有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1644-1668.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202406018 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2024-06-12
修回日期:2024-08-08
发布日期:2024-09-18
基金资助:Received:2024-06-12
Revised:2024-08-08
Published:2024-09-18
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

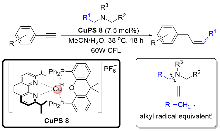
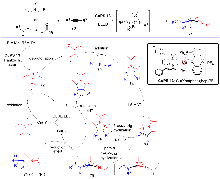
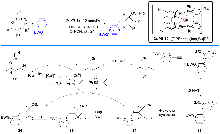
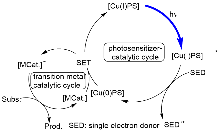
自2008年以来, 可见光驱动的光催化反应成为有机化学和催化化学的研究热点之一. 在众多的光催化反应中, 主流的过渡金属光敏剂主要集中在以钌(II)和铱(III)为代表的贵重金属光催化剂上, 但这类金属光催化剂存在中心金属储量少、价格昂贵及毒性较大等缺点. 近年来, 以丰产金属铜(I)为中心金属的光催化剂被不断开发, 并在光催化反应中获得逐步应用. 特别是基于P/N杂配Cu(I)光催化剂介导的光催化反应受到了化学家的极大关注并迅速发展. 该类金属光催化剂具有中心金属储量丰富、价格低廉和毒性较低的优点, 不仅可以替代钌(II)、铱(III)等贵重金属光催化剂催化常规的光催化反应, 而且还能实现钌(II)、铱(III)等光催化剂所不能完成的光催化反应, 对于高效构建有机分子多样性发挥了重要作用. 根据反应机理的不同, 从单电子转移、铜基光催化剂的双功能催化、双金属协同催化及能量转移四个类型出发, 对P/N杂配Cu(I)光催化剂介导的光催化反应进展进行了综述. 最后对该领域所存在的问题和局限性进行了总结, 并对今后的发展方向作了展望.
周思成, 刘运奎. P/N-杂配铜(I)光催化剂介导的可见光催化反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1644-1668.
Sicheng Zhou, Yunkui Liu. Recent Progresses in P/N-Heteroleptic Cu(I)-Photocatalyst-Mediated Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Reactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1644-1668.
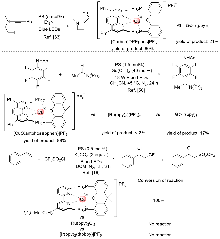












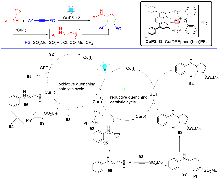








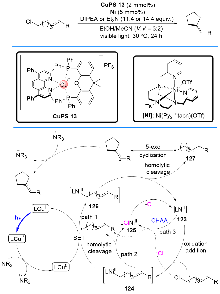



| [1] |
(a)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
(b)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/b913880n pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(李康葵, 龙先扬, 黄岳, 祝诗发, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 658.)
doi: 10.6023/A24030090 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(何明慧, 叶子秋, 林桂庆, 尹晟, 黄心翊, 周旭, 尹颖, 桂波, 汪成, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 784.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040178 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(h)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 359.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120487 pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(i)
pmid: 20532341 |
|
|
(闫英红, 梁平兆, 邹杨, 袁林, 彭孝军, 樊江莉, 张晓兵, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1642.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050243 pmid: 20532341 |
|
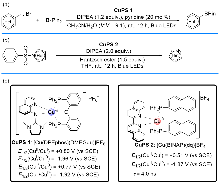
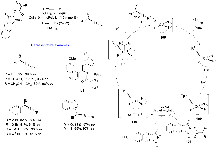
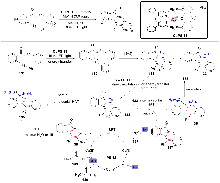
| [2] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
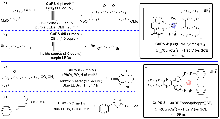
| [3] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [4] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
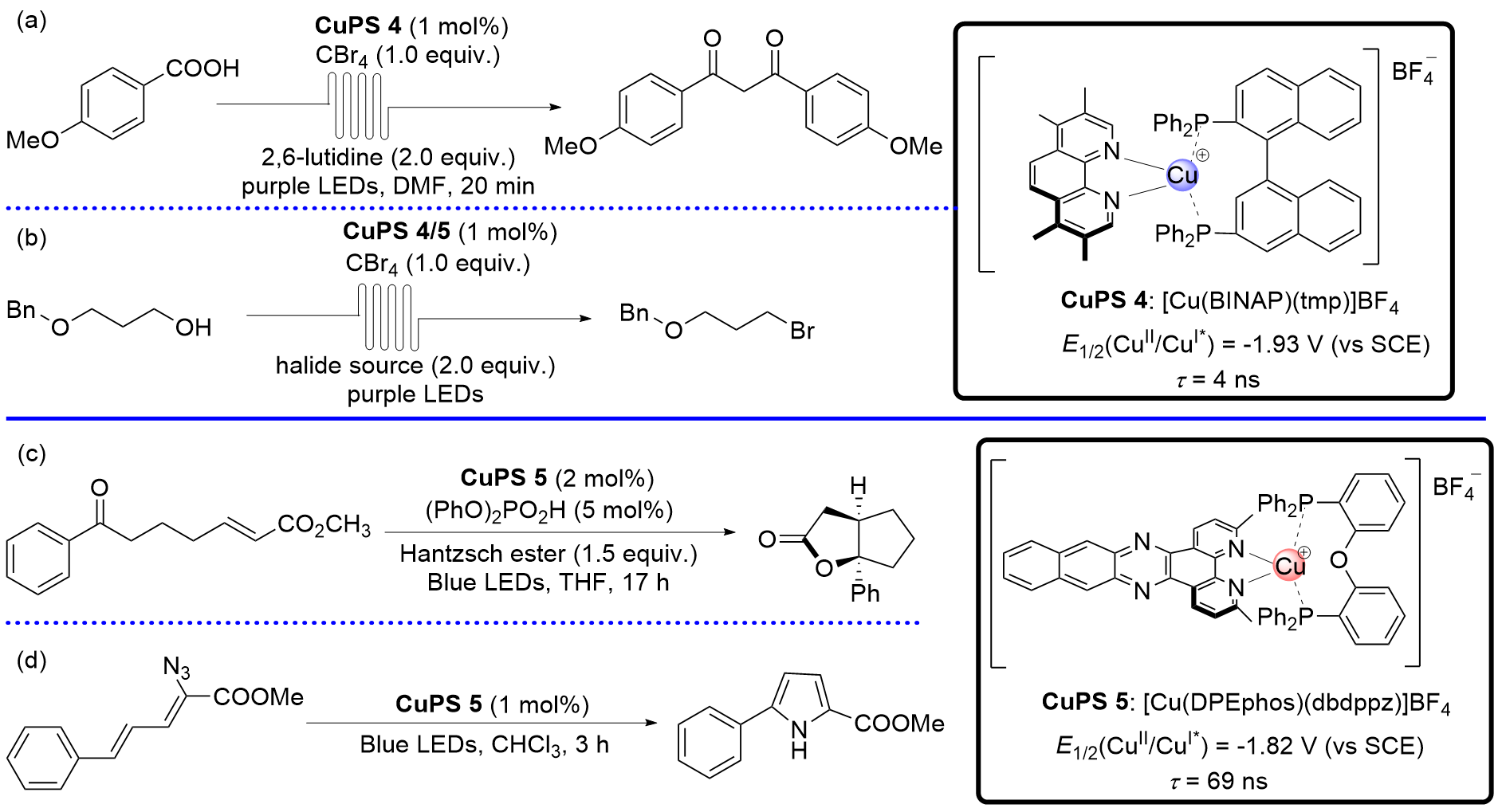
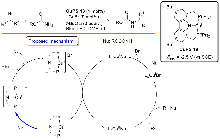
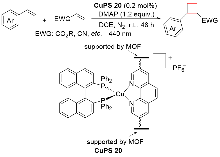
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1021/ol300983b pmid: 22642645 |
| [8] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1002/chem.201405356 pmid: 25413572 |
| [10] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01518 pmid: 28598630 |
|
(b)
pmid: 28598630 |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c00793 pmid: 38587936 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
(a) Hydrogen Transfer Reactions: Reductions and Beyond, Eds.: Guillena, G.; Ramón, D. J. Topics in Current Chemistry Collections, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016.
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
(a)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00054a pmid: 30088504 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 30088504 |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal2490 pmid: 28126814 |
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [1] | 谭燕, 应佳乐, 於兵, 陆展. 可见光促进烯基硅化合物有氧氧化-叠氮化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1684-1690. |
| [2] | 林风, 张艳, 吴明, 刘会艳, 郝文娟, 姜波. 利用可见光引发1,6-烯炔的增环酰化双官能化制备1-茚酮衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1729-1738. |
| [3] | 洪洋, 邓红平. 可见光催化的酸性C(sp3)—H键官能团化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1569-1590. |
| [4] | 马树超, 陈泽乐, 宣俊. 可见光促进偶氮化合物参与的光化学转化[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1669-1683. |
| [5] | 刘俊杰, 赵红平, 胡媛媛, 汪恒昕, 袁伟明. 可见光诱导镍催化烯烃还原Heck反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1691-1697. |
| [6] | 田曈, 陈镤, 黄华文. 可见光诱导芳香醛与苄烯丙二腈环化合成多取代二氢呋喃[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1763-1769. |
| [7] | 贺重隆, 周有康, 段新华, 刘乐. 官能团迁移策略在光驱动不饱和烃双官能团化中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1478-1508. |
| [8] | 李慧, 阿布力米提•阿布都卡德尔, 周磊. 可见光条件下N-苄基苯并三氮唑自由基脱氮气开环合成6-取代菲啶[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1770-1777. |
| [9] | 区洁晴, 屈培珍, 赵亮. 可见光介导下钯催化脂肪族α-溴代三氟甲基的脱溴还原反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1334-1341. |
| [10] | 吴凌苇, 崔浩, 张霄. 水溶性光催化剂介导的水相反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1097-1118. |
| [11] | 赵佳, 甘秋云, 袁耀锋. 自由基磺酰氟化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1206-1222. |
| [12] | 段琛, 沈思语, 赵钰琦, 刘跃, 李薪宇, 张礼智, 李文静. 可见光驱动下蒽醌催化苄基C—H键在水中的氧化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1352-1359. |
| [13] | 蒋洁, 李佳丽, 潘若涵, 陈宇, 刘佳乐, 唐裕才. 可见光诱导2-芳基吲哚与二氟甲基亚磺酸钠二氟甲基化/环化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1239-1248. |
| [14] | 李梦倩, 吕喆, 王少君, 韩宇轩, 崔秀灵. 可见光引发炔烃双官能化反应构筑菲类化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(2): 686-693. |
| [15] | 沈佳斌, 沈超, 章鹏飞. 可见光介导的羰基α位C—H官能团化反应合成萘咪酮类衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(2): 677-685. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
