有机化学 ›› 2019, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 2989-3012.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201904037 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 碳氢活化合辑2018-2019
综述与进展
收稿日期:2019-04-14
发布日期:2019-07-03
通讯作者:
莫冬亮
E-mail:moeastlight@mailbox.gxnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Lei Luab, Li Chengjinga, Mo Donglianga*( )
)
Received:2019-04-14
Published:2019-07-03
Contact:
Mo Dongliang
E-mail:moeastlight@mailbox.gxnu.edu.cn
Supported by:文章分享

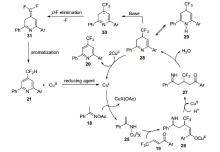
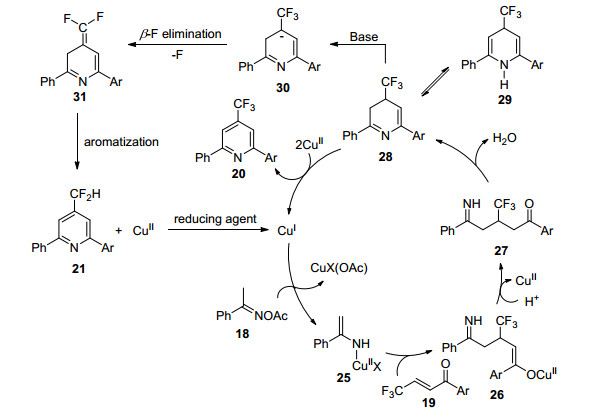
N-O键断裂反应是向化合物中引入含氮、氧官能团的有效策略之一.铜催化剂来源丰富,价格便宜,铜催化剂在有机合成中占有不可替代的地位.铜催化的N-O断裂,由于具有反应条件温和、官能团兼容性好、原子经济性高等优点,在有机合成中被广泛应用于构建C-N和C-O键.N-O键的断裂策略在复杂天然产物及药物分子的合成中都有成功的应用.综述了近些年来铜金属催化N-O断裂的新策略及N-O断裂策略在天然产物和药物分子合成中的应用.
雷禄, 李承璟, 莫冬亮. 铜催化N-O键断裂策略研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(11): 2989-3012.
Lei Lu, Li Chengjing, Mo Dongliang. Recent Advances in Copper-Catalyzed N-O Cleavage Strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019, 39(11): 2989-3012.
| [1] |
Bolotin D. S. Bokach N. A. Demakova M. Y. Kukushkin V. Y. Chem. Rev. 2017 117 13039.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00264 |
| [2] |
(a) Jiao, Y.-X.; Ma, X.-P.; Su, G.-F.; Mo, D.-L. Synthesis. 2017, 49, 933.
doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1588352 |
|
(b) Chen, N.; Xie, J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 11028.
doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1588352 |
|
| [3] |
(a) Shi, W.-M.; Ma, X.-P.; Su, G.-F.; Mo, D.-L. Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 116.
doi: 10.1039/C5QO00122F |
|
(b) Murahashi, S.-I.; Imada, Y. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4684.
doi: 10.1039/C5QO00122F |
|
| [4] |
Lu D.-F. Zhu C.-L. Jia Z.-X. Xu H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014 136 13186.
doi: 10.1021/ja508057u |
| [5] |
Senadi G. C. Lu T.-Y. Dhandabani G. K. Wang J.-J. Org. Lett. 2017 19 1172.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00208 |
| [6] |
Neely J. M. Rovis T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013 135 66.
doi: 10.1021/ja3104389 |
| [7] |
Yeom H.-S. Shin S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014 47 966.
doi: 10.1021/ar4001839 |
| [8] |
(a) Yao, C.-Z.; Xiao, Z.-F.; Liu, J.; Ning, X.-S.; Kang, Y.-B. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2498.
doi: 10.1021/ol500869p |
|
(b) Kumar, C. V. S.; Ramana, C. V. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2870.
doi: 10.1021/ol500869p |
|
| [9] |
(a) Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Qi, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, H. E.; Yi, W. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6999.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01571 |
|
(b) Xia, J.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 3242.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01571 |
|
| [10] |
Nakamura I. Sato Y. Terada M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009 131 4198.
doi: 10.1021/ja900174t |
| [11] |
Sivakumar G. Vijeta A. Jeganmohan M. Chem. Eur. J. 2016 22 5899.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201600471 |
| [12] |
Liu X.-G. Gao H. Zhang S.-S. Li Q. Wang H. ACS Catal. 2017 7 5078.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00677 |
| [13] |
(a) Yang, H.-B.; Pathipati, S. R.; Selander, N. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8441.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b03432 |
|
(b) Ding, D.; Wang, C. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 111324.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b03432 |
|
| [14] |
Tang X. Wu W. Zeng W. Jiang H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018 51 1092.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00611 |
| [15] |
(a) Ma, X.-P.; Liu, F.-P.; Mo, D.-L. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 1069 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A14120888 |
|
(b) Lu, Q.; Yi, H.; Lei, A. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1245.
doi: 10.6023/A14120888 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, C.; Lei, A. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 743 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A14120888 |
|
| [16] |
(a) Ma, D.; Cai, Q. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1450.
doi: 10.1021/ar8000298 |
|
(b) McCann, S. D.; Stahl, S. S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1756.
doi: 10.1021/ar8000298 |
|
| [17] |
Dong X. Liu Q. Dong Y. Liu H. Chem. Eur. J. 2017 23 2481.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201601607 |
| [18] |
Jiang H. Yang J. Tang X. Li J. Wu W. J. Org. Chem. 2015 80 8763.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b01621 |
| [19] |
Fu Y. Wang P. Guo X. Wu P. Meng X. Chen B. J. Org. Chem. 2016 81 11671.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b02081 |
| [20] |
Tan W. W. Ong Y. J. Yoshikai N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017 56 8240.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201704378 |
| [21] |
Bai D. Wang X. Zheng G. Li X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018 57 6633.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201802311 |
| [22] |
Jiang H. Yang J. Tang X. Wu W. J. Org. Chem. 2016 81 2053.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02914 |
| [23] | Ramaraju A. Chouhan N. K. Ravi O. Sridhar B. Bathula S. R. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018 2963. |
| [24] |
Huang H. Cai J. Ji X. Xiao F. Chen Y. Deng G.-J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016 55 307.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201508076 |
| [25] |
Zhao B. Liang H.-W. Yang J. Yang Z. Wei Y. ACS Catal. 2017 7 5612.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01876 |
| [26] |
Zhu C. Zhu R. Zeng H. Chen F. Liu C. Wu W. Jiang H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017 56 13324.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201707719 |
| [27] |
Yang J. Zhao B. Xi Y. Sun S. Yang Z. Ye Y. Jiang K. Wei Y. Org. Lett. 2018 20 1216.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00141 |
| [28] |
Xie Y. Li Y. Chen X. Liu Y. Zhang W. Org. Chem. Front. 2018 5 1698.
doi: 10.1039/C8QO00204E |
| [29] |
Dai X.-J. Engl O. D. León T. Buchwald S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019 58 3407.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201814331 |
| [30] |
Zhao B. Shi Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017 56 12727.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201707181 |
| [31] |
Ai W. Liu Y. Wang Q. Lu Z. Liu Q. Org. Lett. 2018 20 409.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03707 |
| [32] |
Zhu C. Chen F. Liu C. Zeng H. Yang Z. Wu W. Jiang H. J. Org. Chem. 2018 83 14713.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02103 |
| [33] |
An Z. Jiang Y. Guan X. Yan R. Chem. Commun. 2018 54 10738.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC06256K |
| [34] |
Wu J. Zhang J.-Y. Gao P. Xu S.-L. Guo L.-N. J. Org. Chem. 2018 83 1046.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b02714 |
| [35] |
He M. Yan Z. Zhu F. Lin S. J. Org. Chem. 2018 83 15438.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02707 |
| [36] |
Yu X.-Y. Zhao Q.-Q. Chen J. Chen J.-R. Xiao W.-J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018 57 15505.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201809820 |
| [37] |
Wang P. Zhao B. Yuan Y. Shi Z. Chem. Commun. 2019 55 1971.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC10109D |
| [38] |
He Y. Lou J. Wu K. Wang H. Yu Z. J. Org. Chem. 2019 84 2178.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b03175 |
| [39] |
Min Q.-Q. Li N. Chen G.-L. Liu F. Org. Chem. Front. 2019 6 1200.
doi: 10.1039/C9QO00235A |
| [40] |
Tang X. Zhu Z. Qi C. Wu W. Jiang H. Org. Lett. 2016 18 180.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03188 |
| [41] |
Tang X. Yan J. Zhu Z. Zheng M. Wu W. Jiang H. J. Org. Chem. 2016 81 11461.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b02124 |
| [42] |
Zhu Z. Tang X. Cen J. Li J. Wu W. Jiang H. Chem. Commun. 2018 54 3767.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC00445E |
| [43] |
Zhou P. Huang Y. Wu W. Yu W. Li J. Zhu Z. Jiang H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019 17 3424.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB00377K |
| [44] |
Liu H. Yan X. Chen C. Liu Q. Xi C. Chem. Commun. 2013 49 5513.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc41574k |
| [45] |
Zhu Z. Tang X. Li J. Li X. Wu W. Deng G. Jiang H. Chem. Commun. 2017 53 3228.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC00260B |
| [46] |
Yang H.-B. Selander N. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017 15 1771.
doi: 10.1039/C7OB00203C |
| [47] |
Xu L.-L. Wang X. Ma B. Yin M.-X. Lin H.-X. Dai H.-X. Yu J.-Q. Chem. Sci. 2018 9 5160.
doi: 10.1039/C8SC01256C |
| [48] |
Ren Z.-H. Zhao M.-N. Yi Y. Wang Y.-Y. Guan Z.-H. Synthesis 2016 48 1920.
doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1561950 |
| [49] |
Zhu C. Zeng H. Chen F. Liu C. Zhu R. Wu W. Jiang H. Org. Chem. Front. 2018 5 571.
doi: 10.1039/C7QO00874K |
| [50] |
Ke J. Tang Y. Yi H. Li Y. Cheng Y. Liu C. Lei A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015 54 6604.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201501287 |
| [51] |
Reidl T. W. Son J. Wink D. J. Anderson L. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017 56 11579.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201705681 |
| [52] |
He M. Yan Z. Wang W. Zhu F. Lin S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018 59 3706.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.09.007 |
| [53] |
Mo D.-L. Anderson L. L. Angew. Chem. 2013 52 6722.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201301963 |
| [54] |
Yan H. Wang H. Li X. Xin X. Wang C. Wan B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015 54 10613.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201503997 |
| [55] | Wolosewicz K. Michalak M. Adamek J. Furman B. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016 2212. |
| [56] |
Son J. Kim K. H. Mo D.-L. Wink D. J. Anderson L. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017 56 3059.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201611791 |
| [57] |
Kong Y. Liu Y. Wang B. Li S. Liu L. Chang X. Li J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018 360 1240.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201701476 |
| [58] |
Hasegawa M. Nomoto A. Soeta T. Ukaji Y. Chem. Lett. 2017 46 45.
doi: 10.1246/cl.160821 |
| [59] |
Shen W.-B. Sun Q. Li L. Liu X. Zhou B. Yan J.-Z. Lu X. Ye L.-W. Nat. Commun. 2017 8 1748.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01853-1 |
| [60] |
Liu X. Zhang Z.-X. Zhou B. Wang Z.-S. Zheng R.-H. Ye L.-W. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017 15 10156.
doi: 10.1039/C7OB02728A |
| [61] | Wang Z. Han M.-Y. Li P. Wang L. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018 5954. |
| [62] |
Tian Z. Xu J. Liu B. Tan Q. Xu B. Org. Lett. 2018 20 2603.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00798 |
| [63] |
Zou N. Jiao J.-W. Feng Y. Pan C.-X. Liang C. Su G.-F. Mo D.-L. Org. Lett. 2019 21 481.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03767 |
| [64] |
Ma X.-P. Li L.-G. Zhao H.-P. Du M. Liang C. Mo D.-L. Org. Lett. 2018 20 4571.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01761 |
| [65] |
Hu F. Szostak M. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015 357 2583.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201500319 |
| [66] |
Li L. Tan T.-D. Zhang Y.-Q. Liu X. Ye L.-W. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017 15 8483.
doi: 10.1039/C7OB01895A |
| [67] |
Li L. Wang H. Yu S. Wang X. Li X. Org. Lett. 2016 18 3662.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b01716 |
| [68] |
Biswas A. Karmakar U. Nandi S. Samanta R. J. Org. Chem. 2017 82 8933.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b01343 |
| [69] |
Guo S. Yang C. J. Buchwald S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018 140 15976.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b10564 |
| [70] |
Xie F. Shen B. Li X. Org. Lett. 2018 20 7154.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03093 |
| [71] |
Wang F. Xu P. Wang S.-Y. Ji S.-J. Org. Lett. 2018 20 2204.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00525 |
| [72] |
Sheng J. He R. Xue J. Wu C. Qiao J. Chen C. Org. Lett. 2018 20 4458.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01748 |
| [73] |
Galenko E. E. Novikov M. S. Shakirova F. M. Shakirova J. R. Kornyakov I. V. Bodunov V. A. Khlebnikov A. F. J. Org. Chem. 2019 84 3524.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00115 |
| [74] |
Nakamura I. Iwata T. Zhang D. Terada M. Org. Lett. 2012 14 206.
doi: 10.1021/ol203001w |
| [75] |
Nakamura I. Kudo Y. Terada M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013 52 7536.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201302751 |
| [76] |
Nakamera I. Ishida Y. Terada M. Org. Lett. 2014 16 2562.
doi: 10.1021/ol5009608 |
| [77] |
Zhang D. Nakamura I. Terada M. Org. Lett. 2014 16 5184.
doi: 10.1021/ol502541w |
| [78] |
Nakamura I. Onuma T. Zhang D. Terada M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014 55 1178.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.12.105 |
| [79] | Hazra S. Mondal B. Rahaman H. Roy B. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014 2806. |
| [80] |
Zhou S. Yang Z. Chen X. Li Y. Zhang L. Fang H. Wang W. Zhu X. Wang S. J. Org. Chem. 2015 80 6323.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b00767 |
| [81] | Sakae R. Hirano k. Satoh T. Miura M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015 54 613. |
| [82] |
Sakae R. Hirano K. Miura M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015 137 6460.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b02775 |
| [83] |
Hemric B. N. Shen K. Wang Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016 138 5813.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b02840 |
| [84] |
Nakamura I. Jo T. Ishida Y. Tashiro H. Terada M. Org. Lett. 2017 19 3059.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01110 |
| [85] |
Xu Q.-F. Liu Q.-Q. Zhang X. You S.-L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018 57 15204.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201809003 |
| [86] |
Ichikawa S. Zhu S. Buchwald S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018 57 8714.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201803026 |
| [87] |
Ishida Y. Nakamura I. Terada M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018 140 8629.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b03669 |
| [88] |
Wu F. Zhang M. Zhou W. Chen W. Liu M. Wu H. J. Org. Chem. 2018 83 5999.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b00605 |
| [89] |
Yang Z. Jiang K. Chen Y.-C. Wei Y. J. Org. Chem. 2019 84 3725.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00262 |
| [90] |
Wang Q. Li X. Org. Lett. 2016 18 2102.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00727 |
| [91] |
Śnieżek M. Stecko S. Panfil I. Furman B. Chmielewski M. J. Org. Chem. 2013 78 7048.
doi: 10.1021/jo400807c |
| [92] |
Diethelm S. Carreira E. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015 137 6084.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b02574 |
| [93] |
Wang F.-X. Du J.-Y. Wang H.-B. Zhang P.-L. Zhang G.-B. Yu K.-Y. Zhang X.-Z. An X.-T. Cao Y.-X. Fan C.-A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017 139 4282.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b13401 |
| [94] |
Nomura T. Yojoshima T. Fukuyama T. Org. Lett. 2018 20 119.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03555 |
| [1] | 刘杰, 韩峰, 李双艳, 陈天煜, 陈建辉, 徐清. 无过渡金属参与甲基杂环化合物与醇的选择性有氧烯基化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 573-583. |
| [2] | 宋晓, 卿晶, 黎君, 贾雪雷, 吴福松, 黄均荣, 金剑, 游恒志. 铜催化格氏试剂的不对称烯丙基烷基化连续流反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(9): 3174-3179. |
| [3] | 陈玉琢, 孙红梅, 王亮, 胡方芝, 李帅帅. 基于α-氢迁移策略构建杂环骨架的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(7): 2323-2337. |
| [4] | 陆晓雨, 孙晓梅, 钮亚琴, 王俊超, 殷文婧, 高梦婷, 刘孜, 韦正桓, 陶庭骅. 铜催化氟代丙烯酸与氧杂吖丙啶的脱羧交叉偶联反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(6): 2110-2119. |
| [5] | 鲍志成, 李慕尧, 王剑波. 铜催化芳基重氮乙酸酯与双[(频哪醇)硼基]甲烷的偶联反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1808-1814. |
| [6] | 孔德亮, 戴闻, 赵怡玲, 陈艺林, 朱红平. 脒基胺硼基硅宾与单酮和二酮的氧化环加成反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(5): 1843-1851. |
| [7] | 李春生, 连晓琪, 陈莲芬. 铜催化亚砜叶立德与邻苯二胺[4+2]环加成反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1492-1498. |
| [8] | 刘洋, 黄翔, 王敏, 廖建. 铜催化环酮亚胺与β,γ-不饱和N-酰基吡唑不对称Mannich-Type反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1499-1509. |
| [9] | 蒙玲, 汪君. 硫代黄烷酮类衍生物的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 873-891. |
| [10] | 刘春阳, 李燕, 张前. 铜催化环状烯烃烯丙位C(sp3)—H磺酰化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1091-1101. |
| [11] | 段康慧, 唐俊龙, 伍婉卿. 稠杂环化合物的合成及其抗肿瘤活性研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 826-854. |
| [12] | 曾成富, 何媛, 李清, 董琳. Ir(III)催化新型三组分串联三氟乙氧基化反应并一锅法构建复杂酰胺化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1115-1123. |
| [13] | 韩彪, 李维双, 陈舒晗, 张泽浪, 赵雪, 张瑶瑶, 朱磊. 铜催化不饱和化合物硅加成反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 555-572. |
| [14] | 郝二军, 丁笑波, 王珂新, 周红昊, 杨启亮, 石磊. 氮杂环丙烷与不饱和化合物发生[3+2]扩环反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(12): 4057-4074. |
| [15] | 李硕, 王明亮, 周来运, 王兰芝. 磁性纳米负载对甲苯磺酸催化串联合成稠合多环的1,5-苯并氧氮杂䓬类化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(11): 3977-3988. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||