Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (4): 396-408.DOI: 10.6023/A23120529 Previous Articles Next Articles
Original article
雷雅茹a, 熊廷楷a, 于湘涛b, 黄秀兵c, 唐晓龙a,*( ), 易红宏a, 周远松a, 赵顺征a, 孙龙a, 高凤雨a,*(
), 易红宏a, 周远松a, 赵顺征a, 孙龙a, 高凤雨a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-12-11
发布日期:2024-03-05
Yaru Leia, Tingkai Xionga, Xiangtao Yub, Xiubing Huangc, Xiaolong Tanga,*( ), Honghong Yia, Yuansong Zhoua, Shunzheng Zhaoa, Long Suna, Fengyu Gaoa,*(
), Honghong Yia, Yuansong Zhoua, Shunzheng Zhaoa, Long Suna, Fengyu Gaoa,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-11
Published:2024-03-05
Contact:
* E-mail: Share
Yaru Lei, Tingkai Xiong, Xiangtao Yu, Xiubing Huang, Xiaolong Tang, Honghong Yi, Yuansong Zhou, Shunzheng Zhao, Long Sun, Fengyu Gao. Novel Porous Melamine Foam Loaded with MnCe for Highly Selective Electrocatalytic CO2 to Formic Acid[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 396-408.
| Catalysts | Onset potential (V vs. RHE) | exit potential (V vs. RHE) | Selection of experimental sites (V vs. RHE) | Maximum yield rate/ (μg•h–1•cm–2) | Optimum FEf/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnCe-GOMS | –0.06 | –2.99 | –0.2, –0.4, –0,5, –0.6, –0.8, –1.0, –2.0, –2.5 | 746.92 (–0.8 V) | 75.72 (–0.6 V) |
| MnCe-CMS | –0.13 | –3.1 | –0.2, –0.4, –1.0, –2.0, –3.0 | 470.89 (–3.0 V) | 63.04 (–0.4 V) |
| MnCe-CC | 0.58 | –1.06 | 0.0, –0.2, –0.4, –0.8, –1.0 | 78.69 (–0.4 V) | 64.14 (0 V) |
| MnCe-CF | 0.65 | –0.23 | 0.0, –0.1, –0.2 | 489.62 (–0.2 V) | 11.67 (0 V) |
| MnCe-NF | 0.43 | –0.74 | –0.4, –0.5, –0.6, –0.7 | 542.69 (–0.4 V) | 41.47 (–0.4 V) |
| Catalysts | Onset potential (V vs. RHE) | exit potential (V vs. RHE) | Selection of experimental sites (V vs. RHE) | Maximum yield rate/ (μg•h–1•cm–2) | Optimum FEf/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnCe-GOMS | –0.06 | –2.99 | –0.2, –0.4, –0,5, –0.6, –0.8, –1.0, –2.0, –2.5 | 746.92 (–0.8 V) | 75.72 (–0.6 V) |
| MnCe-CMS | –0.13 | –3.1 | –0.2, –0.4, –1.0, –2.0, –3.0 | 470.89 (–3.0 V) | 63.04 (–0.4 V) |
| MnCe-CC | 0.58 | –1.06 | 0.0, –0.2, –0.4, –0.8, –1.0 | 78.69 (–0.4 V) | 64.14 (0 V) |
| MnCe-CF | 0.65 | –0.23 | 0.0, –0.1, –0.2 | 489.62 (–0.2 V) | 11.67 (0 V) |
| MnCe-NF | 0.43 | –0.74 | –0.4, –0.5, –0.6, –0.7 | 542.69 (–0.4 V) | 41.47 (–0.4 V) |


| Adsorption site types | Weak adsorption | Medium adsorption | Strong adsorption | Amount | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# (30~180 ℃) | 2# (180~350 ℃) | 3# (350~430 ℃) | 4# (400~600 ℃) | 5# (600~800 ℃) | |||||
| MnCe-CMS | Area | 34.45 | 14.98 | 3.10 | 35.42 | 95.67 | 183.62 | ||
| Proportion% | 18.76 | 8.16 | 1.69 | 19.29 | 52.10 | 100 | |||
| MnCe-GOMS | Area | 9.28 | 28.01 | 94.40 | 101.29 | 24.48 | 248.18 | ||
| Proportion% | 3.60 | 10.88 | 36.67 | 39.34 | 9.51 | 100 | |||
| Adsorption site types | Weak adsorption | Medium adsorption | Strong adsorption | Amount | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# (30~180 ℃) | 2# (180~350 ℃) | 3# (350~430 ℃) | 4# (400~600 ℃) | 5# (600~800 ℃) | |||||
| MnCe-CMS | Area | 34.45 | 14.98 | 3.10 | 35.42 | 95.67 | 183.62 | ||
| Proportion% | 18.76 | 8.16 | 1.69 | 19.29 | 52.10 | 100 | |||
| MnCe-GOMS | Area | 9.28 | 28.01 | 94.40 | 101.29 | 24.48 | 248.18 | ||
| Proportion% | 3.60 | 10.88 | 36.67 | 39.34 | 9.51 | 100 | |||


| Catalysts | Element content/% | Atomic ratio/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Mn | Ce | Mn3+/Mn | Ce3+/Ce | Oα/O | Oβ/O | ||
| MnCe-CC | 60.10 | 0.37 | 30.33 | 3.60 | 5.57 | 30.75 | 9.30 | 46.81 | 53.19 | |
| MnCe-CMS | 38.00 | 1.20 | 46.55 | 8.67 | 5.58 | 32.29 | 11.09 | 37.69 | 26.81 | |
| MnCe-GOMS | 55.87 | 4.49 | 33.22 | 4.68 | 4.49 | 40.45 | 24.92 | 48.62 | 11.76 | |
| Catalysts | Element content/% | Atomic ratio/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Mn | Ce | Mn3+/Mn | Ce3+/Ce | Oα/O | Oβ/O | ||
| MnCe-CC | 60.10 | 0.37 | 30.33 | 3.60 | 5.57 | 30.75 | 9.30 | 46.81 | 53.19 | |
| MnCe-CMS | 38.00 | 1.20 | 46.55 | 8.67 | 5.58 | 32.29 | 11.09 | 37.69 | 26.81 | |
| MnCe-GOMS | 55.87 | 4.49 | 33.22 | 4.68 | 4.49 | 40.45 | 24.92 | 48.62 | 11.76 | |
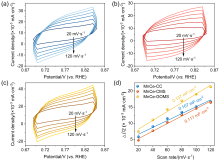

| Parameters | MnCe-CC | MnCe-CMS | MnCe-GOMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| b/(mV•dec–1) | –396 | –1750 | –1169 |
| i0/(mA•cm–2) | 0.042 | 0.783 | 0.575 |
| k0/(cm•s–1) | 7.0×10–6 | 1.23×10–5 | 9.1×10–6 |
| α | –0.149 | –0.034 | –0.051 |
| Parameters | MnCe-CC | MnCe-CMS | MnCe-GOMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| b/(mV•dec–1) | –396 | –1750 | –1169 |
| i0/(mA•cm–2) | 0.042 | 0.783 | 0.575 |
| k0/(cm•s–1) | 7.0×10–6 | 1.23×10–5 | 9.1×10–6 |
| α | –0.149 | –0.034 | –0.051 |
| Catalysts | Carrier | Advantages | Disadvantages | Potentiostatic properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnCe-CMS | Melamine foam (MS) | High FE, high yield and low cost | Low conductivity and poor stability | Wider potential range (–0.2~–3 V) |
| MnCe-GOMS | ||||
| MnCe-CC | Carbon cloth (CC) | Higher FE | Low yield | Narrower potential range (0~–1 V) |
| MnCe-CF | Metal foams | High conductivity and higher yield | Low FE, severe HER competitive response and poor reproducibility | Narrow potential range (<–0.7 V) |
| MnCe-NF |
| Catalysts | Carrier | Advantages | Disadvantages | Potentiostatic properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnCe-CMS | Melamine foam (MS) | High FE, high yield and low cost | Low conductivity and poor stability | Wider potential range (–0.2~–3 V) |
| MnCe-GOMS | ||||
| MnCe-CC | Carbon cloth (CC) | Higher FE | Low yield | Narrower potential range (0~–1 V) |
| MnCe-CF | Metal foams | High conductivity and higher yield | Low FE, severe HER competitive response and poor reproducibility | Narrow potential range (<–0.7 V) |
| MnCe-NF |
| [1] |
(a) Lei, Y. R.; Wang, Z.; Bao, A.; Tang, X. L.; Huang, X. B.; Yi, H. H.; Zhao, S. Z.; Sun, T.; Wang, J. Y.; Gao, F. Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 453, 139663.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.139663 |
|
(b) Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 703. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22010012 |
|
|
(蒋银龙, 李国超, 陈青松, 徐忠宁, 林姗姗, 郭国聪, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 703).
doi: 10.6023/A22010012 |
|
|
(c) Guo, Q.; Fu, J. L.; Zhang, C. Y.; Cai, C. Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. H.; Xu, R. B.; Wang, M. Y. J. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 449. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(郭茜, 富佳龙, 张成燕, 蔡超越, 王城, 周丽华, 许瑞波, 王明艳, 电化学, 2021, 27, 449.)
doi: 10.13208/j.electrochem.200513 |
|
| [2] |
(a) Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L. H.; Fang, L.; Dong, H.; Lu, M.; Dong, L. Z.; Lan, Y. Q.; Zhang, F. M. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304170.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v35.40 |
|
(b) Lan, B. Y.; Shi, H. F. Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica 2014, 30, 2177. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(蓝奔月, 史海峰, 物理化学学报, 2014, 30, 2177).
|
|
| [3] |
(a) Jiang, Q. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2001, 18, 536. (in Chinese)
|
|
(江琦, 应用化学, 2001, 18, 536.)
|
|
|
(b) Song, Z. J.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, J. Y.; Peng, J. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 2068. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202210024 |
|
|
(宋姿洁, 刘俊, 白赢, 厉嘉云, 彭家建, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 2068).
|
|
|
(c) Cui, G. Q.; Hu, Y. Y.; Lou, Y. J.; Zhou, M. X.; Li, Y. M.; Wang, Y. J.; Jiang, G. Y.; Xu, C. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1081. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A23040126 |
|
|
(崔国庆, 胡溢玚, 娄颖洁, 周明霞, 李宇明, 王雅君, 姜桂元, 徐春明, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1081).
doi: 10.6023/A23040126 |
|
|
(d) Liu, C. H.; Guo, X. M.; Zhong, C. L.; Li, L.; Hua, Y. X.; Mao, D. S.; Lu, G. Z. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32, 1405. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
(刘超恒, 郭晓明, 钟成林, 李亮, 华玉喜, 毛东森, 卢冠忠, 无机化学学报, 2016, 32, 1405.)
|
|
| [4] |
Zhang, J. F.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. 2016, 79, 958. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张佳凤, 王黎, 孙杨, 化学通报, 2016, 79, 958.)
|
|
| [5] |
(a) Zhang, W.; Yi, H.; Ma, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhong, J. Adv. Sci. 2017, 5, 1700275.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v5.1 |
|
(b) Cheng, Y.; Yang, S. Z.; Jiang, S. P.; Wang, S. Y. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800440.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v3.9 |
|
| [6] |
Mori, K.; Futamura, Y.; Masuda, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamashita, H. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4094.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12018-7 |
| [7] |
Li, F. J., Electrochim. Acta 2020, 332, 135457.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135457 |
| [8] |
Hussain, N.; Abdelkareem, M. A.; Alawadhi, H.; Elsaid, K.; Olabi, A. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 258, 117757.
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2022.117757 |
| [9] |
Kortlever, R.; Peters, I.; Koper, S.; Koper, M. T. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3916.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00602 |
| [10] |
(a) Zhai, J. R.; Kang, Q. L.; Liu, Q. Y.; Lai, D. W.; Lu, Q. Y.; Gao, F. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 1942.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.096 pmid: 31414823 |
|
(b) Zhang, T.; Verma, S.; Kim, S.; Fister, T. T.; Kenis, P. J.; Gewirth, A. A. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 875, 113862.
doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.113862 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, A.; Liang, Y. X.; Li, H. P.; Zhao, X. Y.; Chen, Y. L.; Zhang, B. Y.; Zhu, W. G.; Zeng, J. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6547.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02782 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(d) Feng, J.; Gao, H.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(e) Su, X. Z.; Jiang, Z. L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H. J.; Zhou, D. N.; Shang, H. S.; Ni, X. M.; Peng, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, W. X. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27699-2 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(f) Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K. T.; Irvine, J. T.; Shin, T. H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100339.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v11.24 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(g) Hod, I.; Sampson, M. D.; Deria, P.; Kubiak, C. P.; Farha, O. K.; Hupp, J. T. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6302.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01767 pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(h) Li, Y.; Adli, N. M.; Shan, W.; Wang, M.; Zachman, M. J.; Hwang, S.; Tabassum, H.; Karakalos, S.; Feng, Z.; Wang, G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 2108.
doi: 10.1039/D2EE00318J pmid: 31414823 |
|
|
(i) Chu, S.; Li, X.; Robertson, A. W.; Sun, Z. Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica 2021, 37, 5.
pmid: 31414823 |
|
| [11] |
Li, X.; Qian, N. K.; Ji, L.; Wu, X. Q.; Li, J. J.; Huang, J. B.; Yan, Y. C.; Yang, D. R.; Zhang, H. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2288.
doi: 10.1039/D2NA00141A |
| [12] |
Ren, X. X.; Gao, Y. G.; Zheng, L. R.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Z. K.; Liu, Y. Y.; Cheng, H. F.; Dai, Y.; Huang, B. B. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100923.
|
| [13] |
Huang, C.; Liu, J. H.; Huang, H. H.; Xu, X. F.; Ke, Z. F. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.06.046 |
| [14] |
(a) Yan, X. C.; Dong, H.; Tong, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L. H.; Du, Y. J.; Ge, J. T.; Fang, W. B.; Zhang, F. M. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 157828.
|
|
(b) Chen, Q.; Kuang, Q.; Xie, Z. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 10. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
|
(陈钱, 匡勤, 谢兆雄, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 10.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080384 |
|
| [15] |
(a) Lei, F.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, K.; Liang, L.; Yao, T.; Pan, B.; Wei, S.; Xie, Y. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12697.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12697 |
|
(b) Li, H.; Oloman, C. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2006, 36, 1105.
doi: 10.1007/s10800-006-9194-z |
|
|
(c) Zhao, Y.; Miao, Z.; Wang, F.; Liang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Diao, L.; Mu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J. J. Environ. 2021, 9, 105515.
|
|
| [16] |
Ma, L. B.; Hu, Y.; Chen, R. P.; Zhu, G. Y.; Chen, T.; Lv, H. L.; Wang, Y. R.; Liang, J.; Liu, H. X.; Yan, C. Z. Nano Energy 2016, 24, 139.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.04.024 |
| [17] |
(a) Wang, R. F.; Liu, Y. C.; Kong, Y. F.; Xie, P.; Zhao, S. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 144049.
|
|
(b) Ning, S. L.; Wang, J. G.; Xiang, D.; Huang, S. B.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. W.; Kang, X. W. J. Catal. 2021, 399, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2021.04.028 |
|
| [18] |
Wang, C. Z.; Tang, X. L.; Yi, H. H.; Gao, F. Y.; Ni, S. Q.; Zhang, R. C.; Shi, Y. R. Colloids Surf., A 2021, 612, 126007.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126007 |
| [19] |
Liang, Z. J.; Fadhel, B.; Schneider, C. J.; Chaffee, A. L. Adsorption 2009, 15, 429.
doi: 10.1007/s10450-009-9192-7 |
| [20] |
Lee, J. S.; Park, G. S.; Kim, S. T.; Liu, M.; Cho, J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3, 1026.
|
| [21] |
Li, W.; Chen, J. W.; Xiao, Z. L.; Xing, J. B.; Yang, C.; Qi, X. P. Carbon 2021, 174, 758.
|
| [22] |
Wu, Y. L.; Yan, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, B. H. J. Shanghai Univ.,Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 29, 2. (in Chinese)
|
|
(吴艳玲, 鄢浩, 戴扬, 张宝华, 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 29, 2).
|
|
| [23] |
Wang, C. Z.; Gao, F. Y.; Yu, Q. J.; Yi, H. H.; Ni, S. Q.; Tang, X. L. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 21079. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王成志, 高凤雨, 于庆君, 易红宏, 倪书权, 唐晓龙, 材料导报, 2021, 35, 21079.)
|
|
| [24] |
Long, C.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Shi, Y. A.; Liu, S. Q.; Tang, Z. Y. Small Methods 2018, 3, 1800369.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v3.3 |
| [25] |
Albero, J.; Peng, Y.; García, H. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5734.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00478 |
| [26] |
Duan, J. Y.; Liu, T. Y.; Zhao, Y. H.; Yang, R. O.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W. B.; Liu, Y. W.; Li, H. Q.; Li, Y. F.; Zhai, T. Y. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2039.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29699-2 |
| [27] |
Lu, X.; Li, Z. Y.; Liu, Y. A.; Tang, B.; Zhu, Y. C.; Razal, J. M.; Pakdel, E.; Wang, J. F.; Wang, X. G. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 246, 118949.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118949 |
| [28] |
(a) Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Shi, L. L.; Liu, S. T.; Zhao, Y. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 424.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.359 |
|
(b) Zhu, H. G.; Chen, D. Y.; An, W.; Li, N. J.; Xu, Q. F.; Li, H.; He, J. H.; Lu, J. M. Small 2015, 11, 5222.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201501004 |
|
| [29] |
Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2014, 195, 145.
doi: 10.1016/j.elspec.2014.07.003 |
| [30] |
Venkataswamy, P.; Jampaiah, D.; Lin, F.; Alxneit, I.; Reddy, B. M. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 299.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.04.220 |
| [31] |
(a) Wang, G. D.; Xiang, W. J.; Liu, H. Z.; Yin, Y. Z.; Ma, D. D.; Ma, J. F. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 10155.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.3c01880 |
|
(b) Zhang, M. X.; Peng, H.; Sun, K. J.; Xie, X.; Lei, X. F.; Liu, S. T.; Ma, G. F.; Lei, Z. Q. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2763.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v40.23 |
|
| [32] |
Wang, Y. H.; Yao, C. Y.; Cao, Y. J.; Zhang, C.; Tang, W. X. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 1137.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.090 |
| [33] |
Zhang, P.; Wang, R. T.; He, M.; Lang, J. W.; Xu, S.; Yan, X. B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1354.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v26.9 |
| [34] |
(a) Gan, G. Q.; Fan, S. Y.; Li, X. Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, C. P.; Guo, X. C.; Tade, M.; Liu, S. M. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14284.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c03701 |
|
(b) Adamu, H.; Dubey, P.; Anderson, J. A. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 380.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.147 |
|
| [35] |
(a) Zhang, L. H.; Shi, Y. M.; Wang, Y.; Shiju, N. R. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902126.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v7.5 |
|
(b) Ortiz-Medina, J.; Wang, Z. P.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Morelos-Gomez, A.; Wang, F.; Yao, X. D.; Terrones, M.; Endo, M. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805717.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.13 |
|
|
(c) Tang, C.; Zhang, Q. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604103.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.13 |
|
| [36] |
(a) Zhu, J. W.; Huang, Y. P.; Mei, W. C.; Zhao, C. Y.; Zhang, C. T.; Zhang, J.; Amiinu, I. S.; Mu, S. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3859.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.12 |
|
(b) Wang, W.; Shang, L.; Chang, G. J.; Yan, C. Y.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. X.; Waterhouse, G. I.; Yang, D. J.; Zhang, T. R. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808276.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.19 |
|
| [37] |
Nethravathi, C.; Rajamathi, M. Carbon 2008, 46, 1994.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2008.08.013 |
| [38] |
Xu, J.; Roghabadi, F. A.; Luo, Y.; Ahmadi, V.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, H. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 140, 165.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.06.028 |
| [39] |
Jia, Y. F.; Li, F.; Fan, K.; Sun, L. C. Adv. Powder Mater. 2021, 1, 1.
|
| [40] |
Birdja, Y. Y.; Pérez-Gallent, E.; Figueiredo, M. C.; Göttle, A. J.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Koper, M. T. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 732.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-019-0450-y |
| [41] |
Mino, L.; Spoto, G.; Ferrari, A. M. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2014, 118, 25016.
doi: 10.1021/jp507443k |
| [42] |
Tang, X. L.; Wang, C. Z.; Gao, F. Y.; Ma, Y. L.; Yi, H. H.; Zhao, S. Z.; Zhou, Y. S. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104399.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104399 |
| [43] |
(a) Shen, B. X.; Zhu, S. W.; Zhang, X.; Chi, G. L.; Patel, D.; Si, M.; Wu, C. F. Fuel 2018, 224, 241.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.080 |
|
(b) Larrubia, M. A.; Ramis, G.; Busca, G. Appl. Catal., B 2000, 27, L145.
doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00150-8 |
|
|
(c) Zawadzki, J.; Wiśniewski, M. Carbon 2003, 41, 2257.
doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00251-3 |
|
| [44] |
Wang, F.; Xie, Z. B.; Liang, J. S.; Fang, B. Z.; Piao, Y. A.; Hao, M.; Wang, Z. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6989.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b02620 |
| [45] |
Wang, C. Z.; Gao, F. Y.; Ko, S. J.; Liu, H. H.; Yi, H. H.; Tang, X. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134729.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134729 |
| [46] |
Ho, C.; Yu, J. C.; Kwong, T.; Mak, A. C.; Lai, S. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4514.
doi: 10.1021/cm0507967 |
| [47] |
Zhu, D. D.; Liu, J. L.; Qiao, S. Z. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3423.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v28.18 |
| [48] |
(a) Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00603 |
|
(b) Kumari, N.; Haider, M. A.; Agarwal, M.; Sinha, N.; Basu, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 16626.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b02860 |
|
| [49] |
Wang, Y. F.; Chen, Z.; Han, P.; Du, Y. H.; Gu, Z. X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, G. F. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7113.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01014 |
| [50] |
Creamer, A. E.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 174.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.105 |
| [51] |
(a) Geng, Z. G.; Kong, X. D.; Chen, W. W.; Su, H. Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, F.; Wang, G. X.; Zeng, J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6054;
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.21 |
|
(b) Liu, L. J.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Zhao, H. L.; Chen, J. T.; Cheng, J. L.; Yang, K. S.; Li, Y. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1097.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02098 |
|
| [52] |
Sheng, S.; Ye, K.; Gao, Y. Y.; Zhu, K.; Yan, J.; Wang, G. L.; Cao, D. X. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 325.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.06.001 |
| [53] |
(a) Yang, X. X.; Chen, X.; Cao, H. L.; Li, C.; Wang, L. L.; Wu, Y. L.; Wang, C. Z.; Li, Y. J. Power Sources 2020, 480, 228741.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228741 |
|
(b) Li, Z. Y.; Yang, Y. S.; Ding, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xie, W. F.; Hu, X. Y.; Wang, B. Chem Catal. 2023, 3, 10.
|
|
| [54] |
Zheng, W.; Nayak, S.; Yuan, W.; Zeng, Z.; Hong, X.; Vincent, K. A.; Tsang, S. C. E. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13901.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC07212G |
| [55] |
Wang, J.; Zheng, M. Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, W. L. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 5441.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00429 |
| [56] |
(a) Wang, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, M.; Geng, Y.; Su, Z. Adv. Theory Simul. 2020, 3, 2000218.
doi: 10.1002/adts.v3.12 |
|
(b) Peng, L. W.; Zhang, Y.; He, R. N.; Xu, N. N.; Qiao, J. L. Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica 2023, 39, 2302037.
|
|
| [57] |
Hummers Jr, W. S.; Offeman, R. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339.
doi: 10.1021/ja01539a017 |
| [1] | Quanyou Feng, Yunlong Zhang, Hao Li, Qianyi Li, Jianping Shen, Mengna Yu, Linghai Xie. Geometry Configuration and Bromo Substitution Effect of Terfluorenes on Amplified Spontaneous Emission Behaviors [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 435-442. |
| [2] | Qi Gu, Xiaxia Liu, Xinyu Zhou, Jiang Li, Xiujing Lin, Yanwen Ma. Recent Progress on Polymer Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Batteries [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 449-457. |
| [3] | Guojing Wang, Yonghui Chen, Xiuqin Zhang, Junsheng Zhang, Junmin Xu, Jing Wang. Magnetic and Photoelectrocatalytic Properties of BiVO4 Surface Heterojunctions Controlled by Oxygen Vacancies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 409-415. |
| [4] | Qing Yang, Xiaoyu Liu, Chen Wang, Minmin Xu, Jianlin Yao. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Studies on the “Hot Spot” Localized Area from Free Collision Behavior of Gold Nanoparticle-Gold Single Crystal Microplate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 281-286. |
| [5] | Qiang Zhang, Huan Wang, Shuai Wang, Yuanyuan Wang, Mei Zhang, Hua Song. Preparation of NiCe(x)/FLRC-TiO2 Catalyst and Its Performance in Hydrodeoxygenation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 287-294. |
| [6] | Yu-Qiang Zhao, Xia Zhang, Yunru Yang, Liping Zhu, Ying Zhou. Design and Synthesis of Aggregation-Induced Emission Photocage Molecules for In Situ Photoactivation Imaging Studies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 265-273. |
| [7] | Guangzheng Huang, Kunwei Li, Yannan Luo, Qiang Zhang, Yuanlong Pan, Honglin Gao. Hydrothermal Treatment for Constructing K Doping and Surface Defects in g-C3N4 Nanosheets Promote Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 314-322. |
| [8] | Bo Wang, Xiangdong Cai, Jianxi Xiao. Tumor-specific Peptide Probes and the Applications in Bioimaging [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 367-376. |
| [9] | Xuepeng Liu, Botong Li, Mingyuan Han, Xianfu Zhang, Jianlin Chen, Songyuan Dai. Research Progress of Self-assembled Hole-transporting Monolayers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 348-366. |
| [10] | Dongbin Zhang, Xinran Yuan, Yanan Xin, Tianhao Liu, Huiguo Han, Guangchao Du, Aijun Teng. Research on Preparation of Nano-flake Sodium Vanadyl Phosphate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 274-280. |
| [11] | Xiaoyu Gu, Jin Li, Qian Sun, Chaoyang Wang. Microcalorimetry Analysis of Thermal Runaway Process in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 146-151. |
| [12] | Cheng-Qiang Wang, Chao Feng. Applications of Nucleophilic Fluorine Sources in the Selective Fluorofunctionalization of Unsaturated Carbon-Carbon Bonds [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 160-170. |
| [13] | Shenna Deng, Changchun Peng, Yunhong Niu, Yun Xu, Yunxiao Zhang, Xiang Chen, Hongmin Wang, Shanshan Liu, Xiao Shen. Radical Brook Rearrangement Mediated Olefin Difunctionalization Involving α-Fluoroalkyl-α-silyl Methanols [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 119-125. |
| [14] | Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue. Computational Study on the Mechanism of Chen’s Reagent as Trifluoromethyl Source [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [15] | Ping Li, Qiyu Yang, Jing Zeng, Ran Zhang, Qiuyan Chen, Fei Yan. Effect of Fluorine Doping on the Performance of Reversible Solid Oxide Cells and Related Kinetic Studies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(1): 36-45. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||