有机化学 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 106-117.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202506035 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
洪赛†, 尹发红†, 陈明慧, 傅滨, 肖玉梅, 覃兆海*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-26
修回日期:2025-08-22
发布日期:2025-09-24
作者简介:† 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Sai Hong, Fahong Yin, Minghui Chen, Bin Fu, Yumei Xiao, Zhaohai Qin*( )
)
Received:2025-07-26
Revised:2025-08-22
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
* E-mail: qinzhaohai@263.net
About author:† The authors contributed equally to this work
Supported by:文章分享
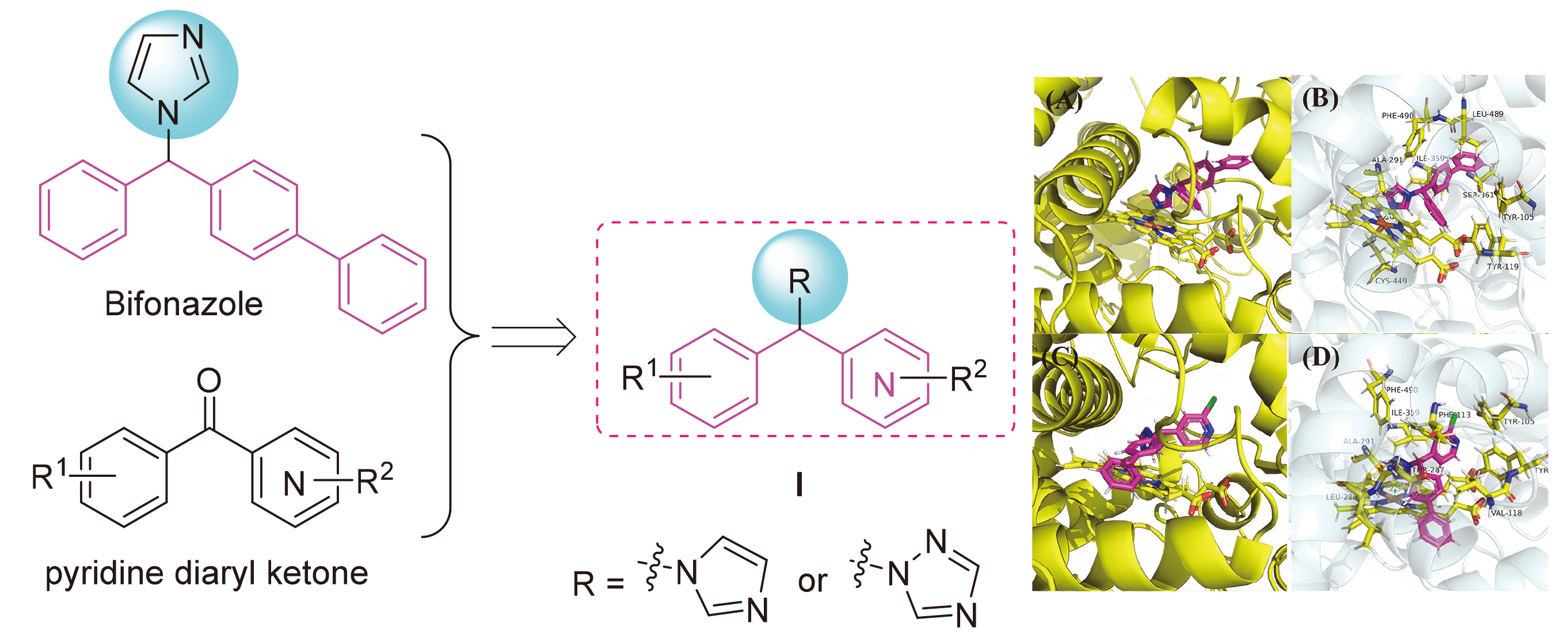
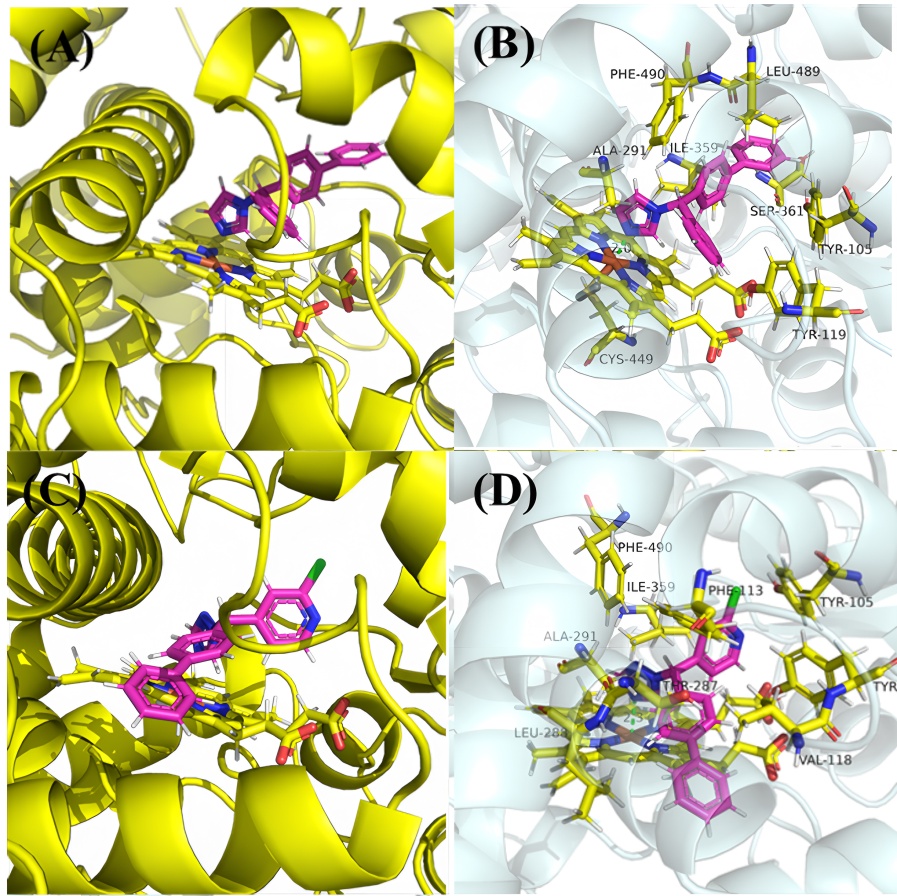
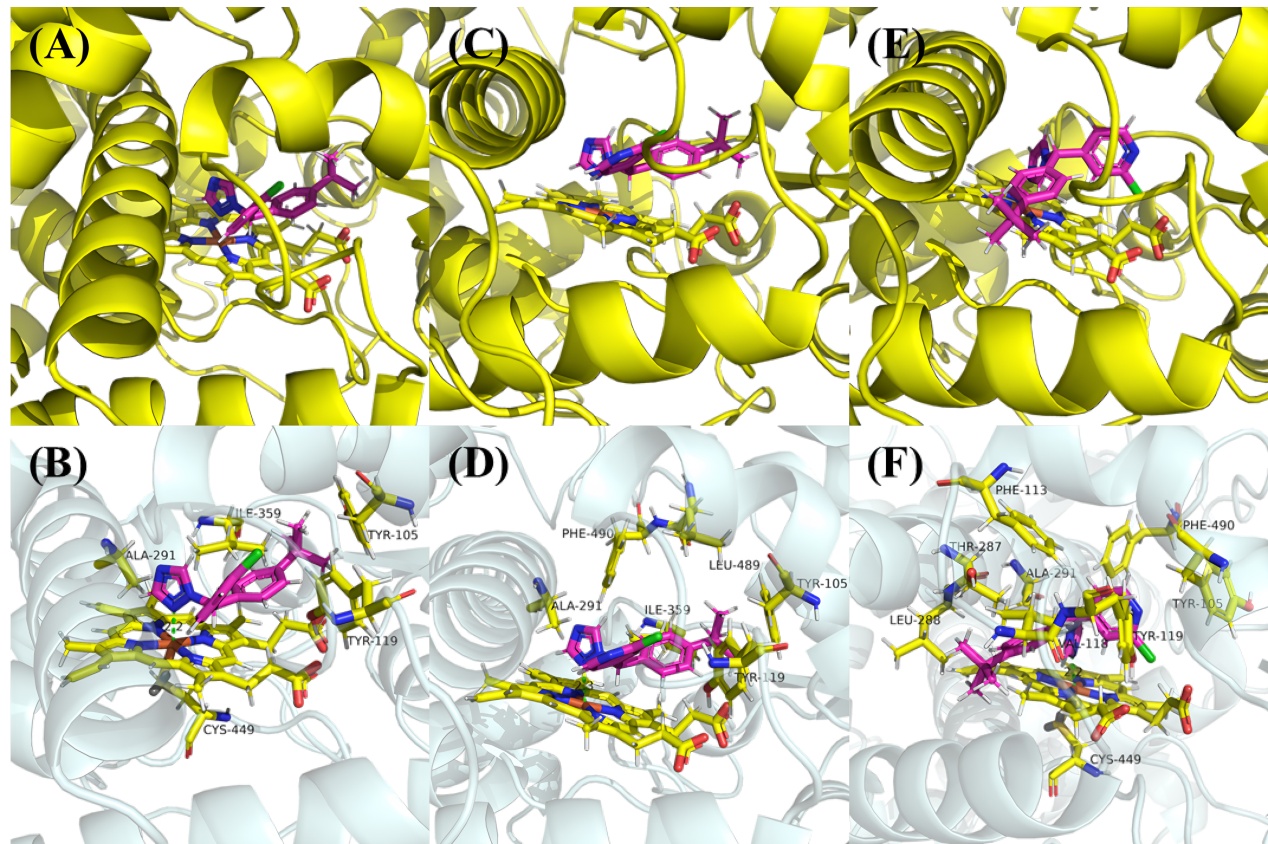
为探索吡啶杂环对唑类杀真菌剂活性的影响, 以联苯苄唑为先导, 以吡啶二芳酮分子插件为原料, 设计合成了24个含吡啶环的1-唑基-1,1-二芳基甲烷类化合物. 对10种植物病原真菌的离体杀菌活性测定结果表明, 部分化合物对多种病原菌表现出良好的抑制效果, 其中4-([1,1'-联苯]-4-基(1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)甲基)-2-氯吡啶(I-12)、1-((4-叔丁基苯基)(3-氯苯基)甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑(I-21)、4-((4-叔丁基苯基)(1H-咪唑-1-基)甲基)-2-氯吡啶(I-23)对Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Fusarium graminearum, Botrytis cinerea, Pythium aphanidermatum等真菌的杀菌活性显著, 化合物I-23对Pythium aphanidermatum的EC50值为14.03 mg/L, 与对照药联苯苄唑(14.87 mg/L)的活性相当. 构效关系分析显示, 咪唑取代的化合物通常活性更高, 而苯环上较大的取代基和化合物的疏水性对活性有积极影响. 分子对接研究进一步揭示了化合物与靶标蛋白可能的结合机制.
洪赛, 尹发红, 陈明慧, 傅滨, 肖玉梅, 覃兆海. 含吡啶环的1-唑基-1,1-二芳基甲烷类化合物的合成及杀菌活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2026, 46(1): 106-117.
Sai Hong, Fahong Yin, Minghui Chen, Bin Fu, Yumei Xiao, Zhaohai Qin. Study on the Synthesis and Fungicidal Activity of 1-Azolyl-1,1- diarylmethanes Containing Pyridine Ring[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2026, 46(1): 106-117.
| Compd. | Inhibition rate/(%, 50 mg/L) | MIRc % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log Pa | R. solanib | S. sclerotiorumb | P. capsicib | C. gloeosporioidesb | F. oxysporumb | F. graminearumb | F. fujikuroib | P. aphanidermatumb | B. cinereab | P. oryzaeb | ||
| I-1 | 3.42 | 22.15±2.51 | 16.80±2.08 | 8.74±0.93 | 18.68±0.54 | 12.18±0.84 | 45.05±0.79 | 25.77±2.43 | 17.37±1.24 | 28.14±1.89 | 50.10±2.15 | 24.5 |
| I-2 | 3.84 | 35.64±2.64 | 29.23±1.98 | 26.81±0.73 | 33.50±0.36 | 26.98±0.42 | 53.91±1.42 | 37.99±3.02 | 31.75±0.35 | 45.08±1.92 | 44.66±1.31 | 36.56 |
| I-3 | 4.25 | 57.46±1.06 | 41.00±0.60 | 55.71±0.20 | 43.34±0.74 | 36.92±0.56 | 57.43±0.34 | 38.22±2.22 | 33.88±1.22 | 63.22±2.16 | 49.28±2.33 | 47.65 |
| I-4 | 4.17 | 60.46±0.43 | 32.10±1.71 | 44.76±0.35 | 43.69±0.41 | 39.11±2.22 | 57.31±1.42 | 51.48±1.40 | 39.77±0.54 | 45.65±0.52 | 36.10±0.57 | 45.04 |
| I-5 | 5.09 | 57.57±1.19 | 43.62±2.67 | 60.49±0.93 | 44.64±1.03 | 41.41±0.63 | 61.85±1.23 | 48.02±0.87 | 42.48±0.41 | 84.41±2.03 | 57.84±3.18 | 54.23 |
| I-6 | 4.64 | 63.82±0.87 | 48.85±0.45 | 57.23±0.88 | 44.40±2.05 | 47.72±0.21 | 62.76±1.04 | 55.74±0.69 | 46.72±0.41 | 58.42±1.04 | 21.61±0.29 | 50.73 |
| I-7 | 5.05 | 65.79±2.81 | 50.16±0.78 | 57.69±0.35 | 48.91±0.21 | 45.05±1.31 | 76.61±2.39 | 55.86±0.87 | 49.08±1.41 | 68.36±1.04 | 26.22±3.21 | 54.37 |
| I-8 | 3.49 | 18.75±3.79 | 17.19±1.18 | 21.45±0.81 | 25.56±0.54 | 20.18±0.42 | 39.03±1.48 | 37.76±3.99 | 33.40±2.84 | 47.12±2.06 | 75.46±0.29 | 33.59 |
| I-9 | 3.09 | 3.18±2.74 | 0.31±0.78 | 2.80±0.70 | 12.40±0.54 | 8.90±0.56 | 37.78±0.39 | 33.15±1.60 | 33.52±1.22 | 44.18±2.07 | 34.29±0.49 | 21.05 |
| I-10 | 3.76 | 21.82±2.19 | 23.99±1.77 | 31.24±0.88 | 32.08±0.71 | 23.70±1.52 | 42.55±0.39 | 45.37±1.20 | 35.29±1.06 | 39.44±1.41 | 78.26±0.99 | 37.37 |
| I-11 | 4.92 | 60.20±0.87 | 54.87±2.08 | 59.91±1.41 | 50.57±0.62 | 37.41±0.36 | 55.95±0.79 | 46.52±1.06 | 53.32±0.61 | 86.78±3.11 | 41.04±0.57 | 54.66 |
| I-12 | 4.61 | 64.80±1.51 | 67.03±0.39 | 53.15±1.95 | 53.77±0.36 | 43.84±0.21 | 75.25±0.52 | 51.48±0.20 | 77.84±0.82 | 88.25±0.85 | 82.54±1.03 | 65.8 |
| I-13 | 2.80 | 15.90±1.55 | 7.12±0.23 | 0.00 | 12.87±0.36 | 8.18±0.21 | 31.77±0.20 | 21.39±2.22 | 15.37±0.41 | 58.87±3.20 | 29.02±1.24 | 20.05 |
| I-14 | 3.91 | 26.75±4.06 | 25.95±0.23 | 21.45±0.53 | 31.96±0.21 | 21.88±1.83 | 56.18±0.39 | 30.61±3.73 | 21.97±0.74 | 18.42±0.39 | 51.91±0.57 | 30.71 |
| I-15 | 3.91 | 19.19±2.33 | 17.32±2.61 | 18.88±1.05 | 21.76±0.62 | 19.46±0.42 | 31.77±1.29 | 25.54±3.81 | 15.49±0.61 | 55.14±1.09 | 38.24±1.71 | 26.28 |
| I-16 | 3.91 | 3.29±2.37 | 8.69±0.82 | 16.90±1.58 | 20.46±0.21 | 15.21±7.31 | 35.51±1.42 | 16.55±2.69 | 12.78±1.14 | 38.64±1.55 | 46.64±0.99 | 21.47 |
| I-17 | 4.29 | 52.96±3.47 | 44.40±0.82 | 50.70±1.26 | 39.90±0.62 | 36.44±1.11 | 48.23±1.77 | 48.48±2.42 | 27.39±0.74 | 52.09±2.18 | 28.19±3.02 | 42.88 |
| I-18 | 4.64 | 54.82±1.52 | 49.63±2.16 | 53.73±0.73 | 44.64±1.03 | 35.10±0.42 | 49.25±0.59 | 42.95±1.38 | 46.49±1.08 | 66.10±1.89 | 27.54±1.51 | 47.03 |
| I-19 | 5.34 | 68.75±0.33 | 65.72±1.59 | 59.91±1.07 | 40.61±1.23 | 61.67±0.76 | 68.44±1.94 | 59.77±0.53 | 48.14±1.47 | 73.79±2.74 | 24.74±2.00 | 57.15 |
| I-20 | 4.64 | 41.34±1.55 | 24.65±0.78 | 39.42±1.15 | 28.99±0.21 | 25.16±1.38 | 48.00±1.71 | 31.77±2.22 | 29.40±0.20 | 47.29±0.24 | 23.09±2.00 | 33.91 |
| I-21 | 5.63 | 65.24±1.33 | 72.53±1.04 | 45.34±1.41 | 46.42±0.21 | 31.59±1.67 | 70.59±0.20 | 42.25±0.35 | 32.11±2.55 | 88.93±0.39 | 43.02±0.57 | 53.8 |
| I-22 | 3.07 | 48.03±3.01 | 0.00 | 24.94±1.01 | 33.14±1.23 | 12.54±2.00 | 56.18±0.39 | 34.65±1.04 | 18.79±2.13 | 0.00 | 74.80±1.31 | 30.31 |
| I-23 | 4.28 | 66.01±1.00 | 11.43±0.45 | 87.18±0.73 | 52.11±0.54 | 28.68±1.89 | 79.11±2.58 | 52.51±1.00 | 84.21±0.82 | 49.04±3.43 | 53.15±2.45 | 56.34 |
| I-24 | 3.55 | 40.24±2.64 | 1.88±0.78 | 34.73±2.27 | 40.02±0.21 | 16.06±0.76 | 61.06±0.52 | 55.62±0.53 | 8.06±0.71 | 6.67±0.85 | 71.34±1.48 | 33.57 |
| Bifonazole | 4.69 | 75.44±4.49 | 90.71±1.59 | 96.39±1.58 | 94.90±0.21 | 91.51±1.17 | 92.28±0.86 | 80.06±0.20 | 72.87±0.38 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 89.42 |
| Compd. | Inhibition rate/(%, 50 mg/L) | MIRc % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log Pa | R. solanib | S. sclerotiorumb | P. capsicib | C. gloeosporioidesb | F. oxysporumb | F. graminearumb | F. fujikuroib | P. aphanidermatumb | B. cinereab | P. oryzaeb | ||
| I-1 | 3.42 | 22.15±2.51 | 16.80±2.08 | 8.74±0.93 | 18.68±0.54 | 12.18±0.84 | 45.05±0.79 | 25.77±2.43 | 17.37±1.24 | 28.14±1.89 | 50.10±2.15 | 24.5 |
| I-2 | 3.84 | 35.64±2.64 | 29.23±1.98 | 26.81±0.73 | 33.50±0.36 | 26.98±0.42 | 53.91±1.42 | 37.99±3.02 | 31.75±0.35 | 45.08±1.92 | 44.66±1.31 | 36.56 |
| I-3 | 4.25 | 57.46±1.06 | 41.00±0.60 | 55.71±0.20 | 43.34±0.74 | 36.92±0.56 | 57.43±0.34 | 38.22±2.22 | 33.88±1.22 | 63.22±2.16 | 49.28±2.33 | 47.65 |
| I-4 | 4.17 | 60.46±0.43 | 32.10±1.71 | 44.76±0.35 | 43.69±0.41 | 39.11±2.22 | 57.31±1.42 | 51.48±1.40 | 39.77±0.54 | 45.65±0.52 | 36.10±0.57 | 45.04 |
| I-5 | 5.09 | 57.57±1.19 | 43.62±2.67 | 60.49±0.93 | 44.64±1.03 | 41.41±0.63 | 61.85±1.23 | 48.02±0.87 | 42.48±0.41 | 84.41±2.03 | 57.84±3.18 | 54.23 |
| I-6 | 4.64 | 63.82±0.87 | 48.85±0.45 | 57.23±0.88 | 44.40±2.05 | 47.72±0.21 | 62.76±1.04 | 55.74±0.69 | 46.72±0.41 | 58.42±1.04 | 21.61±0.29 | 50.73 |
| I-7 | 5.05 | 65.79±2.81 | 50.16±0.78 | 57.69±0.35 | 48.91±0.21 | 45.05±1.31 | 76.61±2.39 | 55.86±0.87 | 49.08±1.41 | 68.36±1.04 | 26.22±3.21 | 54.37 |
| I-8 | 3.49 | 18.75±3.79 | 17.19±1.18 | 21.45±0.81 | 25.56±0.54 | 20.18±0.42 | 39.03±1.48 | 37.76±3.99 | 33.40±2.84 | 47.12±2.06 | 75.46±0.29 | 33.59 |
| I-9 | 3.09 | 3.18±2.74 | 0.31±0.78 | 2.80±0.70 | 12.40±0.54 | 8.90±0.56 | 37.78±0.39 | 33.15±1.60 | 33.52±1.22 | 44.18±2.07 | 34.29±0.49 | 21.05 |
| I-10 | 3.76 | 21.82±2.19 | 23.99±1.77 | 31.24±0.88 | 32.08±0.71 | 23.70±1.52 | 42.55±0.39 | 45.37±1.20 | 35.29±1.06 | 39.44±1.41 | 78.26±0.99 | 37.37 |
| I-11 | 4.92 | 60.20±0.87 | 54.87±2.08 | 59.91±1.41 | 50.57±0.62 | 37.41±0.36 | 55.95±0.79 | 46.52±1.06 | 53.32±0.61 | 86.78±3.11 | 41.04±0.57 | 54.66 |
| I-12 | 4.61 | 64.80±1.51 | 67.03±0.39 | 53.15±1.95 | 53.77±0.36 | 43.84±0.21 | 75.25±0.52 | 51.48±0.20 | 77.84±0.82 | 88.25±0.85 | 82.54±1.03 | 65.8 |
| I-13 | 2.80 | 15.90±1.55 | 7.12±0.23 | 0.00 | 12.87±0.36 | 8.18±0.21 | 31.77±0.20 | 21.39±2.22 | 15.37±0.41 | 58.87±3.20 | 29.02±1.24 | 20.05 |
| I-14 | 3.91 | 26.75±4.06 | 25.95±0.23 | 21.45±0.53 | 31.96±0.21 | 21.88±1.83 | 56.18±0.39 | 30.61±3.73 | 21.97±0.74 | 18.42±0.39 | 51.91±0.57 | 30.71 |
| I-15 | 3.91 | 19.19±2.33 | 17.32±2.61 | 18.88±1.05 | 21.76±0.62 | 19.46±0.42 | 31.77±1.29 | 25.54±3.81 | 15.49±0.61 | 55.14±1.09 | 38.24±1.71 | 26.28 |
| I-16 | 3.91 | 3.29±2.37 | 8.69±0.82 | 16.90±1.58 | 20.46±0.21 | 15.21±7.31 | 35.51±1.42 | 16.55±2.69 | 12.78±1.14 | 38.64±1.55 | 46.64±0.99 | 21.47 |
| I-17 | 4.29 | 52.96±3.47 | 44.40±0.82 | 50.70±1.26 | 39.90±0.62 | 36.44±1.11 | 48.23±1.77 | 48.48±2.42 | 27.39±0.74 | 52.09±2.18 | 28.19±3.02 | 42.88 |
| I-18 | 4.64 | 54.82±1.52 | 49.63±2.16 | 53.73±0.73 | 44.64±1.03 | 35.10±0.42 | 49.25±0.59 | 42.95±1.38 | 46.49±1.08 | 66.10±1.89 | 27.54±1.51 | 47.03 |
| I-19 | 5.34 | 68.75±0.33 | 65.72±1.59 | 59.91±1.07 | 40.61±1.23 | 61.67±0.76 | 68.44±1.94 | 59.77±0.53 | 48.14±1.47 | 73.79±2.74 | 24.74±2.00 | 57.15 |
| I-20 | 4.64 | 41.34±1.55 | 24.65±0.78 | 39.42±1.15 | 28.99±0.21 | 25.16±1.38 | 48.00±1.71 | 31.77±2.22 | 29.40±0.20 | 47.29±0.24 | 23.09±2.00 | 33.91 |
| I-21 | 5.63 | 65.24±1.33 | 72.53±1.04 | 45.34±1.41 | 46.42±0.21 | 31.59±1.67 | 70.59±0.20 | 42.25±0.35 | 32.11±2.55 | 88.93±0.39 | 43.02±0.57 | 53.8 |
| I-22 | 3.07 | 48.03±3.01 | 0.00 | 24.94±1.01 | 33.14±1.23 | 12.54±2.00 | 56.18±0.39 | 34.65±1.04 | 18.79±2.13 | 0.00 | 74.80±1.31 | 30.31 |
| I-23 | 4.28 | 66.01±1.00 | 11.43±0.45 | 87.18±0.73 | 52.11±0.54 | 28.68±1.89 | 79.11±2.58 | 52.51±1.00 | 84.21±0.82 | 49.04±3.43 | 53.15±2.45 | 56.34 |
| I-24 | 3.55 | 40.24±2.64 | 1.88±0.78 | 34.73±2.27 | 40.02±0.21 | 16.06±0.76 | 61.06±0.52 | 55.62±0.53 | 8.06±0.71 | 6.67±0.85 | 71.34±1.48 | 33.57 |
| Bifonazole | 4.69 | 75.44±4.49 | 90.71±1.59 | 96.39±1.58 | 94.90±0.21 | 91.51±1.17 | 92.28±0.86 | 80.06±0.20 | 72.87±0.38 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 89.42 |
| Compd. | EC50 | Regression equation | R2 | 95% confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. oryzae | I-08 | 49.17 | y=-2.54+1.48x | 0.941 | 38.18~70.10 |
| I-10 | 33.34 | y=-2.21+1.44x | 0.984 | 26.81~43.90 | |
| I-12 | 15.67 | y=-1.91+1.59x | 0.985 | 13.20~18.93 | |
| I-22 | 46.03 | y=-2.4+1.45x | 0.960 | 35.31~65.86 | |
| I-24 | 20.77 | y=-1.75+1.33x | 0.997 | 16.87~26.60 | |
| Bifonazole | 1.41 | y=-0.21+1.49x | 0.947 | 0.72~2.12 | |
| B. cinerea | I-05 | 15.25 | y=-1.97+1.66x | 0.992 | 12.94~18.24 |
| I-11 | 14.21 | y=-1.4+1.21x | 0.985 | 11.41~17.92 | |
| I-12 | 21.65 | y=-2.09+1.56x | 0.970 | 18.15~26.57 | |
| I-19 | 22.01 | y=-1.82+1.35x | 0.992 | 17.92~28.13 | |
| I-21 | 16.41 | y=-1.85+1.51x | 0.982 | 13.72~20.02 | |
| Bifonazole | 1.78 | y=-0.38+1.41x | 0.997 | 0.75~3.00 | |
| F. graminearum | I-07 | 22.84 | y=-1.21+0.89x | 0.988 | 16.88~34.18 |
| I-12 | 17.3 | y=-1.15+0.93x | 0.996 | 13.20~24.12 | |
| I-21 | 19.71 | y=-0.76+0.59x | 0.996 | 12.97~36.65 | |
| I-23 | 12.76 | y=-0.78+0.71x | 0.991 | 9.12~18.98 | |
| Bifonazole | 0.1 | y=0.76+0.77x | 0.920 | 0.08~0.15 | |
| P. aphanidermatum | I-12 | 27.54 | y=-2.68+1.86x | 0.976 | 23.41~33.34 |
| I-23 | 14.03 | y=-2.73+2.35x | 0.963 | 9.87~20.48 | |
| Bifonazole | 14.87 | y=-1.97+1.66x | 0.996 | 10.94~21.28 | |
| P. capsici | I-23 | 20.17 | y=-3.95+3.02x | 0.997 | 18.07~22.62 |
| Bifonazole | 6.5 | y=-2.59+3.11x | 0.985 | 5.83~7.23 | |
| S. sclerotiorum | I-21 | 16.53 | y=-1.93+1.57x | 0.963 | 14.00~19.86 |
| Bifonazole | 11.94 | y=-2.01+1.89x | 0.984 | 10.36~13.84 |
| Compd. | EC50 | Regression equation | R2 | 95% confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. oryzae | I-08 | 49.17 | y=-2.54+1.48x | 0.941 | 38.18~70.10 |
| I-10 | 33.34 | y=-2.21+1.44x | 0.984 | 26.81~43.90 | |
| I-12 | 15.67 | y=-1.91+1.59x | 0.985 | 13.20~18.93 | |
| I-22 | 46.03 | y=-2.4+1.45x | 0.960 | 35.31~65.86 | |
| I-24 | 20.77 | y=-1.75+1.33x | 0.997 | 16.87~26.60 | |
| Bifonazole | 1.41 | y=-0.21+1.49x | 0.947 | 0.72~2.12 | |
| B. cinerea | I-05 | 15.25 | y=-1.97+1.66x | 0.992 | 12.94~18.24 |
| I-11 | 14.21 | y=-1.4+1.21x | 0.985 | 11.41~17.92 | |
| I-12 | 21.65 | y=-2.09+1.56x | 0.970 | 18.15~26.57 | |
| I-19 | 22.01 | y=-1.82+1.35x | 0.992 | 17.92~28.13 | |
| I-21 | 16.41 | y=-1.85+1.51x | 0.982 | 13.72~20.02 | |
| Bifonazole | 1.78 | y=-0.38+1.41x | 0.997 | 0.75~3.00 | |
| F. graminearum | I-07 | 22.84 | y=-1.21+0.89x | 0.988 | 16.88~34.18 |
| I-12 | 17.3 | y=-1.15+0.93x | 0.996 | 13.20~24.12 | |
| I-21 | 19.71 | y=-0.76+0.59x | 0.996 | 12.97~36.65 | |
| I-23 | 12.76 | y=-0.78+0.71x | 0.991 | 9.12~18.98 | |
| Bifonazole | 0.1 | y=0.76+0.77x | 0.920 | 0.08~0.15 | |
| P. aphanidermatum | I-12 | 27.54 | y=-2.68+1.86x | 0.976 | 23.41~33.34 |
| I-23 | 14.03 | y=-2.73+2.35x | 0.963 | 9.87~20.48 | |
| Bifonazole | 14.87 | y=-1.97+1.66x | 0.996 | 10.94~21.28 | |
| P. capsici | I-23 | 20.17 | y=-3.95+3.02x | 0.997 | 18.07~22.62 |
| Bifonazole | 6.5 | y=-2.59+3.11x | 0.985 | 5.83~7.23 | |
| S. sclerotiorum | I-21 | 16.53 | y=-1.93+1.57x | 0.963 | 14.00~19.86 |
| Bifonazole | 11.94 | y=-2.01+1.89x | 0.984 | 10.36~13.84 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1002/jhet.v61.2 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00556K |
| [3] |
doi: 10.2217/fmb-2021-0173 pmid: 34783586 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119553 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.067 |
| [6] |
pmid: 16466539 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1007/s12154-008-0010-6 pmid: 19568799 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.06.006 pmid: 20547249 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/0048-3575(73)90005-9 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133215 pmid: 20530488 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.07.018 pmid: 16963187 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115658 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/ps.v26:2 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aac.2024.10.002 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2010.08.017 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.11.013 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2016.04.003 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09543 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105169 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1002/ps.v81.4 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10490 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00032 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.3390/jof10020160 |
| [26] |
pmid: 2670516 |
| [27] |
pmid: 2528693 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
(车传亮, 杨冬燕, 万川, 王家尧, 刘雪莲, 赵峰海, 覃兆海, 农药学学报, 2017, 19, 533.)
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
(慕长炜, 袁会珠, 李楠, 傅滨, 肖玉梅, 马永强, 齐淑华, 覃兆海, 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 1902.)
|
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1021/jf902410x |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules16118945 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1002/ps.v76.6 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2018.04.066 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1021/ac501780z pmid: 25098642 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c00529 pmid: 33655746 |
| [37] |
|
|
(孙家隆, 慕卫, 农药实验技术与指导, 化学工业出版社, 北京, 2009.)
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334 pmid: 19499576 |
| [1] | 崔心怡, 郭丽帆, 马聪璇, 李耘, 梁建华. 抗耐药菌红霉素的结构修饰策略、构效关系及全合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2026, 46(1): 39-73. |
| [2] | 赵友学, 李兮若, 孟洛冰, 李春秀, 范贵生, 许建和. 醇脱氢酶/羰基还原酶与多底物分子适配性研究的进展★[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(9): 3175-3185. |
| [3] | 郭浩哲, 李玉银, 汤培琛, 樊江莉. 机器学习设计有机荧光诊疗分子的研究进展★[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(9): 3203-3212. |
| [4] | 汤敏, 张斌, 王秋实, 方超华, 胡立威, 关丽萍. 基于包含吲哚环、苯并噻吩环的单胺氧化酶和胆碱酯酶抑制活性的查尔酮衍生物设计、合成及生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(8): 2989-3003. |
| [5] | 刘娟娟, 高娅, 罗国勇, 杨韶平. N-异海松酰基-N'-芳酰氨基硫脲的设计、合成、抗肿瘤活性及分子对接[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(12): 4497-4504. |
| [6] | 邱东平, 王兆旭, 张洁, 郭亮. 新型酰亚胺-β-咔啉的设计、合成及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(12): 4362-4374. |
| [7] | 赵瑜, 张紫越, 许书伟, 胡华伟, 吴宏伟, 张琳萍, 陈丰坤. 锯齿形给体-受体齐聚物的设计、合成及光伏性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 4210-4219. |
| [8] | 孙翠萍, 薛雨婷, 陈磅宽. 杂螺烯圆偏振发光材料的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 4048-4069. |
| [9] | 颜逸韬, 陈颖露, 胡涵显, 吴军. 双取代嘧啶-联苯化合物的合成及除草活性和分子作用机制研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 358-366. |
| [10] | 田海平, 刘东东, 裴鸿艳, 叶家麟, 郑子锐, 高一星, 李昌兴, 田欢, 张静, 张立新. 新型苯基吡唑类衍生物的设计、合成和杀虫活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 227-239. |
| [11] | 郑佰峰, 左炀, 陈琼, 吴琼友. 新型苯并噻唑-嘧啶二酮类化合物的设计、合成与除草活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(7): 2371-2376. |
| [12] | 秦丽清, 林桂汕, 段文贵, 崔玉成, 杨卯芳, 李芳耀, 李典鹏. 新型长叶烯基萘满并N-酰基吡唑化合物的合成、抗增殖活性、三维定量构效关系及分子对接研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 1967-1977. |
| [13] | 梁国超, 董婷婷, 纪海莹, 王春艳, 宋亚丽, 张伟. 新型3,3'-((4-氯-2H-硫色烯-3-基)亚甲基)双(1H-吲哚)类拓扑异构酶Ⅱ抑制剂的合成及抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 1949-1956. |
| [14] | 胡懿鸣, 许嘉宇, 汤敏, 刘雅雯, 关丽萍, 金晴昊. 2-(1,3-二氧代异吲哚啉-2-基)-N-苯乙酰胺和2-(3,4-二氢异喹啉-1-基)异吲哚-1,3-二酮类单胺氧化酶(MAO)和胆碱酯酶(ChE)抑制剂的设计、合成和生物活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(6): 1907-1919. |
| [15] | 刘吉永, 吴明慧, 相君成, 庞怀林, 李斌, 吕亮. 新型含(卤代)烷氧基类双酰胺化合物的合成、杀虫活性及构效关系研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(5): 1584-1591. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||