化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (10): 1050-1057.DOI: 10.6023/A24080234 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
黄伊晨a,b, 聂长明a,*( ), 王聪芝b,*(
), 王聪芝b,*( ), 陈树森c, 宋艳c, 李昊c, 石伟群b,*(
), 陈树森c, 宋艳c, 李昊c, 石伟群b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-08-07
发布日期:2024-10-08
基金资助:
Yichen Huanga,b, Changming Niea( ), Congzhi Wangb(
), Congzhi Wangb( ), Shusen Chenc, Yan Songc, Hao Lic, Weiqun Shib(
), Shusen Chenc, Yan Songc, Hao Lic, Weiqun Shib( )
)
Received:2024-08-07
Published:2024-10-08
Contact:
*E-mail: niecm196132@163.com; wangcongzhi@ihep.ac.cn; shiwq@ihep.ac.cn
Supported by:文章分享
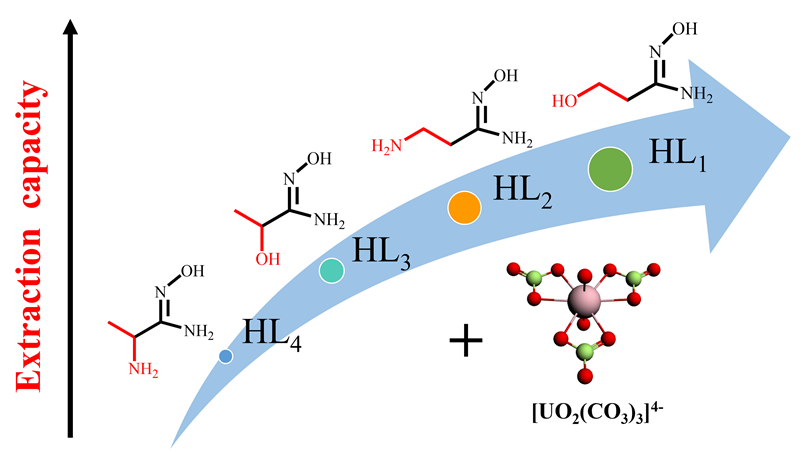
偕胺肟配体对铀酰离子具有较强的配位能力, 在海水提铀领域备受关注. 研究发现偕胺肟配体中引入氨基和羟基等基团能够提高其对铀酰离子的萃取能力. 为了从理论上探究氨基和羟基取代的偕胺肟衍生物用于海水提铀的萃取机理, 本工作采用密度泛函理论(DFT)方法系统研究了四种偕胺肟类配体(HL1: β-羟基-N-羟基丙脒; HL2: β-氨基-N-羟基丙脒; HL3: α-羟基-N-羟基丙脒; HL4: α-氨基-N-羟基丙脒)及其与铀酰离子形成的单取代、双取代、三取代配合物的结构、成键性质以及热力学稳定性. 研究结果表明, 与未修饰的偕胺肟(HAO)配体相比, HL1在水溶液中更容易与[UO2(CO3)3]4−发生取代反应, 可能是一种能够应用于海水提铀的潜在配体. 本工作为高效海水提铀吸附基团的设计与开发提供了理论线索.
黄伊晨, 聂长明, 王聪芝, 陈树森, 宋艳, 李昊, 石伟群. 羟基和氨基取代偕胺肟用于海水提铀的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1050-1057.
Yichen Huang, Changming Nie, Congzhi Wang, Shusen Chen, Yan Song, Hao Li, Weiqun Shi. Theoretical Study of Hydroxyl- and Amino-substituted Amidoxime Ligands for Extraction of Uranium from Seawater[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(10): 1050-1057.
| 铀酰配合物 | U=O (axial) | U—Oa (L−) | U—Ob (L−) | U—N (L−) | U—O (CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.238 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.237 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.241 | — | 0.243 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.243 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.240 | — | 0.250 | 0.240 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.243 | 0.226 | 0.252 | 0.237 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.237 | — | 0.261 | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 0.180 | — | 0.228 | — | 0.235 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 0.182 | 0.233 | 0.246 | — | |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 0.181 | 0.234 | — | 0.243 | — |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 0.179 | 0.237 | — | 0.249 | — |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 0.180 | 0.241 | — | 0.242 | — |
| 铀酰配合物 | U=O (axial) | U—Oa (L−) | U—Ob (L−) | U—N (L−) | U—O (CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.238 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.237 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.241 | — | 0.243 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 0.181 | — | 0.243 | — | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.240 | — | 0.250 | 0.240 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.243 | 0.226 | 0.252 | 0.237 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 0.180 | 0.237 | — | 0.261 | 0.242 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 0.180 | — | 0.228 | — | 0.235 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 0.182 | 0.233 | 0.246 | — | |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 0.181 | 0.234 | — | 0.243 | — |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 0.179 | 0.237 | — | 0.249 | — |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 0.180 | 0.241 | — | 0.242 | — |
| 铀酰配合物 | U=O (axial) | U—Oa (L−) | U—Ob (L−) | U—N (L−) | U—O (CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 1.980 | — | 0.559 | — | 0.492 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 1.976 | — | 0.578 | — | 0.491 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 1.973 | — | 0.523 | — | 0.483 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 1.976 | — | 0.491 | — | 0.502 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 2.042 | 0.498 | — | 0.338 | 0.463 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 2.016 | 0.464 | 0.730 | 0.305 | 0.517 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 2.015 | 0.579 | — | 0.250 | 0.464 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 2.016 | — | 0.686 | — | 0.530 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 1.980 | 0.587 | — | 0.370 | — |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 2.027 | 0.557 | — | 0.378 | — |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 2.039 | 0.554 | — | 0.336 | — |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 2.053 | 0.515 | — | 0.389 | — |
| 铀酰配合物 | U=O (axial) | U—Oa (L−) | U—Ob (L−) | U—N (L−) | U—O (CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 1.980 | — | 0.559 | — | 0.492 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 1.976 | — | 0.578 | — | 0.491 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 1.973 | — | 0.523 | — | 0.483 |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 1.976 | — | 0.491 | — | 0.502 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 2.042 | 0.498 | — | 0.338 | 0.463 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 2.016 | 0.464 | 0.730 | 0.305 | 0.517 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 2.015 | 0.579 | — | 0.250 | 0.464 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 2.016 | — | 0.686 | — | 0.530 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 1.980 | 0.587 | — | 0.370 | — |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 2.027 | 0.557 | — | 0.378 | — |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 2.039 | 0.554 | — | 0.336 | — |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 2.053 | 0.515 | — | 0.389 | — |
| 铀酰配合物 | Q(U) | ΔQ(U) | ΔQ(L) | ΔQ(CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 1.662 | 0.804 | 0.296 | 0.635 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 1.497 | 0.970 | 0.451 | 0.706 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 1.387 | 1.079 | 0.593 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 1.659 | 0.808 | 0.315 | 0.631 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 1.578 | 0.889 | 0.443 | 0.689 |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 1.346 | 1.121 | 0.590 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 1.701 | 0.766 | 0.252 | 0.640 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 1.504 | 0.962 | 0.471 | 0.706 |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 1.347 | 1.119 | 0.584 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 1.694 | 0.773 | 0.276 | 0.630 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 1.632 | 0.835 | 0.416 | 0.689 |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 1.347 | 1.120 | 0.578 | — |
| 铀酰配合物 | Q(U) | ΔQ(U) | ΔQ(L) | ΔQ(CO32−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [UO2(CO3)2(L1)]3− | 1.662 | 0.804 | 0.296 | 0.635 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L1)2]2− | 1.497 | 0.970 | 0.451 | 0.706 |
| [UO2(L1)3]− | 1.387 | 1.079 | 0.593 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L2)]3− | 1.659 | 0.808 | 0.315 | 0.631 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L2)2]2− | 1.578 | 0.889 | 0.443 | 0.689 |
| [UO2(L2)3]− | 1.346 | 1.121 | 0.590 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L3)]3− | 1.701 | 0.766 | 0.252 | 0.640 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L3)2]2− | 1.504 | 0.962 | 0.471 | 0.706 |
| [UO2(L3)3]− | 1.347 | 1.119 | 0.584 | — |
| [UO2(CO3)2(L4)]3− | 1.694 | 0.773 | 0.276 | 0.630 |
| [UO2(CO3)(L4)2]2− | 1.632 | 0.835 | 0.416 | 0.689 |
| [UO2(L4)3]− | 1.347 | 1.120 | 0.578 | — |
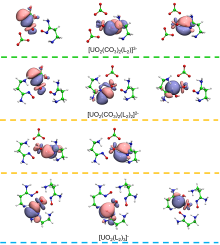

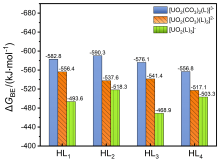

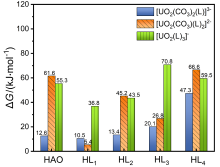

| [1] |
Ahmed, B.; Ahmad, Z.; Ihsan, A.; Khan, M. A.; Fazal, T. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338 126507.
|
| [2] |
Xu, H.; Wang, C.-Z.; Liu, S.-R.; Shi, W.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82 458 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐晗, 王聪芝, 刘峙嵘, 石伟群, 化学学报, 2024, 82 458.)
doi: 10.6023/A24020041 |
|
| [3] |
Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Bo, T.; Huang, S.; Huang, Z.; Shi, W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33 3527.
|
| [4] |
Zhu, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.; Jian, M.-P.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2023, 42 3029 (in Chinese).
|
|
(朱雅静, 徐岩, 简美鹏, 李海燕, 王崇臣, 化工进展, 2023, 42 3029.)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1434 |
|
| [5] |
Tian, G.-X.; Liu, T.-T.; Yang, S.-L. At. Energy Sci. Technol. 2023, 57 1 (in Chinese).
|
|
(田国新, 刘婷婷, 杨素亮, 原子能科学技术, 2023, 57 1.)
doi: 10.7538/yzk.2022.youxian.0885 |
|
| [6] |
Tang, X.-R.; Huang, P.-L.; Ruan, H.-M.; Tang, L.; Gong, X.; Duan, T.; Chen, S.-S; He, R.; Zhu, W.-K. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2023, 45 267 (in Chinese).
|
|
(唐兴睿, 黄鹏玲, 阮昊明, 唐丽, 龚翔, 段涛, 陈树森, 何嵘, 竹文坤, 核化学与放射化学, 2023, 45 267.)
doi: 10.7538/hhx.2023.YX.2021117 |
|
| [7] |
Zhang, D.; Fang, L.; Liu, L. J.; Zhao, B.; Hu, B. W.; Yu, S. J.; Wang, X. K. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320 124204.
|
| [8] |
Tang, N.; Liang, J.; Niu, C. G.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Xing, W. L.; Ye, S. J.; Liang, C.; Guo, H.; Guo, J. Y.; Zhang, Y. F.; Zeng, G. M. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8 7588.
|
| [9] |
Feng, L.; Wang, H.; Feng, T.; Yan, B.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, N. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 61, e202101015.
|
| [10] |
Xie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, S.; Ye, G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52 97.
|
| [11] |
Li, Y.; Zheng, Y. J.; Ahamd, Z.; Zhu, L. X.; Yang, J. J.; Chen, J. P.; Zhang, Z. P. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 491 215234.
|
| [12] |
Li, L.-Y.; Wen, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.-L. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2022, 44 15 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李璐琰, 文君, 胡胜, 汪小琳, 核化学与放射化学, 2022, 44 15.)
|
|
| [13] |
Li, Z.-M.; Niu, Y.-Q.; Su, Y.-T.; Song, Y.; Wang, F.-J.; Gou, Y.-F.; Wang, H.-Z.; Chen, H.-S. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2022, 44 233 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李子明, 牛玉清, 宿延涛, 宋艳, 王凤菊, 勾阳飞, 王海珍, 陈树森, 核化学与放射化学, 2022, 44 233.)
|
|
| [14] |
Liu, Z.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hu, T.-Y.; Ye, G.; Chen, J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. & Technol.) 2021, 61 23 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘泽宇, 谢忆, 王一凡, 胡铜洋, 叶钢, 陈靖, 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 61 23.)
|
|
| [15] |
Sun, B.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.; Jia, X. Ind. Chem. Mater. 2024, 2 154.
|
| [16] |
Yi, T.; Cen, Z.; Ji, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, M.; Liu, S. -H Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2404220.
|
| [17] |
Wang, C. Z.; Lan, J. H.; Wu, Q. Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Y. L.; Wang, X. K.; Chai, Z. F.; Shi, W. Q. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53 9466.
|
| [18] |
Qin, Z.; Ren, Y.; Shi, S.; Yang, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Jia, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, X. L. RSC Adv. 2017, 7 18639.
|
| [19] |
Luan, X. F.; Wang, C. Z.; Wu, Q. Y.; Lan, J. H.; Chai, Z. F.; Xia, L. S.; Shi, W. Q. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126 406.
|
| [20] |
Feng, J.; He, G.-Q.; Wei, Y.-X.; Duan, T.; Zhou, J. New Chem. Mater. 2022, 50 7 (in Chinese).
|
|
(冯健, 何桂强, 魏艳霞, 段涛, 周建, 化工新型材料, 2022, 50 7.)
|
|
| [21] |
Vukovic, S.; Watson, L. A.; Kang, S. O.; Custelcean, R.; Hay, B. P. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51 3855.
doi: 10.1021/ic300062s pmid: 22376298 |
| [22] |
Abney, C. W.; Mayes, R. T.; Piechowicz, M.; Lin, Z.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Veith, G. M.; Dai, S.; Lin, W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9 448.
|
| [23] |
Chi, F.-T.; Li, P.; Xiong, J.; Hu, S.; Gao, T.; Xia, X.-L.; Wang, X.-L. Chinese Physics B 2012, 21 093102.
|
| [24] |
Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, S.; Qin, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, B. Chemosphere 2023, 343 140257.
|
| [25] |
Xia, X.; Liao, Z.; Deng, J.; Yang, G.; Nie, X.; Ma, C.; Cheng, W.; Pan, N.; Zhang, W.; Dong, F. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344 123269.
|
| [26] |
Yu, B.; Zhang, L.; Ye, G.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Ma, S. Nano Res. 2020, 14 788.
|
| [27] |
Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.; Ivanov, A. S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Earl, L. D.; Abney, C. W.; Wojtas, L.; Ma, S. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9 1644.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04032-y pmid: 29691403 |
| [28] |
Alexandratos, S. D.; Zhu, X.; Florent, M.; Sellin, R. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55 4208.
|
| [29] |
Li, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Chen, R.; Zhu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, J. Desalination 2024, 586 117894.
|
| [30] |
Zhen, D.; Liu, C.; Deng, Q.; Li, L.; Grimes, C. A.; Yang, S.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16 27804.
|
| [31] |
Zhang, J.; Glezakou, V.-A. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2021, 121, e26553.
|
| [32] |
Zhang, J.; Dolg, M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18 3003.
doi: 10.1039/c5cp06313b pmid: 26738568 |
| [33] |
Zhang, J.; Dolg, M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17 24173.
doi: 10.1039/c5cp04060d pmid: 26327507 |
| [34] |
Zhang, J. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156 204108.
|
| [35] |
Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; Mackerell Jr., A. D. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31 671.
doi: 10.1002/jcc.21367 pmid: 19575467 |
| [36] |
Pomogaev, V.; Tiwari, S. P.; Rai, N.; Goff, G. S.; Runde, W.; Schneider, W. F.; Maginn, E. J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15 15954.
|
| [37] |
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A. V.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B. G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H. P.; Ortiz, J. V.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Williams; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery Jr., J. A.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M. J.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E. N.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T. A.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A. P.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 16, Revision B. 01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2016.
|
| [38] |
Ustynyuk, Y. A.; Alyapyshev, M. Y.; Babain, V. A.; Ustynyuk, N. A. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2016, 85 917.
|
| [39] |
Su, L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Lan, J.; Shi, W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35 109402.
|
| [40] |
Su, L.-L.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Lan, J.-H.; Shi, W.-Q. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63 9478.
|
| [41] |
Andrae, D.; Häußermann, U.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuß, H. Theor. Chim. Acta 1991, 78 247.
|
| [42] |
Dolg, M.; Wedig, U.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 86 866.
|
| [43] |
Moellmann, J.; Grimme, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118 7615.
|
| [44] |
Andzelm, J.; Kölmel, C.; Klamt, A. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103 9312.
|
| [45] |
Baldridge, K.; Klamt, A. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 106 6622.
|
| [46] |
Barone, V.; Cossi, M. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102 1995.
|
| [47] |
Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24 669.
|
| [48] |
Luan, X.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Xia, L.-S.; Shi, W.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80 708 (in Chinese).
|
|
(栾雪菲, 王聪芝, 夏良树, 石伟群, 化学学报, 2022, 80 708.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010054 |
|
| [49] |
Luan, X.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lan, J.-H.; Chai, Z.-F.; Xia, L.-S.; Shi, W.-Q. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51 11381.
|
| [50] |
Camaioni, D. M.; Schwerdtfeger, C. A. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109 10795.
pmid: 16863129 |
| [51] |
Reed, A. E.; Curtiss, L. A.; Weinhold, F. Chem. Rev. 2002, 88 899.
|
| [52] |
Lu, T. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161 082503.
|
| [53] |
Lu, T.; Chen, F. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33 580.
|
| [54] |
Politzer, P.; Murray, J. S. Reviews in Computational Chemistry, Vol. 2, Eds.: Kenny, B. L.; Donald, B. B., Wiley, New York, 1991, pp. 273-303.
|
| [55] |
Bader, R. F. W.; Matta, C. F. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40 5603.
pmid: 11599960 |
| [56] |
Lu, T.; Chen, Q. J. Comput. Chem. 2022, 43 539.
|
| [57] |
Xu, H.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lan, J.-H.; Chai, Z.-F.; Liu, Z.-R.; Shi, W.-Q. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399 124411.
|
| [58] |
Clark, T.; Hennemann, M.; Murray, J. S.; Politzer, P. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13 291.
|
| [59] |
Wiberg, K. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 90 59.
|
| [60] |
Reed, A. E.; Weinstock, R. B.; Weinhold, F. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83 735.
|
| [61] |
Espinosa, E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Molins, E. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117 5529.
|
| [62] |
Spencer, S.; Gagliardi, L.; Handy, N. C.; Ioannou, A. G.; Skylaris, C.-K.; Willetts, A.; Simper, A. M. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103 1831.
|
| [63] |
Neuefeind, J.; Soderholm, L.; Skanthakumar, S. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108 2733.
|
| [64] |
Cao, Z.; Balasubramanian, K. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123 114309.
|
| [65] |
Grimme, S. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124 034108.
|
| [66] |
Schwabe, T.; Grimme, S. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9 3397.
pmid: 17664963 |
| [67] |
Biczysko, M.; Panek, P.; Scalmani, G.; Bloino, J.; Barone, V. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2010, 6 2115.
|
| [1] | 王海成, 马海燕. 爪形氨基酚氧基锌氯化物催化环氧化物和酸酐共聚研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 577-588. |
| [2] | 王筑城, 刘磊, 朱梦媛, 孙悦, 赵晴, 丁玉寅, 陆继鑫, 王存国, 李奇, 贺爱华, 叶付臣. 1,5-二氨基蒽醌(AAQ)复合材料用作锂离子电池新型正极材料的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 589-595. |
| [3] | 王治业, 肖博怀. 利用平面σ-芳香性增强电子输运能力[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 520-526. |
| [4] | 赵雨晴, 梁栋, 贾吉慧, 余荣民, 卢灿忠. 具有双吸电子基团D-A型配体的Ag(I)发光配合物的合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 486-492. |
| [5] | 崔勇康, 成守飞, 凌琳, 李玉学, 吕龙. 二氟氨基二硝甲基芳香杂环含能材料的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 377-386. |
| [6] | 赵玉强, 张霞, 杨芸如, 朱立平, 周莹. 聚集诱导发射光笼分子的设计合成及原位光激活成像研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 265-273. |
| [7] | 黄广龙, 薛小松. “陈试剂”作为三氟甲基源机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [8] | 王镜焱, 马海燕. 2,6-二亚甲基吡啶桥联双(氨基酚氧基)钠、钾配合物的合成及催化外消旋丙交酯开环聚合研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1058-1068. |
| [9] | 张正初, 熊炜, 吕华. α-螺旋聚氨基酸交联的水凝胶的制备和材料特性★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1113-1119. |
| [10] | 梁雪峰, 荆剑, 冯昕, 赵勇泽, 唐新员, 何燕, 张立胜, 李慧芳. 共价有机框架COF66/COF366的电子结构: 从单体到二维平面聚合物[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 717-724. |
| [11] | 杨爽, 王宁宜, 杭青青, 张宇辰, 石枫. 邻羟基苯基取代的对亚甲基苯醌参与的催化不对称反应研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 793-808. |
| [12] | 刘坜, 郑刚, 范国强, 杜洪光, 谭嘉靖. 4-酰基/氨基羰基/烷氧羰基取代汉斯酯参与的有机反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [13] | 杨磊, 葛娇阳, 王访丽, 吴汪洋, 郑宗祥, 曹洪涛, 王洲, 冉雪芹, 解令海. 一种基于芴的大环结构的有效降低内重组能的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 613-619. |
| [14] | 张少秦, 李美清, 周中军, 曲泽星. 多共振热激活延迟荧光过程的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 124-130. |
| [15] | 王娟, 肖华敏, 谢丁, 郭元茹, 潘清江. 铜掺杂与氮化碳复合氧化锌材料结构和二氧化氮气体传感性质的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||