有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 4290-4297.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202506033 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
刘若雨a,*( ), 梁炳玉b, 陈书阳a, 孙红先a, 孙一冰a, 叶勇c,*(
), 梁炳玉b, 陈书阳a, 孙红先a, 孙一冰a, 叶勇c,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-26
修回日期:2025-08-08
发布日期:2025-10-09
通讯作者:
刘若雨, 叶勇
基金资助:
Ruoyu Liua,*( ), Bingyu Liangb, Shuyang Chena, Hongxian Suna, Yibing Suna, Yong Yec,*(
), Bingyu Liangb, Shuyang Chena, Hongxian Suna, Yibing Suna, Yong Yec,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-26
Revised:2025-08-08
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Ruoyu Liu, Yong Ye
Supported by:文章分享
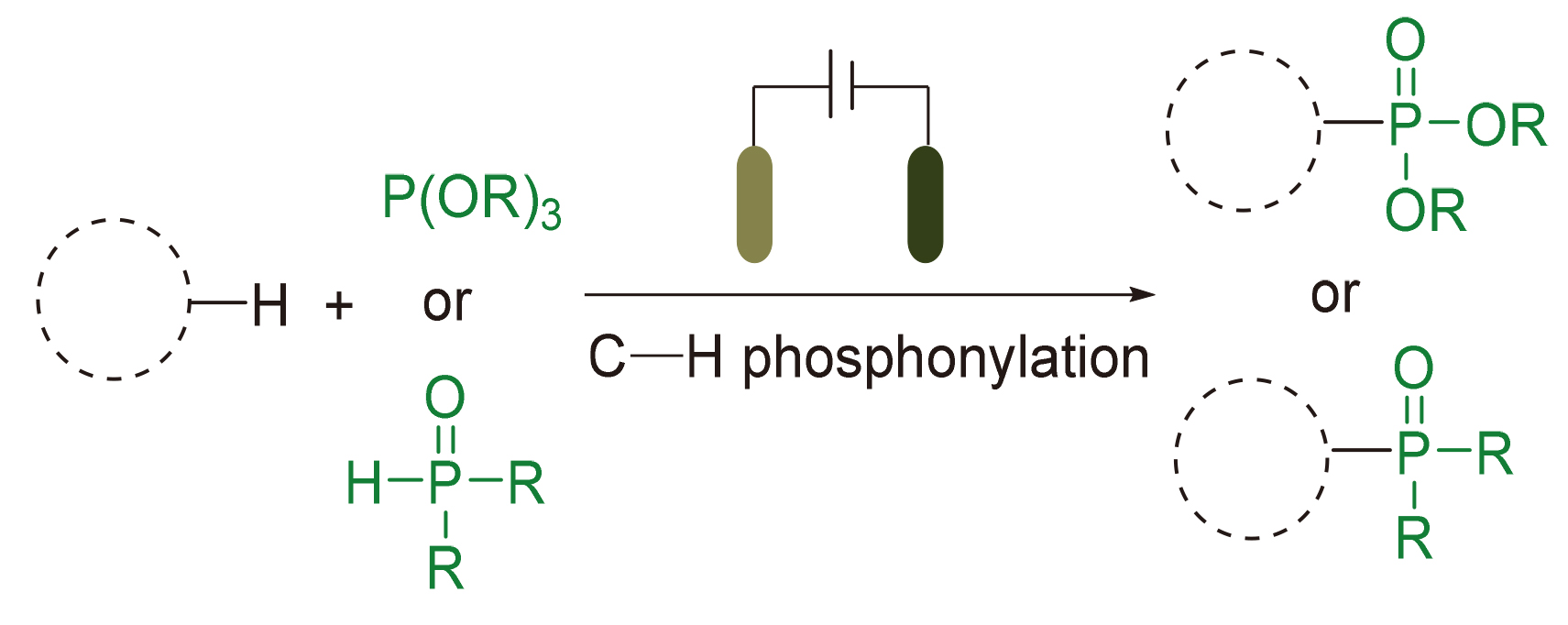
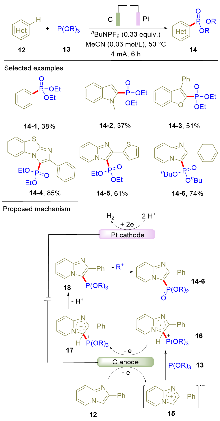
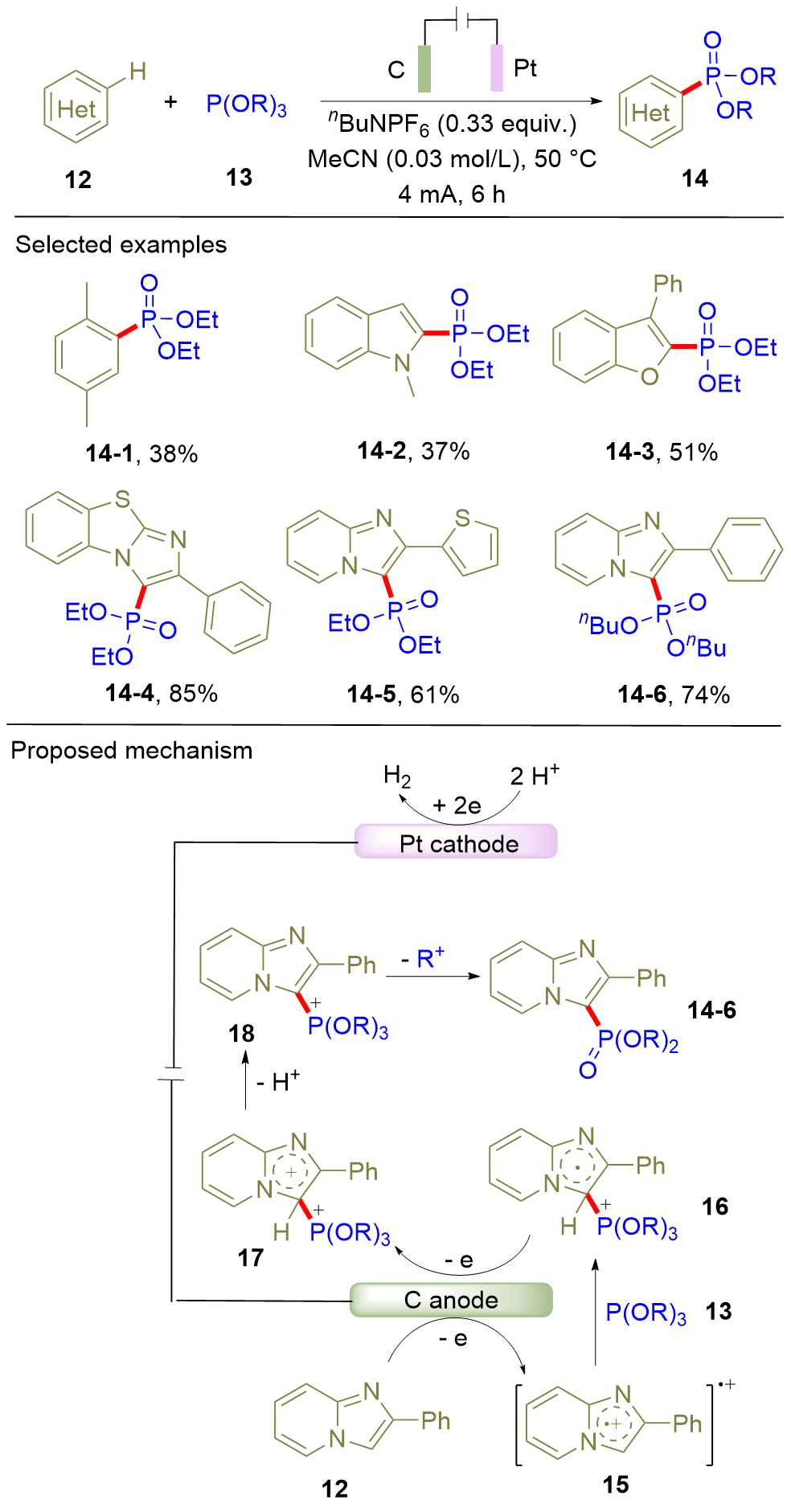
膦酰化的(杂)芳烃作为一类重要的有机膦化合物, 在有机催化、药物化学以及材料科学等领域展现出广泛的应用价值. 其中, (杂)芳烃的碳-氢膦酰化反应因其原子经济性和步骤简洁性, 成为构建该类化合物的最有效策略之一. 近年来, 随着有机电化学的快速发展, 电驱动的碳-氢膦酰化反应取得了重要突破. 与传统方法相比, 电化学策略具有如下显著优势: 一方面以电子替代传统化学氧化剂, 提高了反应的原子经济性; 另一方面反应条件温和, 表现出优异的官能团兼容性. 综述了(杂)芳烃电化学碳-氢膦酰化的最新研究进展, 重点阐述了反应机理, 阐明了方法的适用范围. 为便于读者理解, 依据电解模式(直接电解与间接电解), 将所讨论的反应体系划分为两大类.
刘若雨, 梁炳玉, 陈书阳, 孙红先, 孙一冰, 叶勇. (杂)芳烃的电化学碳-氢膦酰化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(12): 4290-4297.
Ruoyu Liu, Bingyu Liang, Shuyang Chen, Hongxian Sun, Yibing Sun, Yong Ye. Recent Advances of C—H Phosphonylation of (Hetero)arenes under Electrochemical Conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(12): 4290-4297.
| [1] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(80)80245-0 |
|
(b)
|
|
| [2] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00971 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02454 |
|
|
(c)
|
|
| [3] |
(a)
doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1705978 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b02418 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1002/chem.v23.50 |
|
| [4] |
(a)
doi: 10.6023/A22060260 |
|
(王振华, 马聪, 方萍, 徐海超, 梅天胜, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1115.)
doi: 10.6023/A22060260 |
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1007/s11426-023-1735-x |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202403010 |
|
|
(李永梅, 孙亮博, 徐坤, 曾程初, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 668.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202403010 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310033 |
|
|
(朱子乐, 李鹏飞, 仇友爱, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 871.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310033 |
|
| [5] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2025.111216 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/D5GC00186B |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v18.8 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310032 |
|
|
(周兰, 何红, 杨德巧, 侯中伟, 王磊, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 981.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202310032 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202500006 |
|
|
(张浩南, 徐坤, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 722.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202500006 |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00953100 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1039/C9GC01474H |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1002/ajoc.v8.11 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1039/C5CC08049E |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1039/C9CC00975B |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140946 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1021/jo00112a034 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26960-y pmid: 34785664 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c00549 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31178-7 pmid: 35715392 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2021.04.009 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1039/D4SC06219A |
| [1] | 赵佳, 甘秋云, 袁耀锋. 自由基磺酰氟化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1206-1222. |
| [2] | 李永梅, 孙亮博, 徐坤, 曾程初. 基于2,3-二氯-5,6-二氰基-1,4-苯醌(DDQ)的电/光电催化在碳-氢和碳-氟键官能化中的应用进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(2): 668-676. |
| [3] | 张欢, 崔中赫, 朱林, 李超忠. 可见光催化烷基醇经噻蒽盐的脱羟基(次)膦酰化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(12): 4468-4480. |
| [4] | 夏泽豪, 张新胜, 钮东方. 循环萃取耦合电解策略绿色合成高浓度对苯二酚[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(12): 4384-4389. |
| [5] | 郭国菊, 吴启龙, 董宇振, 张洁, 石永佳, 柳清, 杨道山. 光/电化学驱动硫代磷酸酯类化合物的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(10): 3719-3740. |
| [6] | 伍智林, 罗伟, 丁柔, 辛翠, 王从洋, 何卫民. N-芳基丙烯酰胺与自由基级联环化合成2-吲哚酮研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(10): 3691-3700. |
| [7] | 李颖, 胡硕真, 方卫, 肖星, 张新胜. 乙醇胺电氧化合成甘氨酸的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(10): 3873-3884. |
| [8] | 靳瑞文, 王连杰, 宋跃, 刘小培, 王俊伟, 李中贤. 基于成环策略构建苯并呋喃的合成研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(9): 2742-2759. |
| [9] | 陈倩, 韩召斌, 丁奎岭. 过渡金属催化芳香碳环的选择性不对称氢化[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(7): 2063-2076. |
| [10] | 方新月, 黄雅雯, 胡新伟, 阮志雄. 电化学修饰氨基酸和多肽类化合物的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 903-926. |
| [11] | 何蔺恒, 夏稳, 周玉祥, 于贤勇. 电催化N-芳基甘氨酸和苯并[e][1,2,3]噁噻嗪-2,2-二氧化物的串联脱羧环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 997-1004. |
| [12] | 周兰, 何红, 杨德巧, 侯中伟, 王磊. N-苄基丙烯酰胺的电化学三氟甲基化/螺环化合成三氟甲基取代2-氮杂螺[4.5]癸烷[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 981-988. |
| [13] | 叶增辉, 刘华清, 张逢质. 有机光电催化合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 840-870. |
| [14] | 黄健, 张文珍. 碳氮键参与的电化学阴极还原反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 825-839. |
| [15] | Hasil Aman, 常瑞, 叶俊涛. 氧化型光电催化促进的C—H键官能团化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(3): 728-747. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||