有机化学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 2699-2710.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202212026 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 二氧化碳虚拟合辑
综述与进展
廖旭a,b, 王泽宇b, 唐武飞a,*( ), 林金清b,*(
), 林金清b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-20
修回日期:2023-03-28
发布日期:2023-04-21
基金资助:
Xu Liaoa,b, Zeyu Wangb, Wufei Tanga( ), Jinqing Linb(
), Jinqing Linb( )
)
Received:2022-12-20
Revised:2023-03-28
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

多孔有机聚合物(POPs)是一类由有机结构单元通过共价键连接而成的新型多孔材料, 具有合成方法多样、孔性质可调、孔道结构稳定、密度较低、比表面积大等优点, 已在气体吸附、分离与贮存、光电器件、传感以及非均相催化等方面展现出了重要的应用价值. 碳捕集、利用与封存(CCUS)技术作为大幅度减少化石能源二氧化碳(CO2)排放的重要途径, 其中将CO2催化转化为有价值的燃料或者工业增值产品是解决可再生能源利用以及实现绿色化学发展的潜在有效方法. 综述了共价有机框架(COFs)、共价三嗪框架(CTFs)、超交联聚合物(HCPs)、共轭微孔聚合物(CMPs)和自具微孔聚合物(PIMs)等多孔材料的合成、性质以及近几年在化学固定CO2方面取得的进展, 并对POPs在CO2催化方面的应用前景进行了展望.
廖旭, 王泽宇, 唐武飞, 林金清. 多孔有机聚合物用于化学固定二氧化碳的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2699-2710.
Xu Liao, Zeyu Wang, Wufei Tang, Jinqing Lin. Progress in Porous Organic Polymer for Chemical Fixation of Carnbon Dioxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2699-2710.

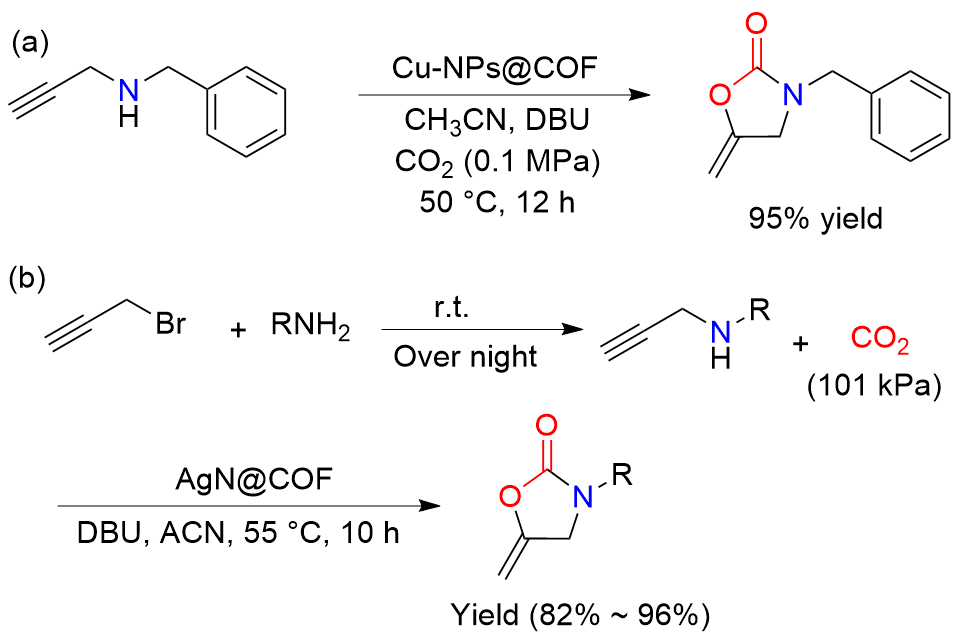
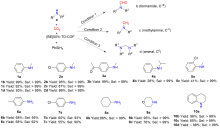
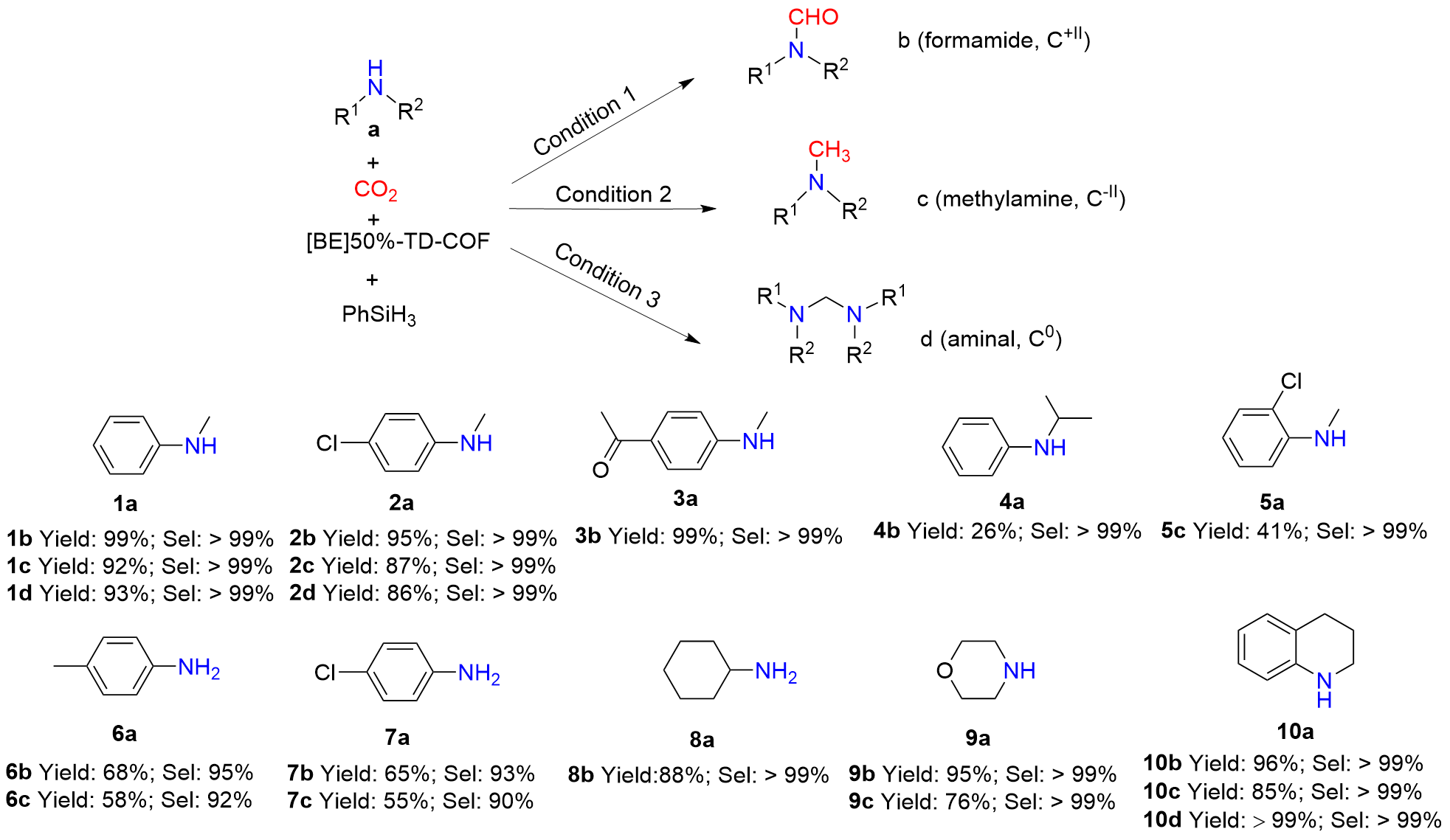
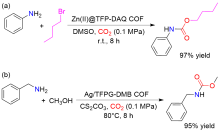
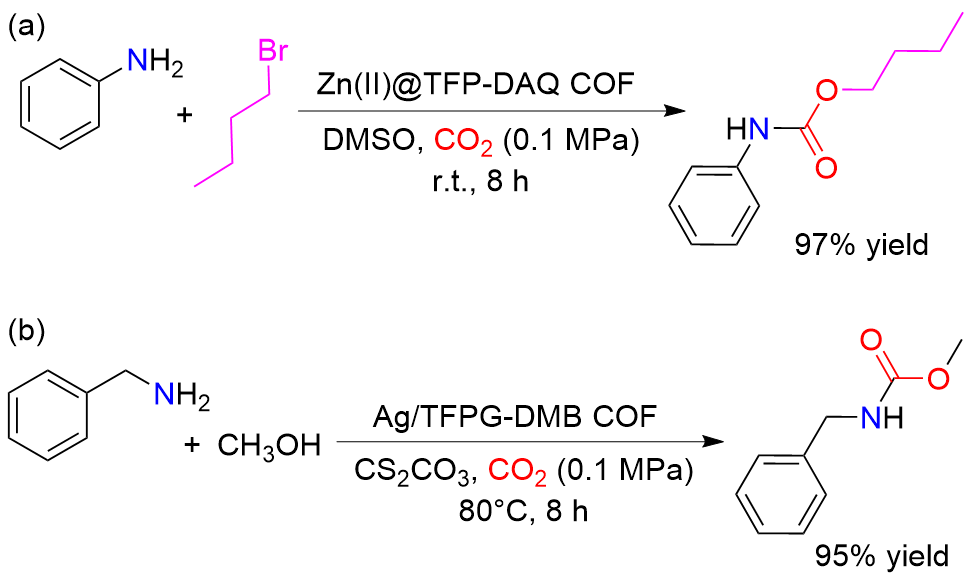
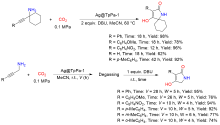





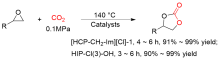

| [1] |
Tortajada, A.; Julia-Hernandez, F.; Borjesson, M.; Moragas, T.; Martin, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15948.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.49 |
| [2] |
Tyne, R. L.; Barry, P. H.; Lawson, M.; Byrne, D. J.; Warr, O.; Xie, H.; Hillegonds, D. J.; Formolo, M.; Summers, Z. M.; Skinner, B.; Eiler, J. M.; Ballentine, C. J. Nature 2021, 600, 670.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04153-3 |
| [3] |
Li, M.; Yang, K.; Abdinejad, M.; Zhao, C.; Burdyny, T. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11892.
doi: 10.1039/D2NR03310K |
| [4] |
Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, S.; Cheng, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 2221. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003039 |
|
( 周聪, 李渺, 于金涛, 孙松, 成江, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2221.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003039 |
|
| [5] |
Du, J.; Huang, O.; Tan, B. Chem. Asian J. 2021, 16, 3833.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v16.23 |
| [6] |
Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Q.; Li, Y.; He, H. J. Environ Sci. 2023, 125, 811.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.02.025 |
| [7] |
Desgagnes, A.; Iliuta, M. C. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140214.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140214 |
| [8] |
Thubsuang, U.; Manmuanpom, N.; Chokaksornsan, N.; Sommut, C.; Singhawat, K.; Payaka, A.; Wongkasemjit, S.; Chaisuwan, T. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 155120.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155120 |
| [9] |
Wang, H.; Chuai, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1376.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c19502 |
| [10] |
Liang, J.; Chen, R. P.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, T. T.; Wang, X. S.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1570.
doi: 10.1039/c6sc04357g pmid: 28451286 |
| [11] |
Wu, Q. J.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2978.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00326 |
| [12] |
He, C.; Liang, J.; Zou, Y. H.; Yi, J. D.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab157.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab157 |
| [13] |
Liang, J.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. EnergyChem 2021, 3, 100064.
doi: 10.1016/j.enchem.2021.100064 |
| [14] |
Ebadi A, A.; Sanaeepur, H.; Luque, R.; Garcia, H.; Chen, B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7427.
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00442A |
| [15] |
Lu, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, J. P.; Yang, M. Y.; Cai, Y. P.; Li, S. L.; Lan, Y. Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200003.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.15 |
| [16] |
Yang, Y. L.; Wang, Y. R.; Gao, G. K.; Liu, M.; Miao, C.; Li, L. Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, Z. Y.; Chen, Y.; Xin, Z.; Li, S. L.; Li, D. S.; Lan, Y. Q. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1439.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.08.063 |
| [17] |
Cai, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Liu, F.; Zhao, T.; Tao, D. J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138946.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138946 |
| [18] |
Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. N. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 42, 91.
|
| [19] |
Yang, D. H.; Tao, Y.; Ding, X.; Han, B. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 761.
doi: 10.1039/D1CS00887K |
| [20] |
He, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, S.; Liu, Z. Q.; Zhu, M. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 1306.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63936-0 |
| [21] |
Song, K. S.; Fritz, P. W.; Coskun, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 9831.
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00727D |
| [22] |
Xu, Z. Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D. W.; Li, Z. T. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3777. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003070 |
|
( 徐子悦, 罗驿, 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 3777.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003070 |
|
| [23] |
Lee, J. S. M.; Cooper, A. I. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 2171.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00399 |
| [24] |
Cote, A. P.; Yaghi, O. M. Science 2005, 310, 1166.
doi: 10.1126/science.1120411 |
| [25] |
Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Jin, S. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2856.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.065 |
| [26] |
Tan, L. X.; Tan, B. E. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3322.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00851H |
| [27] |
Kuhn, P.; Antonietti, M.; Thomas, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3450.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
| [28] |
Jiang, J. X.; Su, F.; Trewin, A.; Wood, C. D.; Campbell, N. L.; Niu, H.; Dickinson, C.; Ganin, A. Y.; Rosseinsky, M. J.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Cooper, A. I. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8574.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v46:45 |
| [29] |
Ben, T.; Ren, H.; Ma, S.; Cao, D.; Lan, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, F.; Simmons, J. M.; Qiu, S. L.; Zhu, G. S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9457.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200904637 |
| [30] |
Chen, J.; Longo, M.; Fuoco, A.; Esposito, E.; Monteleone, M.; Comesana, G. B.; Carolus, J. J.; McKeown, N. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215250.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.8 |
| [31] |
Guan, Q.; Zhou, L. L.; Dong, Y. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1475.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c11071 pmid: 36646043 |
| [32] |
Geng, K.; He, T.; Liu, R.; Dalapati, S.; Tan, K. T.; Li, Z.; Tao, S.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, D. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00550 |
| [33] |
Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chenm, Y. ; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 708.
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00827F |
| [34] |
Asokan, K.; Patil, M. K.; Mukherjee, S. P.; Sukumaran, S. B.; Nandakumar, T. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202201012.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v17.24 |
| [35] |
Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107201.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.007 |
| [36] |
Fu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Ai, S. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140154.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140154 |
| [37] |
Zhang, Z.; Kang, C.; Peh, S. B.; Shi, D.; Yang, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14992.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05309 |
| [38] |
Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, Q. Energy Stor. Mater. 2023, 55, 498.
|
| [39] |
Cui, B.; Fu, G. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1679.
doi: 10.1039/D1NR07614K |
| [40] |
Yao, S.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Xi, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm. 202212466.
|
| [41] |
Yu, G.; Wang, C. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 1437. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 于歌, 汪成, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 1437.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202003018 |
|
| [42] |
Yue, J. Y.; Song, L.-P.; Wang, Y. T.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y.; Tang, B. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14419.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03179 |
| [43] |
Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3826. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202107030 |
|
( 陈育萱, 陈奇, 张占辉, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3826.)
|
|
| [44] |
Wu, C.; Li, X.; Shao, M.; Kan, J.; Wang, G.; Geng, Y.; Dong, Y. B. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4559.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.01.065 |
| [45] |
Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ju, J.; Yan, Q.; Arumugam, V.; Jing, X.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 485.
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63487-X |
| [46] |
Li, W. Y.; Wan, J. J.; Kan, J. L.; Wang, B.; Song, T.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, L. L.; Li, Y. A.; Dong, Y. B. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 1453.
doi: 10.1039/D2SC05732H |
| [47] |
Saptal, V.; Shinde, D. B.; Banerjee, R.; Bhanage, B. M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 6152.
doi: 10.1039/C6CY00362A |
| [48] |
Yin, M.; Wang, L.; Tang, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55674.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c18226 |
| [49] |
Khatun, R.; Biswasa, S.; Biswas, I. H.; Riyajuddin, S.; Haque, N.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. M. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 40, 101180.
|
| [50] |
Cao, Q.; Zhang, L. L.; Zhou, C.; He, J. H.; Marcomini, A.; Lu, J. M. Appl. Catal. B. 2021, 294, 120238.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120238 |
| [51] |
He, C.; Si, D. H.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207478.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.40 |
| [52] |
Mu, Z. J.; Ding, X. S.; Chen, Z. Y.; Han, B. H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41350.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b14671 |
| [53] |
Sarkar, P.; Hazra, A.; Riyajuddin, C. S.; Biswas, S.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. M. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 744.
doi: 10.1039/C9NJ04673A |
| [54] |
Chowdhury, A. H.; Chowdhury, I. H.; Biswas, S.; Islam, S. M. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111050.
|
| [55] |
Ghosh, S.; Molla, R. A.; Kayal, U.; Bhaumik, A.; Islam, S. M. Dalton. Trans. 2019, 48, 4657.
doi: 10.1039/C9DT00017H |
| [56] |
Chakraborty, D.; Shekhar, P.; Singh, H. D.; Kushwaha, R.; Vinod, C. P.; Vaidhyanathan, R. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 4767.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v14.24 |
| [57] |
Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kan, J. L.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y. B. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 7363.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02721 |
| [58] |
Zhang, L.; Bu, R.; Liu, X.-Y.; Mu, P.-F.; Gao, E. Q. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 7620.
doi: 10.1039/D1GC02118D |
| [59] |
Toland, W. G. US US3060179, 1962.
|
| [60] |
Miller, G. H. US 3775380, 1973.
|
| [61] |
Ren, S.; Bojdys, M. J.; Dawson, R.; Laybourn, A.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Adams, D. J.; Cooper, A. I. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2357.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201200751 |
| [62] |
Meier, C. B.; Sprick, R. S.; Monti, A.; Guiglion, P.; Lee, J. M.; Zwijnenburg, M. A.; Cooper, A. I. Polymer 2017, 126, 283.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.04.017 |
| [63] |
Wang, K. W.; Yang, L. M.; Wang, X.; Guo, L. P.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S. B.; Tan, B.; Cooper, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14149.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201708548 |
| [64] |
Zhao, Y.; Huang, H. L.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, C. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 329, 111526.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111526 |
| [65] |
Dai, W.; Li, Q.; Long, J.; Mao, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zou, J.; Luo, X. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 62, 102101.
|
| [66] |
Roeser, J.; Kailasam, K.; Thomas, A. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1793.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v5.9 |
| [67] |
Lan, X. W.; Du, C.; Cao, L. L.; She, T. T.; Li, Y. M.; Bai, G. Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 38953.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b14743 |
| [68] |
Lan, X. W.; Li, Y. M.; Du, C.; She, T. T.; Li, Q.; Bai, G. Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 8560.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v25.36 |
| [69] |
Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhao, R.; Yang, S. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 3119.
doi: 10.1039/D0CY02473B |
| [70] |
Singh, G.; Nagaraja, C. M. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 63, 102132.
|
| [71] |
Tan, L. X.; Tan, B. E. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 530. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15020096 |
|
( 谭良骁, 谭必恩, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 530.)
doi: 10.6023/A15020096 |
|
| [72] |
Davankov, V. A.; Rogozhin, S. V.; Tsyurupa, M. P. US 3729457, 1971
|
|
[Chem. Abstr. 1971, 75, 6841.]
|
|
| [73] |
Liao, X.; Pei, B.; Ma, R.; Kong, L.; Gao, X.; He, J.; Luo, X.; Lin, J. Q. Catalysts 2022, 12, 62.
doi: 10.3390/catal12010062 |
| [74] |
Liao, X.; Xiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Kong, L.; Gao, X.; He, J.; Hou, W.; Peng, C.; Lin, J. Q. Sustainable Energy Fuels 2022, 6, 2846.
doi: 10.1039/D2SE00143H |
| [75] |
Ren, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tao, L.; Ji, H. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 2919.
doi: 10.1007/s10562-020-03527-y |
| [76] |
Molla, R. A.; Bhanja, P.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. S.; Bhaumik, A.; Islam, S. M. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1939.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201700069 |
| [77] |
Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A.; Riyajuddin, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chowdhury, A. H.; Ghosh, K.; Islam, S. K. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 1055.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v12.4 |
| [78] |
Xie, Y.; Wang, T. T.; Liu, X. H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W. Q. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1960.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2960 |
| [79] |
Xie, Y.; Wang, T. T.; Liu, X. H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W. Q. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2110.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201402162 |
| [80] |
Zhou, F.; Deng, Q.; Huang, N.; Zhou, W.; Deng, W. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10516.
doi: 10.1002/slct.v5.34 |
| [81] |
Zhang, X.; Qiu, B.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Mai, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 110758.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110758 |
| [82] |
Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Bian, Y.; Lv, H.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, R.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Mai, W.; Li, Y.; Li, T. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 58, 101924.
|
| [83] |
Ma, D. X.; Liu, K.; Li, J. X.; Shi, Z. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15050.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03517 |
| [84] |
Pan, Y.; Zhai, X. F.; Yin, J.; Zhang, T. Q.; Ma, L. J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Meng, J. Q. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 2231.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v12.10 |
| [1] | 刘露, 张曙光, 胡仁威, 赵晓晓, 崔京南, 贡卫涛. 基于多羟基柱[5]芳烃的酚醛多孔聚合物合成及CO2催化转化[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2808-2814. |
| [2] | 莫百川, 陈春霞, 彭进松. 木质素及其衍生物负载金属催化剂在有机合成中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(4): 1215-1240. |
| [3] | 王睿, 高朗, 周岑, 张霄. 苯基吩噻嗪多孔有机聚合物催化的非活化末端烯烃的卤代全氟烷基化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1136-1145. |
| [4] | 陈鑫, 陈春霞, 彭进松. 纤维素及其衍生物负载铜催化有机反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(4): 1319-1336. |
| [5] | 宗玲博, 陈建宾, 任新意, 张国营, 贾肖飞. 有机聚合物负载铑催化剂在氢甲酰化反应中的应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(8): 2308-2321. |
| [6] | 徐子悦, 罗驿, 王辉, 张丹维, 黎占亭. 有机多孔聚合物非均相催化可见光诱导有机转化[J]. 有机化学, 2020, 40(11): 3777-3793. |
| [7] | 吕小妹, 阮建成, 陈新志, 钱超. 交联壳聚糖微球负载铜水相催化Ullmann反应[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(6): 1720-1726. |
| [8] | 徐鹏, 段新红. 以水为溶剂的铃木-宫浦偶联反应最新研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2019, 39(12): 3315-3327. |
| [9] | 侯亚东, 庞海霞, 杨超, 惠永海. 介孔分子筛MCM-41固载席夫碱与Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O催化合成螺[吲哚-噻唑啉酮]衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(8): 2036-2044. |
| [10] | 侯亚东, 董秀芝, 杨超, 惠永海, 解正峰. MCM-41负载杂多酸水相中催化亚胺和丙二腈的加成-消去反应[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(7): 1749-1754. |
| [11] | 徐缓, 张茂元, 黄香, 史大斌. MIL-101负载Pd纳米颗粒高效非均相催化苯并呋喃选择性C2位芳基化[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(4): 832-839. |
| [12] | 邢刘桩, 侯亚东, 邢雪建, 惠永海. MCM-41@席夫碱-Mn(OAc)2在水相中催化合成氧杂蒽衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(4): 912-918. |
| [13] | 孔胜男, Abaid Ullah Malik, 钱雪峰, 舒谋海, 肖文德. 多孔有机聚合物负载钌催化的β-酮酸酯的不对称氢化[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(3): 656-664. |
| [14] | 庞楚明, 罗时荷, 郝志峰, 高健, 黄召昊, 余家海, 余思敏, 汪朝阳. 多孔有机聚合物材料的合成与荧光传感应用[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(10): 2606-2624. |
| [15] | 孔胜男, 钱雪峰, 舒谋海, 肖文德. 联萘酚功能化多孔有机聚合物催化的不对称加成反应[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(10): 2754-2760. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||