有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 136-150.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202406019 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
徐晶a,b, 张娟b, 高文超b, 孟凡会c, 杨朋c,d, 常宏宏b,e,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-12
修回日期:2024-08-13
发布日期:2024-09-18
基金资助:
Jing Xua,b, Juan Zhangb, Wenchao Gaob, Fanhui Mengc, Peng Yangc,d, Honghong Changb,e( )
)
Received:2024-06-12
Revised:2024-08-13
Published:2024-09-18
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

在许多反应中通常不可避免地产生水或需要水, 水在反应中起着溶剂、反应物、副产物、催化剂或质子转移剂的作用, 在多相催化体系中可作为溶剂改善底物的亲水性, 进而促进反应的进行, 但在催化合成领域普遍认为水分子是一种破坏性因素, 会破坏金属活性位点, 导致催化剂性能下降甚至失活. 传统金属催化剂大多具有“水不稳定性”, 因此疏水催化剂或疏水微环境的构建及性能探究成为了研究热点. 以疏水催化剂为核心, 详细总结了以Pt、Pd、Fe、Co、Cu、Au、Ti、Rh等金属为活性位点设计并制备疏水催化剂的研究进展, 对疏水催化剂在氧化、还原、偶联及CO2转化等有机反应中的应用进行了归纳和分析, 阐释了针对特定反应体系构建具有适宜“亲疏水效应”催化剂, 并实现目标分子高效合成面临的挑战, 并对该领域未来的发展趋势进行了展望.
徐晶, 张娟, 高文超, 孟凡会, 杨朋, 常宏宏. 疏水型催化剂在有机合成反应中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 136-150.
Jing Xu, Juan Zhang, Wenchao Gao, Fanhui Meng, Peng Yang, Honghong Chang. Application of Hydrophobic Catalysts in Organic Synthesis Reactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(1): 136-150.


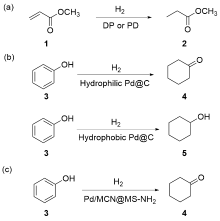

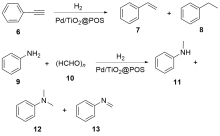





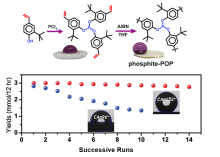



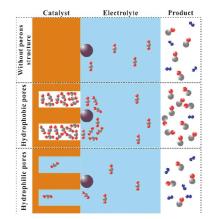



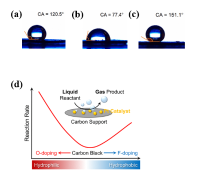



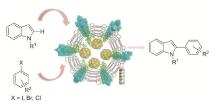
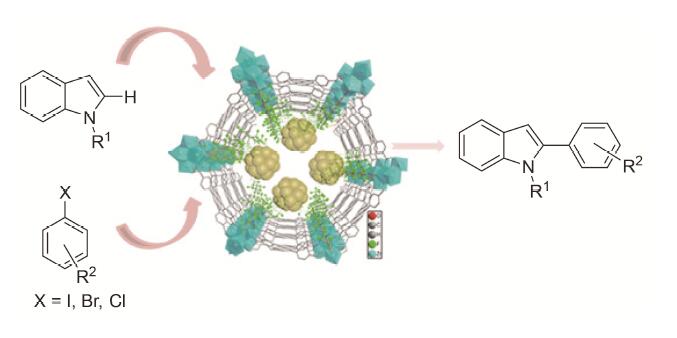
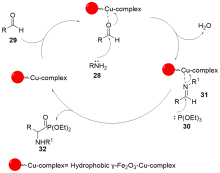

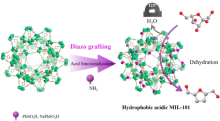

| [1] |
Roberts, M. W. Catal. Lett. 2000, 67, 1.
|
| [2] |
Rafati, A.; Tahvildari, K.; Nozari, M. Energy Sources, Part A 2019, 41, 1062.
|
| [3] |
Yamamoto, K.; Nameki, R.; Sogawa, H.; Takata, T. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151870.
|
| [4] |
Wang, H. L.; Yuan, H. K.; Wang, X. Z.; Zhao, J.; Wei, D. C.; Shi, F. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 2348.
|
| [5] |
Cao, Y. L.; Ding, L.; Qiu, Z. G.; Zhang, H. P. Catal. Commun. 2020, 143, 106048.
|
| [6] |
Papastavrou, A. T.; Kidonakis, M.; Stratakis, M.; Orfanopoulos, M. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 13324.
|
| [7] |
Liu, N.; Qiao, N. N.; Liu, F. S.; Wang, S. H.; Liang, Y. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1218, 128537.
|
| [8] |
Campelo, J. M.; Luna, D.; Luque, R.; Marinas, J. M.; Romero, A. A. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 18.
|
| [9] |
Louloudi, A.; Papayannakos, N. Appl. Catal., A 2000, 204, 167.
|
| [10] |
Musa, S.; Fronton, S.; Vaccaro, L.; Gelman, D. Organometallics 2013, 32, 3069.
|
| [11] |
Landis, C. R. Science 2015, 347, 29.
|
| [12] |
Tang, L.; Guo, X. F.; Yang, Y.; Zha, Z. G.; Wang, Z. Y. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6145.
|
| [13] |
Tang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhang, S.; Zha, Z.; Wang, Z. Y. Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 114.
|
| [14] |
Davies, P. R. Top. Catal. 2016, 59, 671.
|
| [15] |
Wang, Y. H.; Gao, W. G.; Li, K. Z.; Zheng, Y. N.; Xie, Z. H.; Na, W.; Chen, J. G. G.; Wang, H. Chem 2020, 6, 419.
|
| [16] |
Wischert, R.; Laurent, P.; Coperet, C.; Delbecq, F.; Sautet, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14430.
|
| [17] |
Wolf, M.; Fischer, N.; Claeys, M. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 962.
|
| [18] |
Xu, Y. F.; Li, X. Y.; Gao, J. H.; Wang, J.; Ma, G. Y.; Wen, X. D.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. W.; Ding, M. Y. Science 2021, 371, 610.
|
| [19] |
Li, X. S.; Wang, X.; Roy, K.; van Bokhoven, J. A.; Artiglia, L. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5783.
|
| [20] |
Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. W. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19841.
|
| [21] |
Borup, R.; Meyers, J.; Pivovar, B.; Kim, Y. S.; Mukundan, R.; Garland, N.; Myers, D.; Wilson, M.; Garzon, F.; Wood, D.; Zelenay, P.; More, K.; Stroh, K.; Zawodzinski, T.; Boncella, J.; Mcgrath, J. E.; Inaba, M.; Miyatake, K.; Hori, M.; Ota, K.; Ogumi, Z.; Miyata, S.; Nishikata, A.; Siroma, Z.; Uchimoto, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Kimijima, K.; Iwashita, N. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3904.
|
| [22] |
Sun, Q.; Chen, M.; Aguila, B.; Nguyen, N.; Ma, S. Q. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 201, 317.
|
| [23] |
Augier, F.; Koudil, A.; Royon, L. A.; Muszynski, L.; Yanouri, Q. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 255.
|
| [24] |
Lin, J. D.; Bi, Q. Y.; Tao, L.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Y. M.; He, H. Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y. D. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1720.
|
| [25] |
Liu, D. H.; He, H. L.; Wang, J. J.; Zhou, S. Y.; Zeng, T. W; Gao, X. Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yi, X. F.; Zheng, A. M.; Zhang, Y. B.; Li, Z. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9974.
|
| [26] |
Camblor, M. A.; Corma, A.; Esteve, P.; Martinez, A.; Valencia, S. Chem. Commun. 1997, 8, 795.
|
| [27] |
Sun, Q.; Jin, Y. Y.; Zhu, L. F.; Wang, L.; Meng, X. J.; Xiao, F. S. Nano Today 2013, 8, 342.
|
| [28] |
Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, F. J.; Meng, X. J.; Mao, J. X.; Xiao, F. S. Catal. Today 2015, 242, 249.
|
| [29] |
Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Meng, X. J.; Zhang, W. P.; Zhang, J.; Pan, S. X.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, F. S. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2012.
|
| [30] |
Wang, C. T.; Liu, L. J.; Li, H. J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F. S. Matter 2023, 6, 2697.
|
| [31] |
Xing, Z.; Shi, K. G.; Parsons, Z. S.; Feng, X. X. ACS Catal. 2023. 13, 2780.
|
| [32] |
Inumaru, K.; Ishihara, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Okuhara, T.; Yamanaka, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7625.
|
| [33] |
Panchal, B.; Zhao, Q. J.; Liu, B. J.; Sun, Y. Z.; Zhao, C. L.; Bian, K.; Chia-Hung, H.; Wang, J. X. Mol. Catal. 2023, 548, 113458.
|
| [34] |
Zhang, Y.; Ni, C.; Shi, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, W. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 1189.
|
| [35] |
Wang, S. S.; Wang, J. L.; Li, X. X.; Yang, M. D.; Wu, Y. L. Catalysts 2022, 12, 995.
|
| [36] |
Wan, K. T.; Davis, M. E. Nature 1994, 370, 449.
|
| [37] |
Omota, F.; Dimian, A. C.; Bliek, A. Appl. Catal., A 2005, 294, 121.
|
| [38] |
Makowski, P.; Cakan, R. D.; Antonietti, M.; Goettmann, F.; Titirici, M. M. Chem. Commun. 2008, 8, 999.
|
| [39] |
Zhang, F. W.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. M.; Yang, H. Q. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102811.
|
| [40] |
Huang, G.; Yang, Q. H.; Xu, Q.; Yu, S. H.; Jiang, H. L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 128, 7505.
|
| [41] |
Wang, H. L.; Gao, Z. Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Wei, R. P.; Zhang, J. P.; Shi, F. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8305.
|
| [42] |
Liu, W. G.; Liu, J. C.; Liu, X. L.; Zheng, H. N.; Liu, J. ACS Catal. 2022, 13, 530.
|
| [43] |
Lv, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y. N.; He, Y. F.; Li, D. Q. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 53, 232.
|
| [44] |
Chalmers, J. A.; Moon, H.; Ausman, S. F.; Chuang, C. H.; Scott, S. L. Top. Catal. 2023, 66, 1143.
|
| [45] |
Chen, X. Y.; Qian, P. P.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z. L.; Fang, C. Z.; Xu, X. J.; Chen, W. Z.; Wu, P.; Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, J. S.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, W. N.; Huo, F. W. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3936.
|
| [46] |
Cao, Y. P.; Zhang, A. Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 31, 577 (in Chinese).
|
|
(曹云苹, 张爱清, 有机化学, 2011, 31, 577.)
|
|
| [47] |
Yuan, K.; Song, T. Q.; Wang, D. W.; Zhang, X. T.; Gao, X.; Zou, Y.; Dong, H. L.; Tang, Z. Y.; Hu, W. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5708.
|
| [48] |
Heiman, B. D.; Dotan, A.; Dodiuk, H.; Kenig, S. Polymers 2021, 13, 539.
|
| [49] |
Van, C. T.; Underhill, D.; Veiga, R. M.; Sievers, C.; Medlin, J. W. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3619.
|
| [50] |
Porosoff, M. D.; Yan, B. H.; Chen, J. G. G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 62.
|
| [51] |
Ye, J. Y.; Liu, C. J.; Mei, D. H.; Ge, Q. F. J. Catal. 2014, 317, 44.
|
| [52] |
Li, A.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, G. Y.; Schmidt, B. V. K. J.; Zhu, W. J.; Yuan, X. T.; Huo, H. L.; Gong, J. L.; Antonietti, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14549.
|
| [53] |
Shi, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Gao, J.; Ma, H.; Ma, J. P.; Xu, J. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9591.
|
| [54] |
Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Verma, G.; Liu, X. L.; Dai, Z. F.; Deng, F.; Meng, X. J.; Xiao, F. X.; Ma, S. Q. Chem 2016, 1, 628.
|
| [55] |
Han, B.; Zhao, L.; Song, Y. K.; Zhao, Z. R.; Yang, D. F.; Liu, R.; Liu, G. H. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 2920.
|
| [56] |
Sun, D. R.; Kim, D. P. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20589.
|
| [57] |
Cui, Y. J.; Cheng, Y. H.; Yang, C. L.; Su, Y. S.; Yao, D. F.; Liufu, B. P.; Li, J. L.; Fang, Y. W.; Liu, S. Y.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Wang, X. M.; Song, Y. B.; Li, Z. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 11229.
|
| [58] |
Kamegawa, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamashita, H. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3697.
|
| [59] |
Deng, Z. Y.; Wang, W.; Mao, L. H.; Wang, C. F.; Chen, S. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4178.
|
| [60] |
Ma, G. F.; Syzgantseva, O. A.; Huang, Y.; Stoian, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. L.; Luo, W.; Jiang, M. Y.; Li, S. M.; Chen, C. J.; Syzgantseva, M. A.; Yan, S.; Chen, N. Y.; Peng, L.; Li, J.; Han, B. X. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 501.
|
| [61] |
Wu, J. G.; Saito, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Watanabe, T. Appl. Catal., A 2001, 218, 235.
|
| [62] |
Tan, M. H.; Tian, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K. Z.; Xiao, L. W.; Liang, J. M.; Ma, Q. X.; Yang, G. H.; Tsubaki, N.; Tan, Y. S. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4633.
|
| [63] |
Fang, W.; Wang, C. T.; Liu, Z. Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H. J.; Xu, S. D.; Zheng, A. M.; Qin, X. D.; Liu, L. J.; Xiao, F. S. Science 2022, 377, 406.
|
| [64] |
Zhang, J. X.; Mao, D. L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D. F. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144461.
|
| [65] |
Corma, A.; Domine, M.; Gaona, J. A.; Jorda, J. L.; Navarro, M. T.; Rey, F; Nemeth, L. T.; Rey, F.; Perez, P. J.; Tsuji, J.; McCullochd, B.; Nemeth, L. T. Chem. Commun. 1998, 20, 2211.
|
| [66] |
Sotelo, J. L.; Van Grieken, R.; Martos, C. Chem. Commun. 1999, 6, 549.
|
| [67] |
Sakamoto, T.; Pac, C. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 10009.
|
| [68] |
Iwai, Y.; Gligorich, K. M.; Sigman, M. S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3219.
|
| [69] |
Shi, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Gao, J.; Xu, J. Chem.-Asian J. 2017, 12, 2404.
|
| [70] |
Ebbach, C.; Senkovska, I.; Unmuussig, T.; Fischer, A.; Kaskel, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20915.
|
| [71] |
Tian, J.; Wang, C. H.; Wu, J. W.; Sun, D. H.; Li, Q. B. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138351.
|
| [72] |
Law, K. Y. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 686.
|
| [73] |
Xing, Z.; Hu, X.; Feng, X. F. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1694.
|
| [74] |
Shi, K. G.; Parsons, Z. S.; Xiao, F. S. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 2919.
|
| [75] |
Manabe, K.; Mori, Y.; Wakabayashi, T.; Nagayama, S.; Kobayashi, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7202.
|
| [76] |
Gounder, R.; Davis, M. E. J. Catal. 2013, 308, 176.
|
| [77] |
Zhang, Q.; Shu, X. Z.; Lucas, J. M.; Toste, F. D.; Somorjai, G. A.; Alivisatos, A. P. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 379.
|
| [78] |
Zapata, P. A.; Huang, Y.; Gonzalez, B. M. A.; Resasco, D. E. J. Catal. 2013, 308, 82.
|
| [79] |
Zapata, P. A.; Faria, J.; Ruiz, M. P.; Jentoft, R. E.; Resasco, D. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8570.
|
| [80] |
Niu, L. J.; Liu, Z. W.; Liu, G. H.; Li, M. X.; Zong, X. P.; Wang, D. D.; An, L.; Qu, D.; Sun, X. M.; Wang, X. Y.; Sun, Z. C. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3886.
|
| [81] |
Mobaraki, A.; Movassagh, B.; Karimi, B. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 472, 123.
|
| [82] |
Huang, Y. B.; Shen, M.; Wang, X. S.; Huang, P.; Chen, R. P.; Lin, Z. J.; Cao, R. J. Catal. 2016, 333, 1.
|
| [83] |
Sobhani, S.; Khakzad, F. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3877.
|
| [84] |
Petkova, D.; Borlinghaus, N.; Sharma, S.; Kaschel, J.; Lindner, T.; Klee, J.; Jolit, A.; Haller, V.; Heitz, S.; Britze, K.; Dietrich, J.; Braje, W. M.; Handa, S. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12612.
|
| [85] |
Zhong, Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, P. X.; Li, H.; Deng, Q.; Zeng, Z. L.; Wang, J.; Deng, S. G. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 59, 22068.
|
| [86] |
Yuan, Q.; Song, X. G.; Feng, S. Q.; Jiang, M.; Yan, L.; Li, J. W.; Ding, Y. J. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 472.
|
| [87] |
Oozeerally, R.; Burnett, D. L.; Chamberlain, T. W.; Kashtiban, R. J.; Huband, S.; Walton, R. I.; Degirmenci, V. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 2517.
|
| [88] |
Tian, Y. M.; Silva, W.; Gschwind, R. M.; Konig, B. Science 2024, 383, 750.
|
| [89] |
Levin, E.; Ivry, E.; Diesendruck, C. E.; Lemcoff, N. G. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4607.
|
| [90] |
Yuan, W. T.; Zhu, B. E.; Li, X. Y.; Hansen, T. W.; Ou, Y.; Fang, K.; Yang, H. S.; Zhang, Z.; Wagner, J. B.; Wang, Y, G.; Wang, Y. Science 2020, 367, 428.
|
| [91] |
Merte, L. R.; Peng, G. W.; Bechstein, R.; Rieboldt, F.; Farberow, C. A.; Grabow, L. C.; Kudernatsch, W.; Wendt, S.; Lægsgaard, E.; Mavrikakis, M.; Besenbacher, F. Science 2012, 336, 889.
|
| [92] |
Mou, T. Y.; Pillai, H. S.; Wang, S. W.; Wan, M. Y.; Han, X.; Schweitzer, N. M.; Che, F. L.; Xin, H. L. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 122.
|
| [93] |
Chandler, D. Nature 2002, 417, 491.
|
| [94] |
Chen, X. P.; Meng, C. X.; Li, M. N.; Chu, S. M.; Zhu, X. X.; Xu, K.; Liu, L. T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, F. H.; Li, F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 28007 (in Chinese).
|
|
(陈乡萍, 孟晨湘, 李梦娜, 楚尚敏, 朱欣欣, 许凯, 刘澜涛, 王涛, 张凤华, 李飞, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 28007.)
|
|
| [95] |
Cortes-Clerget, M.; Yu, J. L.; Kincaid, J. R. A.; Walde, P.; Gallou, F.; Lipshutz, B. H. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4237.
|
| [96] |
Narayan, S.; Finn, M. G.; Fokin, V. V.; Kolb, H. C.; Sharpless, K. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3275.
|
| [97] |
Tang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zou, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5, 335.
|
| [98] |
Tang, L.; Wang, P.; Fan, Y.; Yang, X.; Wan, C.; Zha, Z. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3565.
|
| [99] |
Yuan, H. Y.; Yang, H. G.; Hu, P.; Wang, H. F. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 6835.
|
| [100] |
Wang, D. S.; Han, Y. Z.; Tan, Y. S.; Tsubaki, N. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 446.
|
| [101] |
Mullen, G. M.; Mullins, C. B. Science 2014, 345, 1564.
|
| [102] |
Nie, X. W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H. Z.; Luo, W. J.; Janik, M. J.; Chen, Y. G.; Guo, X. W.; Song, C. S. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4873.
|
| [103] |
Tsou, J.; Magnoux, P.; Guisnet, M.; Orfao, J. J. M.; Figueiredo, J. L. Appl. Catal., B 2005, 57, 117.
|
| [104] |
Jung, Y. S.; Marcus, R. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5492.
|
| [105] |
Yu, H. M.; Ziegler, C.; Oszcipok, M.; Zobel, M.; Hebling, C. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1199.
|
| [106] |
Liu, D. H.; He, H. L.; Wang, J. J.; Zhou, S. Y.; Zeng, T.; Gao, X. Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yi, X. F.; Zheng, A. M.; Zhang, Y. B.; Li, Z. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9974.
|
| [1] | 田勋, 邓国刚, 羊晓东. 钴催化C(sp2)—H活化构建苯并含氮杂环骨架的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(2): 655-667. |
| [2] | 周岑, 赵新, 张霄. 三聚苯环化反应的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 42-55. |
| [3] | 李永胜, 唐小雯, 李旭, 杨鹏. (S)-(6-氧代哌啶-3-基)氨基甲酸叔丁酯的工艺开发与放大[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 220-226. |
| [4] | 曹素芳, 刘云云, 万结平. α-三氟甲基酮的合成及其脱氟转化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(1): 86-103. |
| [5] | 高晋彬, 陆颖琪, 张辉, 高利柱, 熊兴泉. 生物质基催化剂在CO2化学转化中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(9): 2732-2741. |
| [6] | 宫清宝, 吕翔, 于长江, 李婉婉, 赵全胜, 焦莉娟, 郝二红. 聚集诱导发光活性氟硼吡啶肼醛腙染料的合成、晶体结构及光学性质[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(8): 2545-2553. |
| [7] | 张雅芳, 黄轩, 林琪, 钟海琼, 翁志强, 吴伟. 噻唑类化合物的合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(5): 1458-1479. |
| [8] | 孙一平, 陈德茂, 何玲, 王祖利. Na2S2O8介导的咪唑并[1,2-α]吡啶与杂芳胺在无金属条件下的C—H胺化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(5): 1667-1674. |
| [9] | 程晓红, 刘发龙, 孙进博, 张锐. 一种用于次氯酸根实时高灵敏度检测的络合物基荧光探针[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1284-1292. |
| [10] | 麦尔哈巴•居来提, 布鲁努尔•玉散, 阿不都热合曼•乌斯曼. 无催化剂和无添加剂条件下直接合成N-磺酰基胍类化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(4): 1276-1283. |
| [11] | 佘春艳, 王安静, 刘珊, 舒文明, 余维初. 芳乙酰叠氮的制备及其在有机合成中的应用进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 481-507. |
| [12] | 李路瑶, 贺忠文, 张振国, 贾振华, 罗德平. 三芳基碳正离子在有机合成中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(2): 421-437. |
| [13] | 赵永哲, 孔翔飞, 张俊良, 杨俊锋. 含膦负载催化剂的合成及应用研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(12): 3587-3608. |
| [14] | 潘旭玲, 黄有. 有机膦催化合成中环化合物的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(12): 3609-3620. |
| [15] | 龙姣, 刘白雪, 张双双, 朱园园, 古双喜. 镍催化1,3-二烯的不对称氢官能团化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(11): 3309-3320. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||