化学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (1): 64-72.DOI: 10.6023/A25080290 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
张庆堂a,*( ), 杜纯阳a, 高鹏飞a, 王晓梅b,*(
), 杜纯阳a, 高鹏飞a, 王晓梅b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-08-26
发布日期:2025-12-02
基金资助:
Qingtang Zhanga,*( ), Chunyang Dua, Pengfei Gaoa, Xiaomei Wangb,*(
), Chunyang Dua, Pengfei Gaoa, Xiaomei Wangb,*( )
)
Received:2025-08-26
Published:2025-12-02
Contact:
* E-mail: zhqt137@lut.edu.cn;wxmei06@163.com
Supported by:文章分享
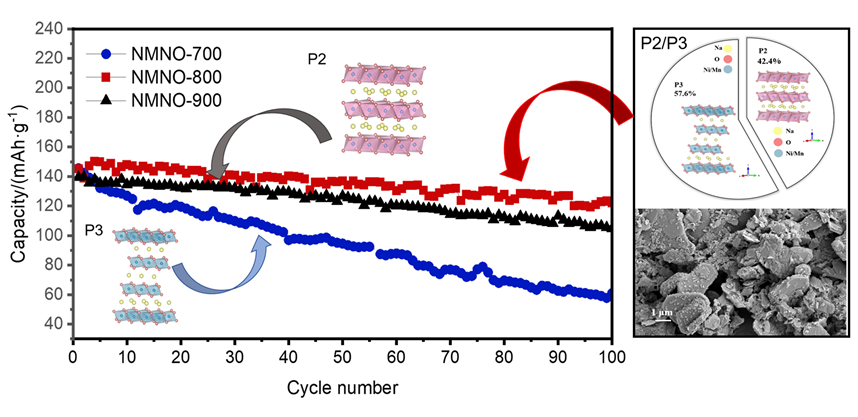
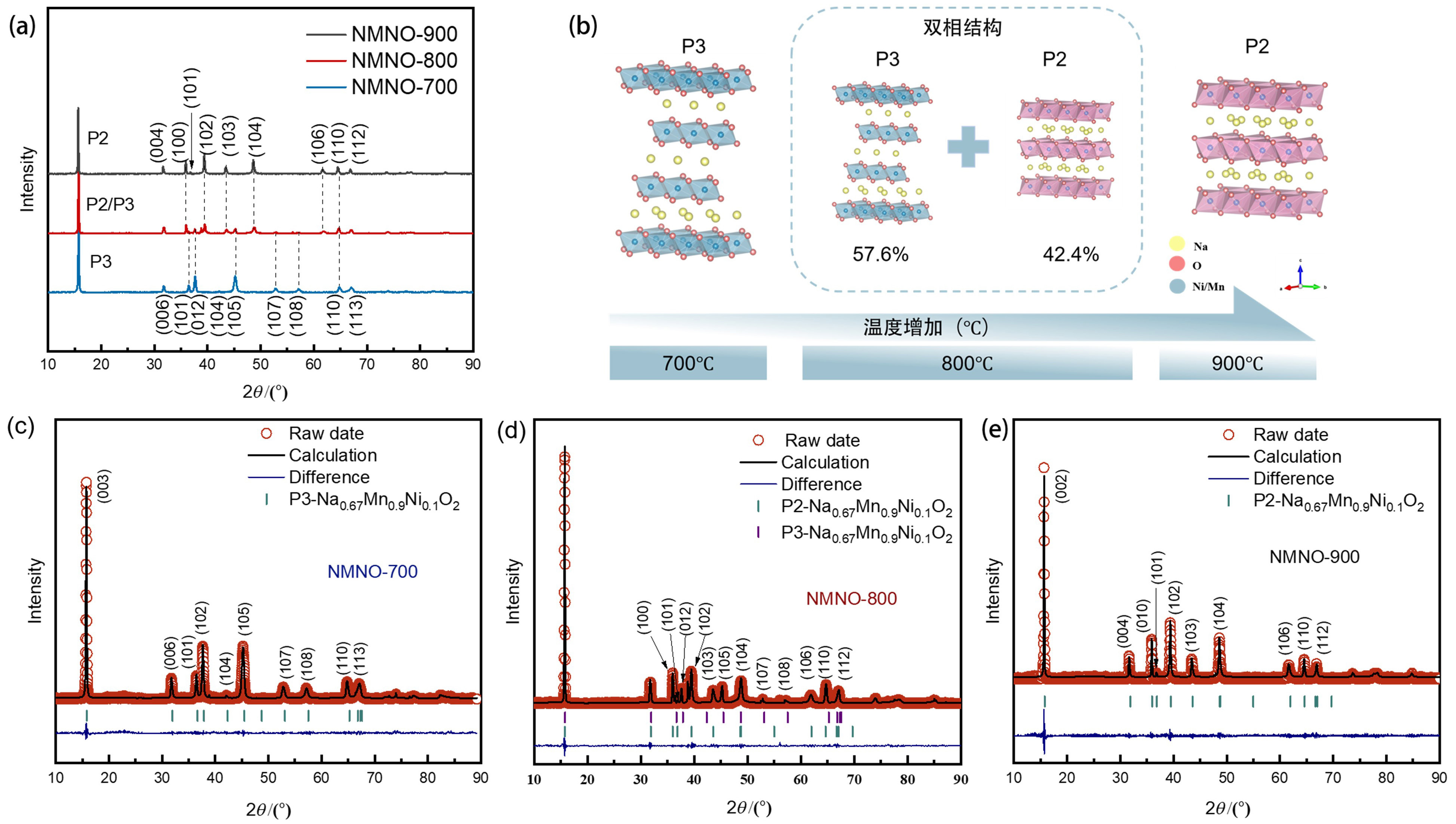
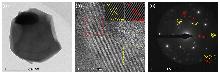
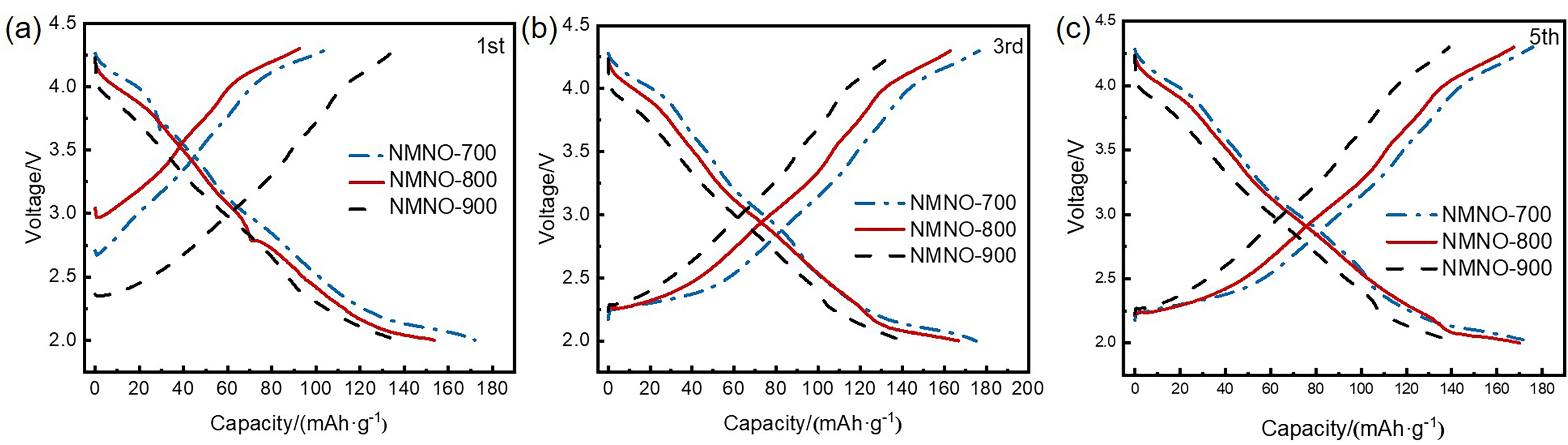
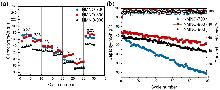
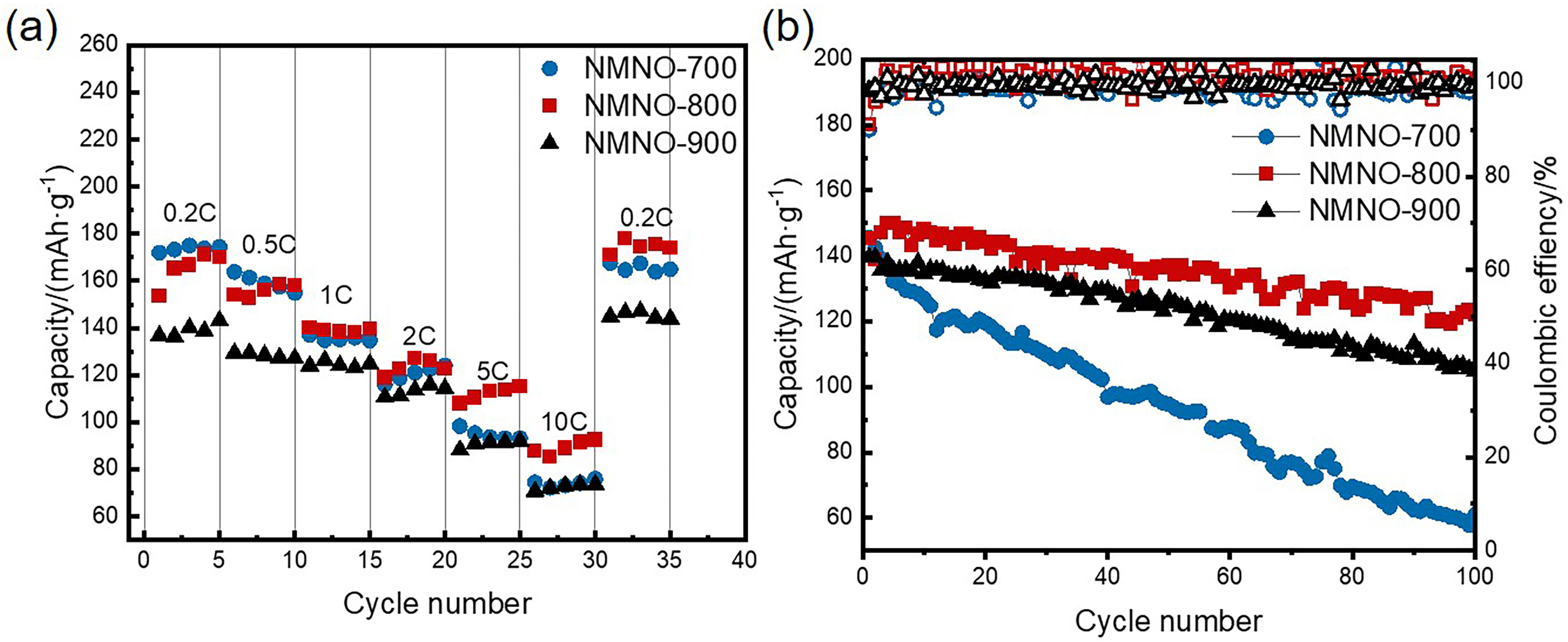
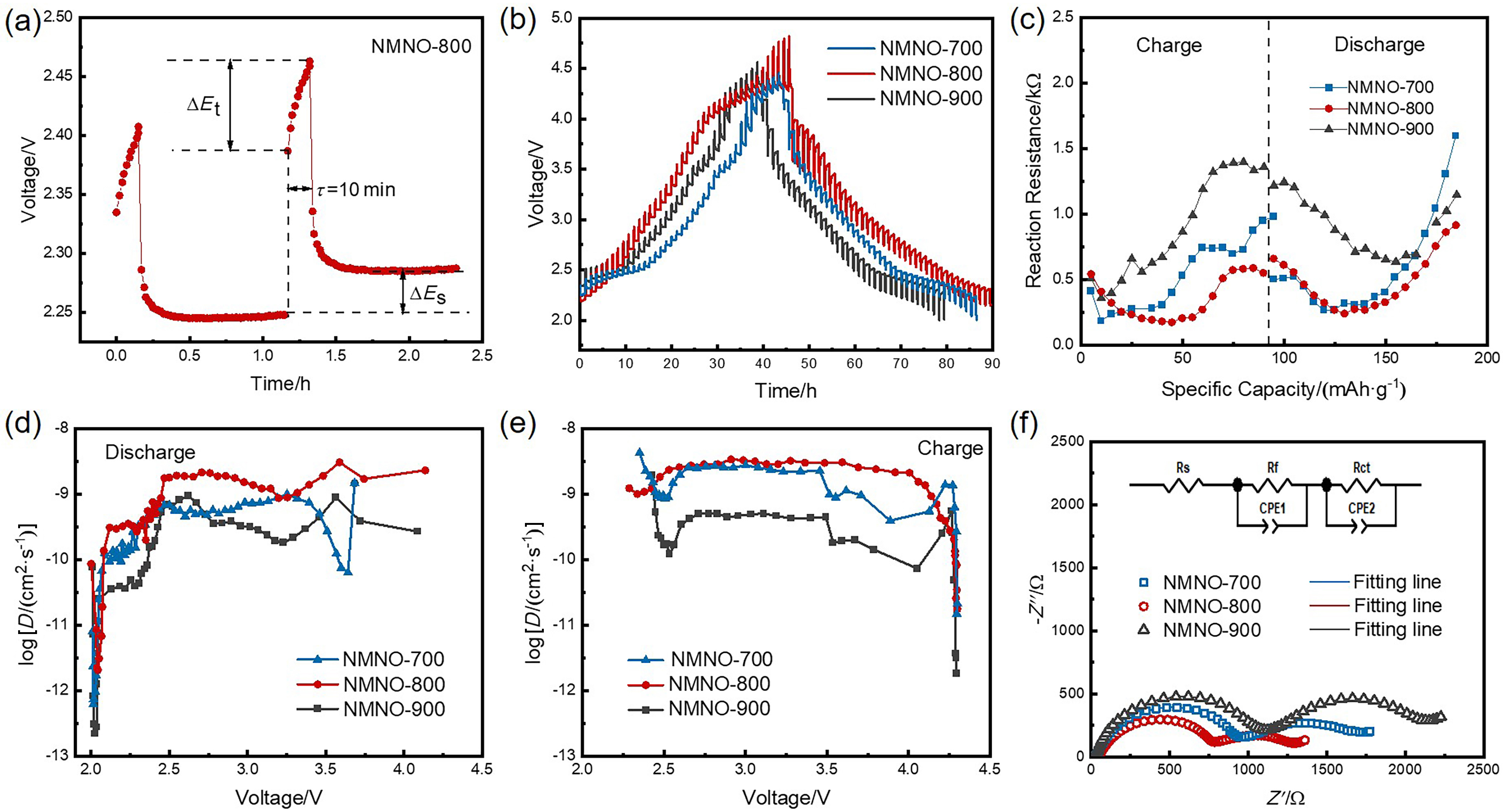
富锰层状氧化物因比容量高、成本低等优势, 成为备受关注的钠离子电池正极材料. 然而, 该材料在深度脱钠状态下的容量衰减和合成过程中结构易受煅烧温度影响, 为其应用带来了巨大挑战. 本工作采用自蔓延燃烧合成, 通过调控煅烧温度, 制备了一种P2/P3双相结构Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2 (NMNO-800)正极材料. X射线衍射结果表明, 煅烧温度的改变可以促使多相材料形成, 当煅烧温度在700和900 ℃时, NMNO-700和NMNO-900分别为P3相结构(空间群R3m)和P2相结构(空间群P63/mmc), 而当煅烧温度为800 ℃时, NMNO-800呈现出稳定的P2/P3双相结构, 经计算确定两相比例分别为42.4%和57.6%. 扫描电子显微镜分析表明, NMNO-800为纳微复合结构, 微米颗粒分布在1.94~2.57 μm之间, 同时微米级片状颗粒表面附着许多纳米颗粒. NMNO-800结合P2相和P3相的优势, 既有P2相的稳定结构, 又具有P3相的高初始容量, 展现出优异的电化学性能. 该材料在0.2 C下表现出165.44 mAh/g的高可逆比容量, 10 C大倍率下仍有89.18 mAh/g的可逆容量, 在0.5 C下循环100次后容量保持率为84.2%, 显著优于单相层状氧化物. 恒流间歇滴定技术(GITT)和电化学阻抗谱(EIS)分析表明, 具有P2/P3双相结构的NMNO-800表现出较高的钠离子扩散系数.
张庆堂, 杜纯阳, 高鹏飞, 王晓梅. 富锰P2/P3双相Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2自蔓延燃烧合成与储钠性能[J]. 化学学报, 2026, 84(1): 64-72.
Qingtang Zhang, Chunyang Du, Pengfei Gao, Xiaomei Wang. Self-propagating Combustion Synthesis and Sodium Storage Performance of Manganese-rich P2/P3 Biphasic Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 64-72.
| Sample | P2-Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2 | P3-Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | ||
| NMNO-700 | — | — | — | — | 0.285 | 0.285 | 1.679 | 0.11879 | |
| NMNO-800 | 0.287 | 0.287 | 1.122 | 0.08051 | 0.287 | 0.287 | 1.675 | 0.12027 | |
| NMNO-900 | 0.288 | 0.288 | 1.129 | 0.08126 | — | — | — | — | |
| Sample | P2-Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2 | P3-Na0.67Mn0.9Ni0.1O2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | ||
| NMNO-700 | — | — | — | — | 0.285 | 0.285 | 1.679 | 0.11879 | |
| NMNO-800 | 0.287 | 0.287 | 1.122 | 0.08051 | 0.287 | 0.287 | 1.675 | 0.12027 | |
| NMNO-900 | 0.288 | 0.288 | 1.129 | 0.08126 | — | — | — | — | |


| 测试元素 | 样品质量m0/g | 元素含量w/% | 元素物质的量/mol | 物质的量比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 0.1030 | 14.3005% | 6.407×10-4 | 0.65 |
| Mn | 47.0286% | 8.817×10-4 | 0.89 | |
| Ni | 5.6639% | 9.940×10-5 | 0.1 |
| 测试元素 | 样品质量m0/g | 元素含量w/% | 元素物质的量/mol | 物质的量比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 0.1030 | 14.3005% | 6.407×10-4 | 0.65 |
| Mn | 47.0286% | 8.817×10-4 | 0.89 | |
| Ni | 5.6639% | 9.940×10-5 | 0.1 |



| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2025.110993 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.163565 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.6023/A24110356 |
|
(刘继洪, 祝佳鹏, 张旭, 张纪阳, 黄超洋, 贾桂霄, 安胜利, 化学学报, 2025, 83, 101.)
doi: 10.6023/A24110356 |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.164736 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v21.23 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.172272 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.148257 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.07.010 |
| [46] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2025.181577 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v5.8 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.6023/A21060260 |
|
(谢佶晟, 肖竹梅, 左文华, 杨勇, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1232.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060260 |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v21.17 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v36.16 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61065-w |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1063/5.0187281 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.esci.2023.100186 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30942-z |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.163001 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v17.7 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2024.01.025 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.109428 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v64.1 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.06.239 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [1] | 陆继承, 苟蕾, 刘小九, 樊小勇, 李东林. 铁弹Zr0.92Y0.08O2对层状LiMnO2正极材料充放电循环行为的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 844-852. |
| [2] | 张贤碧, 项爽, 唐有根, 孙旦, 李欢欢, 王海燕. 钠离子电池硫酸铁钠正极的关键问题及设计策略★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 947-961. |
| [3] | 刘继洪, 祝佳鹏, 张旭, 张纪阳, 黄超洋, 贾桂霄, 安胜利. 锂离子电池富锂层状正极材料Li-Ni-Mn-O应变机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(2): 101-109. |
| [4] | 王舒玮, 张建勋, 成业, 章立寒, 田华军, 李宝华. 梯度多孔结构设计提升高镍层状氧化物正极材料高压循环稳定性[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(11): 1134-1141. |
| [5] | 何家伟, 焦柳, 程雪怡, 陈光海, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 金属有机框架衍生的空心碳纳米笼的结构调控与锂硫电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 896-902. |
| [6] | 黄擎, 丁瑞, 陈来, 卢赟, 石奇, 张其雨, 聂启军, 苏岳锋, 吴锋. Na2PO3F对LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2材料的复合改性及机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 150-158. |
| [7] | 薛晓兰, 张洋, 石美瑜, 李天琳, 黄天龙, 戚继球, 委福祥, 隋艳伟, 金钟. 有机电极材料在非水系金属镁二次电池中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1618-1628. |
| [8] | 邱凯, 严铭霞, 赵守旺, 安胜利, 王玮, 贾桂霄. Al掺杂的锂离子电池层状正极材料Li(Li0.17Ni0.17Al0.04Fe0.13Mn0.49)O2结构稳定性及氧离子氧化的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1146-1153. |
| [9] | 林碧霞, 黄颖珊, 陈帅, 邢震宇. 钠硒电池关键材料的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 641-648. |
| [10] | 李童心, 李东林, 张清波, 高建行, 孔祥泽, 樊小勇, 苟蕾. 大孔高镍LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2正极材料的制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 678-684. |
| [11] | 马慧, 张桓荣, 薛面起. 水系钠离子电池的研究进展及实用化挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 388-405. |
| [12] | 张璐, 王文凤, 张洪明, 韩树民, 王利民. 水系锌离子电池研究进展和挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 158-175. |
| [13] | 李燕丽, 于丹丹, 林森, 孙东飞, 雷自强. α-MnO2纳米棒/多孔碳正极材料的制备及水系锌离子电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 200-207. |
| [14] | 董瑞琪, 吴锋, 白莹, 吴川. 钠离子电池硬碳负极储钠机理及优化策略[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1461-1476. |
| [15] | 梁其梅, 郭昱娇, 郭俊明, 向明武, 刘晓芳, 白玮, 宁平. 亚微米去顶角八面体LiNi0.08Mn1.92O4正极材料制备及高温电化学性能[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1526-1533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||