有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1523-1547.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202408018 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2024-08-14
修回日期:2024-11-04
发布日期:2024-11-27
基金资助:
Fangfang Tana,*( ), Mengxin Shib, Wenmin Zhangb, Yang Lib,*(
), Mengxin Shib, Wenmin Zhangb, Yang Lib,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-14
Revised:2024-11-04
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

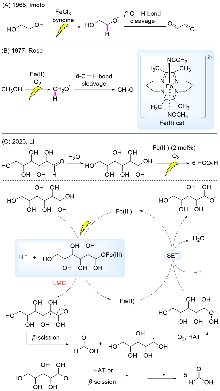
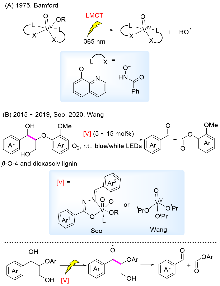
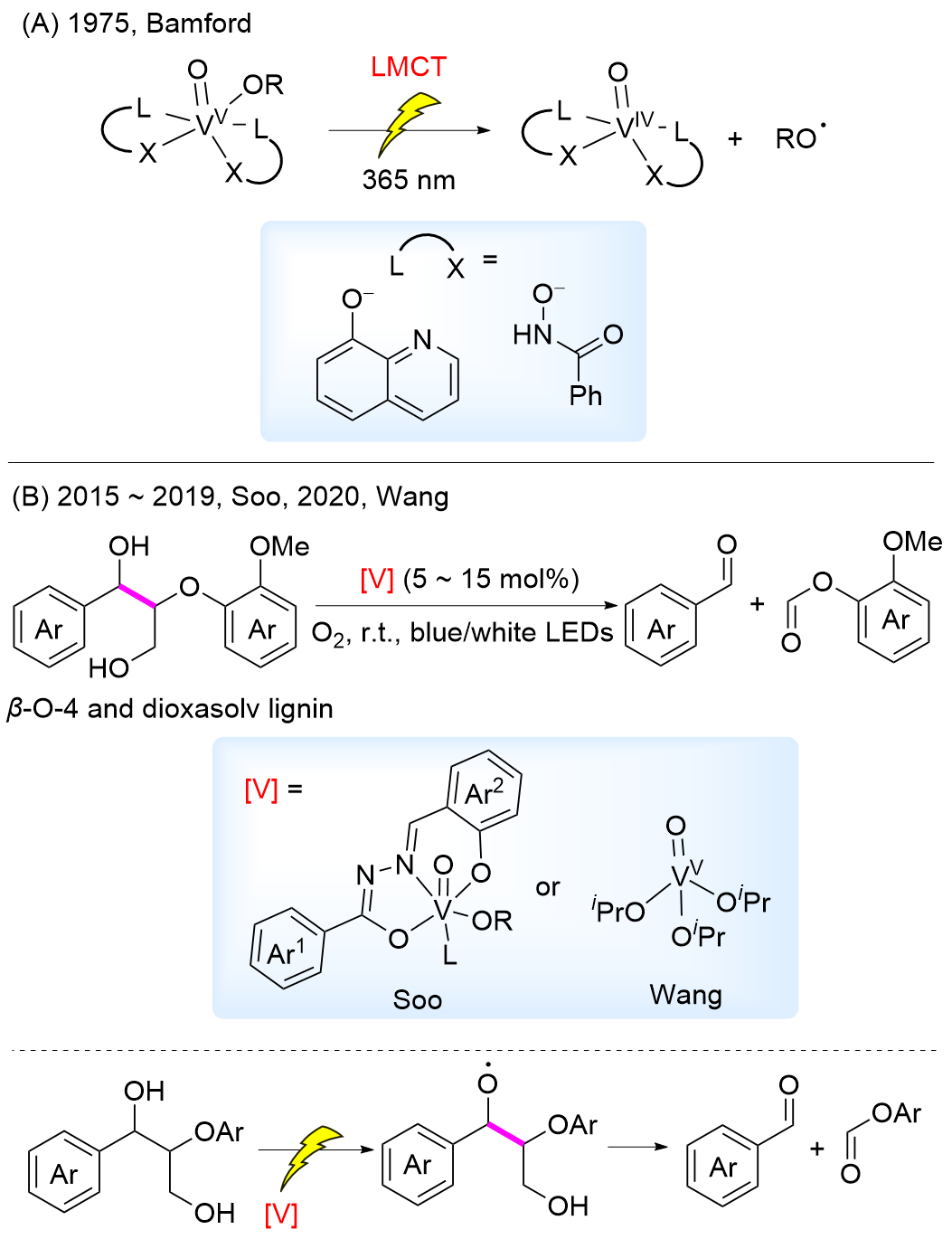
非粮生物质作为地球上最丰富的可再生资源之一, 具有替代化石资源生产高附加值化学品及绿色能源的潜能. 光催化是在温和条件下通过光照诱导产生活性物种引发的相关转化, 因此备受关注. 系统综述了光催化中主要的均相与非均相催化体系, 通过光照产生自由基引发生物质中最主要成分纤维素、半纤维素和木质素相关的C—C键和C—O键断裂进行转化的研究进展, 旨在为设计高效、高选择性的光催化生物质转化体系提供参考, 促进生物质在温和条件下增值转化. 文末对光催化生物质转化进行了总结与展望.
谭芳芳, 史孟欣, 张文敏, 李洋. 光催化生物质相关转化[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1523-1547.
Fangfang Tan, Mengxin Shi, Wenmin Zhang, Yang Li. Photoinduced Catalysis for Biomass-Related Conversions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1523-1547.

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/cr900354u pmid: 20218547 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00354 pmid: 26523853 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
(余家国, 李鑫, 曹少文, 向全军, 新型太阳燃料光催化材料, 武汉理工大学出版社, 武汉, 2019, pp. 1-49.)
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
(李灿, 太阳能转换科学与技术, 科学出版社, 北京, 2020, pp. 1-24.)
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.1021/cr200177j pmid: 22702235 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201300370 pmid: 23913576 |
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07770 pmid: 26291730 |
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
doi: 10.1021/cr5001892 pmid: 25234429 |
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14915-8 pmid: 32107386 |
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c00830 pmid: 33904731 |
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
doi: 10.1021/ja4113462 pmid: 24367945 |
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b04172 |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1021/ja4113462 pmid: 24367945 |
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08933 pmid: 30277767 |
| [138] |
|
| [1] | 谭永波, 舒洪波, 黄华文. 光诱导N-芳基丙烯酰胺参与的吲哚酮合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(6): 2086-2108. |
| [2] | 姚嫣, 付年凯. 光电化学金属催化研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(6): 1819-1837. |
| [3] | 高根伟, 李震, 李炎, 陆熹. 光/镍协同催化C(sp2)—C(sp3)键构建研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(6): 1905-1919. |
| [4] | 李慧, 阿布力米提•阿布都卡德尔, 周磊. 可见光条件下N-苄基苯并三氮唑自由基脱氮气开环合成6-取代菲啶[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1770-1777. |
| [5] | 周思成, 刘运奎. P/N-杂配铜(I)光催化剂介导的可见光催化反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1644-1668. |
| [6] | 陈雨佳, 刘志林, 陈凯, 向皞月, 阳华. 无金属、光催化氧化苄基C—H键以获得羰基官能团[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1755-1762. |
| [7] | 李顺曦, 游力栩, 李玉龙, 舒伟. 光介导氨及其等价体参与的碳氮成键反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1460-1477. |
| [8] | 黄嘉浩, 黄雅豪, 胡鹏. 氢原子转移介导的光催化C(sp3)—H键氧化反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1509-1522. |
| [9] | 蒋晨阳, 尹艳丽, 江智勇. 光酶催化不对称自由基加成反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1614-1633. |
| [10] | 吴昊岩, 赫明月, 马军安, 张发光. 三芳胺在光催化反应中的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1634-1643. |
| [11] | 吴利华, 杨建静, 闫克鲁, 许丽荣, 文江伟. 单原子光催化有机合成研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1591-1613. |
| [12] | 谭燕, 应佳乐, 於兵, 陆展. 可见光促进烯基硅化合物有氧氧化-叠氮化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1684-1690. |
| [13] | 陈旭欣, 张丹丹, 龙鸿新, 刘国凯. 无需光敏剂光诱导炔丙酸酯自由基二氟甲基化合成3-二氟甲基香豆素[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1739-1746. |
| [14] | 林风, 张艳, 吴明, 刘会艳, 郝文娟, 姜波. 利用可见光引发1,6-烯炔的增环酰化双官能化制备1-茚酮衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1729-1738. |
| [15] | 洪洋, 邓红平. 可见光催化的酸性C(sp3)—H键官能团化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1569-1590. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||