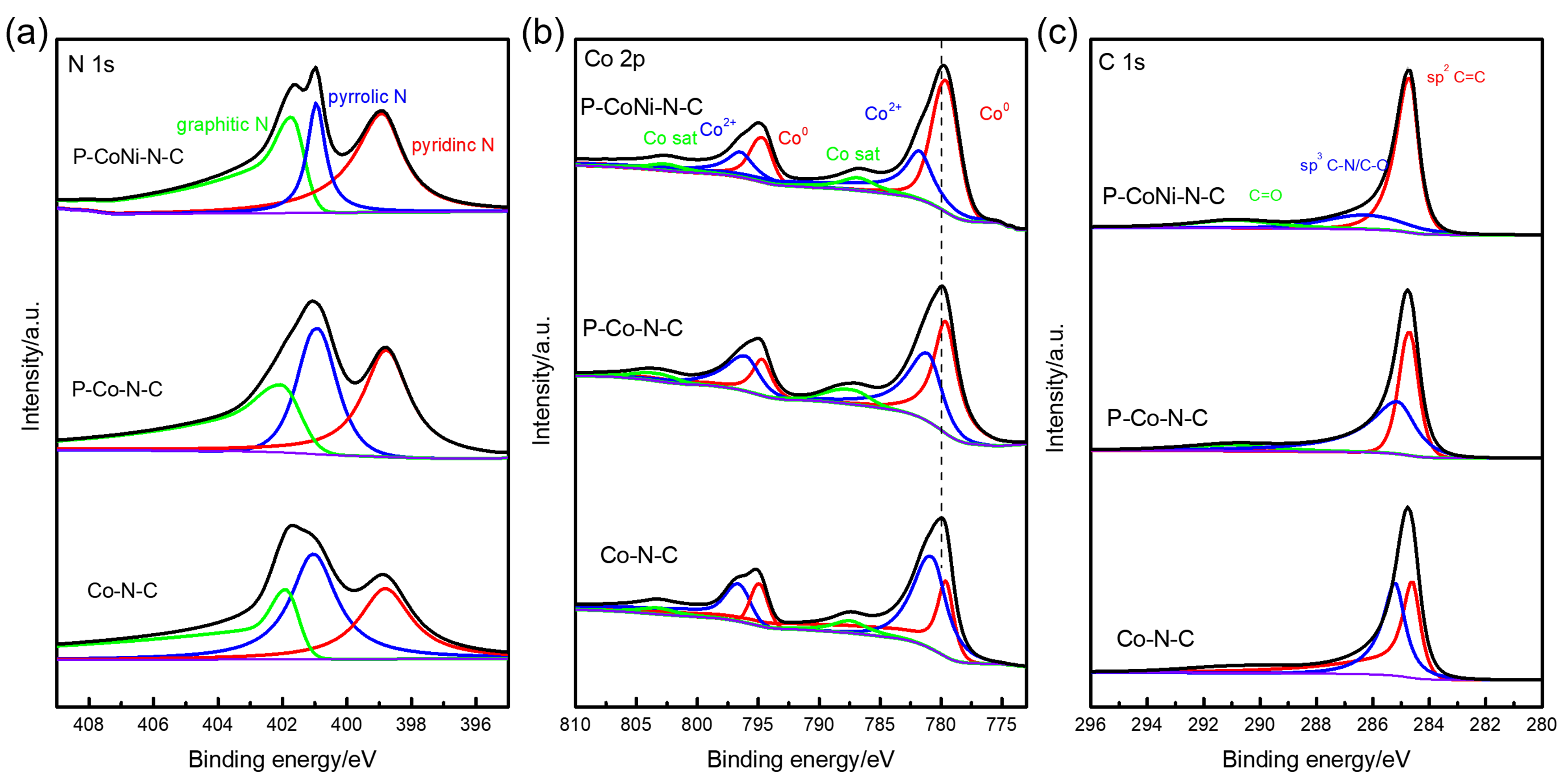
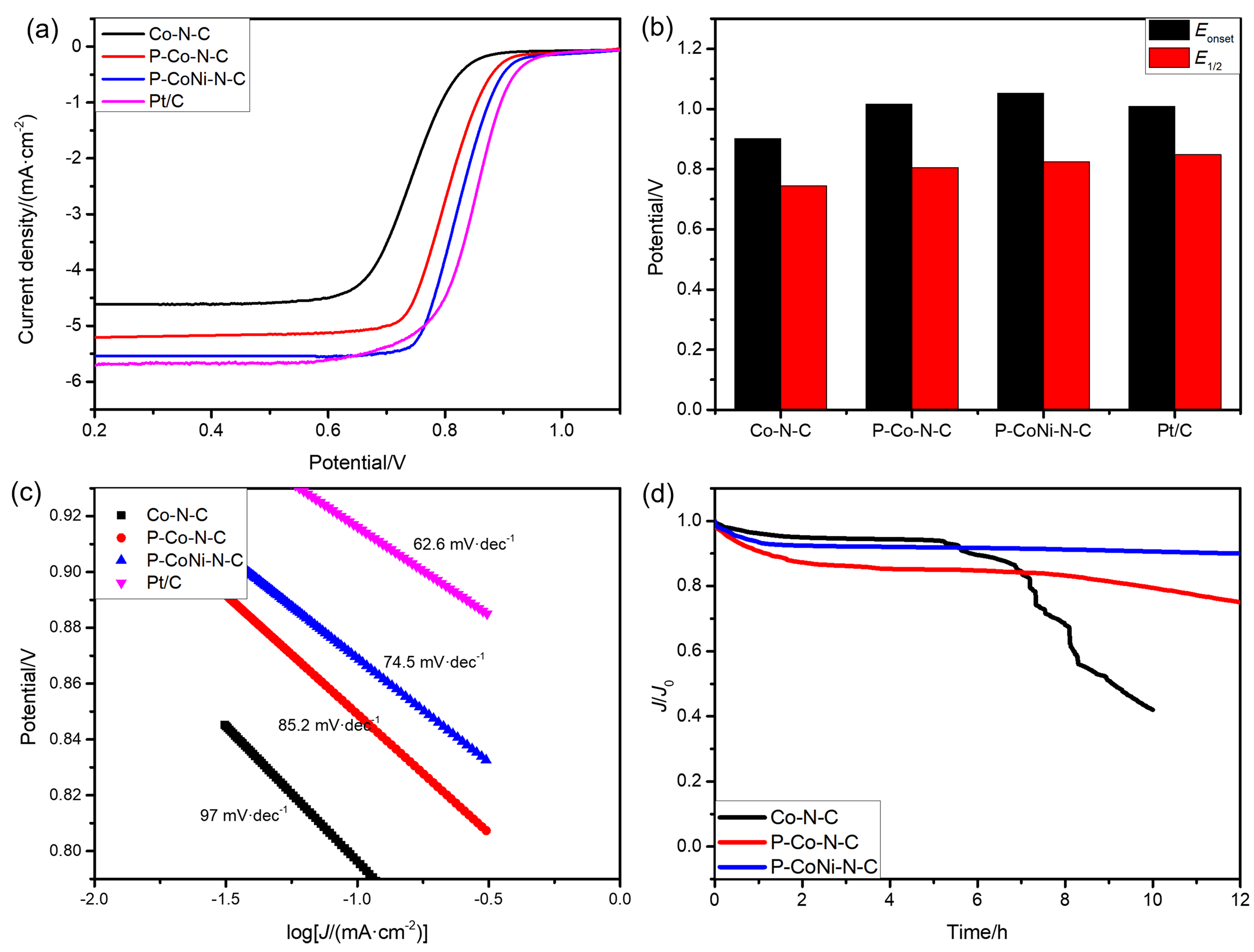
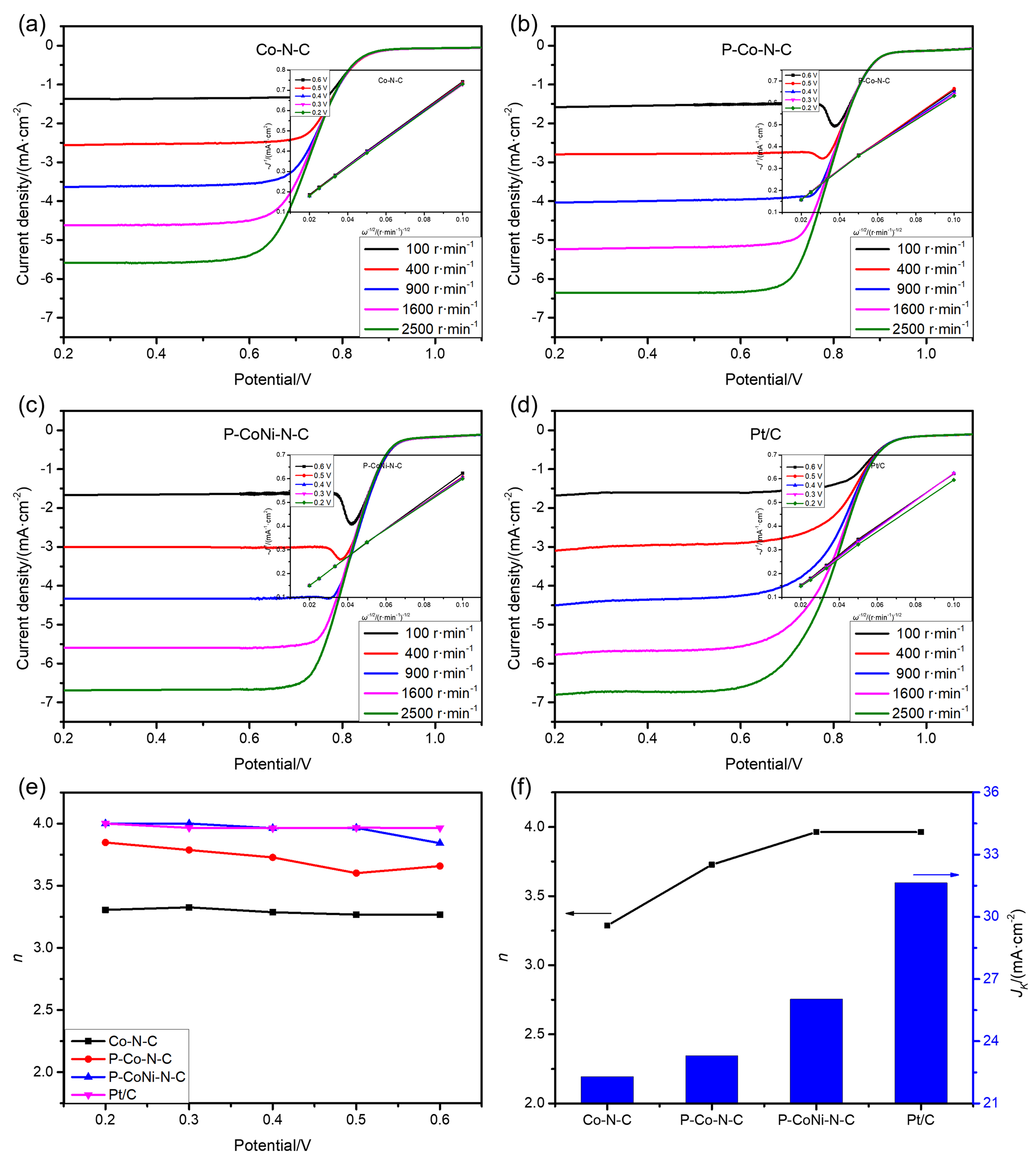
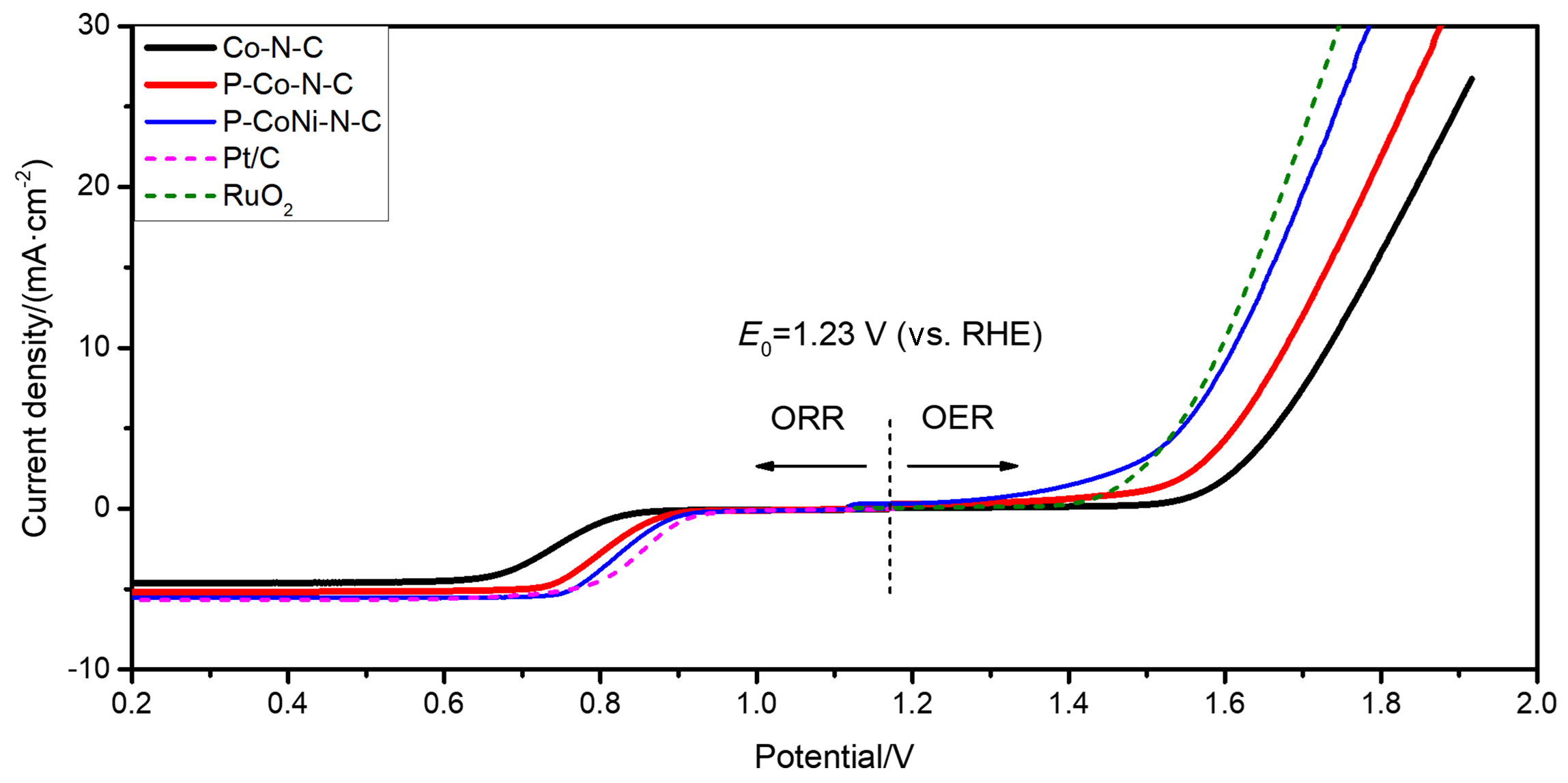
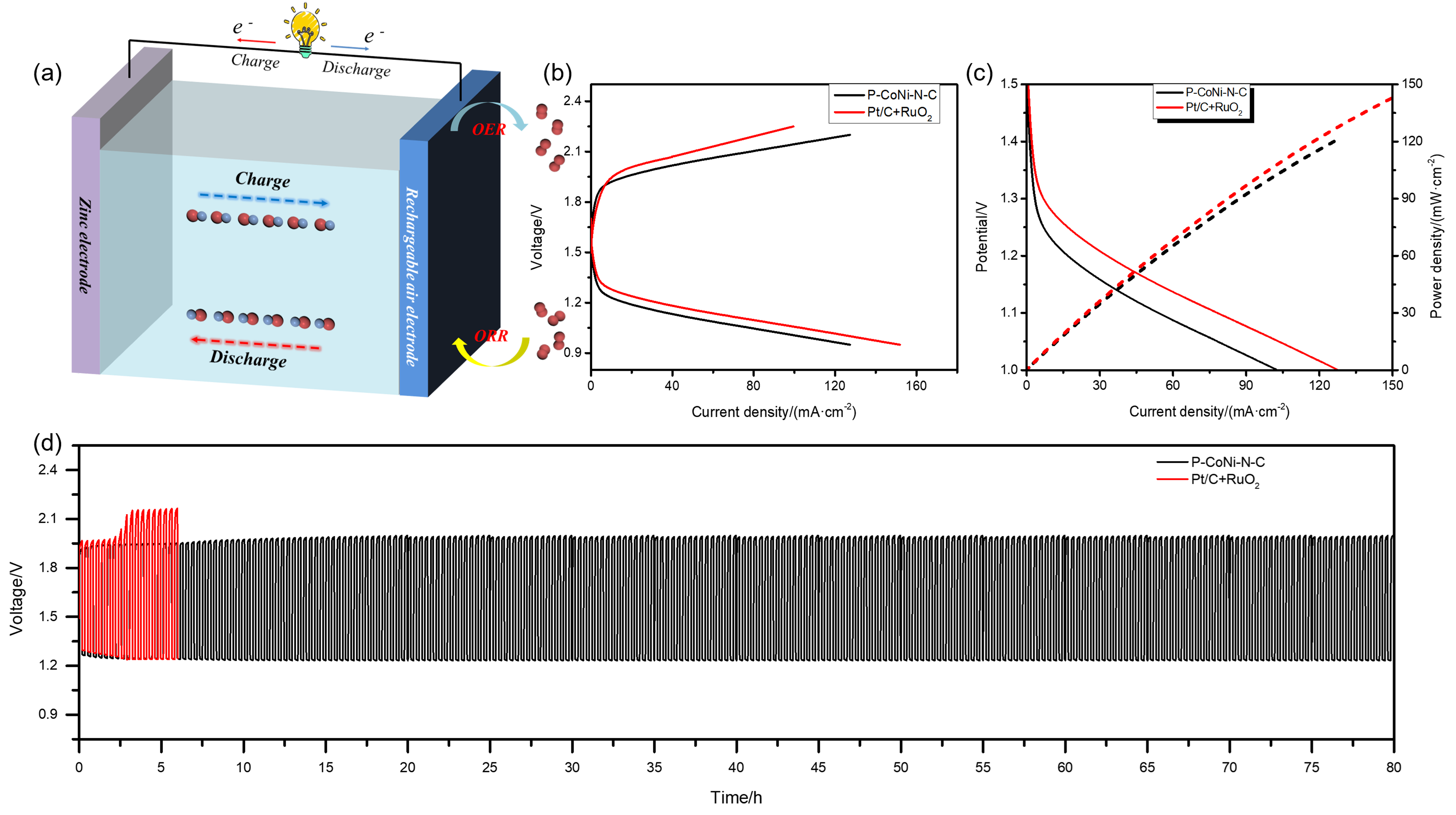
双效氧电极中的氧还原反应(ORR)和析氧反应(OER)是众多电化学储能技术的基石, 包括燃料电池、水电解等. 然而, ORR/OER过程均涉及多步质子/电子耦合传递, 导致氧电极反应动力学缓慢且需要施加高活化过电位才可发生, 因此探寻合适的电催化剂以降低反应势垒和加快电子传输是提高能量转化效率的关键. 本工作报道了一种双金属协同催化与界面工程耦合调控策略, 该策略可通过聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)辅助热解将Co/Ni双金属有机框架(MOF)前驱体转化为钴镍合金纳米粒子嵌入的分级多孔碳材料(P-CoNi-N-C). 实验结果显示: P-CoNi-N-C具有几乎接近于Pt/C的ORR性能(起始电位为1.053 V, 半波电位为0.825 V, 电子转移数为3.96)和出色的OER性能(Ej=10为1.609 V, 过电位为0.379 V, 1.60 V电势下P-CoNi-N-C的质量活性为Co-N-C的5倍). 同样地, P-CoNi-N-C具有优异的长期稳定性, 其电流衰减率仅为0.84%•h-1. 表征结果验证了P-CoNi-N-C优异的双功能活性源于其分级多孔结构、优化中间体吸附能和独特的异质界面结构的协同作用. 此外, P-CoNi-N-C催化剂在可充电锌空气电池展现出优异的电化学性能(充电电流密度为127 mA•cm-2, 功率密度为127.3 mW•cm-2)和循环稳定性(80 h后容量保持率为92%).
税子怡, 尹书睿, 邓锦涛, 许留云, 郭莉. 聚乙烯吡咯烷酮辅助金属有机框架衍生分级多孔碳材料的制备及其双功能催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2026, 84(1): 53-63.
Ziyi Shui, Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Assisted Synthesis of Metal-organic Framework-Derived Hierarchically Porous Carbon for Bifunctional Electrocatalysis[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 53-63.


| SBET/ (m2•g-1) | SMicro/ (m2•g-1) | SMeso/ (m2•g-1) | VPore/ (cm3•g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-N-C | 188 | 46 | 142 | 0.19 |
| P-Co-N-C | 285 | 54 | 231 | 0.32 |
| P-CoNi-N-C | 296 | 58 | 238 | 0.34 |
| SBET/ (m2•g-1) | SMicro/ (m2•g-1) | SMeso/ (m2•g-1) | VPore/ (cm3•g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-N-C | 188 | 46 | 142 | 0.19 |
| P-Co-N-C | 285 | 54 | 231 | 0.32 |
| P-CoNi-N-C | 296 | 58 | 238 | 0.34 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c02289 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1002/adsu.v9.3 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v14.7 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.6023/A24050152 |
|
(税子怡, 于思乐, 陆伟, 许留云, 刘庆叶, 赵炜, 刘益伦, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 1039.)
doi: 10.6023/A24050152 |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00553 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v36.26 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v63.16 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.6023/A18080357 |
|
(王艺霖, 王敏杰, 李静, 魏子栋, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 84.)
doi: 10.6023/A18080357 |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.4c06280 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c05171 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c04851 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v21.1 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1021/ja511539a |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v7.17 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2548 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.6023/A22040143 |
|
(闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1084.)
doi: 10.6023/A22040143 |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c00459 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2515 pmid: 27325100 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01942 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.6023/A23080374 |
|
(刘健, 欧金花, 李泽平, 蒋婧怡, 梁荣涛, 张文杰, 刘开建, 韩瑜, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1701.)
doi: 10.6023/A23080374 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1039/C3CC48112C |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.10.049 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1039/C8CC02646G |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v26.45 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.10 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2017.03.027 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1002/aesr.v2.8 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.16 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v17.16 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.34 |
| [1] | 叶舣, 黄正义, 赵兴雷, 赵娅俐, 刘龙杰, 吴武凤, 魏嫣莹. 垂直排列金属有机框架纳米片膜实现高效H2传输[J]. 化学学报, 2026, 84(1): 129-134. |
| [2] | 翁惠琼, 黄河, 王雯菲, 李和国, 李晓鹏, 张守鑫, 李树华, 赵越, 吴玉芳, 乔智威. 基于MOFid赋能下的AI大数据挖掘高性能化学战剂吸附材料[J]. 化学学报, 2026, 84(1): 8-19. |
| [3] | 江惠星, 郑丽彬, 陈小丰, 张珍珍, 陈秋水, 杨黄浩. 基于钛基金属有机框架的孔径调控策略及其在海水提铀中的应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(9): 987-992. |
| [4] | 朱永朝, 刘冰洁, 梁文杰, 徐海. 多功能MOFs隔离膜用于锂硫电池的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 861-867. |
| [5] | 高春, 张松涛, 庞欢. 金属有机框架复合材料★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 962-980. |
| [6] | 吴子林, 张璐, 陈杨, 李晋平, 李立博. 乙烷选择性金属有机框架材料的结构设计与分离应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 917-936. |
| [7] | 王跃, 邹莹, 张元, 郑舒婕, 王恒宇, 刘天赋, 李仁富. 锆基金属有机框架材料在氧传感器上的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 45-51. |
| [8] | 王南南, 陈玉贞. CoNi-MOF-74/泡沫镍衍生的CoNi@C/NF复合物用于高效有机电合成[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 621-628. |
| [9] | 周何鑫, 崔青云, 胡雪敏, 杨文秀, 田肖, 王硕. 金属有机框架衍生氮掺杂碳限域钴原子簇催化硝基化合物转移加氢[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 503-510. |
| [10] | 刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [11] | 税子怡, 于思乐, 陆伟, 许留云, 刘庆叶, 赵炜, 刘益伦. Mn掺杂Co3O4双功能电催化剂在碱性介质下氧还原和析氧反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1039-1049. |
| [12] | 李萍, 杨琪玉, 曾婧, 张然, 陈秋燕, 闫飞. 氟掺杂对可逆固体氧化物电池性能的影响及相关动力学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 36-45. |
| [13] | 孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立. 高分散共轭聚合物-金属有机框架纳米立方体的制备及抗肿瘤应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [14] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [15] | 殷政, 赵英博, 曾明华. 动态化学与材料和非晶物理新关联——金属有机框架玻璃的挑战、进展与新机遇[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 246-252. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||