有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 4128-4142.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202503003 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
代鸿宇a, 孙红红a, 魏培发b,*( ), 管伟江a,*(
), 管伟江a,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-03
修回日期:2025-06-01
发布日期:2025-06-19
基金资助:
Hongyu Daia, Honghong Suna, Peifa Weib,*( ), Weijiang Guana,*(
), Weijiang Guana,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-03
Revised:2025-06-01
Published:2025-06-19
Contact:
*E-mail: pfwei@ahu.edu.cn; wjguan@mail.buct.edu.cn
Supported by:文章分享
聚集诱导发光(AIE)光敏剂即便处于高分子化或聚集态, 仍能维持强荧光特性且高效产生活性氧(ROS), 已成为新一代光动力治疗(PDT)候选材料. 围绕近年研究领域中分子电子结构与分子运动调控策略的相关进展, 重点梳理了构建供体-受体(D-A)框架的合成策略(如Suzuki-Miyaura偶联、Stille偶联、Buchwald-Hartwig偶联、Sonogashira偶联、Knoevenagel缩合), 调控π共轭骨架的合成策略(如Heck反应、Vilsmeier-Haac反应), 增强自旋轨道耦合(SOC)的合成策略(如Menshutkin反应、点击反应、金属配位反应), 以及分子运动限制策略(聚合物封装和纳米颗粒负载). 通过多维分子设计与材料工程协同, AIE光敏剂已在近红外成像与深部PDT疗效方面取得了显著进展. 展望未来, 可以借助机器学习辅助的分子筛选和多模态递送平台, 加速AIE光敏剂向临床深部实体瘤精准光疗的转化.
代鸿宇, 孙红红, 魏培发, 管伟江. 高效聚集诱导发光光敏剂的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 4128-4142.
Hongyu Dai, Honghong Sun, Peifa Wei, Weijiang Guan. Strategies for the Synthesis of High-Efficiency Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(11): 4128-4142.


| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111838 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c01206 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b15577 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c18835 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00251 |
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.27 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1002/advs.v6.5 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1039/D2DT02410A |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115985 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c11868 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1039/d0tb00262c pmid: 32219270 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.59 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06872 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00616G |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1039/D1SC00045D |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01051K |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1039/D2CS01021F |
| [57] |
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.024.202404130 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.215863 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109521 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.3c00500 |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v9.17 |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1039/D1TB02610K |
| [63] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules27227981 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00398 |
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v18.17 |
| [67] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2023.102109 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c02176 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0201 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00381 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1039/C7BM00392G |
| [13] |
doi: S0223-5234(17)30681-5 pmid: 28943196 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00606 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.31 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02416-0 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114028 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.16 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.45 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1039/D3TB00545C |
| [25] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules20057528 pmid: 25919276 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c04256 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1007/s41664-023-00261-3 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03550 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.155471 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.06.003 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1039/D1DT02955J |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121476 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2023.111765 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2018.02.023 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1039/D2SC05454J |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v36.47 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c03700 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/advs.v9.4 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.36 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c02260 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c12319 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1039/D3CC06247C |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110652 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.155782 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c02085 |
| [1] | 祝辉, 吴鹏, 钟晨鸣, 李舒铭, 林钢, 刘雪粉, 罗书平. 供体-受体-供体(D-A-D)型芳香酮设计合成与光催化C(sp3)—H偶联反应性能研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(9): 3441-3449. |
| [2] | 闫鹏泽, 高淑莉, 李天瑞, 苗金玲, 蒋绪川, 聂永. 碳硼烷聚集诱导发光化合物的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(8): 2677-2697. |
| [3] | 李滢, 梁正会, 钟智薇, 韦幼迎, 刘清然, 展军颜, 甘春芳. 雌甾羟肟酸衍生物的合成及体外抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(8): 3017-3027. |
| [4] | 张威光, 张国锋, 李梦, 李雪莲, 包书红, 葛李宵, 施志平, 申强强, 姚李, 朱三娥. I型和II型D-π-A半花菁光敏剂的合成、光物理性质与活性氧生成机制[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(7): 2509-2519. |
| [5] | 白雪, 谢祎黎, 李君缘, 莫梓华, 万清. 高效率阳离子型光敏剂的设计及其在低辐照剂量光动力抗菌中应用[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 4143-4151. |
| [6] | 陈怡萱, 赵征. 聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力抗菌治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 3998-4012. |
| [7] | 陈冰燕, 孙洁, 熊玲红, 何学文. 非典型核酸结构的荧光点亮成像检测[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(11): 4082-4107. |
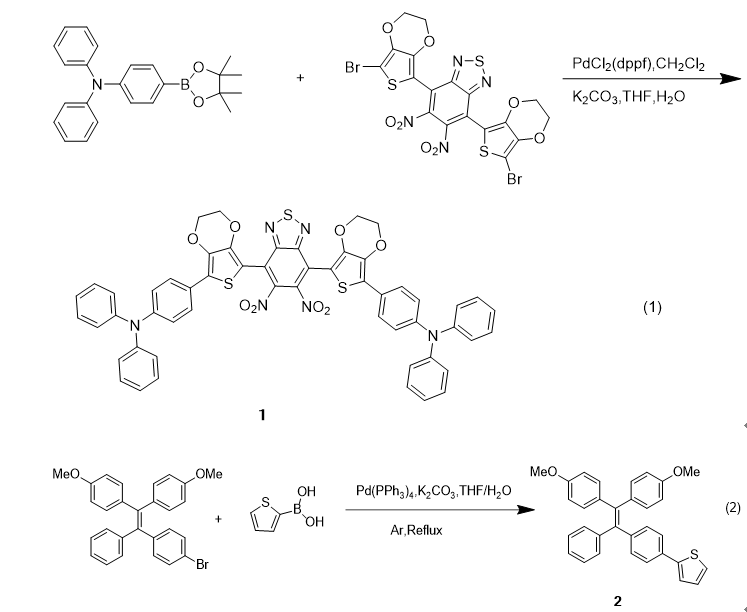
| [8] | 董子璇, 苏军军, 潘宏斐, 任相魁, 陈志坚. 基于三芳胺修饰苯并噻二唑单元偶联的近红外聚集诱导发光分子[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 205-211. |
| [9] | 胡甲松, 李春娟, 徐斌, 田文晶. 固态荧光光开关分子研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2425-2440. |
| [10] | 黄伟庚, 高翼亭, 孙妍, 燕鼎元, 王东, 唐本忠. 聚集诱导发光材料用于肿瘤光学诊疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2413-2424. |
| [11] | 孟子翔, 田秀梅, 张天富. 聚集诱导发光材料在肿瘤光治疗应用中的最新进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2441-2452. |
| [12] | 谢志鑫, 黎少玲, 刘威, 严楷, 蒋涛, 刘一苇, Md. Monarul Islam, 冯星. 窄化芘基发光分子半峰宽的合成策略[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2504-2512. |
| [13] | 何俊初, 伍俊琪, 王江辉, 徐静文, 唐本忠, 赵祖金. 以二苯基硅杂吖啶为电子给体的蓝色聚集诱导延迟荧光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2513-2522. |
| [14] | 沈钇灼, 罗康为, 徐清洋, 张鉴予, 孙景志, 张浩可, 唐本忠. 弱作用基有机发光材料[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2453-2468. |
| [15] | 贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠. 利用光诱导电子转移机制构筑I型聚集诱导发光光敏剂用于光动力治疗[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2530-2537. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||