有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (9): 2760-2773.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202204023 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
葛天鹏a,b, 杨彦辰b,c, 李淳朴b, 张剑a,*( ), 柳红a,b,*(
), 柳红a,b,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-08
修回日期:2022-05-19
发布日期:2022-06-08
通讯作者:
张剑, 柳红
作者简介:基金资助:
Tianpeng Gea,b, Yanchen Yangb,c, Chunpu Lib, Jian Zhanga( ), Hong Liua,b(
), Hong Liua,b( )
)
Received:2022-04-08
Revised:2022-05-19
Published:2022-06-08
Contact:
Jian Zhang, Hong Liu
About author:Supported by:文章分享

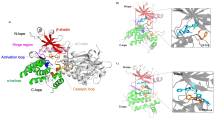
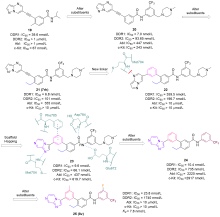
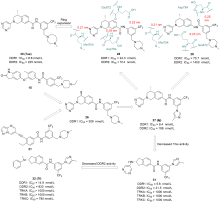
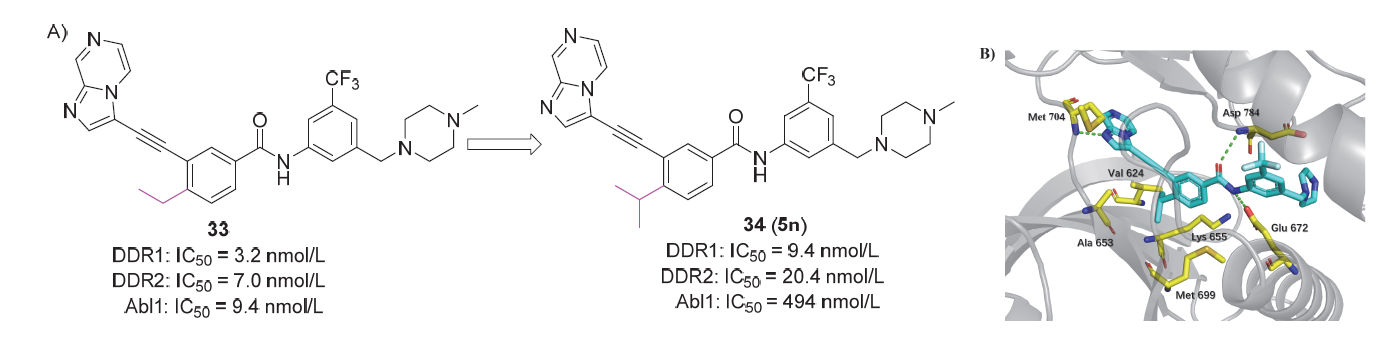
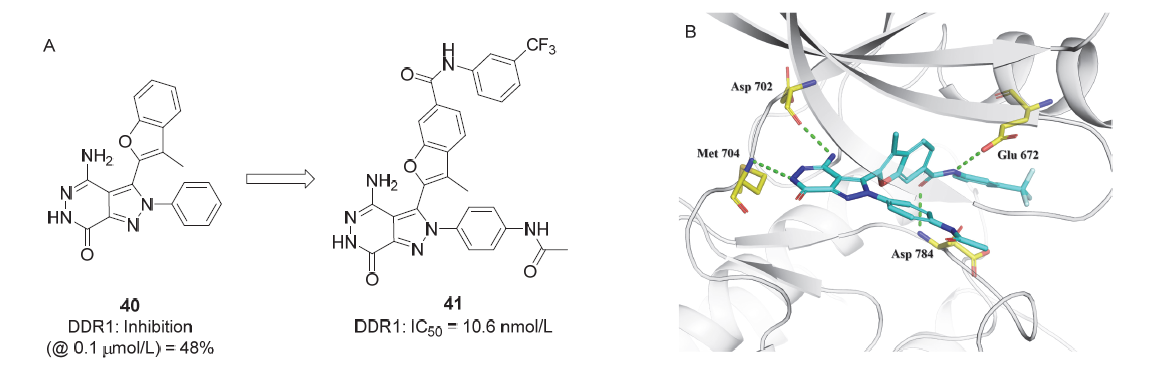
盘状结构域受体1 (discoidin domain receptor 1, DDR1)是一种胶原激活的受体酪氨酸激酶, 在调节细胞分化、增殖、粘附、迁移、侵袭和基质重塑等重要过程中发挥关键作用. DDR1的过度表达或激活与炎症发生、发展以及肿瘤侵袭、转移等过程密切相关, 因此DDR1是治疗炎症、纤维化和恶性肿瘤等疾病的潜在靶标. 自20世纪90年代初, 多种DDR1小分子抑制剂相继被报道, 重点介绍了DDR1的结构功能、作用机制和信号通路, 从药物化学的角度总结DDR1小分子抑制剂的设计方法、构效关系和药理活性.
葛天鹏, 杨彦辰, 李淳朴, 张剑, 柳红. 盘状结构域受体1 (DDR1)激酶抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(9): 2760-2773.
Tianpeng Ge, Yanchen Yang, Chunpu Li, Jian Zhang, Hong Liu. Research Progress of Discoid Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2760-2773.







| [1] |
Elkamhawy, A.; Lu, Q.; Nada, H.; Woo, J.; Quan, G.; Lee, K. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22010001 |
| [2] |
Borza, C. M.; Pozzi, A. Matrix Biol. 2014, 34, 185.
doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.002 |
| [3] |
Shrivastava, A.; Radziejewski, C.; Campbell, E.; Kovac, L.; Mc- Glynn, M.; Ryan, T. E.; Davis, S.; Goldfarb, M. P.; Glass, D. J.; Lemke, G.; Yancopoulos, G. D. Mol. Cell. 1997, 1, 25.
pmid: 9659900 |
| [4] |
Agarwal, G.; Kovac, L.; Radziejewski, C.; Samuelsson, S. J. Biochemistry. 2002, 41, 11091.
pmid: 12220173 |
| [5] |
Matada, G. S. P.; Das, A.; Dhiwar, P. S.; Ghara, A. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 535.
doi: 10.1007/s00044-020-02694-2 |
| [6] |
Carafoli, F.; Mayer, M. C.; Shiraishi, K.; Pecheva, M. A.; Chan, L. Y.; Nan, R.; Leitinger, B.; Hohenester, E. Structure. 2012, 20, 688.
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.02.011 |
| [7] |
Noordeen, N. A.; Carafoli, F.; Hohenester, E.; Horton, M. A.; Leitinger, B. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22744.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603233200 pmid: 16774916 |
| [8] |
Leitinger, B. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 265.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154013 pmid: 21568710 |
| [9] |
Carafoli, F.; Hohenester, E. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Proteins Proteomics 2013, 1834, 2187.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014 |
| [10] |
Alves, F.; Saupe, S.; Ledwon, M.; Schaub, F.; Hiddemann, W.; Vogel, W. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1321.
pmid: 11344127 |
| [11] |
Playford, M. P.; Butler, R. J.; Wang, X. C.; Katso, R. M.; Cooke, I. E.; Ganesan, T. S. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 620.
pmid: 8796349 |
| [12] |
Leitinger, B. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16761.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301370200 pmid: 12611880 |
| [13] |
Leitinger, B.; Kwan, A. P. L. Matrix Biol. 2006, 25, 355.
pmid: 16806867 |
| [14] |
Hou, G.; Vogel, W.; Bendeck, M. P. J. Clin. Invest. 2001, 107, 727.
pmid: 11254672 |
| [15] |
Ongusaha, P. P.; Kim, J. il; Fang, L.; Wong, T. W.; Yancopoulos, G. D.; Aaronson, S. A.; Lee, S. W. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1289.
pmid: 12628922 |
| [16] |
Das, S.; Ongusaha, P. P.; Yang, Y. S.; Park, J. M.; Aaronson, S. A.; Lee, S. W. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8123.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1215 |
| [17] |
Kim, H. G.; Hwang, S. Y.; Aaronson, S. A.; Mandinova, A.; Lee, S. W. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17672.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.236612 |
| [18] |
Huang, Y.; Arora, P.; McCulloch, C. A.; Vogel, W. F. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1637.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.046219 pmid: 19401332 |
| [19] |
Hidalgo-Carcedo, C.; Hooper, S.; Chaudhry, S. I.; Williamson, P.; Harrington, K.; Leitinger, B.; Sahai, E. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 49.
doi: 10.1038/ncb2133 pmid: 21170030 |
| [20] |
Jönsson, M.; Andersson, T. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2043.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.11.2043 pmid: 11493640 |
| [21] |
Hansen, C.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A. C.; Andersson, T.; Vogel, W. F. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 4011.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.09.003 |
| [22] |
Shintani, Y.; Fukumoto, Y.; Chaika, N.; Svoboda, R.; Wheelock, M. J.; Johnson, K. R. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 1277.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.200708137 pmid: 18362184 |
| [23] |
Payne, L. S.; Huang, P. H. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 900.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000164 pmid: 24828669 |
| [24] |
Iwai, L. K.; Chang, F.; Huang, P. H. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 161.
doi: 10.4161/cam.22572 pmid: 23154445 |
| [25] |
Iwai, L. K.; Payne, L. S.; Luczynski, M. T.; Chang, F.; Xu, H.; Clinton, R. W.; Paul, A.; Esposito, E. A.; Gridley, S.; Leitinger, B.; Naegle, K. M.; Huang, P. H. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 501.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20121750 pmid: 23822953 |
| [26] |
Kerroch, M.; Guerrot, D.; Vandermeersch, S.; Placier, S.; Mesnard, L.; Jouanneau, C.; Rondeau, E.; Ronco, P.; Boffa, J. J.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Dussaule, J. C. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4079.
doi: 10.1096/fj.11-194902 |
| [27] |
Foehr, E. D.; Tatavos, A.; Tanabe, E.; Raffioni, S.; Goetz, S.; Dimarco, E.; De LUCA, M.; Bradshaw, R. A. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 973.
pmid: 10783152 |
| [28] |
Gremmels, H.; Bevers, L. M.; Fledderus, J. O.; Braam, B.; Jan Van Zonneveld, A.; Verhaar, M. C.; Joles, J. A. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 751, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.01.005 pmid: 25595727 |
| [29] |
Kamohara, H.; Yamashiro, S.; Galligan, C.; Yoshimura, T. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2724.
pmid: 11606478 |
| [30] |
Ferri, N.; Carragher, N. O.; Raines, E. W. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1575.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63716-9 |
| [31] |
Lu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, X.; Smaill, J. B.; Ding, K. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1550.
doi: 10.1002/med.21488 |
| [32] |
Ford, C. E.; Lau, S. K.; Zhu, C. Q.; Andersson, T.; Tsao, M. S.; Vogel, W. F. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 808.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603614 |
| [33] |
Castro-Sanchez, L.; Soto-Guzman, A.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Martinez- Orozco, R.; Salazar, E. P. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 843.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.07.004 pmid: 20709424 |
| [34] |
Castro-Sanchez, L.; Soto-Guzman, A.; Guaderrama-Diaz, M.; Cortes-Reynosa, P.; Salazar, E. P. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 463.
doi: 10.1007/s10585-011-9385-9 |
| [35] |
Sun, X.; Wu, B.; Chiang, H. C.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Liu, J.; Rozeboom, A. M.; Harris, B. T.; Blommaert, E.; Gomez, A.; Garcia, R. E.; Zhou, Y.; Mitra, P.; Prevost, M.; Zhang, D.; Banik, D.; Isaacs, C.; Berry, D.; Lai, C.; Chaldekas, K.; Latham, P. S.; Brantner, C. A.; Popratiloff, A.; Jin, V. X.; Zhang, N.; Hu, Y.; Pujana, M. A.; Curiel, T. J.; An, Z.; Li, R. Nature 2021, 599, 673.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04057-2 |
| [36] |
Jin, H.; Ham, I. H.; Oh, H. J.; Bae, C. A.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y. B.; Son, S. Y.; Chwae, Y. J.; Han, S. U.; Brekken, R. A.; Hur, H. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1590.
doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0710 |
| [37] |
Van Cutsem, E.; Sagaert, X.; Topal, B.; Haustermans, K.; Prenen, H. Lancet 2016, 388, 2654.
doi: S0140-6736(16)30354-3 pmid: 27156933 |
| [38] |
Lee, J. H.; Poudel, B.; Ki, H. H.; Nepali, S.; Lee, Y. M.; Shin, J. S.; Kim, D. K. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1.
|
| [39] |
Park, H. S.; Kim, K. R.; Lee, H. J.; Choi, H. N.; Kim, D. K.; Kim, B. T.; Moon, W. S. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 1435.
|
| [40] |
Shimada, K.; Nakamura, M.; Ishida, E.; Higuchi, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Tsujikawa, K.; Konishi, N. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 39.
|
| [41] |
Deng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Hui, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, Z.; Ning, Y. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 1.
doi: 10.1186/s13048-016-0301-4 |
| [42] |
Jeitany, M.; Leroy, C.; Tosti, P.; Lafitte, M.; Le Guet, J.; Simon, V.; Bonenfant, D.; Robert, B.; Grillet, F.; Mollevi, C.; El Messaoudi, S.; Otandault, A.; Canterel‐Thouennon, L.; Busson, M.; Thierry, A. R.; Martineau, P.; Pannequin, J.; Roche, S.; Sirvent, A. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, 1.
doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708365 |
| [43] |
Kumari, N.; Saxena, S.; Agrawal, U. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 27, 51.
|
| [44] |
Krazinski, B. E.; Kiewisz, J.; Sliwinska-Jewsiewicka, A.; Kowalczyk, A. E.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Godlewski, J.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Dziegiel, P.; Kmiec, Z. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2019, 16, 179.
doi: 10.21873/cgp.20124 |
| [45] |
Reger de Moura, C.; Battistella, M.; Sohail, A.; Caudron, A.; Feugeas, J. P.; Podgorniak, M. P.; Pages, C.; Mazouz Dorval, S.; Marco, O.; Menashi, S.; Fridman, R.; Lebbé, C.; Mourah, S.; Jouenne, F. Pigm. Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 697.
|
| [46] |
Ram, R.; Lorente, G.; Nikolich, K.; Urfer, R.; Foehr, E.; Nagavarapu, U. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 76, 239.
doi: 10.1007/s11060-005-6874-1 |
| [47] |
Prakoura, N.; Chatziantoniou, C. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 1.
|
| [48] |
Guerrot, D.; Kerroch, M.; Placier, S.; Vandermeersch, S.; Trivin, C.; Mael-Ainin, M.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Dussaule, J. C. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 83.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.023 |
| [49] |
Kothiwale, S.; Borza, C. M.; Lowe, E. W.; Pozzi, A.; Meiler, J. Drug Discovery Today 2015, 20, 255.
doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.09.025 |
| [50] |
Day, E.; Waters, B.; Spiegel, K.; Alnadaf, T.; Manley, P. W.; Buchdunger, E.; Walker, C.; Jarai, G. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 44.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.014 |
| [51] |
Rix, U.; Remsing Rix, L. L.; Terker, A. S.; Fernbach, N. V.; Hantschel, O.; Planyavsky, M.; Breitwieser, F. P.; Herrmann, H.; Colinge, J.; Bennett, K. L.; Augustin, M.; Till, J. H.; Heinrich, M. C.; Valent, P.; Superti-Furga, G. Leukemia 2010, 24, 44.
doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.228 pmid: 19890374 |
| [52] |
Fowler, A. J.; Hebron, M.; Missner, A. A.; Wang, R.; Gao, X.; Kurd-Misto, B. T.; Liu, X.; Moussa, C. E. H. Drugs R&D 2019, 19, 149.
|
| [53] |
Ren, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Wen, D.; Long, H.; Luo, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Leng, F.; Lang, X.; Bai, Y.; She, M.; Tu, Z.; Pan, J.; Ding, K. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 879.
doi: 10.1021/jm301581y |
| [54] |
Canning, P.; Tan, L.; Chu, K.; Lee, S. W.; Gray, N. S.; Bullock, A. N. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 2457.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.04.014 pmid: 24768818 |
| [55] |
El-Damasy, A. K.; Cho, N. C.; Nam, G.; Pae, A. N.; Keum, G. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1587.
doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201600224 pmid: 27405013 |
| [56] |
Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Ren, X.; Ding, K. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3287.
doi: 10.1021/jm5012319 |
| [57] |
Davis, M. I.; Hunt, J. P.; Herrgard, S.; Ciceri, P.; Wodicka, L. M.; Pallares, G.; Hocker, M.; Treiber, D. K.; Zarrinkar, P. P. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1046.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1990 |
| [58] |
Sun, X.; Phan, T. N.; Jung, S. H.; Kim, S. Y.; Cho, J. U.; Lee, H.; Woo, S. H.; Park, T. K.; Yang, B. S. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 510.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.187328 |
| [59] |
Dou, X.; Huang, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, G.; Jin, H.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 201, 112445.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112445 |
| [60] |
Kim, H. G.; Tan, L.; Weisberg, E. L.; Liu, F.; Canning, P.; Choi, H. G.; Ezell, S. A.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Mandinova, A.; Griffin, J. D.; Bullock, A. N.; Liu, Q.; Lee, S. W.; Gray, N. S. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2145.
doi: 10.1021/cb400430t |
| [61] |
Kim, H. G.; Tan, L.; Weisberg, E. L.; Liu, F.; Canning, P.; Choi, H. G.; Ezell, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Mandinova, A.; Bullock, A. N.; Liu, Q.; Lee, S. W.; Gray, N. S. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 840.
doi: 10.1021/cb5000949 |
| [62] |
Jeffries, D. E.; Borza, C. M.; Blobaum, A. L.; Pozzi, A.; Lindsley, C. W. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 29.
doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00382 pmid: 31938459 |
| [63] |
Wang, Q.; Tang, B.; Sun, D.; Dong, Y.; Ji, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Luo, M.; Tan, Q.; Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, R.; Zang, Y.; Shen, J.; Xiong, B.; Li, J.; Chen, D. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1943.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.11.012 pmid: 35847490 |
| [64] |
Gao, M.; Duan, L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Ding, K. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3281.
doi: 10.1021/jm301824k |
| [65] |
Mo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Zou, J.; Luo, J.; Tu, Z. C.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Ding, K.; Lu, X. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 379.
doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00495 |
| [66] |
Wang, Z.; Bian, H.; Bartual, S. G.; Du, W.; Luo, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Mo, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tu, Z.; Ren, X.; Lu, X.; Brekken, R. A.; Yao, L.; Bullock, A. N.; Su, J.; Ding, K. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5911.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00140 |
| [67] |
Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bartual, S. G.; Luo, J.; Xu, T.; Du, W.; Xun, Q.; Tu, Z.; Brekken, R. A.; Ren, X.; Bullock, A. N.; Liang, G.; Lu, X.; Ding, K. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 327.
doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00497 |
| [68] |
Zhu, D.; Huang, H.; Pinkas, D. M.; Luo, J.; Ganguly, D.; Fox, A. E.; Arner, E.; Xiang, Q.; Tu, Z. C.; Bullock, A. N.; Brekken, R. A.; Ding, K.; Lu, X. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7431.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00365 |
| [69] |
Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pinkas, D. M.; Fox, A. E.; Luo, J.; Huang, H.; Cui, S.; Xiang, Q.; Xu, T.; Xun, Q.; Zhu, D.; Tu, Z.; Ren, X.; Brekken, R. A.; Alex, N. Bullock, A. N.; Liang, G.; Ding, K.; Lu, X. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7977.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01045 |
| [70] |
Richter, H.; Satz, A. L.; Bedoucha, M.; Buettelmann, B.; Petersen, A. C.; Harmeier, A.; Hermosilla, R.; Hochstrasser, R.; Burger, D.; Gsell, B.; Gasser, R.; Huber, S.; Hug, M. N.; Kocer, B.; Kuhn, B.; Ritter, M.; Rudolph, M. G.; Weibel, F.; Molina-David, J.; Kim, J. J.; Santos, J. V.; Stihle, M.; Georges, G. J.; Bonfil, R. D.; Fridman, R.; Uhles, S.; Moll, S.; Faul, C.; Fornoni, A.; Prunotto, M. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 37.
doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00866 pmid: 30452219 |
| [71] |
Dong, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K. X.; Sun, L. P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115876.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115876 |
| [72] |
Zhavoronkov, A.; Ivanenkov, Y. A.; Aliper, A.; Veselov, M. S.; Aladinskiy, V. A.; Aladinskaya, A. V.; Terentiev, V. A.; Polykovskiy, D. A.; Kuznetsov, M. D.; Asadulaev, A.; Volkov, Y.; Zholus, A.; Shayakhmetov, R.; Zhebrak, A.; Minaeva, L. I.; Zagribelnyy, B. A.; Lee, L. H.; Soll, R.; Madge, D.; Xing, L.; Guo, T.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1038.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0224-x pmid: 31477924 |
| [73] |
Tan, X.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Tong, X.; Xu, T.; Cui, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, M. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 103.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01205 |
| [1] | 徐欢, 吴鸿飞, 张晓鸣, 路星星, 孙腾达, 亓悦, 林誉凡, 杨新玲, 张莉, 凌云. 含1,2,3,4-四氢异喹啉片段磺酰肼和酰肼类化合物的设计、合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 725-733. |
| [2] | 高建飞, 李瞬依, 何玉龙, 李英霞, 王贺瑶, 黄二芳, 胡春. 作为FABP4/5抑制剂喹啉类化合物的设计合成与生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(2): 636-645. |
| [3] | 孙昌兴, 张福豪, 张欢, 李鹏辉, 姜林. 新型2-(1-甲基-1H-吡唑-4-基)嘧啶-4-甲酰胺的设计、合成、杀菌活性及分子对接研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(1): 229-235. |
| [4] | 梁光平, 王维, 朱绪秀, 梁光焰, 杨俊, 王道平. 新型齐多夫定与4-苯胺喹唑啉骨架拼接产物的合成及体外抗肿瘤活性[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(9): 2793-2805. |
| [5] | 张蓉, 郜祥, 陈玲玲, 南发俊. 噻唑-噁唑串联杂环类RNA剪接抑制剂的发现及构效关系研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(9): 2925-2939. |
| [6] | 杨竣喆, 许子超, 李淳朴, 程远征, 柳红. 原肌球蛋白受体激酶(TRK)抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 2055-2069. |
| [7] | 王春霞, 胡晓东, 许斌, 曹春阳. 靶向新型冠状病毒SARS-CoV-2主蛋白酶的抗病毒药物研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 1974-1999. |
| [8] | 王长凯, 孙腾达, 张学博, 杨新玲, 路星星, 徐欢, 石发胜, 张莉, 凌云. 新型含氟吡唑酰肼类化合物的设计合成与生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1527-1536. |
| [9] | 雍灿, 李芸, 毕涛, 陈国凤, 郑东霞, 王周玉, 张园园. 基于D-半乳糖衍生的小分子半乳糖凝集素抑制剂的合成及活性研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1307-1325. |
| [10] | 蔡铭, 邵亮, 杨帆, 张继虹, 俞飞. 五环三萜葡萄糖缀合物的设计、合成及体外抗流感病毒活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(5): 1453-1462. |
| [11] | 孔媛芳, 杨彬, 庄严, 张京玉, 孙德梅, 董春红. 基于二肽基肽酶4 (DPP-4)靶点设计的五种降糖活性杂环合成及构效关系研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(3): 770-784. |
| [12] | 李丰兴, 卢昕, 刘旭, 苏路路, 李小六, 陈华. 苯并咪唑并氮杂糖的结构修饰及其β-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(9): 3643-3651. |
| [13] | 李英俊, 林乐弟, 刘季红, 高立信, 盛丽, 靳焜, 刘雪洁, 杨鸿境, 李佳. 新型含咔唑环和芳环/芳稠杂环的N-酰腙衍生物的合成及蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶1B (PTP1B)抑制活性评价[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(9): 3593-3607. |
| [14] | 陈超, 胡晓东, 王春喜, 蓝文贤, 吴小余, 曹春阳. 基于靶标结构及作用机制的抗艾滋病药物研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(8): 3015-3033. |
| [15] | 陆棋, 叶飞霞, 孙晓彤, 翁建全, 余茜, 胡德玄. 新型拟天然芪类拓扑异构酶I抑制剂的设计与合成[J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(8): 3321-3329. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||