有机化学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1569-1590.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202407049 上一篇 下一篇
综述与进展
收稿日期:2024-07-31
修回日期:2024-09-11
发布日期:2024-11-08
基金资助:
Yang Honga,b, Hongping Denga,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-31
Revised:2024-09-11
Published:2024-11-08
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

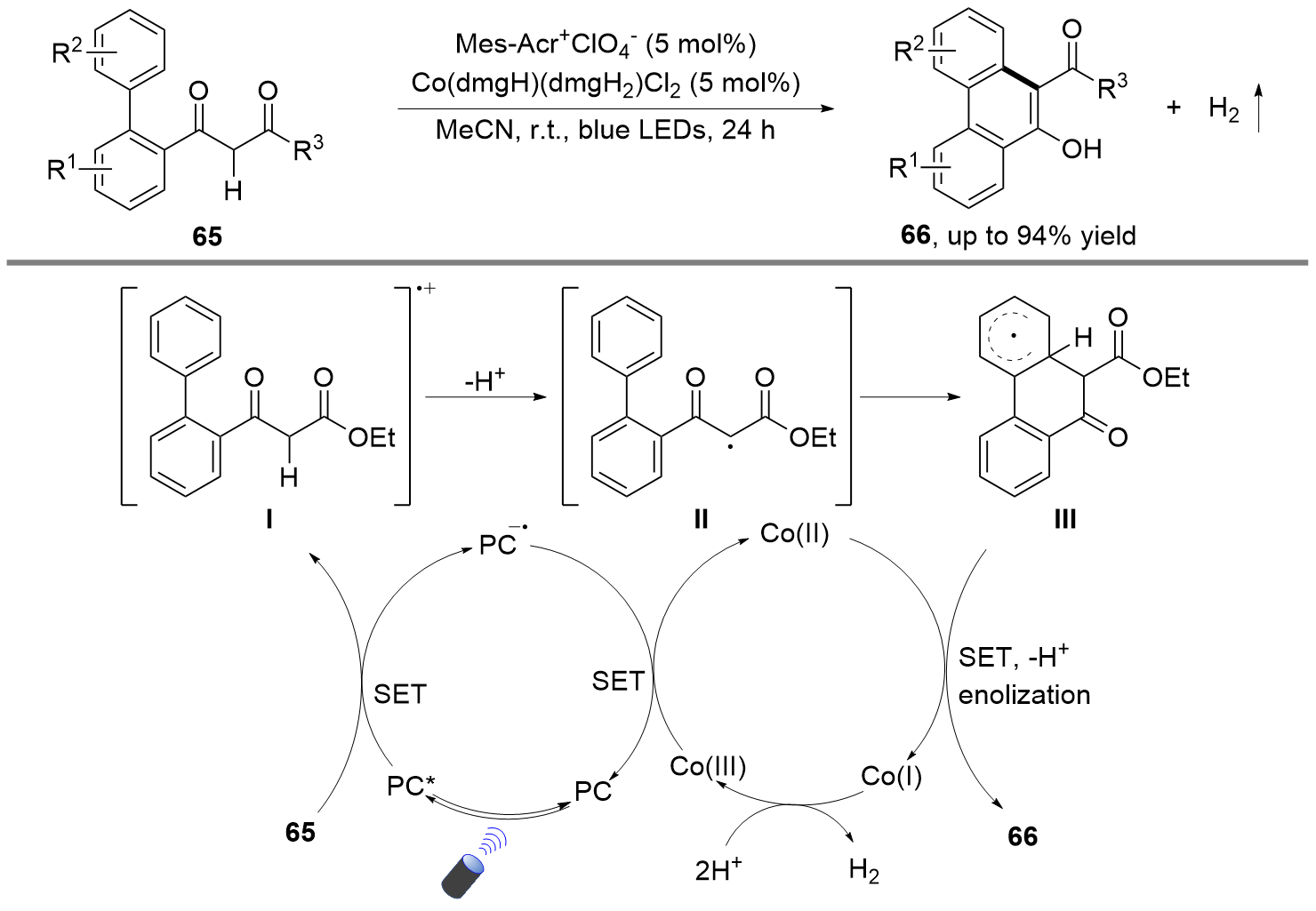
由于含酸性C(sp3)—H键的化合物来源广泛、廉价易得等, 且反应产物易于转化, 其作为亲核试剂被广泛应用于有机合成中. 最近十年, 由于可见光催化的C(sp3)—H键官能团化反应具有反应条件温和、原子及步骤经济性高等优点,其研究取得了快速的发展. 在可见光催化条件下, 含酸性C(sp3)—H键的化合物较易转化为亲电性烷基自由基中间体, 实现一系列以前难以实现的转化, 为该类化合物的高效利用提供了一种新的思路. 此综述着重介绍在没有等物质的量的氧化剂存在的条件下, 可见光催化的酸性C(sp3)—H键官能团化反应的最近研究进展. 根据酸性C(sp3)—H键的活化模式, 将反应的催化类型分为光致氧化还原催化、光致氧化还原协同有机胺催化和光致氧化还原协同氢原子转移催化. 同时, 对一些代表性的反应机理和产物应用也做了介绍.
洪洋, 邓红平. 可见光催化的酸性C(sp3)—H键官能团化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1569-1590.
Yang Hong, Hongping Deng. Research Progress on Photocatalyzed Protic C(sp3)—HFunctionalization[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2025, 45(5): 1569-1590.
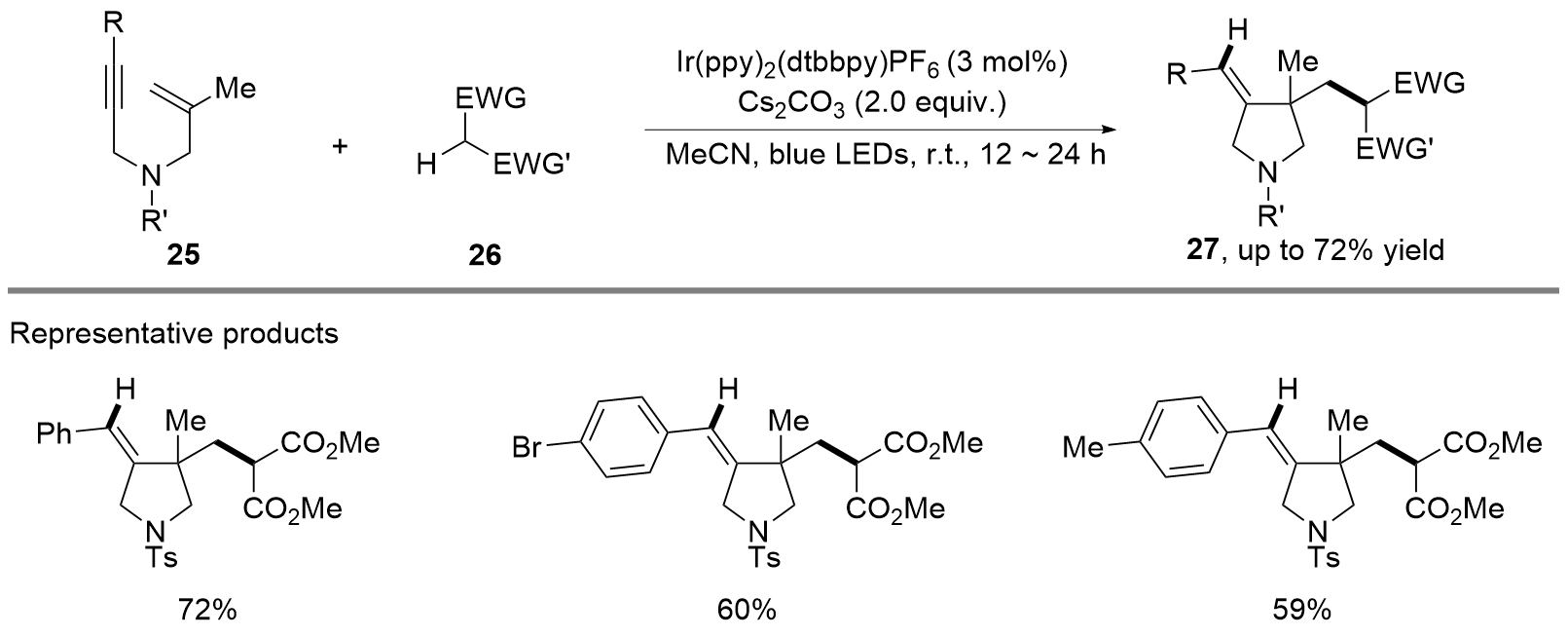

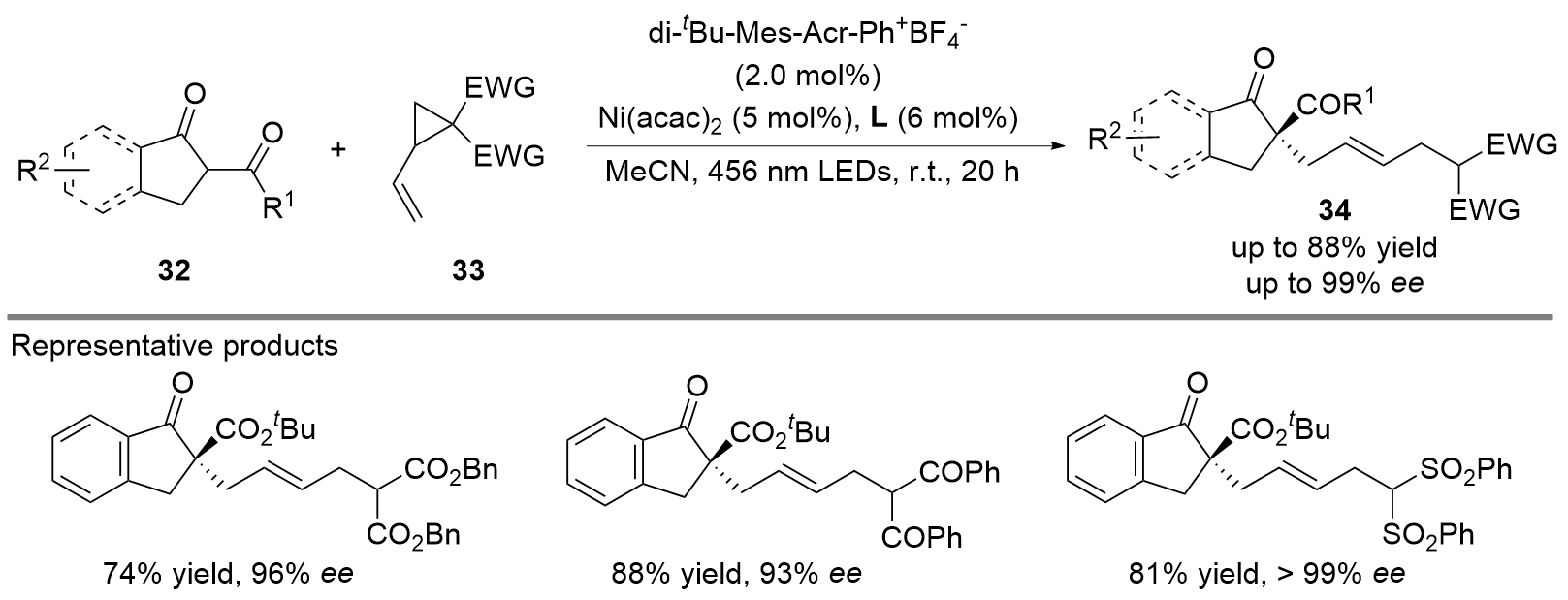

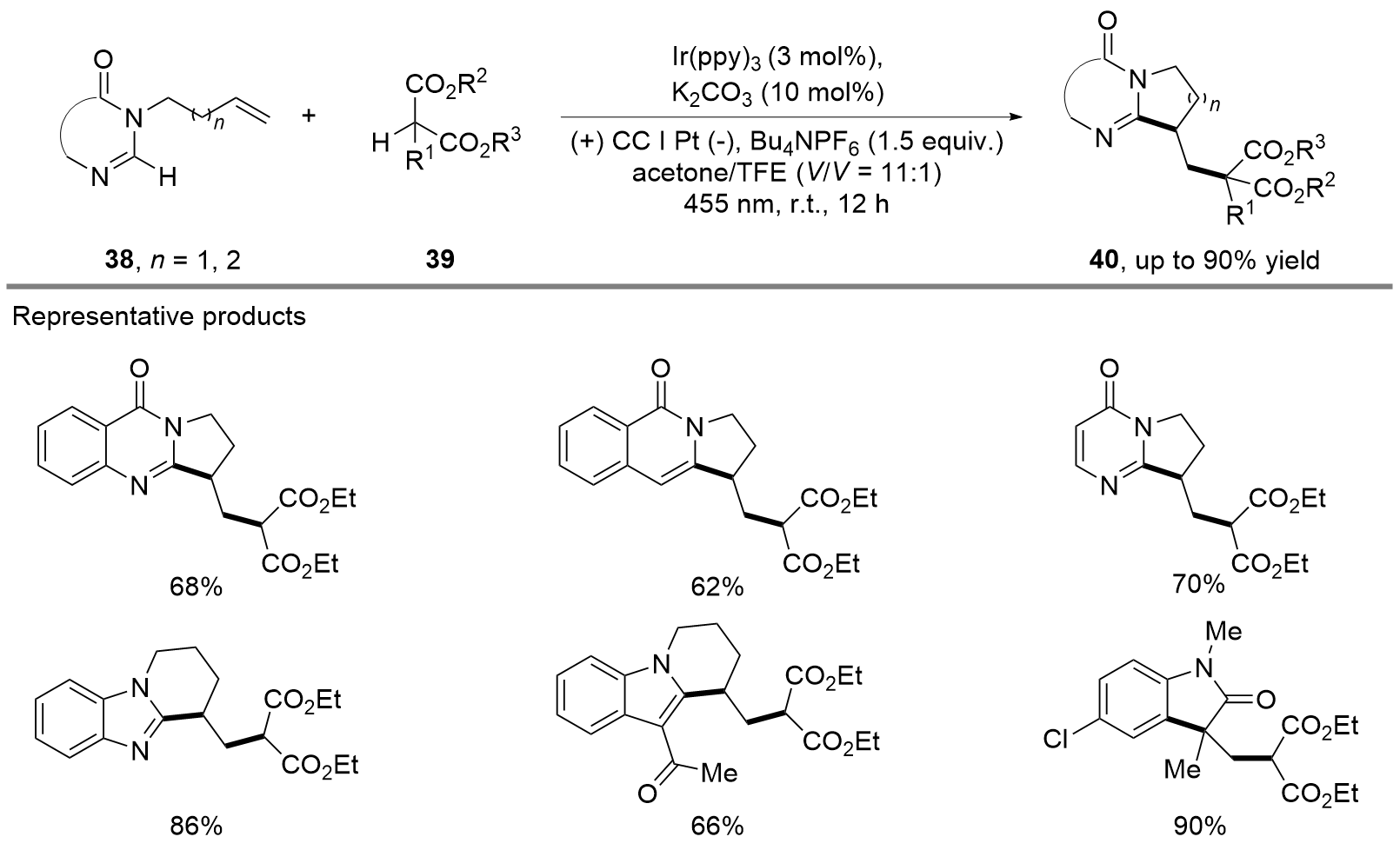

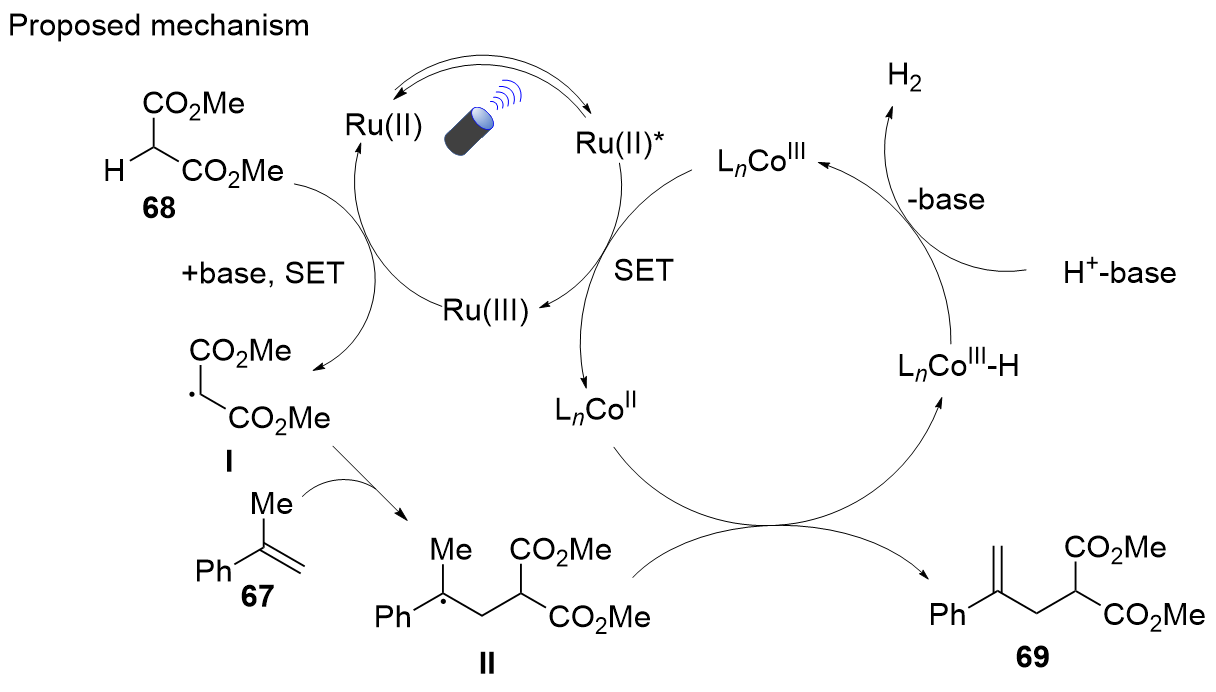
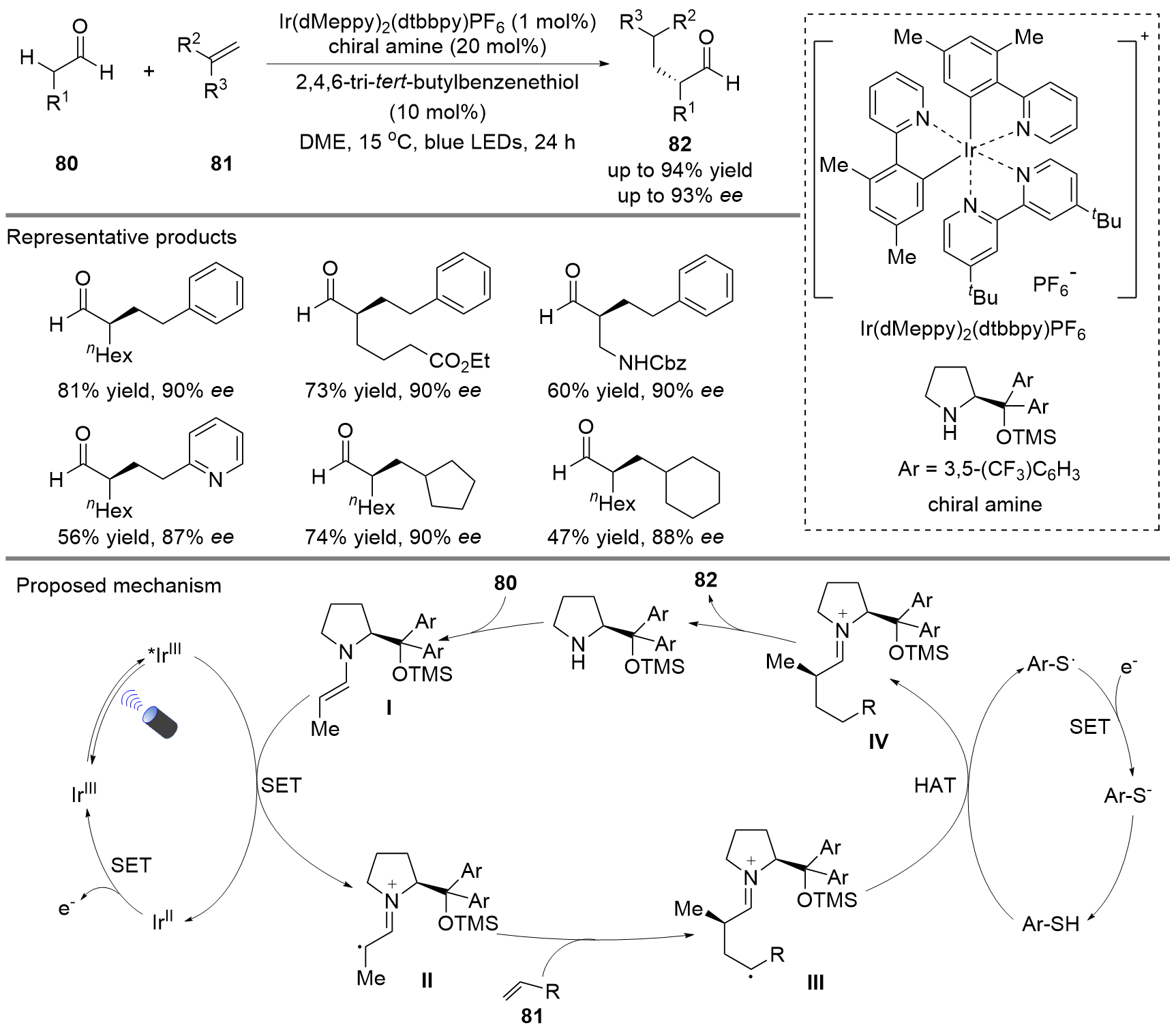





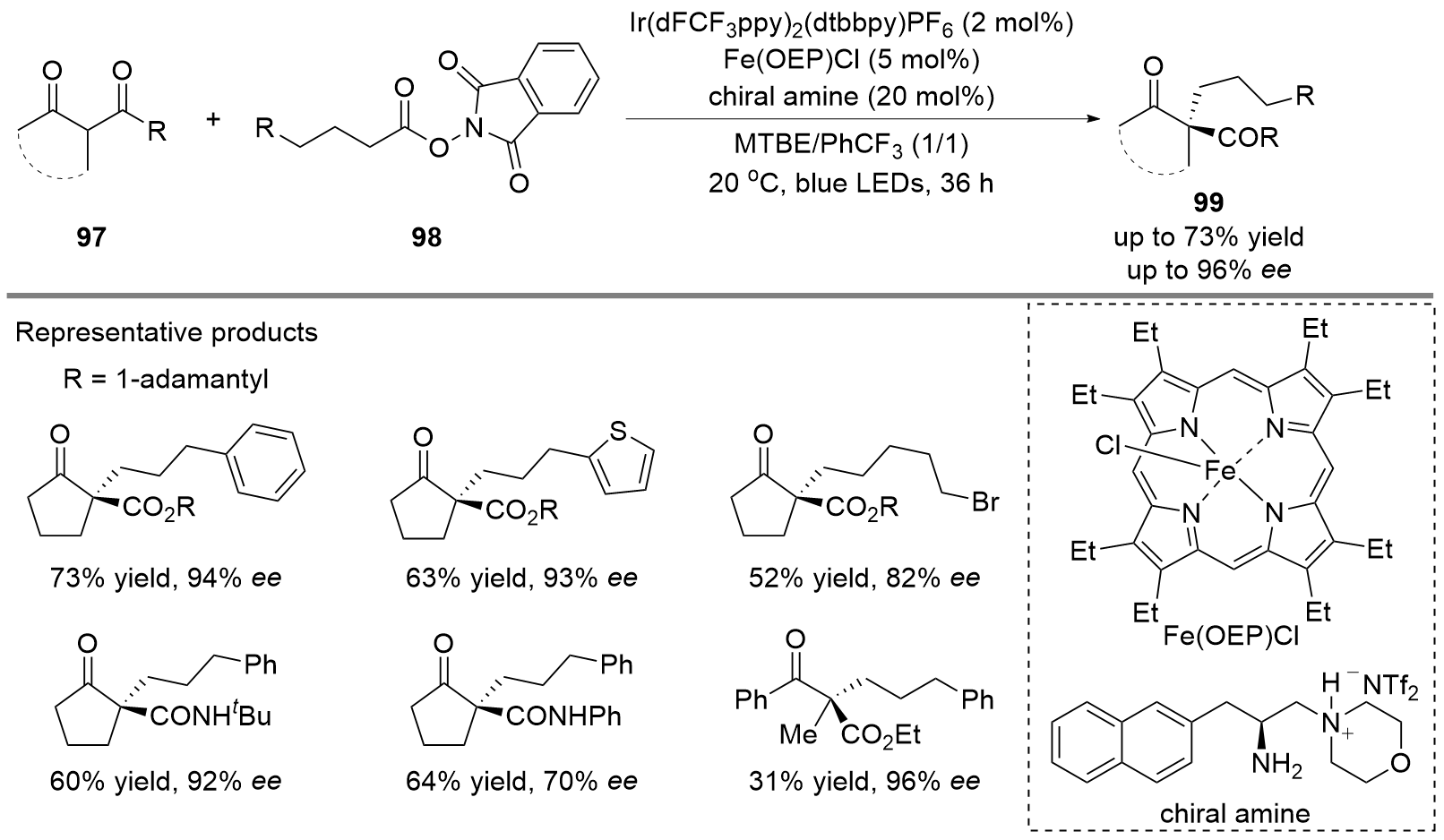
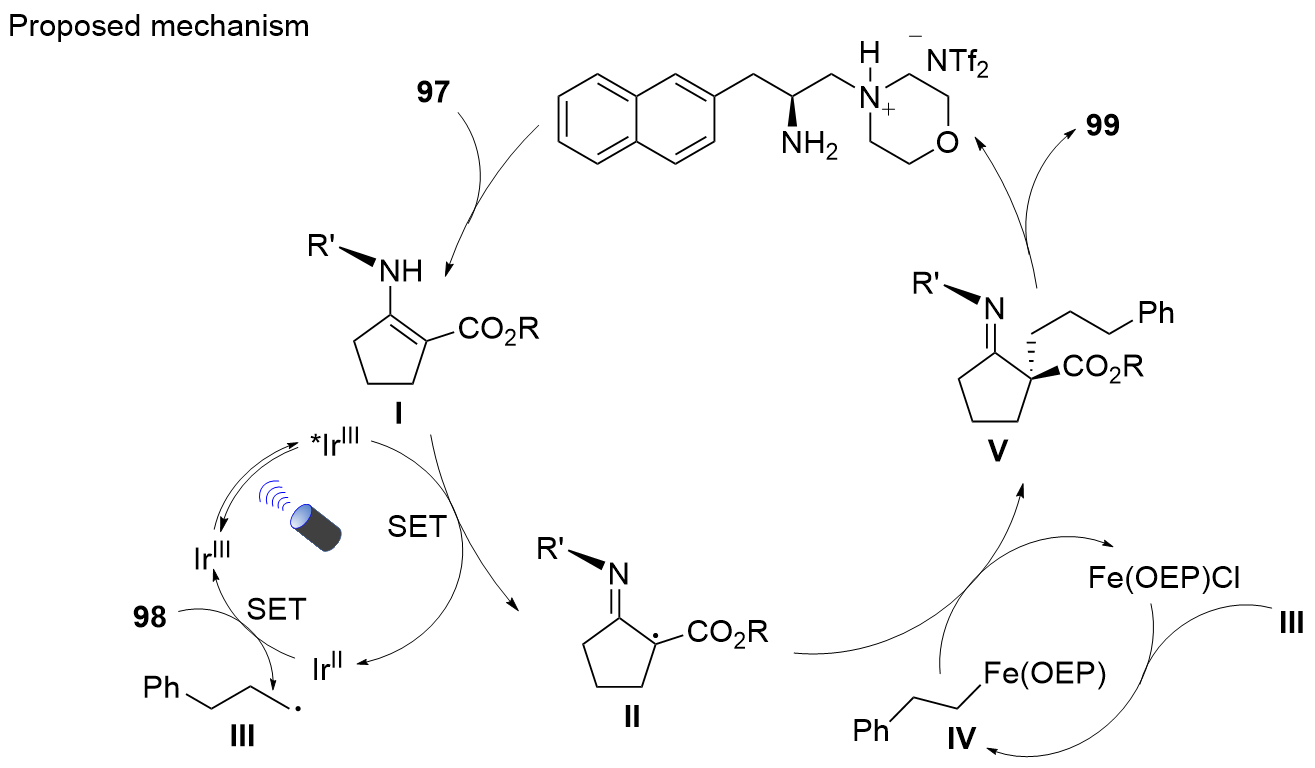
| [1] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1038/s41570-021-00284-3 pmid: 37118440 |
| [6] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
|
(e)
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
| [9] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
|
(e)
|
|
|
(f)
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c07436 pmid: 37846890 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1039/d3sc06476j pmid: 38487219 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2797 pmid: 29064486 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [1] | 谭燕, 应佳乐, 於兵, 陆展. 可见光促进烯基硅化合物有氧氧化-叠氮化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1684-1690. |
| [2] | 林风, 张艳, 吴明, 刘会艳, 郝文娟, 姜波. 利用可见光引发1,6-烯炔的增环酰化双官能化制备1-茚酮衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(5): 1729-1738. |
| [3] | 赵佳, 甘秋云, 袁耀锋. 自由基磺酰氟化反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1206-1222. |
| [4] | 段琛, 沈思语, 赵钰琦, 刘跃, 李薪宇, 张礼智, 李文静. 可见光驱动下蒽醌催化苄基C—H键在水中的氧化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(4): 1352-1359. |
| [5] | 沈佳斌, 沈超, 章鹏飞. 可见光介导的羰基α位C—H官能团化反应合成萘咪酮类衍生物[J]. 有机化学, 2025, 45(2): 677-685. |
| [6] | 傅艳华, 徐畅, 张超, 王怡莎, 冯高峰. 可见光诱导铁催化氮杂环的羟甲基化[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(7): 2265-2273. |
| [7] | 曹香雪, 贾雅会, 殷世纪, 徐亮, 韦玉, 宋欢欢. 可见光诱导二氢喹唑啉酮碳碳键断裂与三氟甲基取代烯烃的脱氟烷基化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(5): 1549-1557. |
| [8] | 张澳龙, 杨晗, 程佩栋, 姚阳, 孙松. 可见光促进烯烃与丙二酸酯、CO2的碳-羧化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(10): 3159-3168. |
| [9] | 徐辉, 蒋慧娴, 阚磊, 徐佩, 朱旭. 可见光诱导甲酸盐参与的炔烃氢羧基化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(10): 3241-3248. |
| [10] | 朱彦硕, 王红言, 舒朋华, 张克娜, 王琪琳. 烷氧自由基引发1,5-氢原子转移实现C(sp3)—H键官能团化的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 1-17. |
| [11] | 童红恩, 郭宏宇, 周荣. 可见光促进惰性碳-氢键对羰基的加成反应进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024, 44(1): 54-69. |
| [12] | 赵瑜, 张凯, 白育斌, 张琰图, 史时辉. 无金属条件下可见光催化与溴盐协同促进烯烃的氢硅化反应研究[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2837-2847. |
| [13] | 杨晓娜, 郭宏宇, 周荣. 可见光促进有机硅化合物参与的化学转化[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(8): 2720-2742. |
| [14] | 高艳华, 张银潘, 张妍, 宋涛, 杨勇. 可见光驱动表面富含氧空位Nb2O5催化醇氧化反应[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(7): 2572-2579. |
| [15] | 赵金晓, 魏彤辉, 柯森, 李毅. 可见光催化合成二氟烷基取代的多环吲哚化合物[J]. 有机化学, 2023, 43(3): 1102-1114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||