Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 3223-3232.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202406017 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
何君a, 王红星a,*( ), 余成龙b,c, 张艳茹b,c, 王莹b, 王燕燕b,c, 张龙博b,c, 郭佳b,c, 钱庆利b,c,*(
), 余成龙b,c, 张艳茹b,c, 王莹b, 王燕燕b,c, 张龙博b,c, 郭佳b,c, 钱庆利b,c,*( ), 韩布兴b,c,d,*(
), 韩布兴b,c,d,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-12
修回日期:2024-07-29
发布日期:2024-08-30
基金资助:
Jun Hea, Hongxing Wanga,*( ), Chenglong Yub,c, Yanru Zhangb,c, Ying Wangb, Yanyan Wangb,c, Longbo Zhangb,c, Jia Guob,c, Qingli Qianb,c,*(
), Chenglong Yub,c, Yanru Zhangb,c, Ying Wangb, Yanyan Wangb,c, Longbo Zhangb,c, Jia Guob,c, Qingli Qianb,c,*( ), Buxing Hanb,c,d,*(
), Buxing Hanb,c,d,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-12
Revised:2024-07-29
Published:2024-08-30
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:Share
Jun He, Hongxing Wang, Chenglong Yu, Yanru Zhang, Ying Wang, Yanyan Wang, Longbo Zhang, Jia Guo, Qingli Qian, Buxing Han. Nanoflower-Shaped Ir/MoS2 Catalyst for Highly Selective Production of Formate by CO2 Hydrogenation[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3223-3232.


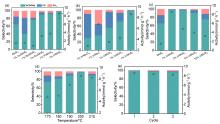

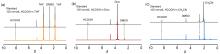

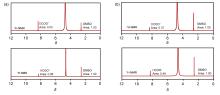

| [1] |
He, M.; Sun, Y.; Han, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 134, e202112835.
|
| [2] |
Qian, Q.; Han, B. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad160.
|
| [3] |
Ma, Z.; Legrand, U.; Pahija, E.; Tavares, J.; Boffito, D. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 803.
|
| [4] |
Wang, X. S.; Yang, X.; Chen, C. H.; Li, H. F.; Huang, Y. B.; Cao, R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 22. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王旭生, 杨胥, 陈春辉, 李红芳, 黄远标, 曹荣, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 22.)
doi: 10.6023/A21100455 |
|
| [5] |
Bulushev, D.; Ross, J. Catal. Rev. 2018, 60, 544.
|
| [6] |
Weilhard, A.; Qadir, M.; Sans, V.; Dupont, J. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1628.
|
| [7] |
Álvarez, A.; Bansode, A.; Urakawa, A.; Bavykina, A.; Wezendonk, T.; Makkee, M.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9804.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00816 pmid: 28656757 |
| [8] |
Ma, R.; Song, G. G.; Xi, Q. Z.; Yang, L.; Li, E. Q.; Duan, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 2196. (in Chinese)
|
|
(马蓉, 宋格格, 奚秋贞, 杨柳, 李二庆, 段征, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2196.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201901040 |
|
| [9] |
Deokar, G.; Vignaud, D.; Arenal, R.; Louette, P.; Colomer, J. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 075604.
|
| [10] |
Wang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ji, Q.; Lu, Z.; Xu, G.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, R.; Yu, L.; Tian, Z.; Deng, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202307086.
|
| [11] |
Bharath, G.; Rambabu, K.; Morajkar, P.; Jayaraman, R.; Theerthagiri, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, M.; Banat, F. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124980.
|
| [12] |
Mitchell, C.; Terranova, U.; Beale, A.; Jones, W.; Morgan, D.; Sankar, M.; Leeuw, N. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 779.
|
| [13] |
Fu, X.; Peres, L.; Esvan, J.; Amiens, C.; Philippot, K.; Yan, N. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8931.
|
| [14] |
Schaub, T.; Paciello, R. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 32, 7278.
|
| [15] |
Huang, W. B.; Qiu, L. Q.; Ren, F. Y.; He, L. N. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 3914. (in Chinese)
|
|
(黄文斌, 邱丽琪, 任方煜, 何良年, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 3914.)
|
|
| [16] |
Zhou, Y.; Liu, F.; Geng, S.; Yao, M.; Ma, J.; Cao, J. Mol. Catal. 2023, 547, 113288.
|
| [17] |
Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Yang, F.; Feng, L. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 87, 144.
|
| [18] |
Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, X.; Long, X.; Chang, C.; Yang, Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130337.
|
| [19] |
Chang, C.; Tsai, Z.; Lin, K.; Nian, Y. J. Photochem. Photobiol.,A 2023, 445, 115027.
|
| [20] |
Dong, H.; Gong, C.; Addou, R.; McDonnell, S.; Azcatl, A.; Qin, X.; Wang, W.; Hinkle, C.; Wallace, R. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38977.
|
| [21] |
Hao, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; You, H.; Fang, J. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 10449.
|
| [22] |
Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 136, 4.
|
| [23] |
Luo, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M.; Ge, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, D.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Xing, W. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2120.
|
| [24] |
Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ji, J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yao, X.; Gu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wan, H.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 571, 151200.
|
| [25] |
Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Cheng, D.; Cao, D. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900653.
|
| [1] | Jinbin Gao, Yingqi Lu, Hui Zhang, Lizhu Gao, Xingquan Xiong. Application of Biobased Catalysts in Chemical Conversion of CO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(9): 2732-2741. |
| [2] | Julaiti Maierhaba, Yusan Bulunuer, Wusiman Abudureheman. Catalyst- and Additive-Free Direct Synthesis of N-Sulfonyl Guanidines [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(4): 1276-1283. |
| [3] | Yufei Zhou, Xiaofei Jia. Progress in Heterogeneous Catalyzed Tandem Reactions Based on Hydroformylation [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3147-3158. |
| [4] | Qiuting Zhao, Wenguang Wang. Iron-Catalyzed Selective Hydrogenation and Hydroboration/Hydrosilylation of CO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3106-3116. |
| [5] | Kaiyue Wang, Mingnuo Xu, Bo Li, Guangpeng Wu. Application of Bifunctional Thiourea Catalyst in One Pot Preparation of Polypeptides and Cyclic Carbonates [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3206-3212. |
| [6] | Hui Xu, Huixian Jiang, Lei Kan, Pei Xu, Xu Zhu. Visible-Light-Induced Selective Hydrocarboxylation of Alkynes with Formate [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3241-3248. |
| [7] | Jianwen Li, Tao Wang, Sheng Tao, Fei Chen, Min Li, Ning Liu. N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Pyridine Molybdenum Complex Supported over SBA-15 for Converting of Carbon Dioxide into Cyclic Carbonates [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3213-3222. |
| [8] | Xuewei Chen, Fangcai Yu, Chuanhong Tian. 1,1'-Methylenediimidazolium-Based Multiple Hydrogen-Bond Donor Catalysts Facilitate the Cycloaddition of CO2 with Epoxides under Atmospheric Pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(10): 3198-3205. |
| [9] | Jianghu Dong, Liangming Xuan, Chi Wang, Chenxi Zhao, Haifeng Wang, Qiongjiao Yan, Wei Wang, Fen'er Chen. Recent Advances in Visible-Light-Induced C(3)—H Functionalization of Quinoxalinones under Transition-Metal-Free or Photocatalyst-Free [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 111-136. |
| [10] | Qianfan Zhao, Yongzheng Chen, Shiming Zhang. Application and Mechanism Study of Carbon-Based Metal-Free Catalysts in Organic Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(1): 137-147. |
| [11] | Kai Lu, Haoqi Qu, Xi Chen, Hui Qiu, Jing Zheng, Mengtao Ma. Catalyst-Free and Solvent-Free Hydroboration of Alkynes and Alkenes with Catecholborane [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(6): 2197-2205. |
| [12] | Baichuan Mo, Chunxia Chen, Jinsong Peng. Research Progress in Application of Lignin and Its Derivatives Supported Metal Catalysts in Organic Synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(4): 1215-1240. |
| [13] | Sining Qin. Research Progress in C—S Coupling Reactions of Aryl Halides [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(11): 3761-3783. |
| [14] | Tiantian Liu, Xinhong Duan. Recent Progress in the Construction of Chiral 3-Substituted Indoles by Asymmetric Friedel-Crafts Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(11): 3695-3712. |
| [15] | Zhiyuan Chen, Mengwei Yang, Jianlin Xu, Yunhe Xu. Regioselective Synthesis of β-Silyl-Substituted Vinylphosphine Oxides via Copper-Catalyzed Protosilylation of Dialkynylphosphine Oxides [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(10): 3598-3607. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||