Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (1): 73-85.DOI: 10.6023/A25040118 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2025-04-14
发布日期:2025-08-26
Yichun Loua, Chengli Hea,b, Linrui Wanga, Xiaoli Cuia,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-14
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
* E-mail: xiaolicui@fudan.edu.cn; Tel.: 13817061363
Share
Yichun Lou, Chengli He, Linrui Wang, Xiaoli Cui. Mechanochemical Urea Synthesis Using Nitrogen, Water and Carbon Dioxide with TiO2 under Mild Conditions: An Experimental and Theoretical Study[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 73-85.
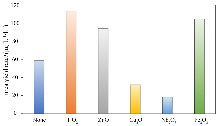
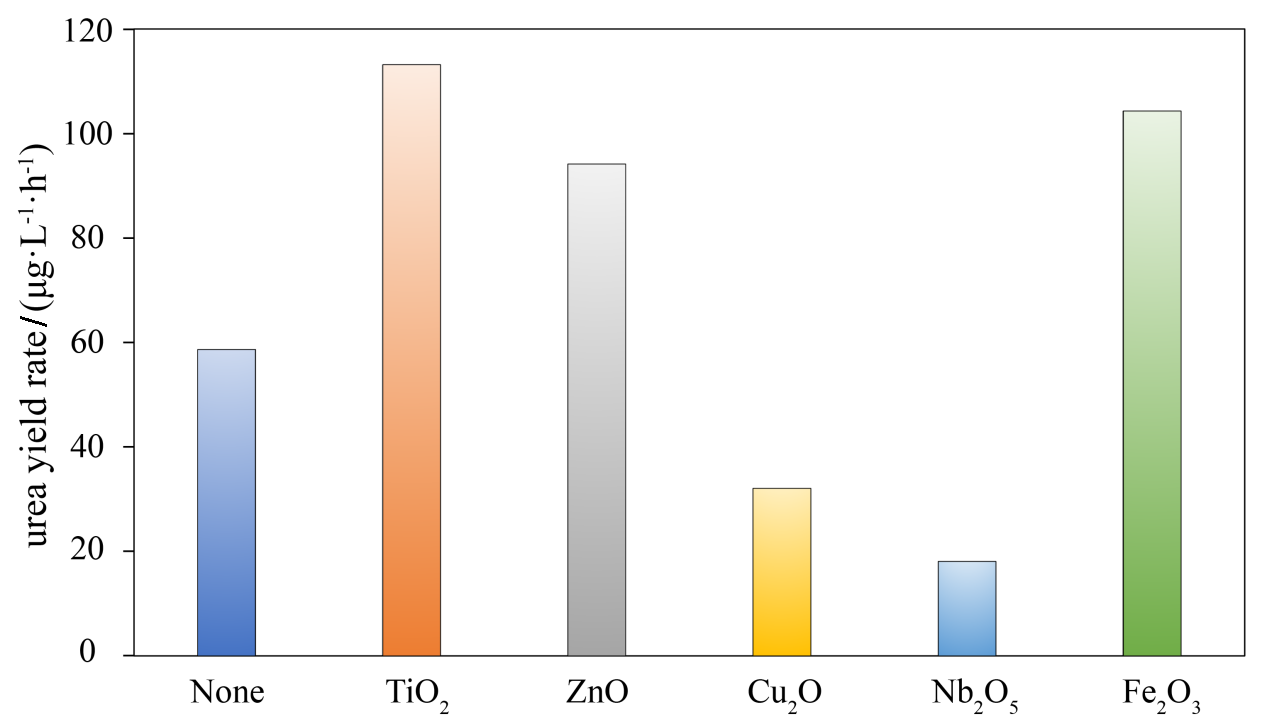
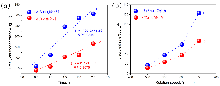
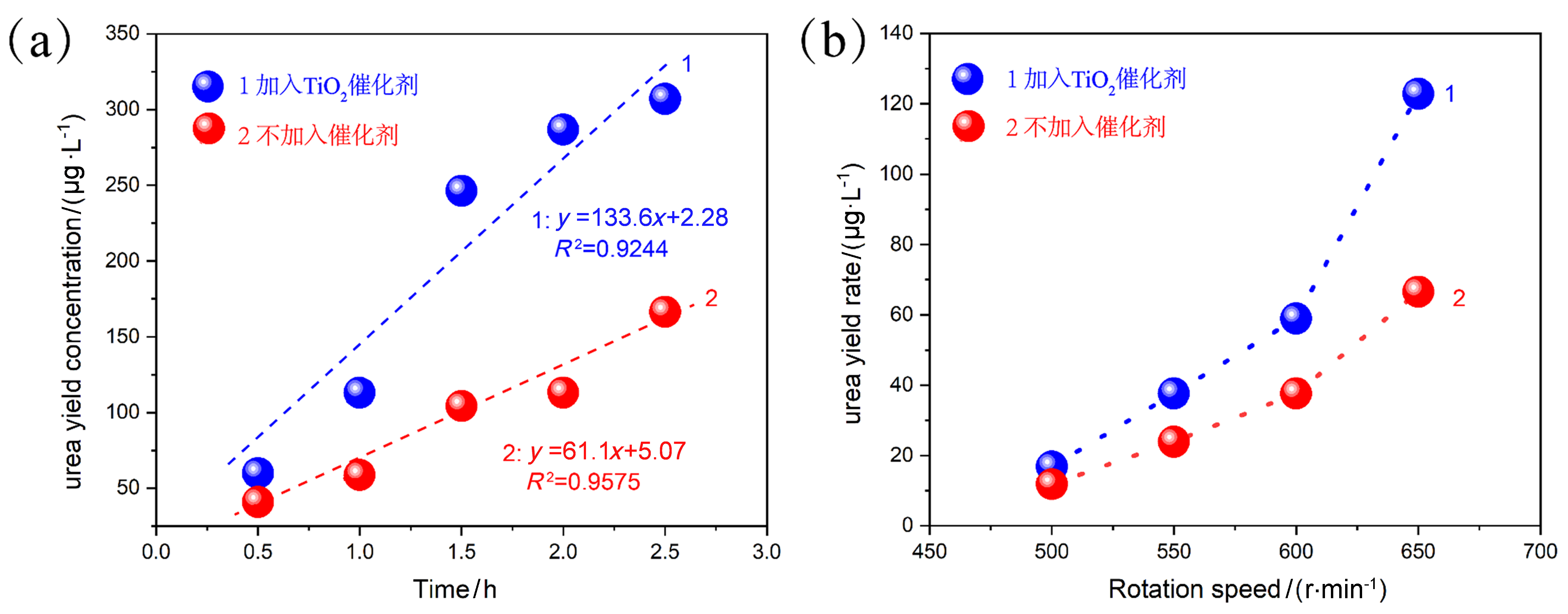
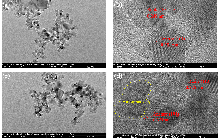

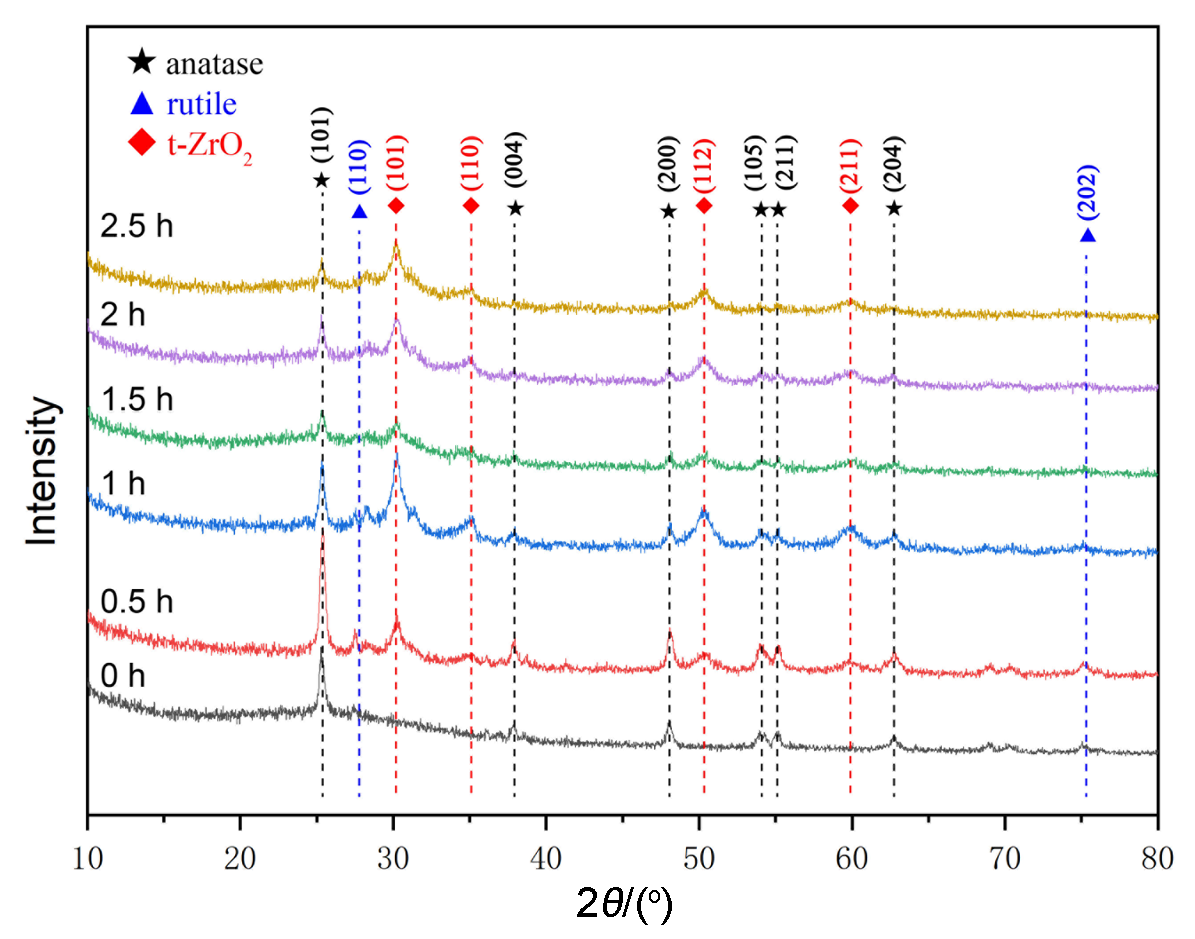
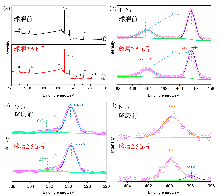

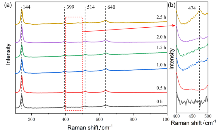
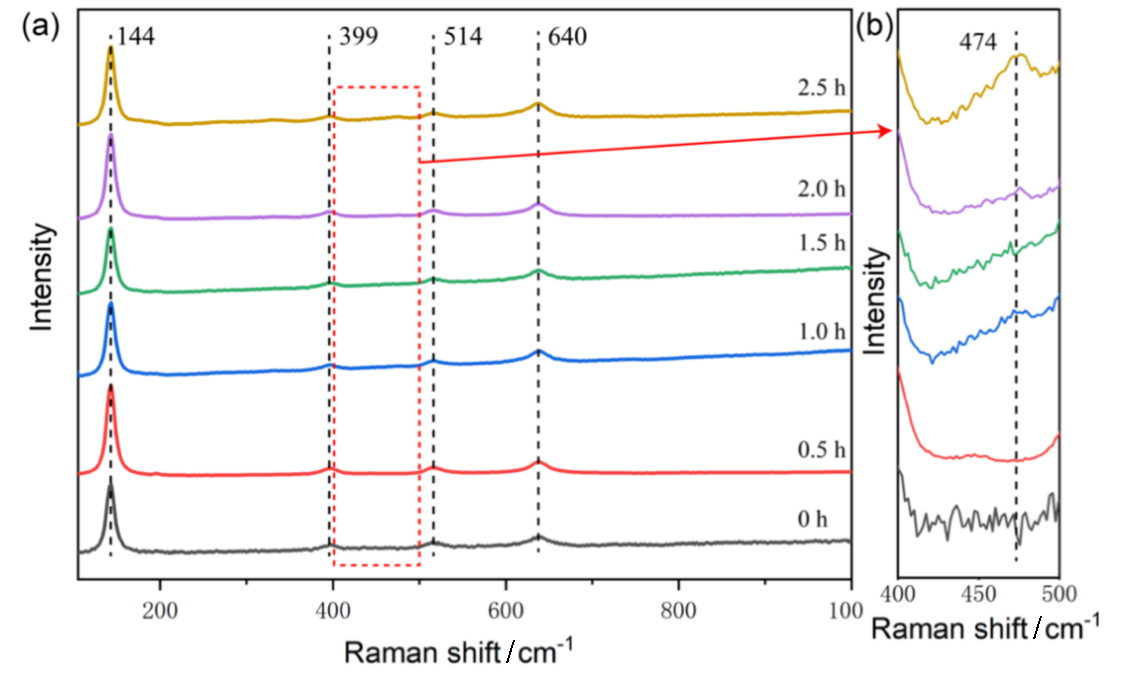
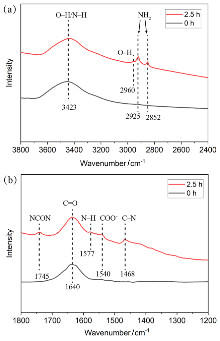
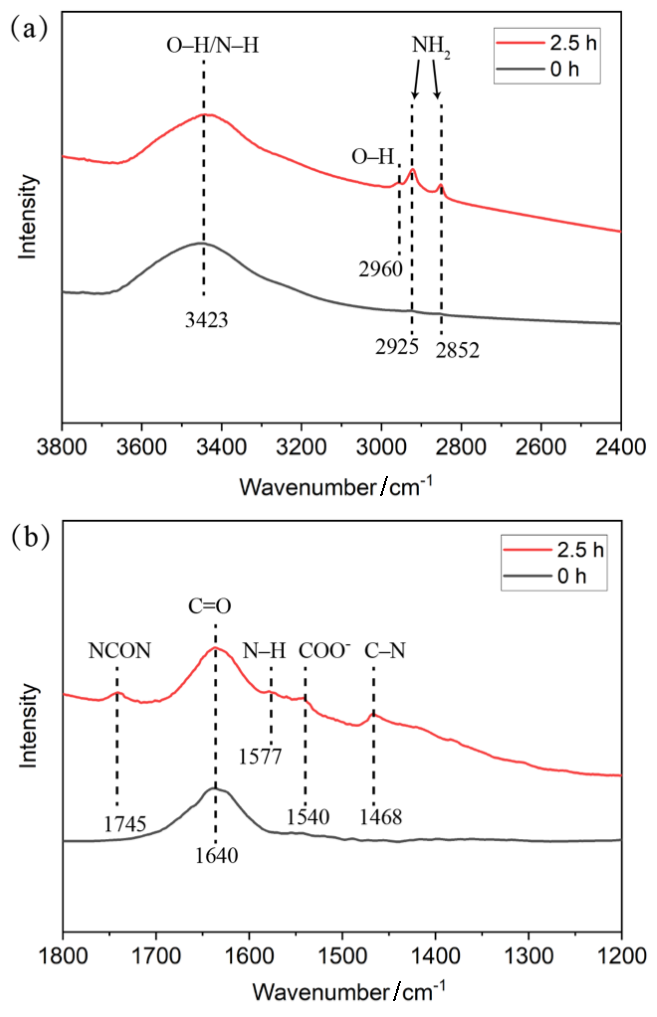
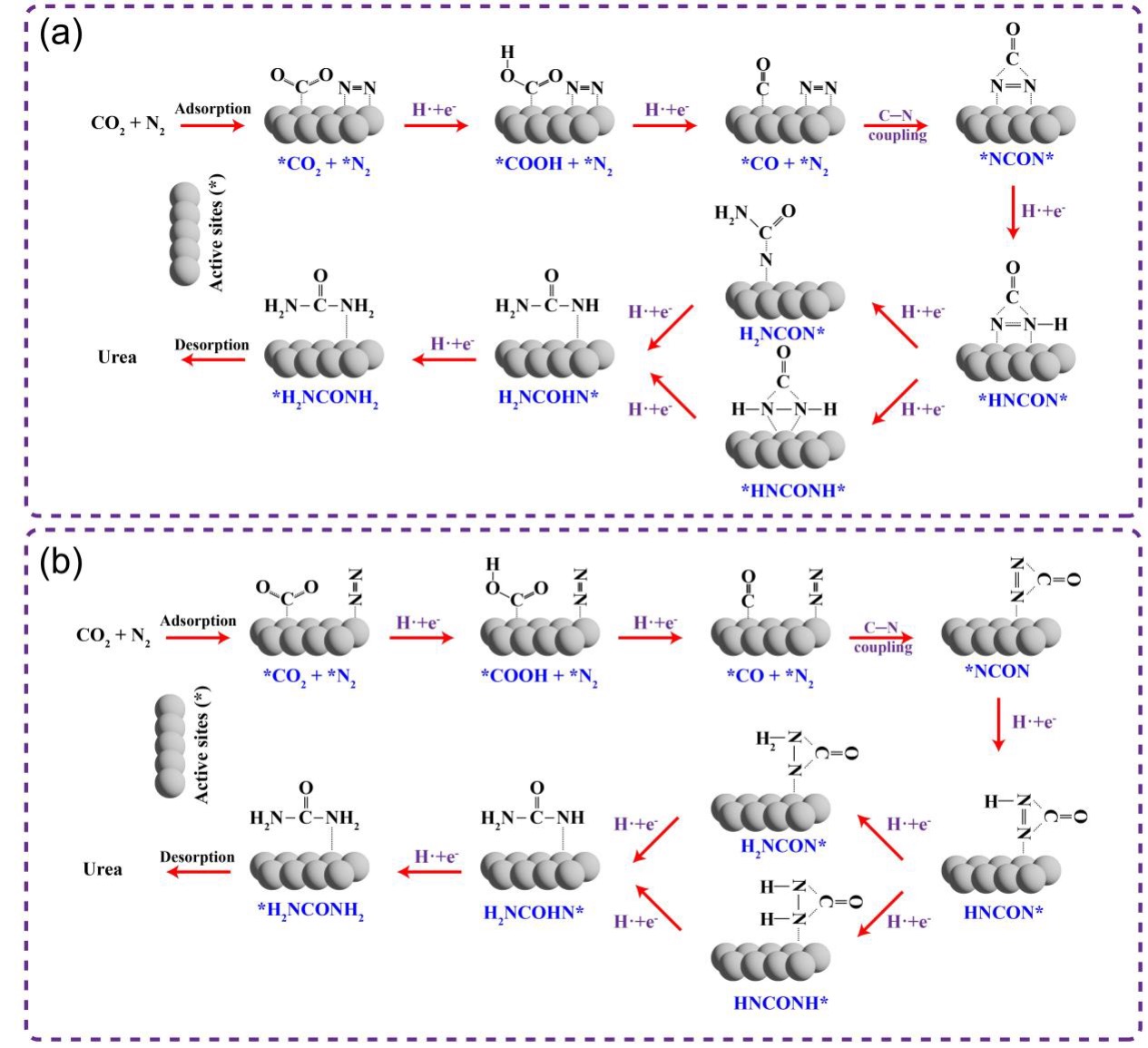
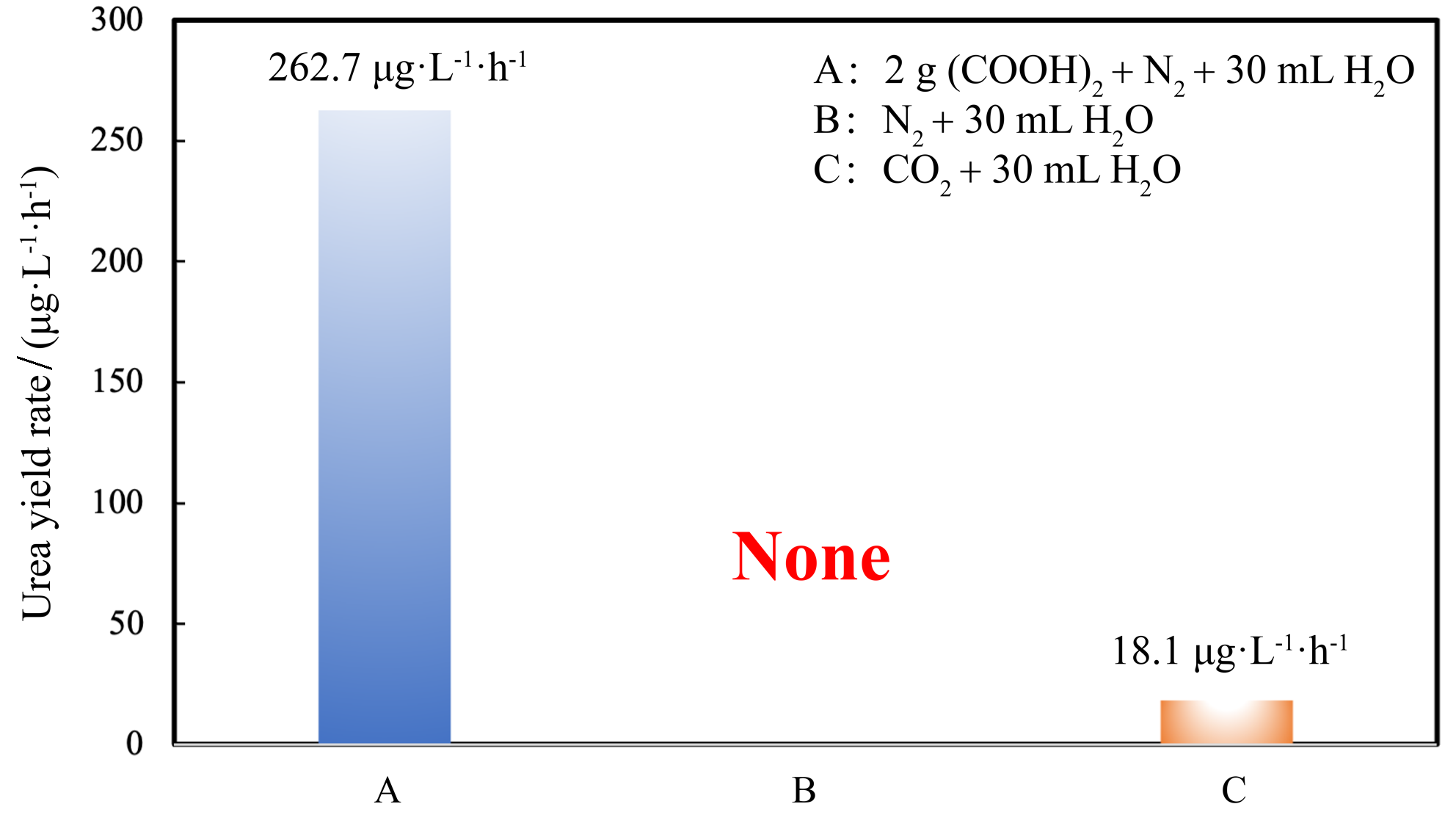
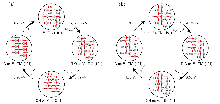
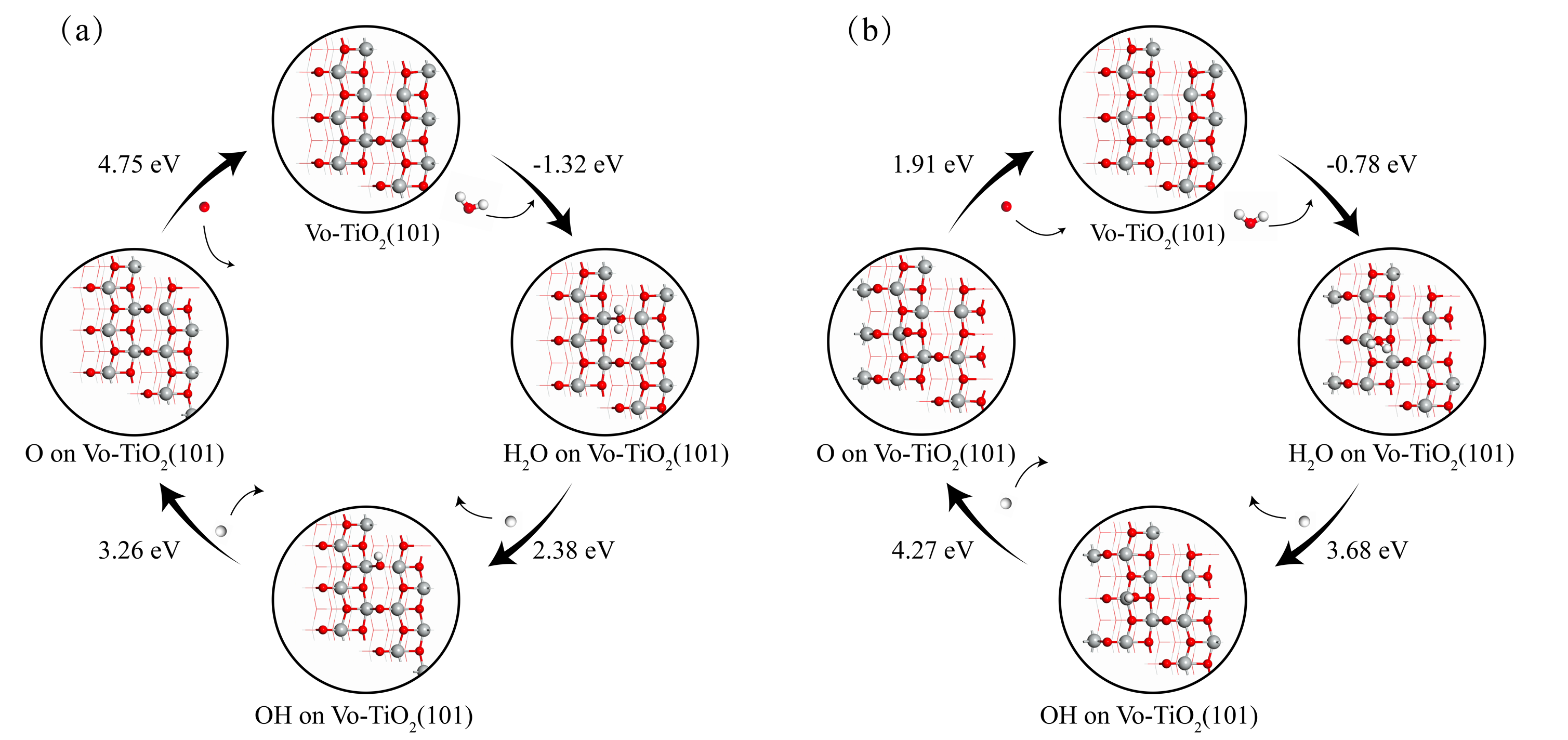
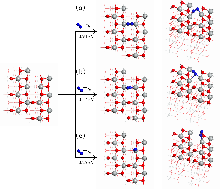
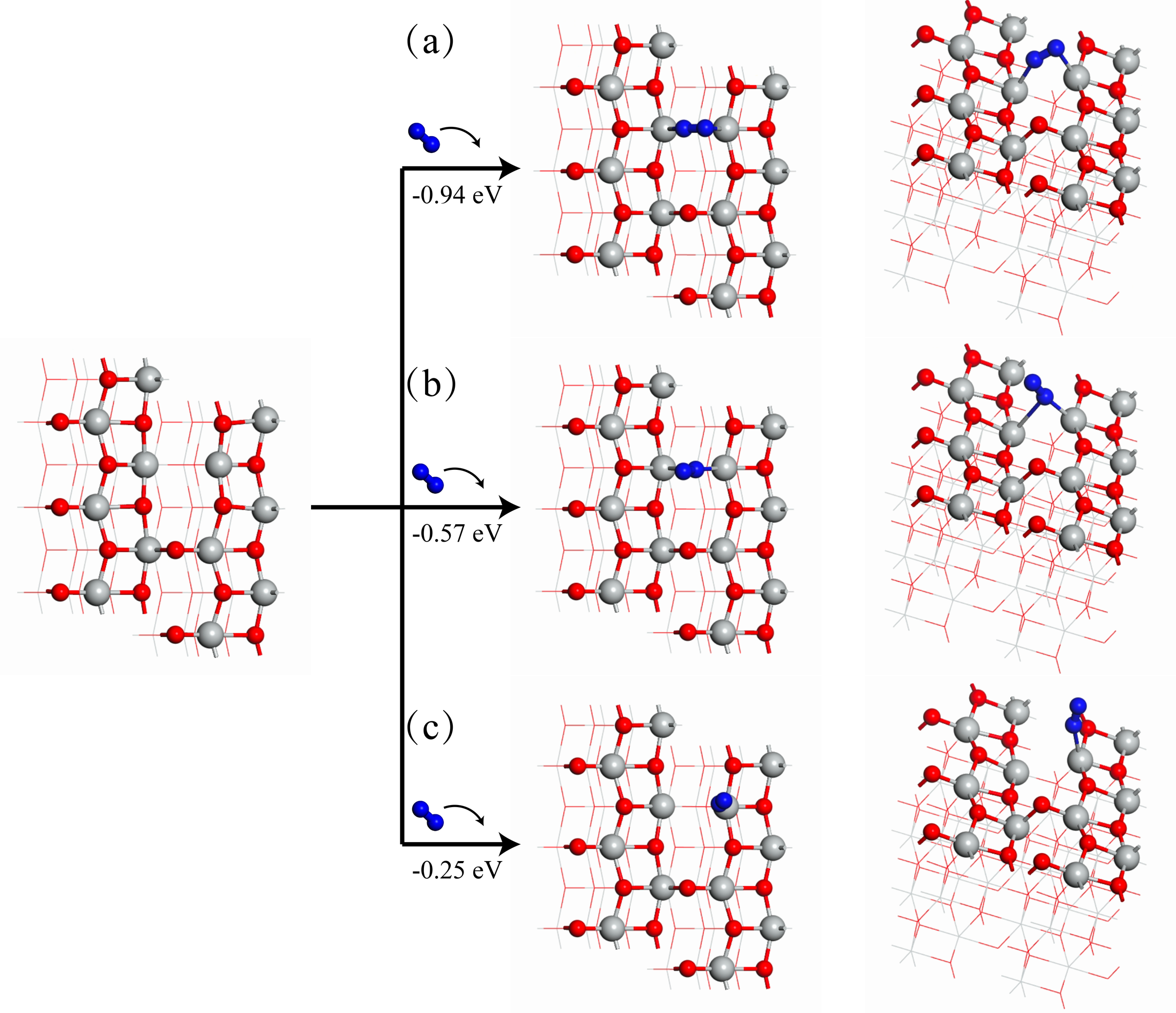
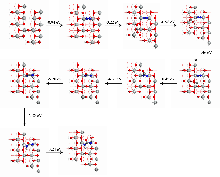

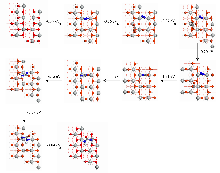
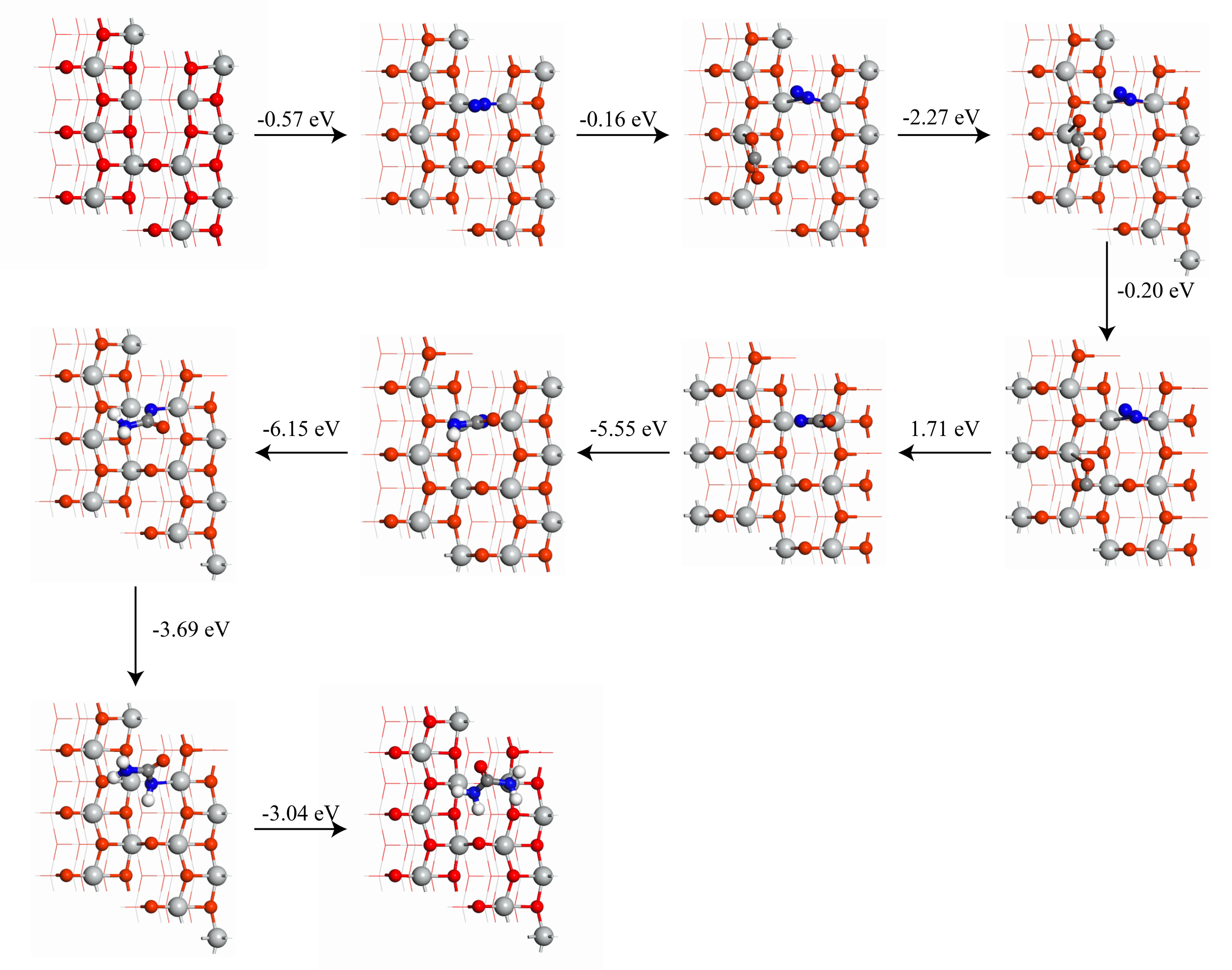
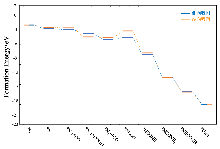
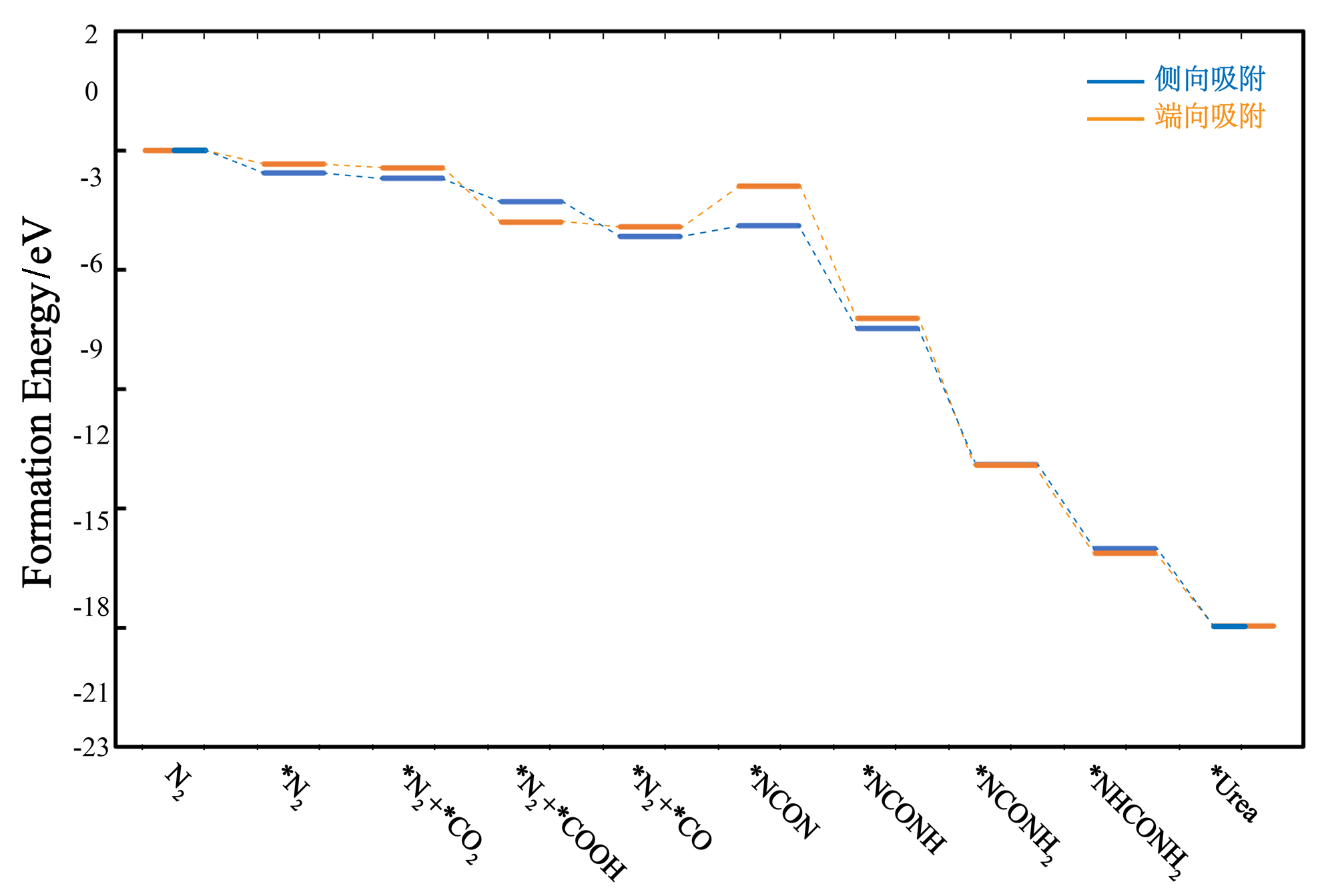
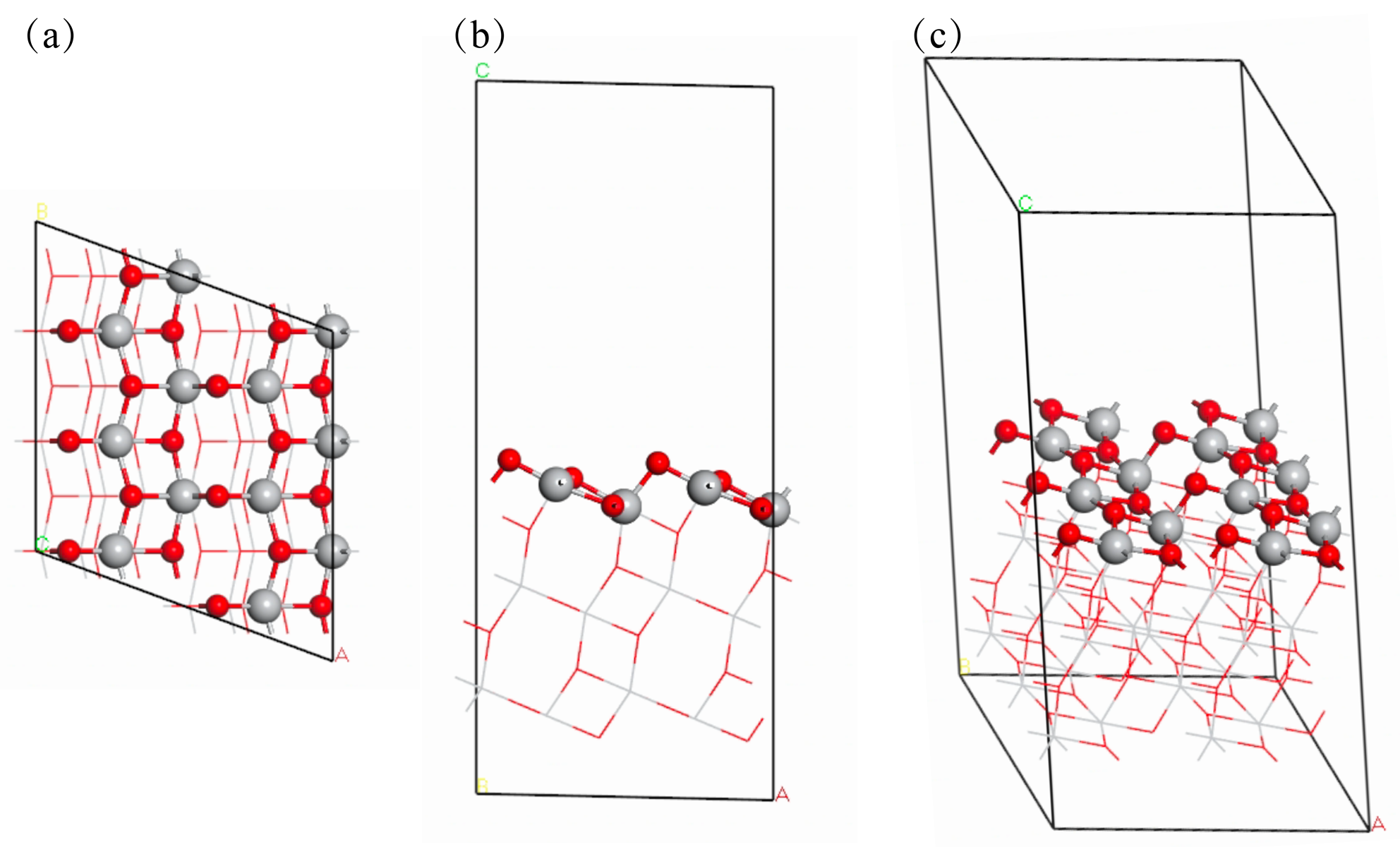
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c03298 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2024.04.004 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v63.23 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/ngeo325 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.834 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/ente.v4.11 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4218 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c05811 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.054 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.33 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.10 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.17 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.3 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b04393 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1039/D0MH00081G |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1039/C1CS15171A |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202411009 |
|
(许秋玲, 孙瑞芬, 王均亮, 何晓山, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 2416.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202411009 |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.46 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.6023/A24090273 |
|
(刘雨涵, 高盼, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 1114.)
doi: 10.6023/A24090273 |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202300062 |
|
(王官武, 潘虹, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 4010.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202300062 |
|
| [23] |
|
|
(冯浩洋, 邵晓阳, 王振华, 潘翔城, 科学通报, 2024, 69, 3412.)
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-00809-9 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38050-2 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60715-3 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c05643 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10888-5 pmid: 31253834 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.025 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05156 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1061051 pmid: 11452117 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119287 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.180 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b06450 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules27249032 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1021/jp0273934 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1021/j100267a018 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1039/D2TA00661H |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.3762/bjnano.6.86 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.07.033 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c03451 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v63.48 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12101 pmid: 29320173 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1021/ma00162a008 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.1 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1039/D1RA07060F |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.33 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.43 |
| [52] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123146 |
|
| [53] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24400-5 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c01895 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126033 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1038/s41557-020-0481-9 pmid: 32541948 |
| [57] |
|
| [1] | Zhihao Yao, Wei Zhang, Zhaoyi Zhou, Dancong Li, Kaikai Zhang, Tao Liu, Wenkai Hu, Shouan Cheng, Mingxuan Hu, Yujia Liu. Study on Synergistic Modulation of LaMnO3 Electronic Structure and CO Selective Catalytic Reduction Reaction Mechanism via Sr/Fe [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 30-42. |
| [2] | Yuqi Zhang, Jinze Liu, Dongxu Xue, Yuxiang Shi, Weixian Zhang. Mechanochemistry: Pollutant Transformation Mechanism and Environmental Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(9): 1055-1071. |
| [3] | Shoufei Cheng, Jing Li, Lin Ling, Yuxue Li, Long Lu. Density Functional Theory Research on Decomposition Mechanisms of Nitroglycerin [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 833-843. |
| [4] | Xin Wang, Yiwei Shi, Ruijie Yang, Zhiguo Song, Min Wang. Solvent-Free “One-Pot” Biginelli Reaction Catalyzed by Mononuclear Cd(II) Complex Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Ligands [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(7): 674-684. |
| [5] | Yi-Lin Lu, Shengjie Dong, Fangchao Cui, Tingting Bo, Zhuo Mao. Theoretical Construction of Hittorf’s Violet Phosphorene/SnS2 van der Waals Heterojunction as Direct Photocatalyst for Overall Water Splitting [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(4): 377-389. |
| [6] | Minghui Chen, Boxin Zhang, Tao Wei, Zhaoxue Sun, Yaqing Feng, Bao Zhang. Theoretical Calculation Studies on Interlayer Displacement Behavior and Photogenerated Carrier Dynamics of Covalent Triazine Frameworks [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(2): 93-100. |
| [7] | Naixin Zhang, Weiqun Shi, Congzhi Wang. Theoretical Studies of Divalent Actinide Complexes AnB8 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1523-1529. |
| [8] | Ying Ma, Weixi Chen, Yuchen Liu, Ziyi Liu, Tao Wu, An-Hui Lu, Dongqi Wang. Density Functional Theory Study of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Oxidation Mode [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(1): 52-59. |
| [9] | Yuqing Zhao, Dong Liang, Jihui Jia, Rongmin Yu, Can-Zhong Lu. Synthesis and Characterization of an Emissive Ag(I) Complex with a D-A Type Ligand Containing Two Electron-withdrawing Groups [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 486-492. |
| [10] | Yu-Qiang Zhao, Xia Zhang, Yunru Yang, Liping Zhu, Ying Zhou. Design and Synthesis of Aggregation-Induced Emission Photocage Molecules for In Situ Photoactivation Imaging Studies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 265-273. |
| [11] | Guanglong Huang, Xiao-Song Xue. Computational Study on the Mechanism of Chen’s Reagent as Trifluoromethyl Source [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [12] | Yuhan Liu, Pan Gao. Direct Borylation of Organohalides Using Mechanochemically Generated Calcium-Based Heavy Grignard Reagents (R-CaX) [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(11): 1114-1119. |
| [13] | Yichen Huang, Changming Nie, Congzhi Wang, Shusen Chen, Yan Song, Hao Li, Weiqun Shi. Theoretical Study of Hydroxyl- and Amino-substituted Amidoxime Ligands for Extraction of Uranium from Seawater [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(10): 1050-1057. |
| [14] | Xuefeng Liang, Jian Jing, Xin Feng, Yongze Zhao, Xinyuan Tang, Yan He, Lisheng Zhang, Huifang Li. Electronic Structure of Covalent Organic Frameworks COF66 and COF366: from Monomers to Two-Dimensional Framework [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 717-724. |
| [15] | Chuwen Luo, Chaoying Kong, Zhaohui Tang. Research Progress in Sonochemistry for Biomedical Applications★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 836-842. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||